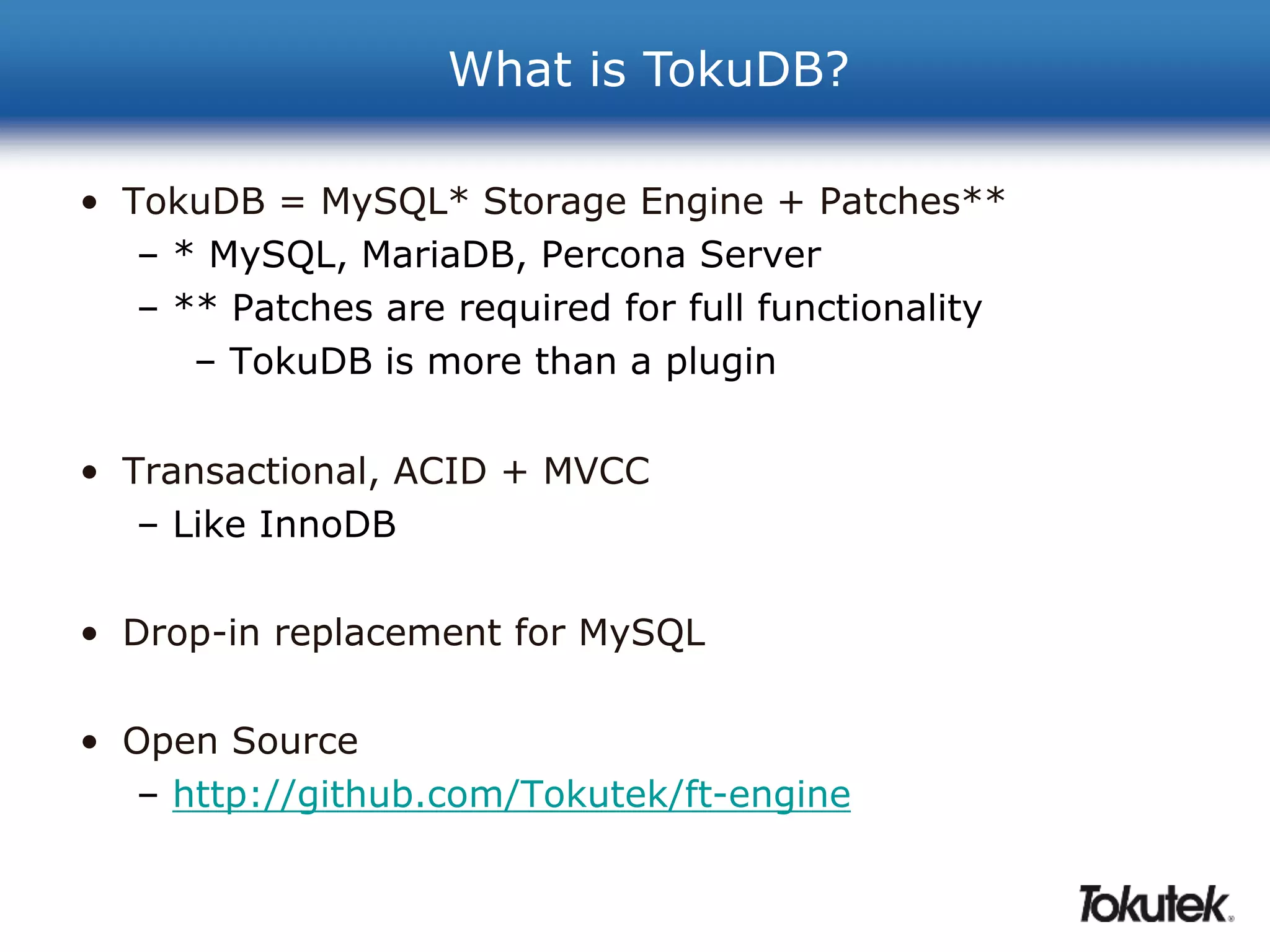
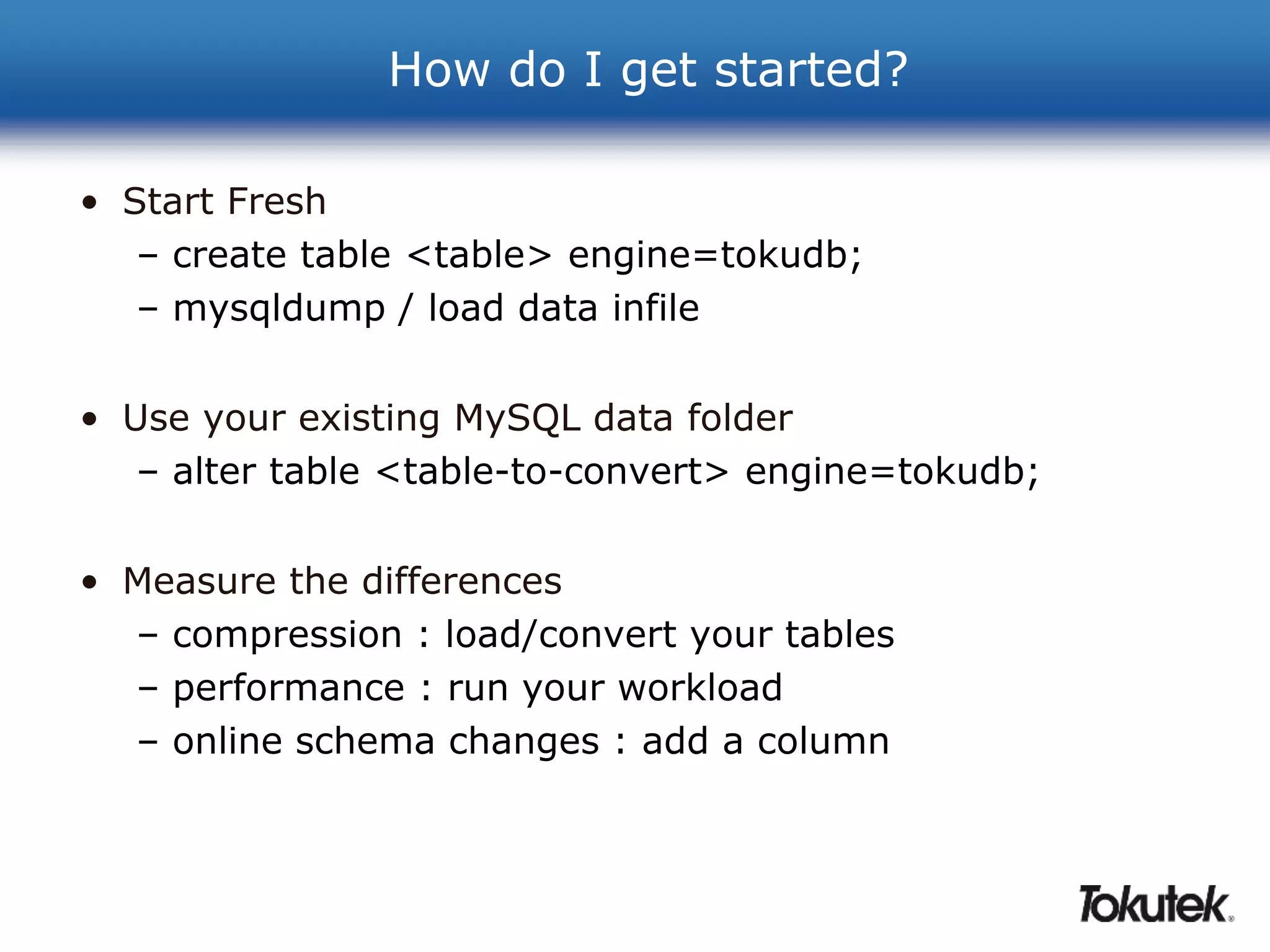
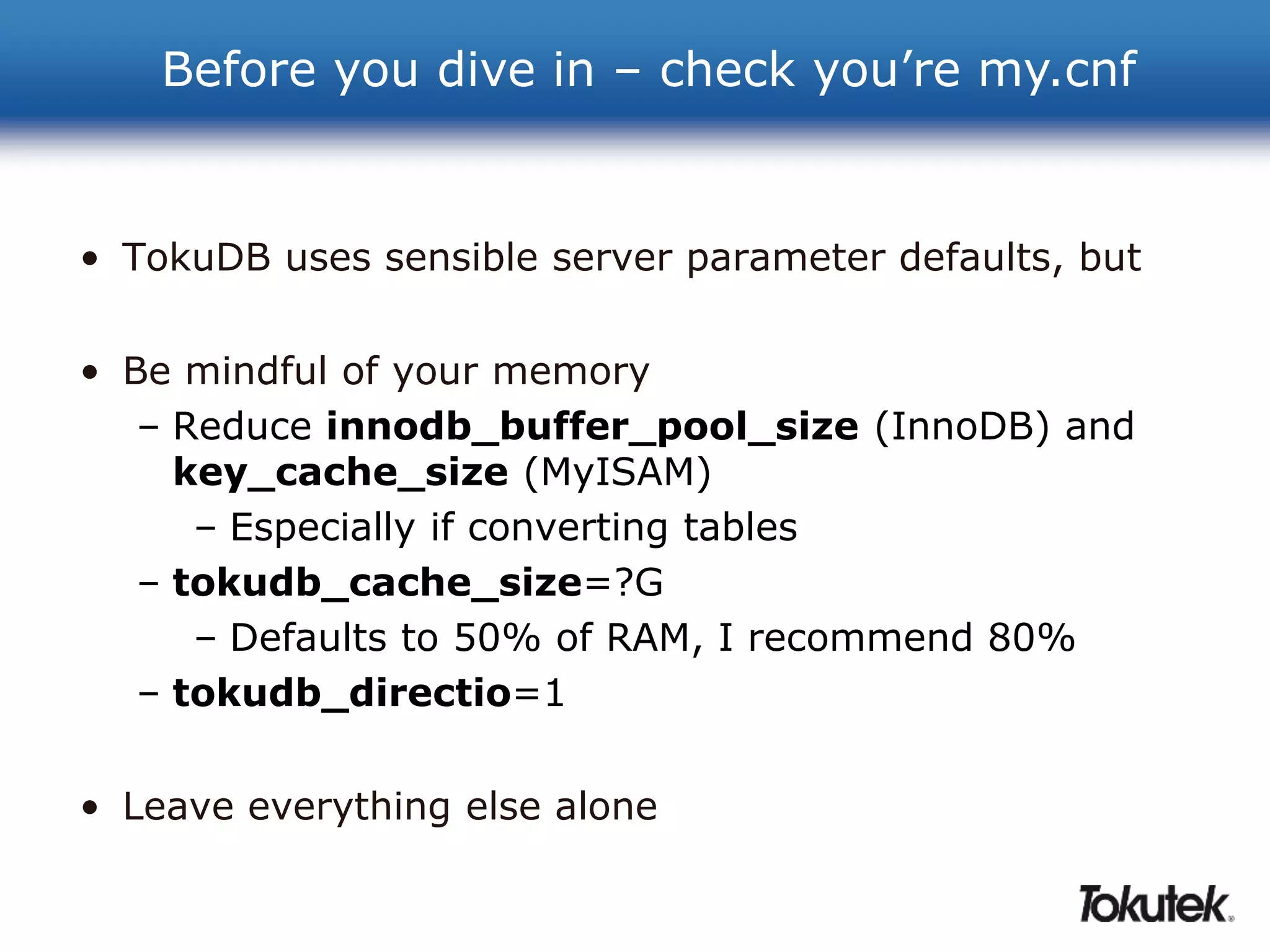
