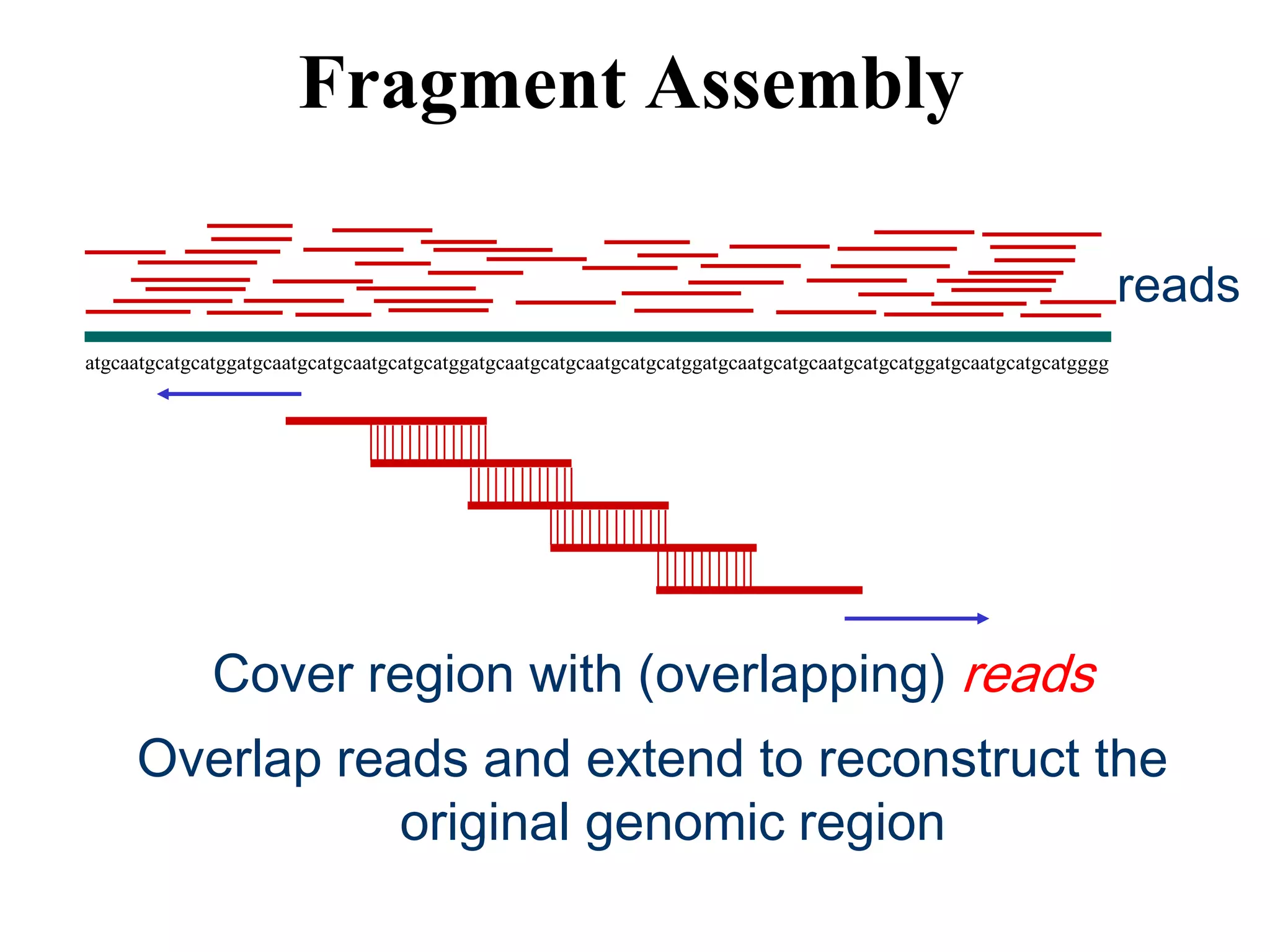
