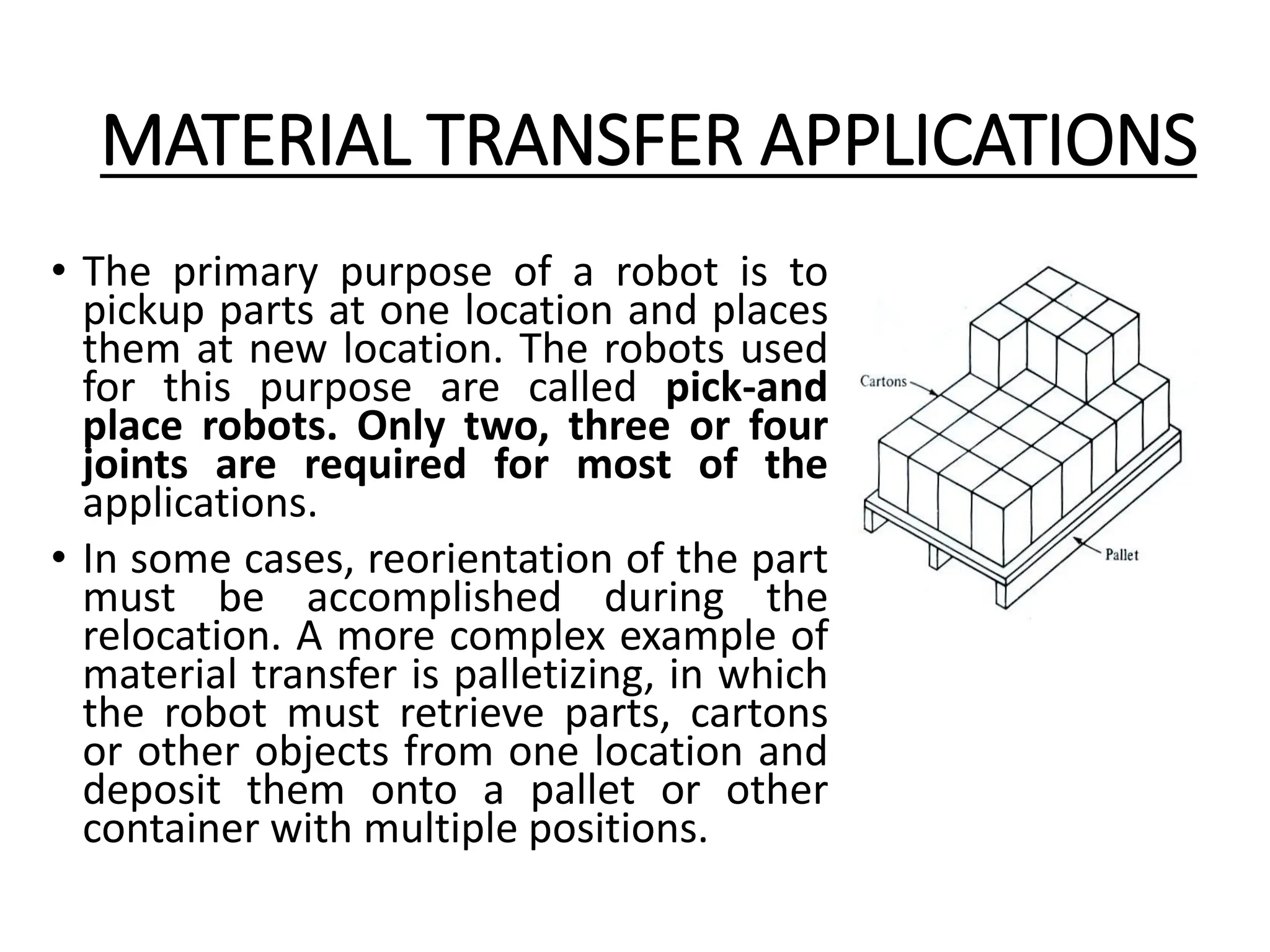
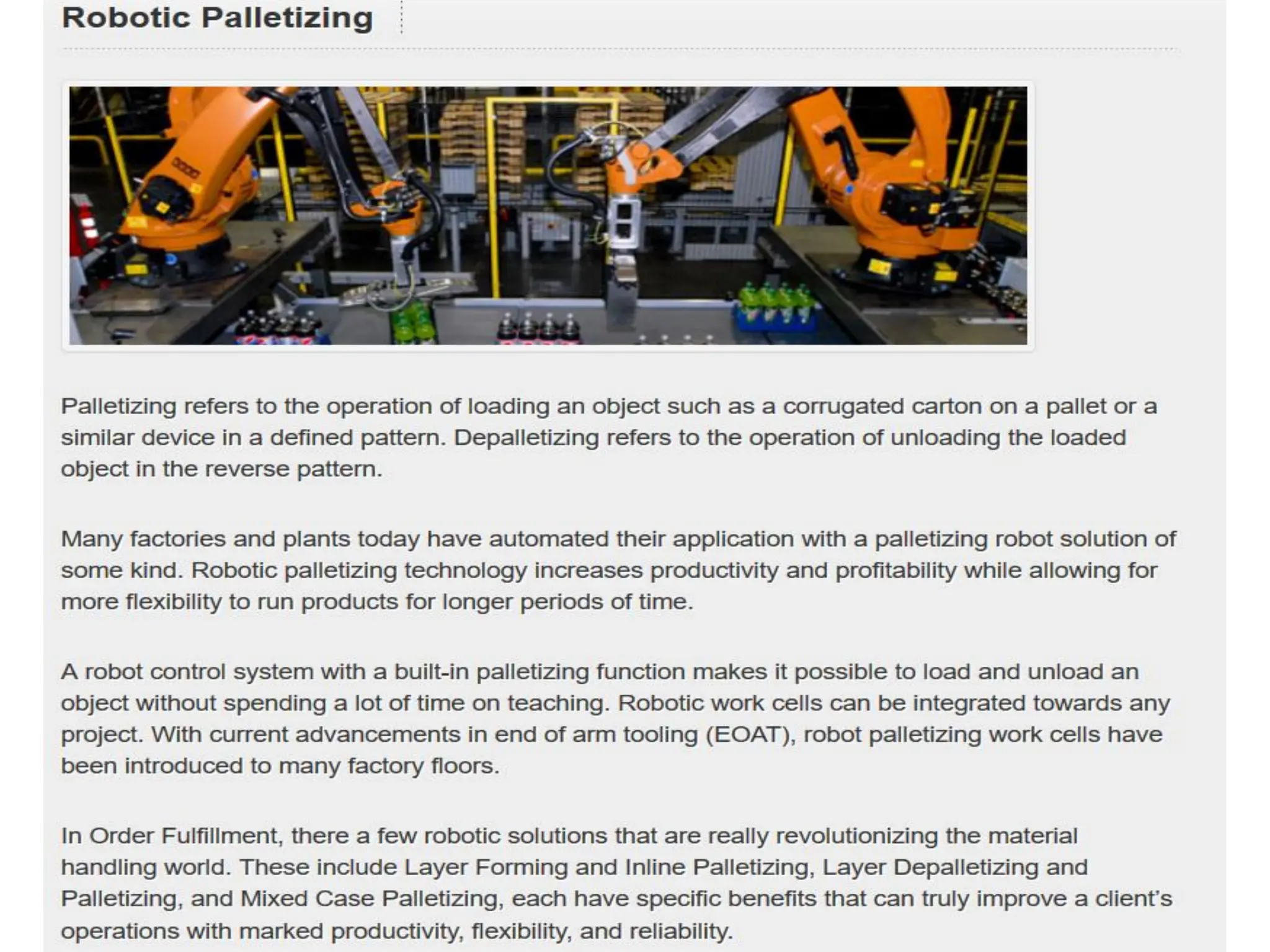
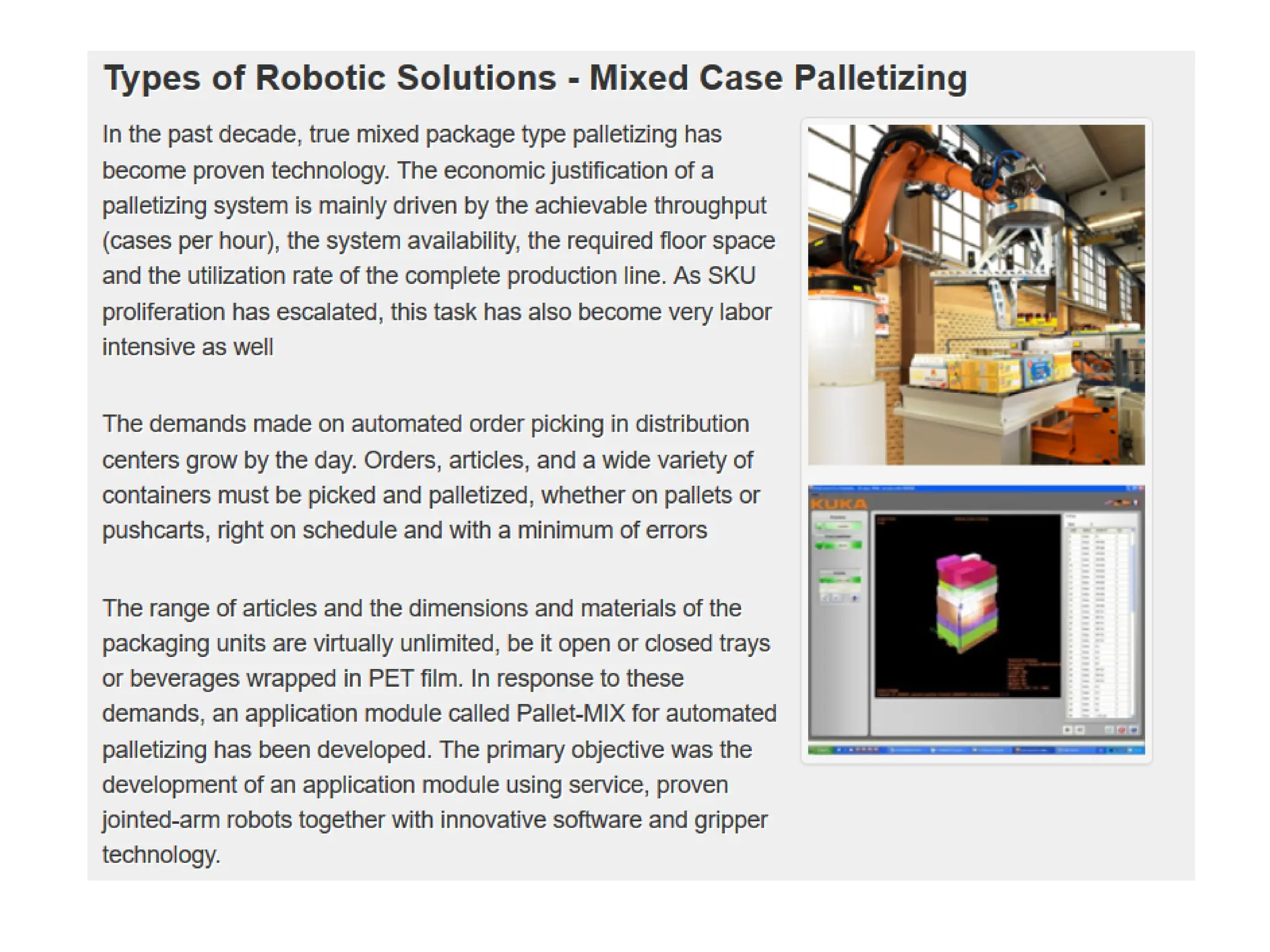
The document outlines the applications of robots in various industries, particularly in manufacturing, where they perform tasks such as material handling, machine loading and unloading, and processing operations like welding and spray coating. It discusses the assembly systems involving robots and the potential future advancements in robot technology, including artificial intelligence and enhanced sensory capabilities. Future robots are envisioned to undertake complex tasks in challenging environments, including maintenance, security, and domestic applications.