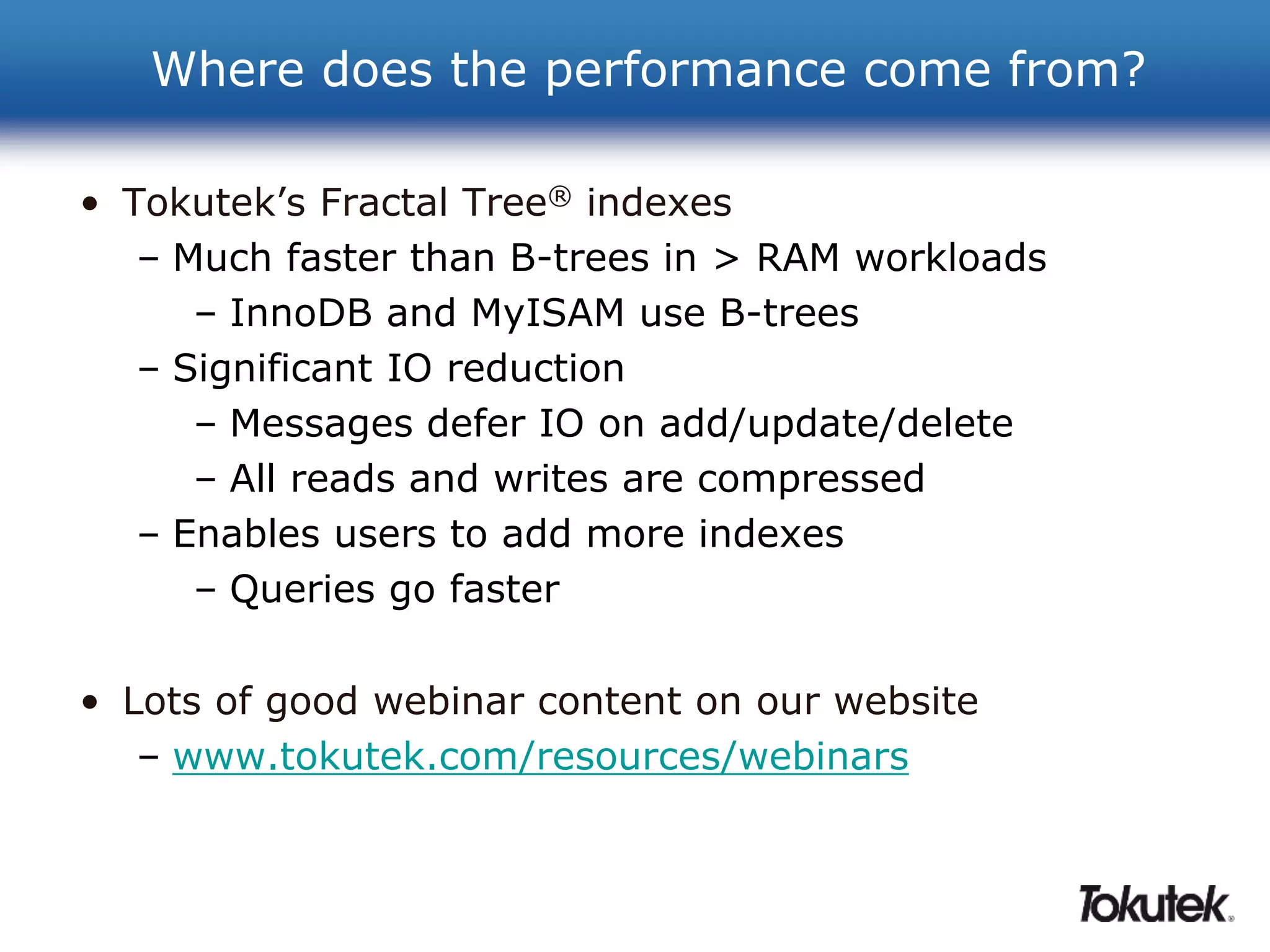
Tokutek offers high-performance storage engines, such as TokuDB, for MySQL, MariaDB, and MongoDB, which significantly