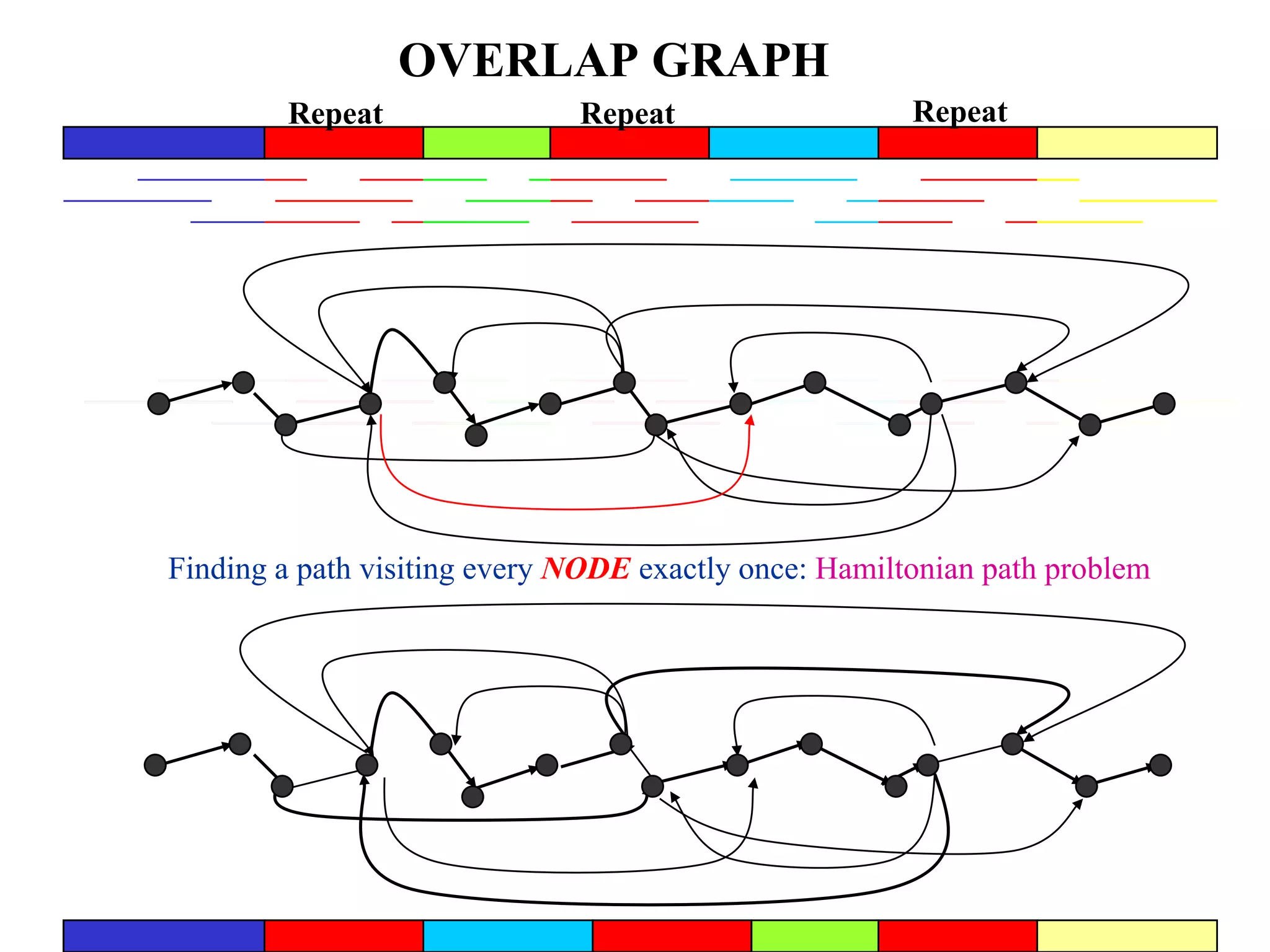
