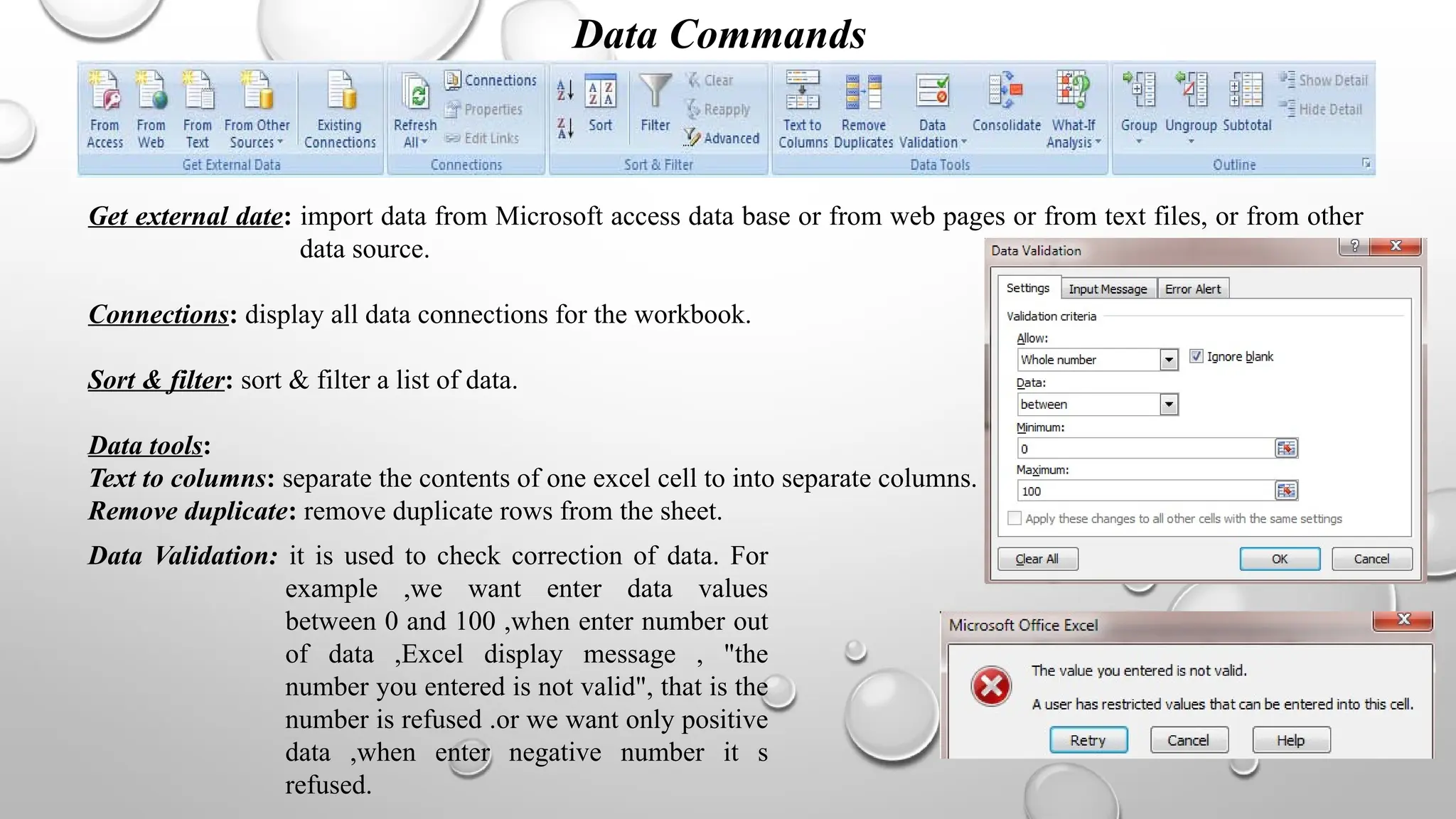
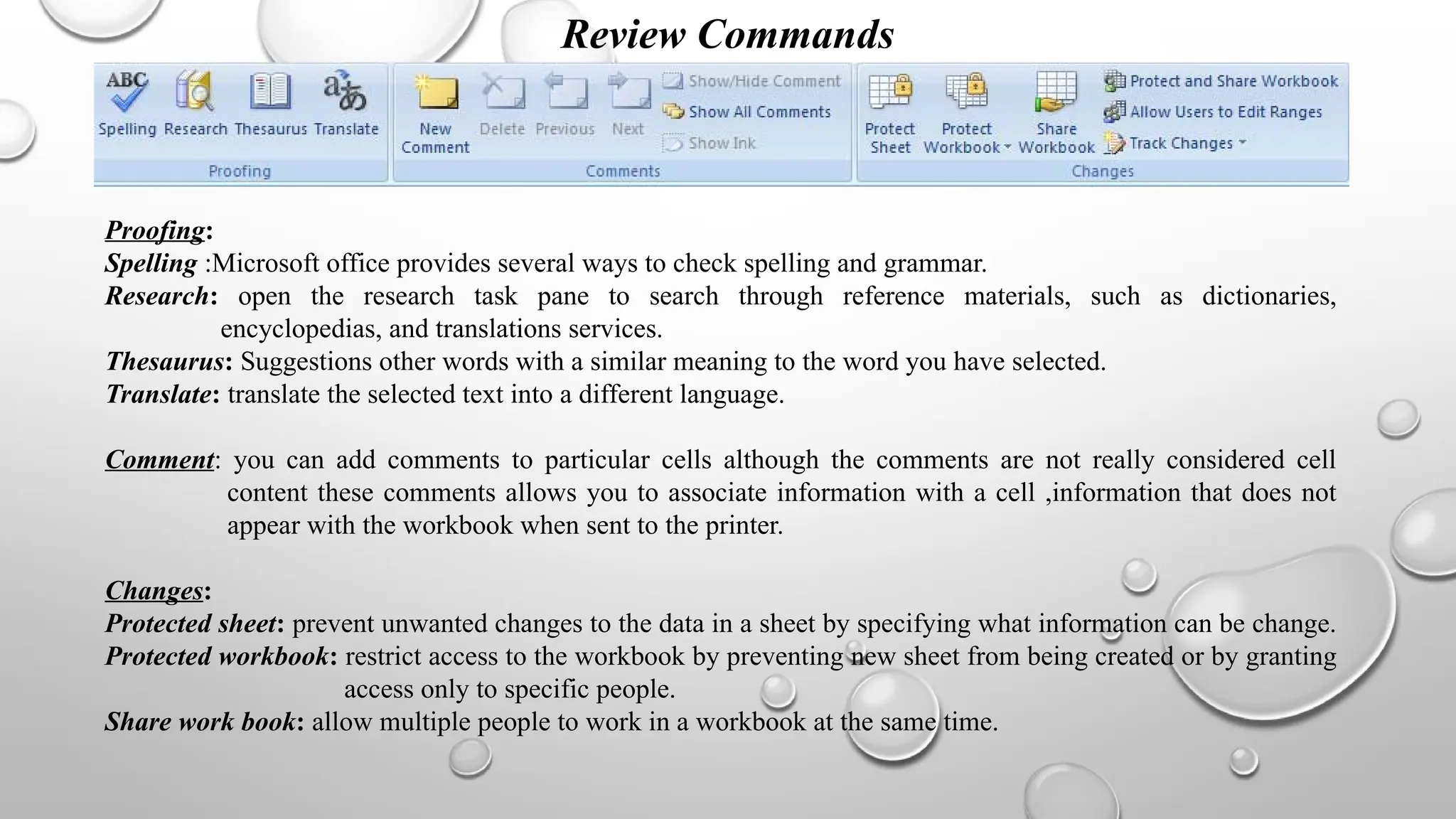
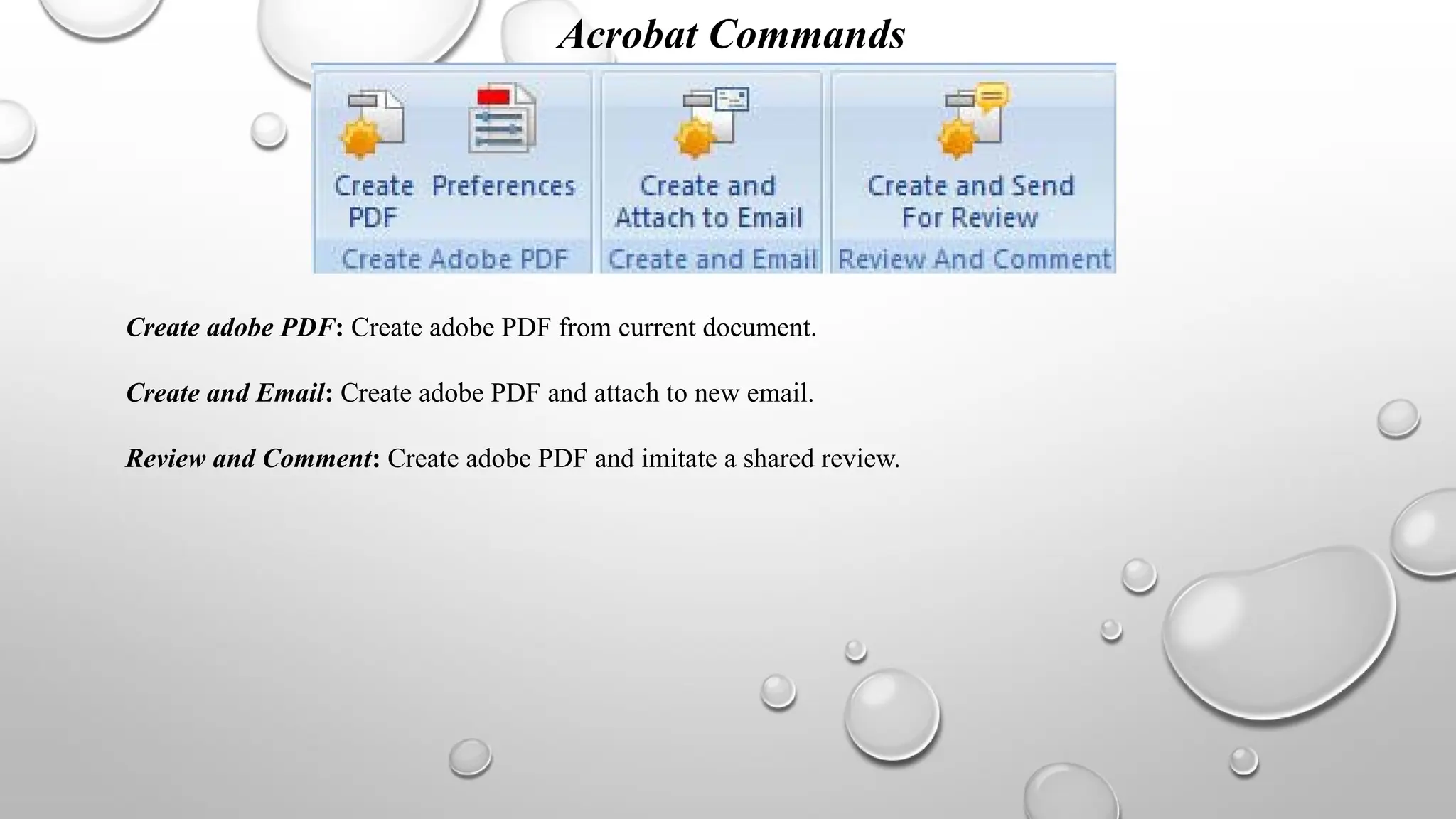
The document outlines various commands and features available in Excel, including tools for page layout, data management, formula entry, and review commands. It details options for adjusting themes, margins, page orientation, data validation, and error checking, as well as capabilities for collaboration and document sharing. Additional components discussed include formula auditing processes, importation of external data, and capabilities for creating PDF documents from Excel.