enhance performance and efficiency without requiring code rewrites. Key benefits include improved insertion speeds, reduced storage needs, and advanced online schema changes. TokuDB utilizes fractal tree indexing for superior performance in high-volume data environments, supporting compression for both space and speed advantages.







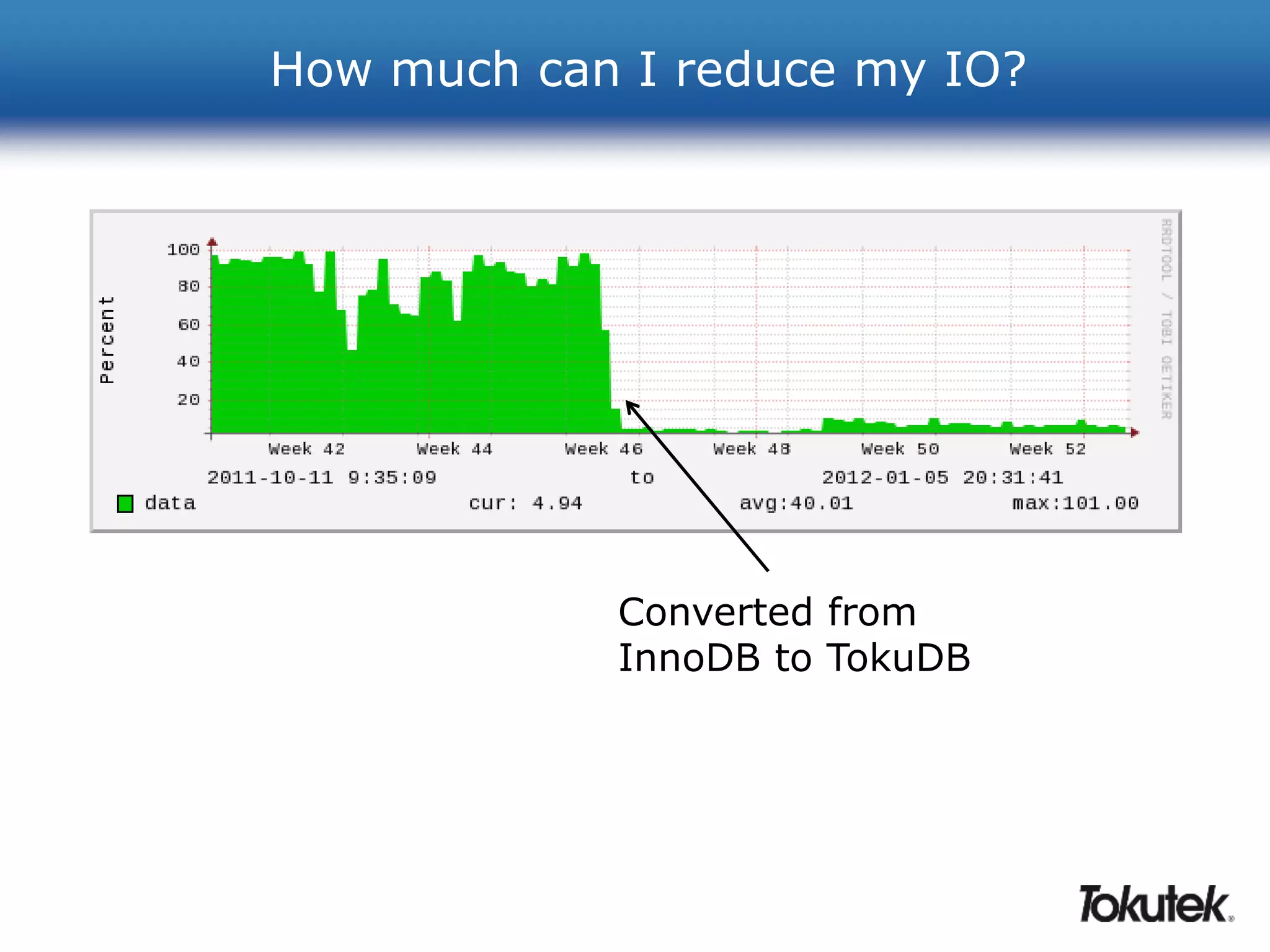
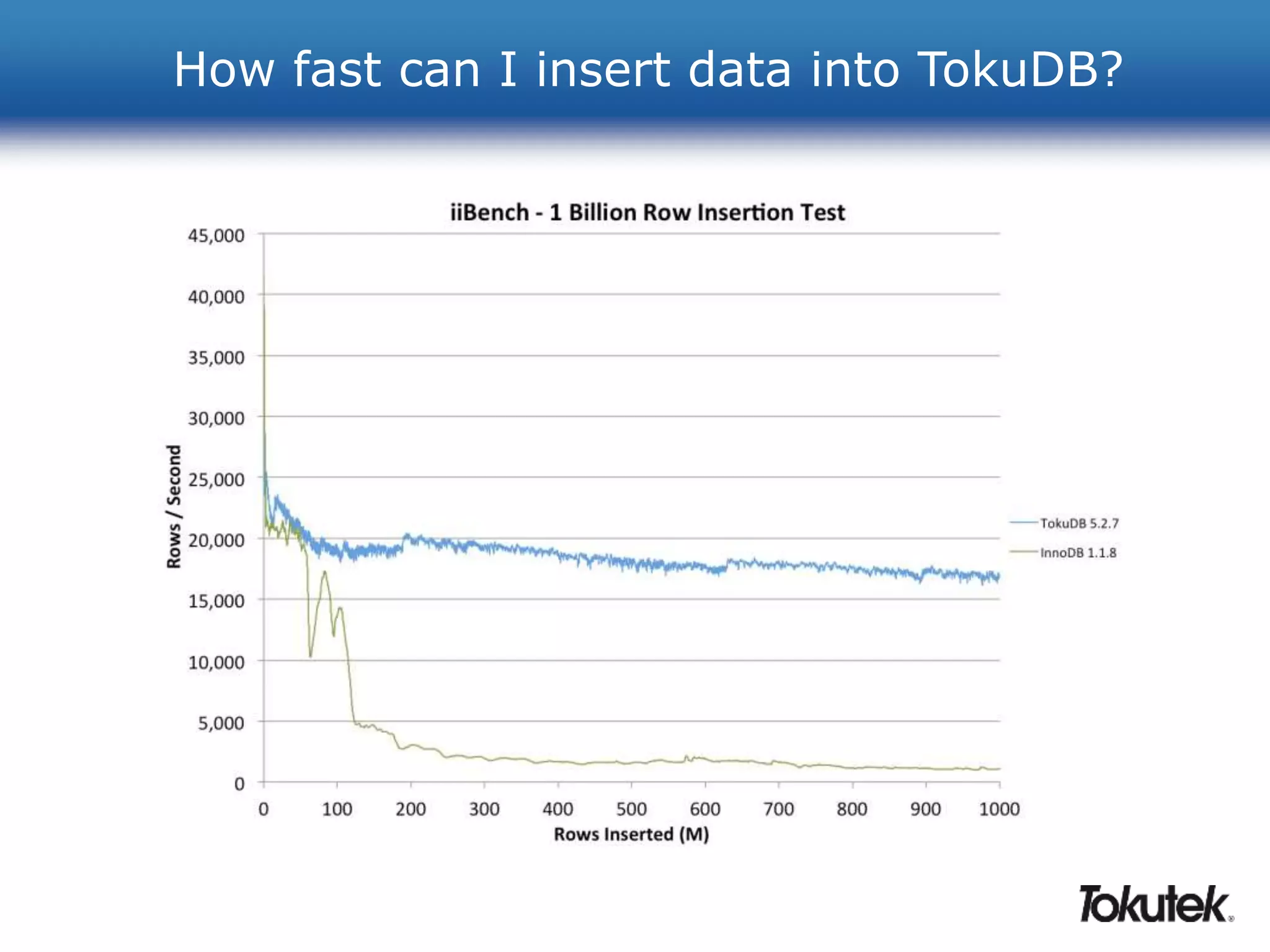