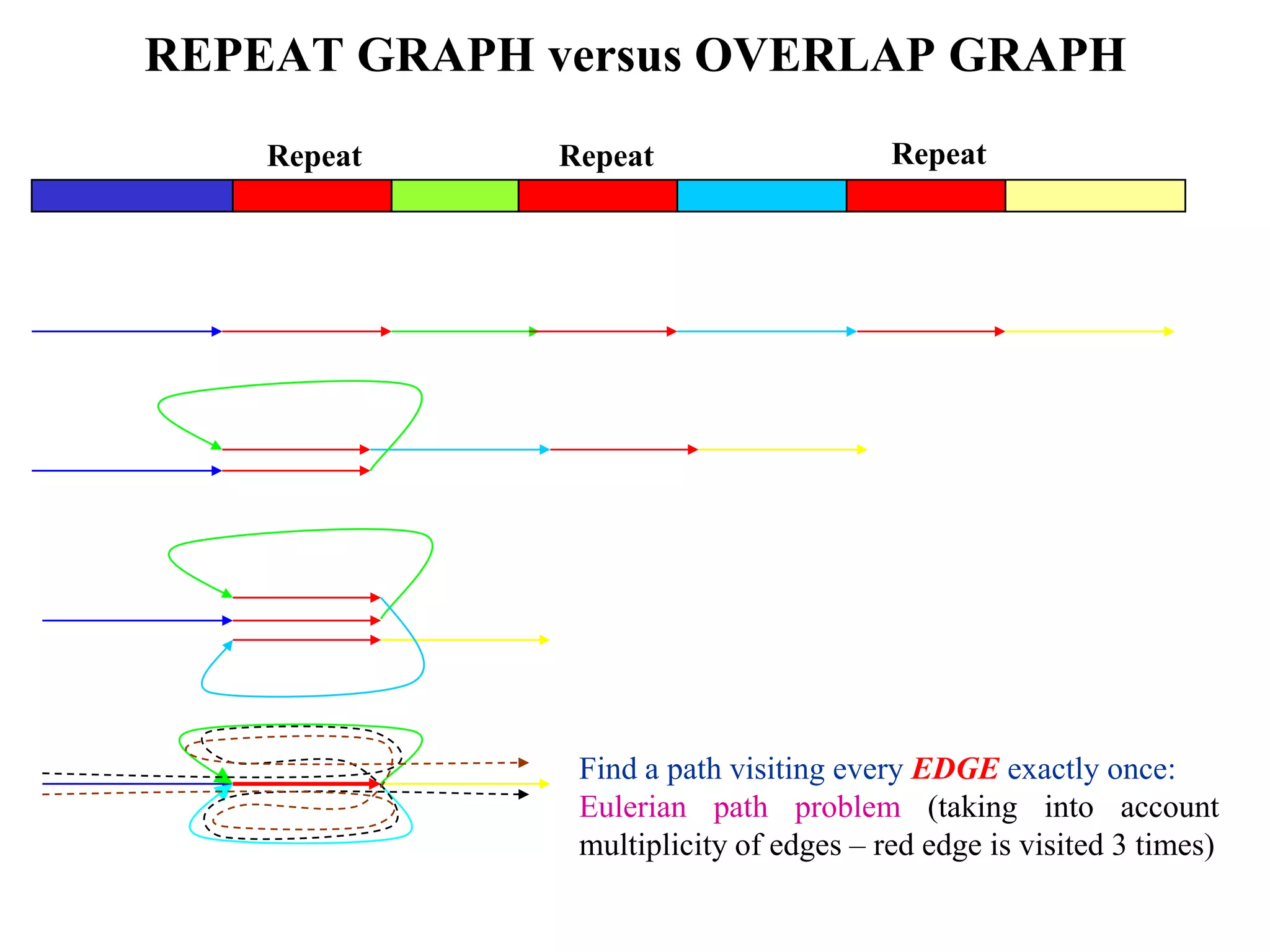
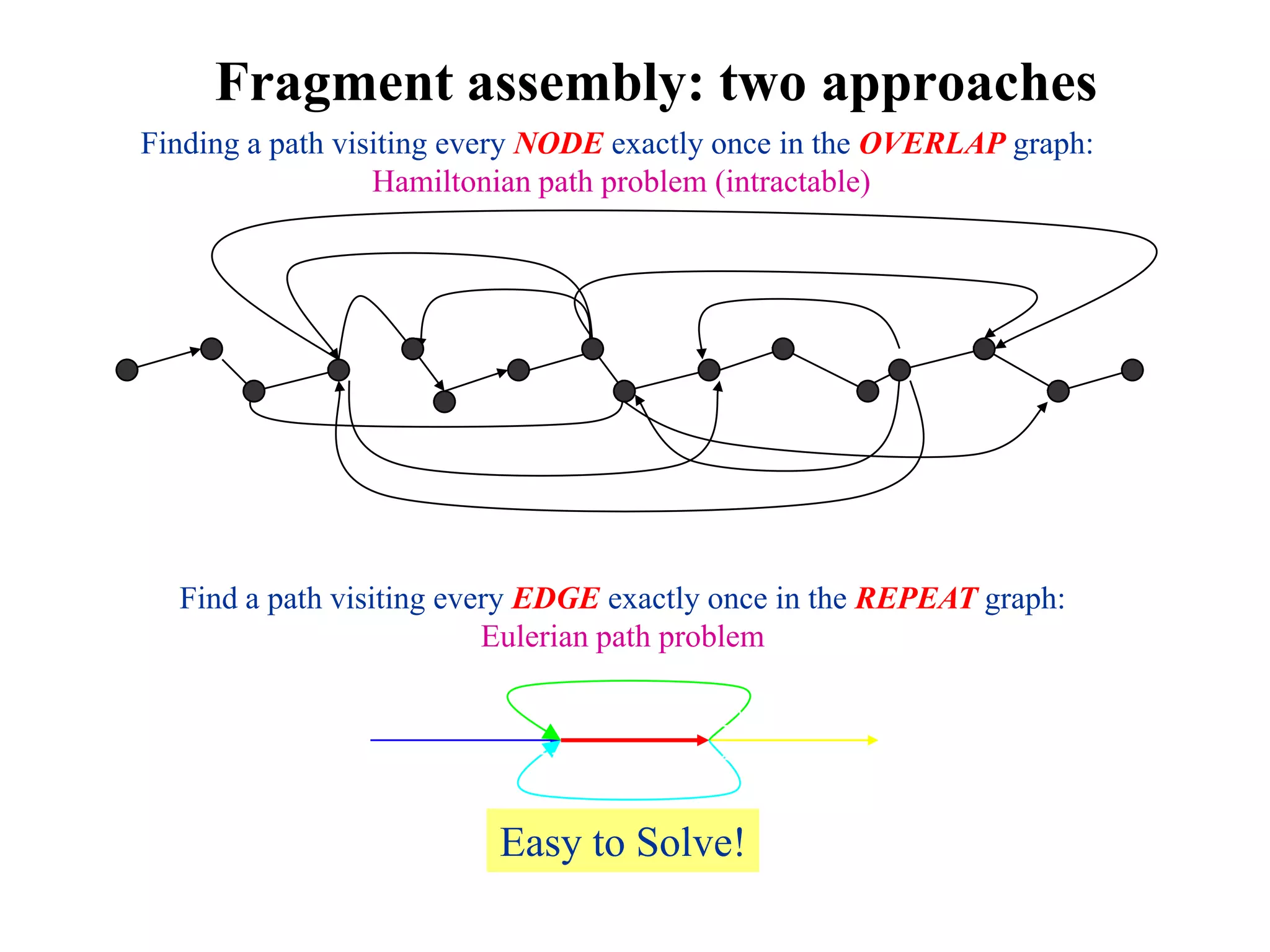
