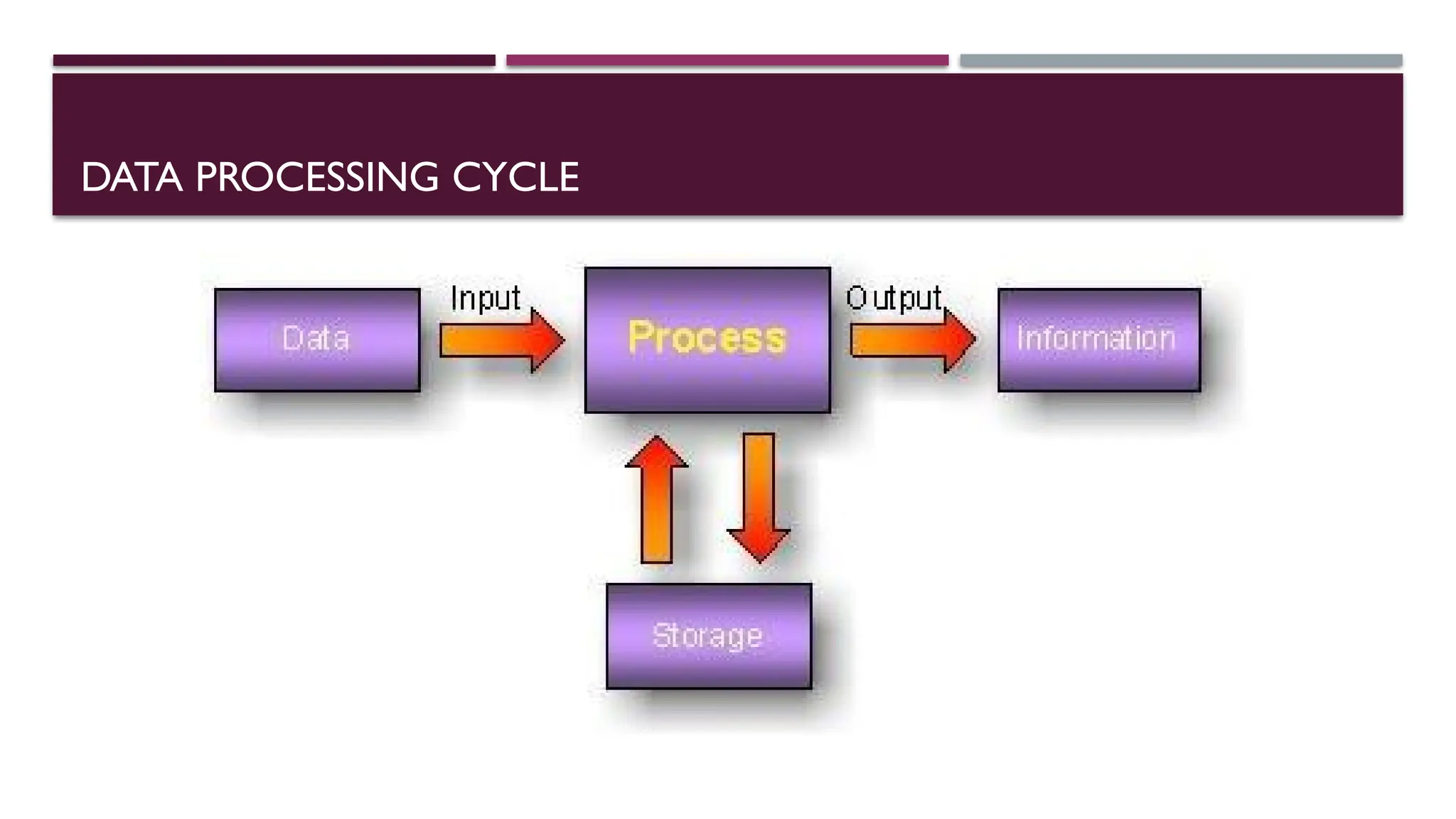
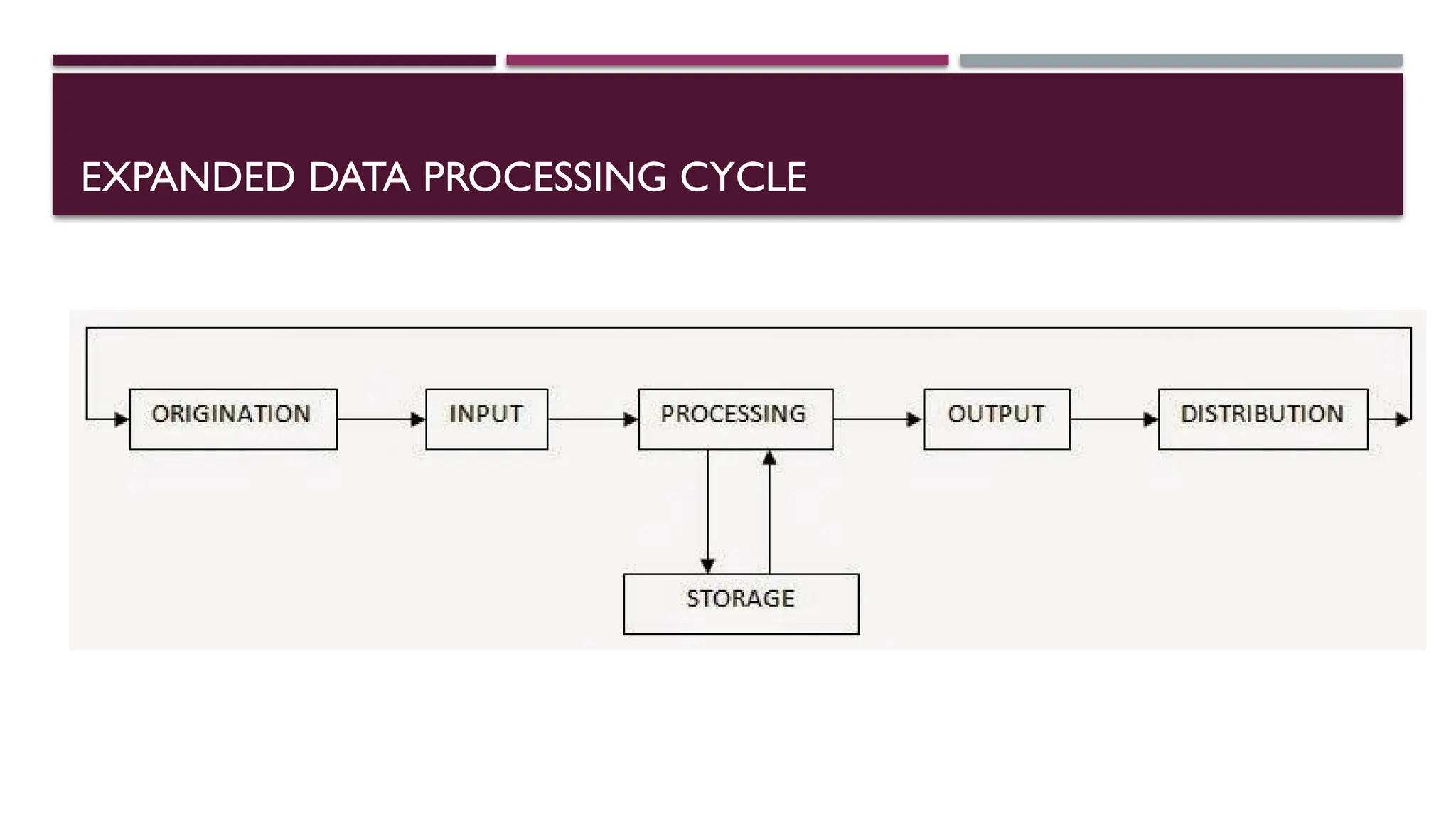
The document outlines the objectives and operations involved in data processing, defining data as raw facts that require manipulation to become useful information. It describes the data processing cycle, including steps such as recording, verifying, duplicating, classifying, sorting, calculating, summarizing, merging, storing, retrieving, and providing feedback. Additionally, it covers methods of processing data, including batch, online, real-time, and distributed processing.