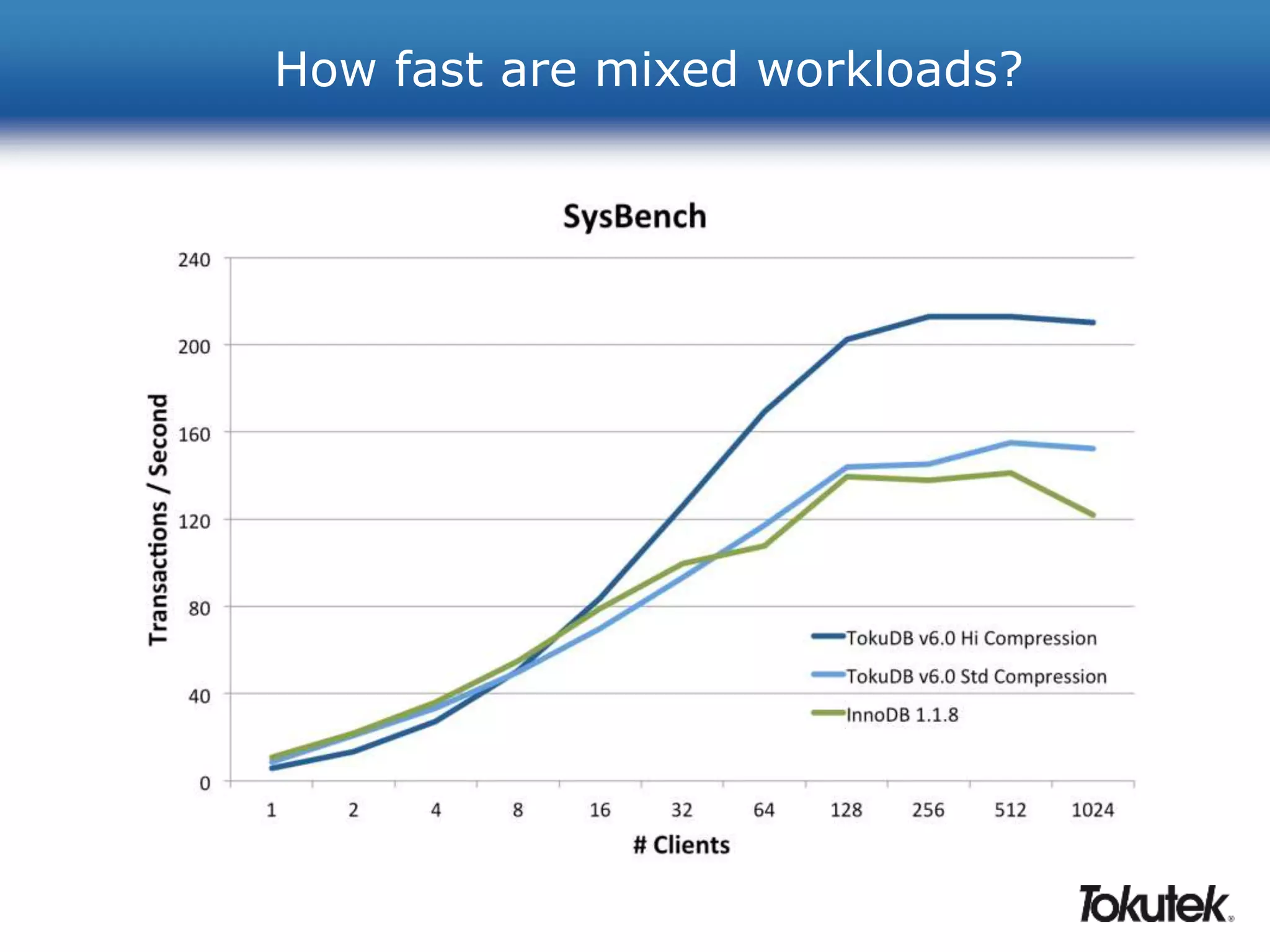
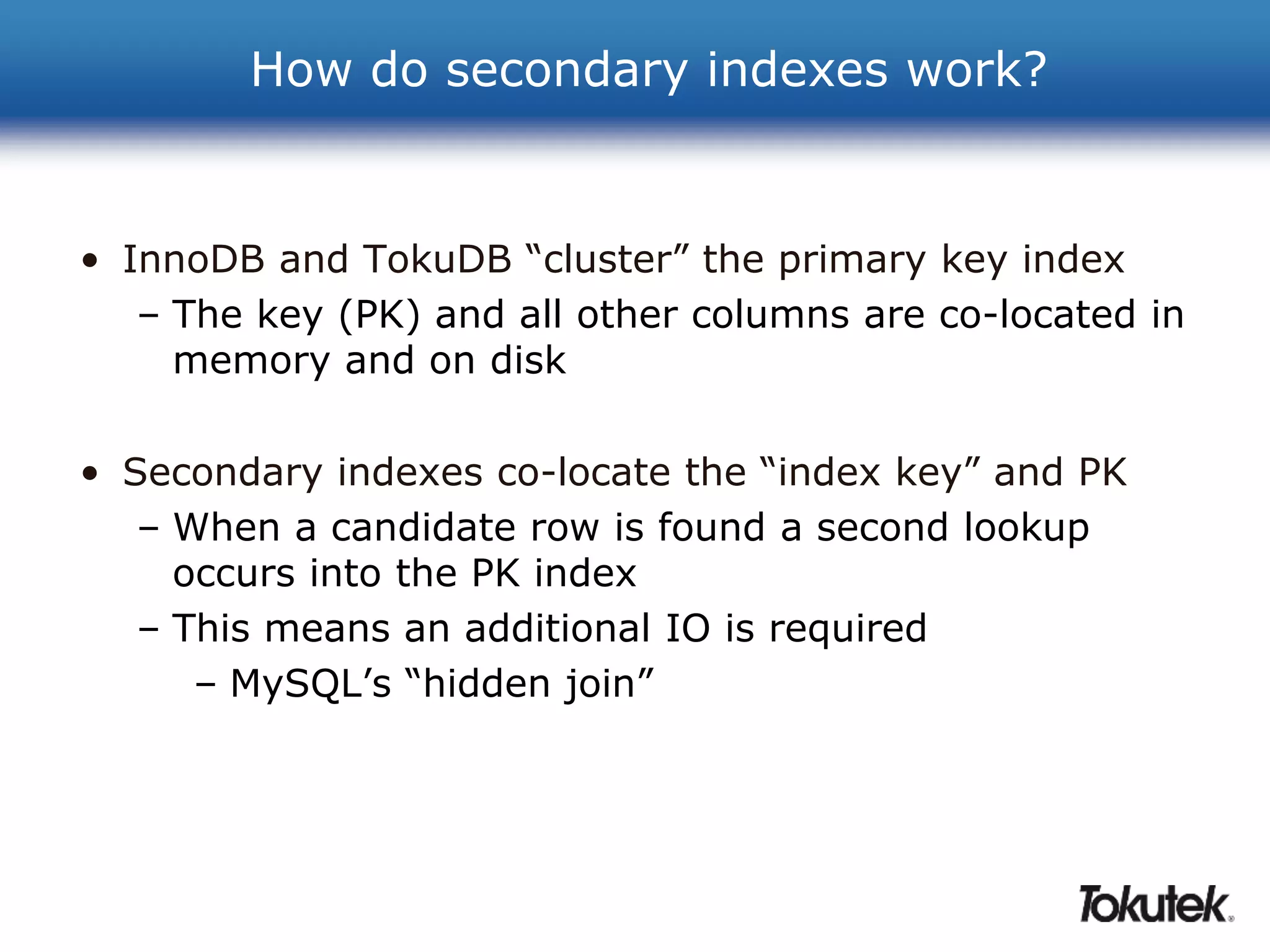
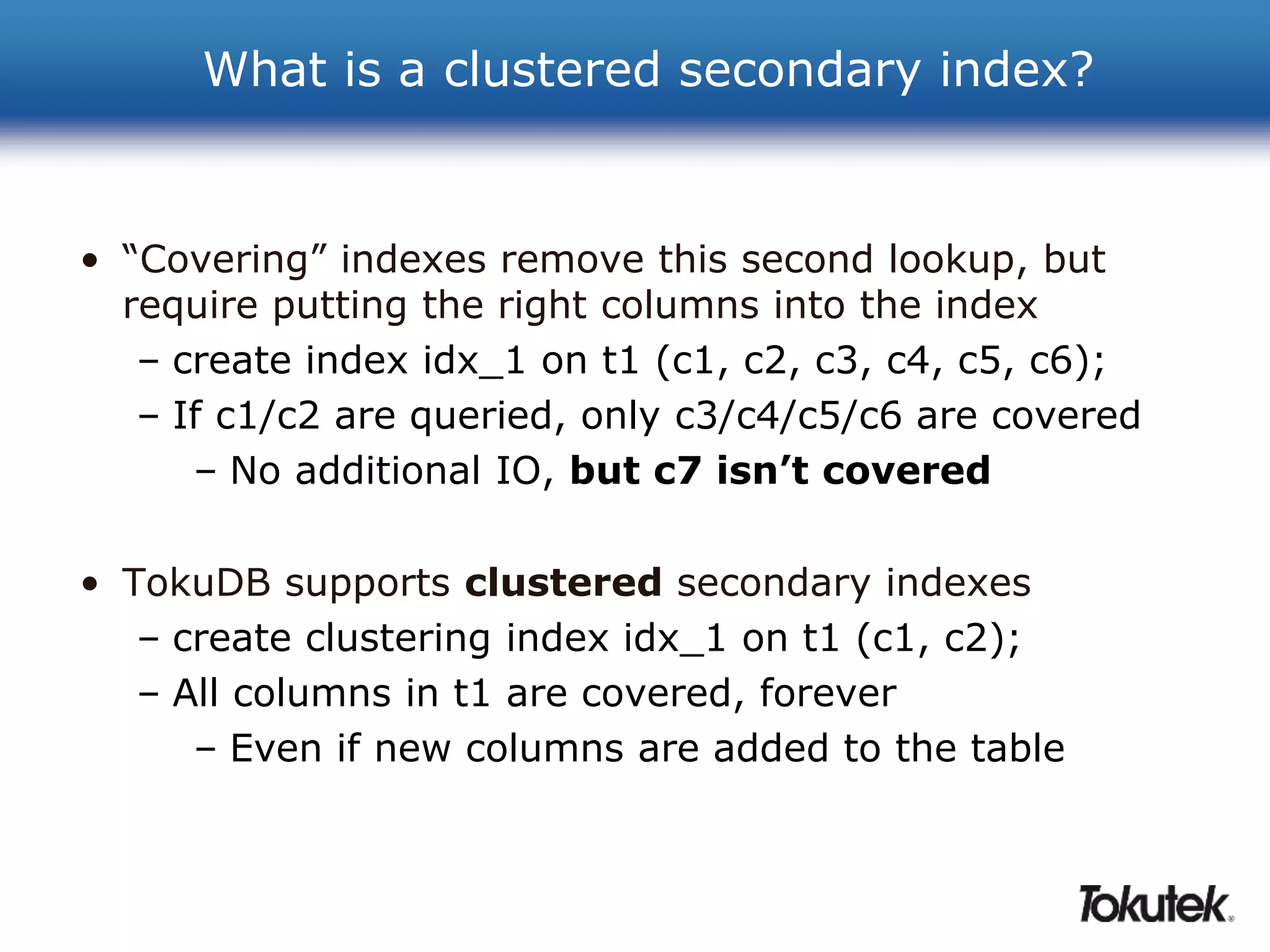

![How can I use less storage?