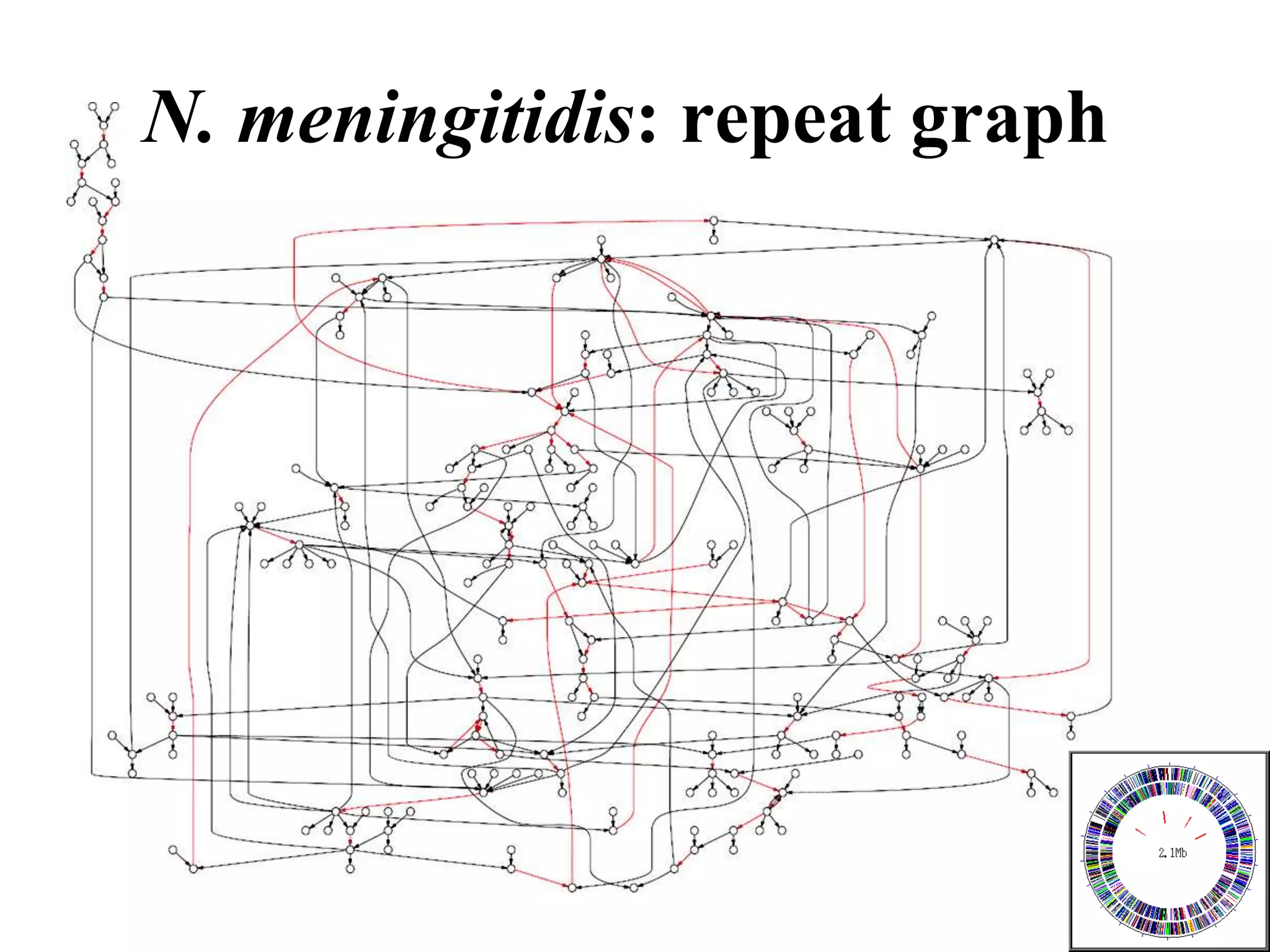
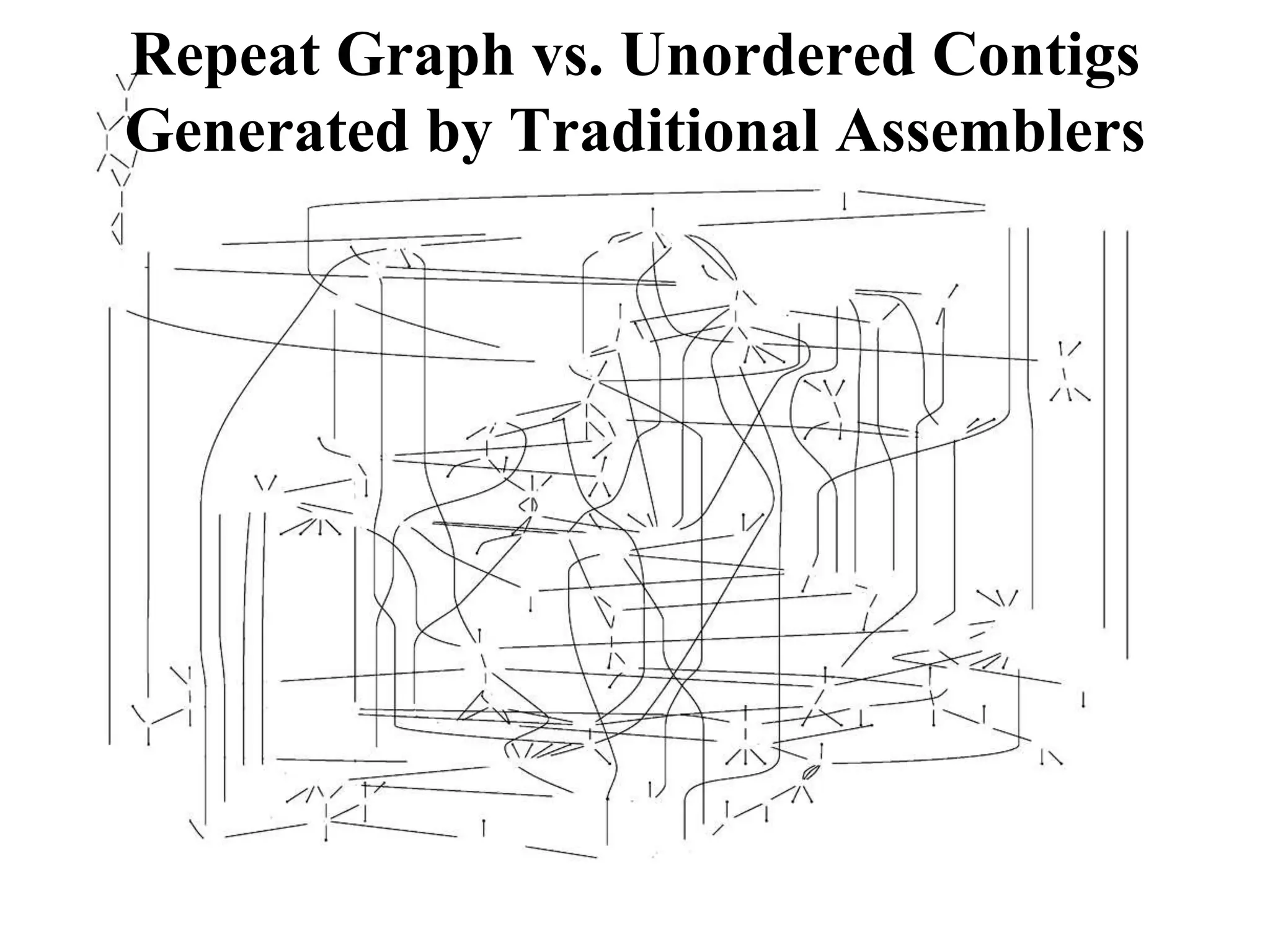