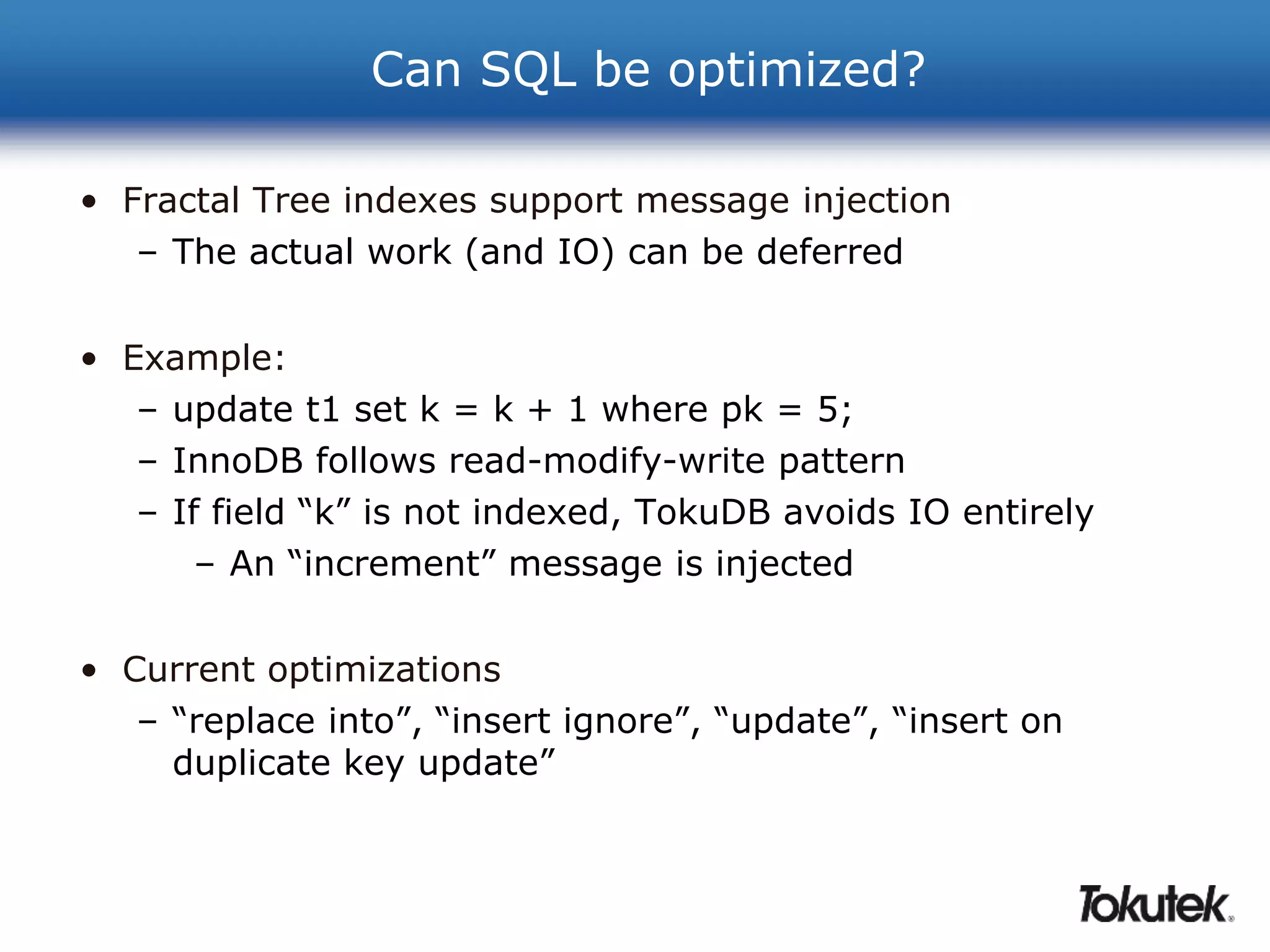
• Compression, compression, compression!
• All IO in TokuDB is compressed
– Reads and writes
– Usually ~5x compression (but I’ve seen 25x or more)
• TokuDB [currently] supports 3 compression algorithms
– lzma = highest compression (and high CPU)
– zlib = high compression (and much less CPU)
– quicklz = medium compression (even less CPU)
– pluggable architecture, lz4 and snappy “in the lab”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20140128-webinar-get-more-out-of-mysql-with-tokudb-140319063324-phpapp02-141015032859-conversion-gate02/75/20140128-webinar-get-more-out-of-mysql-with-tokudb-140319063324-phpapp02-24-2048.jpg)