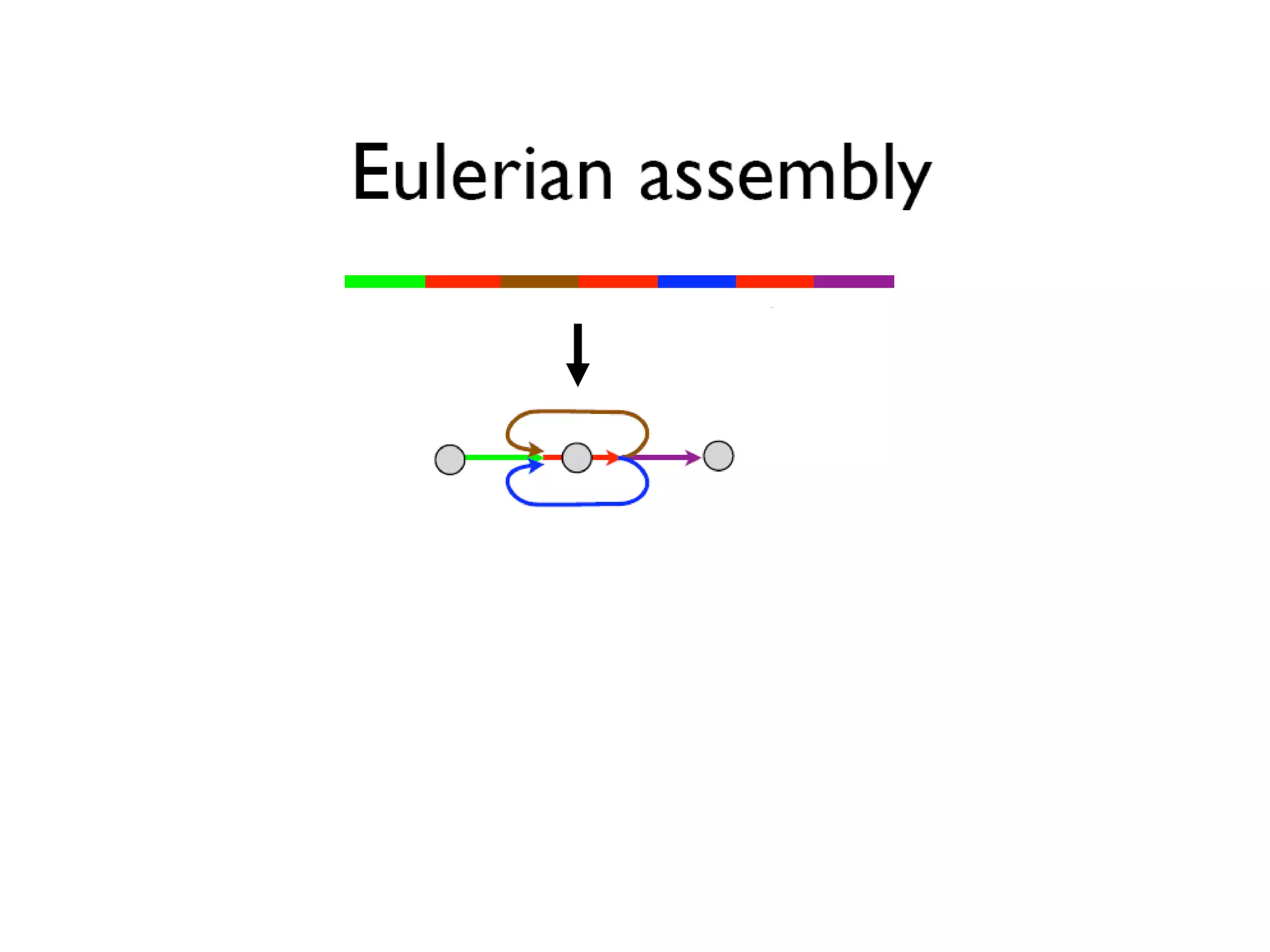
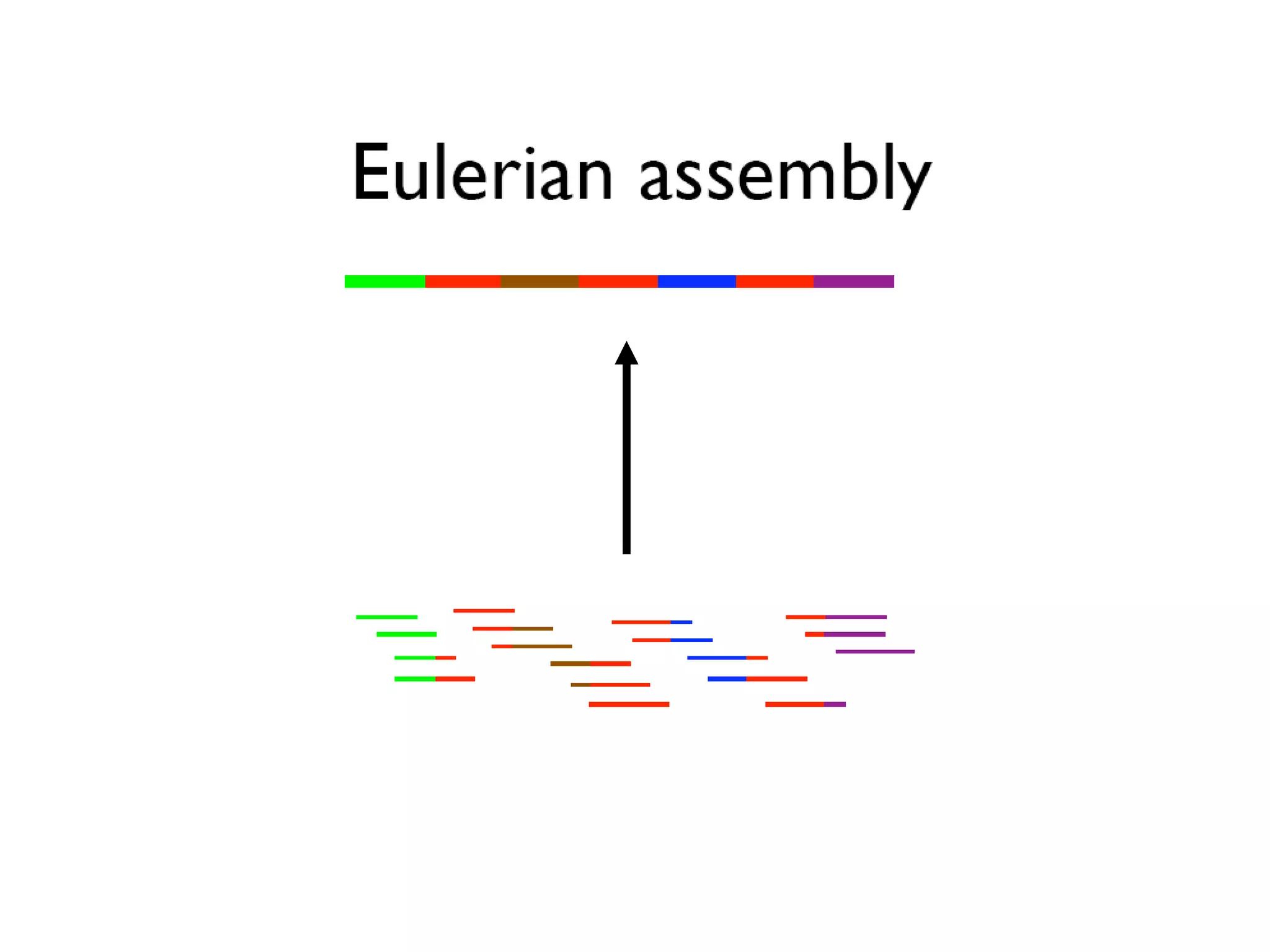
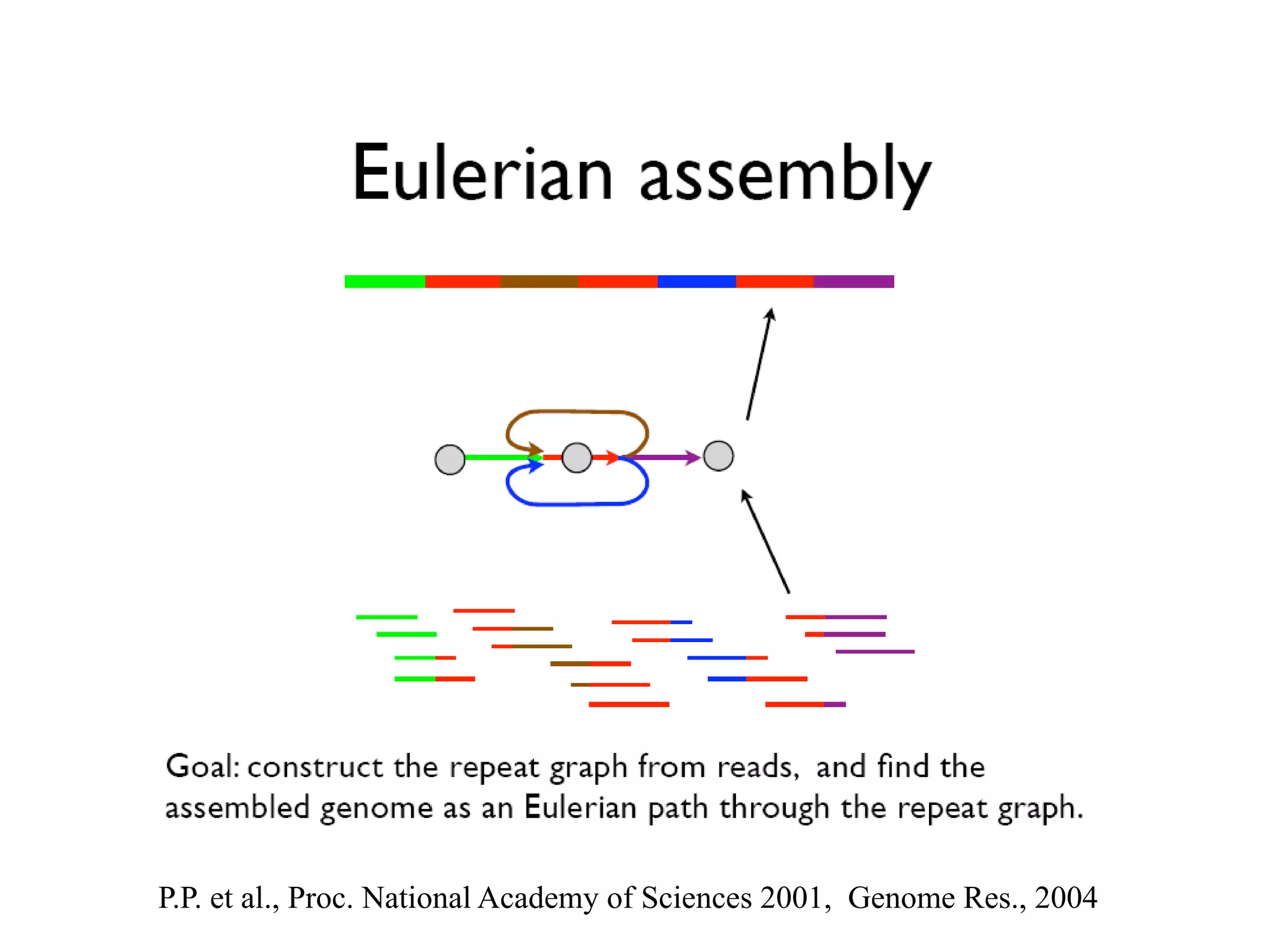