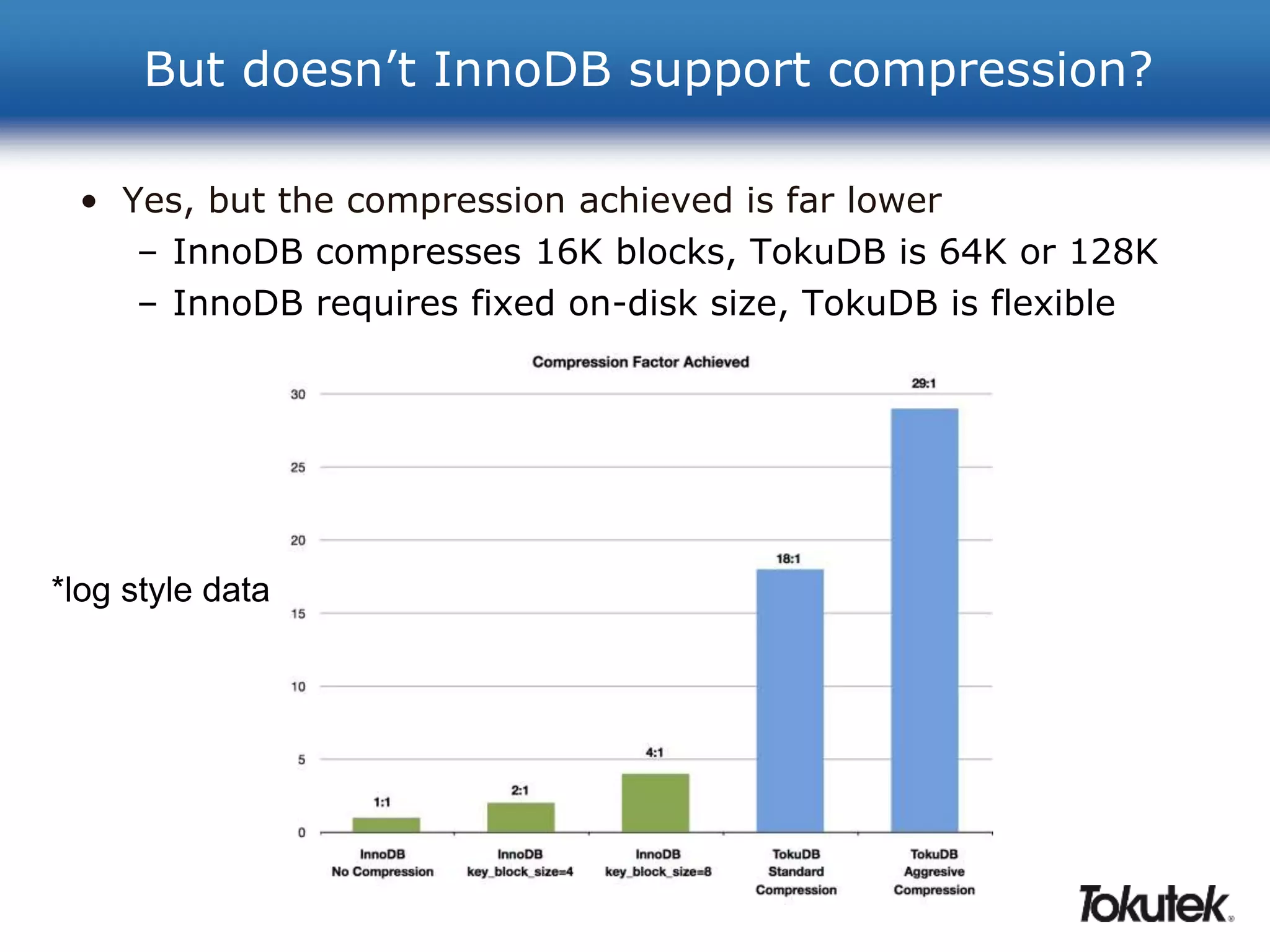
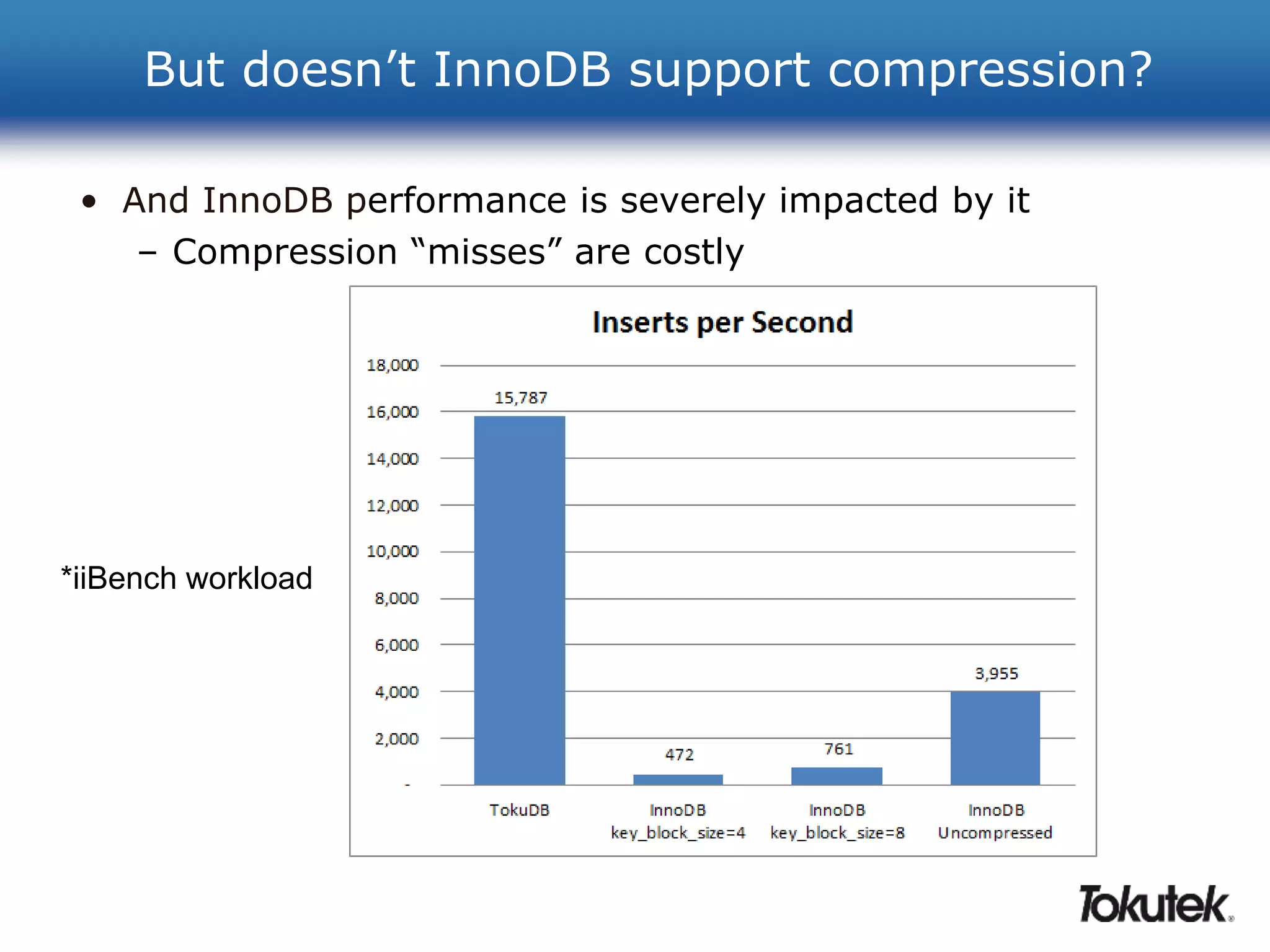
![How do I compress my data in TokuDB?
create table t1 (c1 bigint not null primary key)
engine=tokudb
row_format=[tokudb_lzma | tokudb_zlib | tokudb_quicklz];
NOTE: Compression is not optional in TokuDB, we use
compression to provide performance advantages as well as save
space.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20140128-webinar-get-more-out-of-mysql-with-tokudb-140319063324-phpapp02-141015032859-conversion-gate02/75/20140128-webinar-get-more-out-of-mysql-with-tokudb-140319063324-phpapp02-27-2048.jpg)