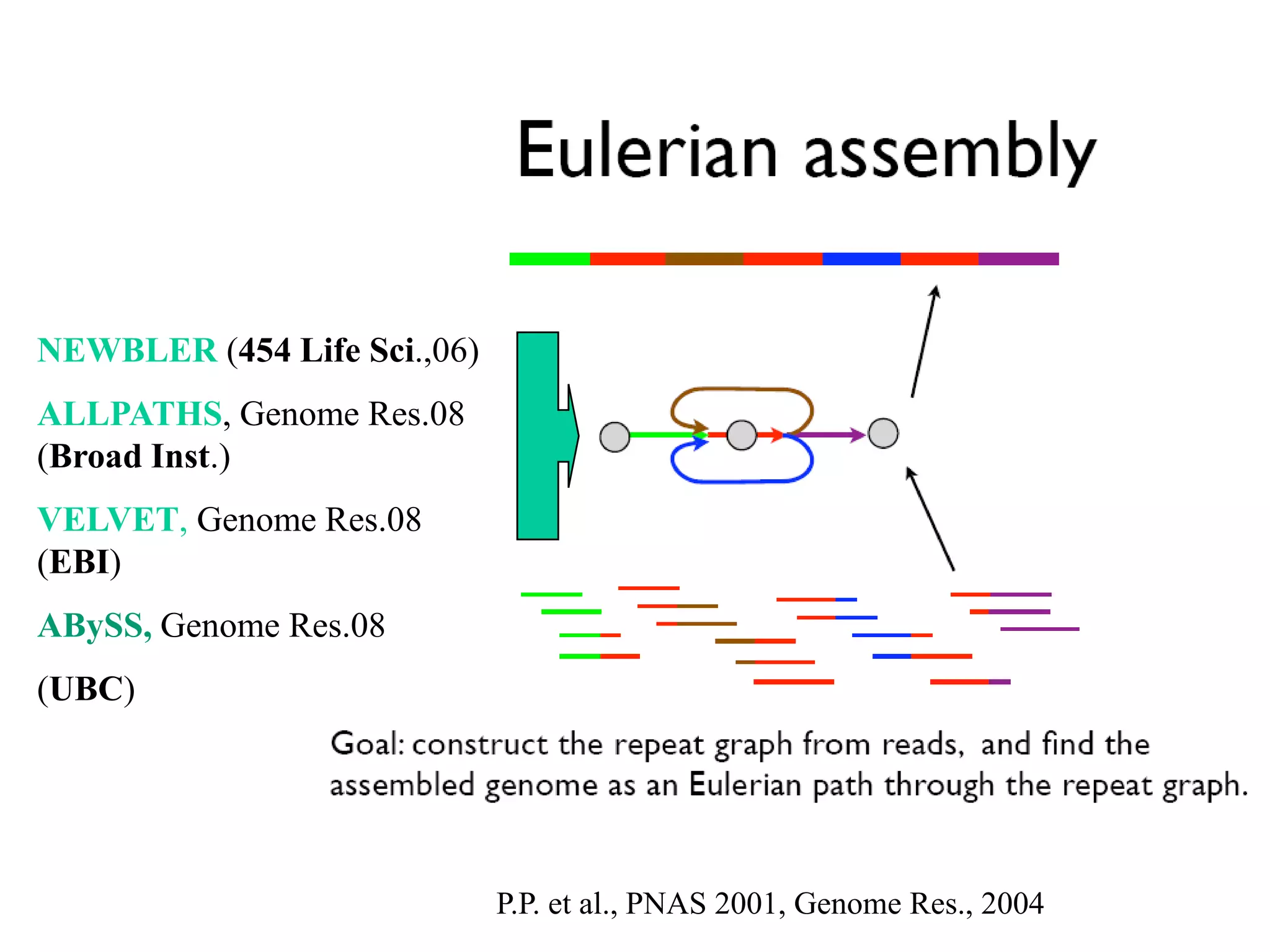
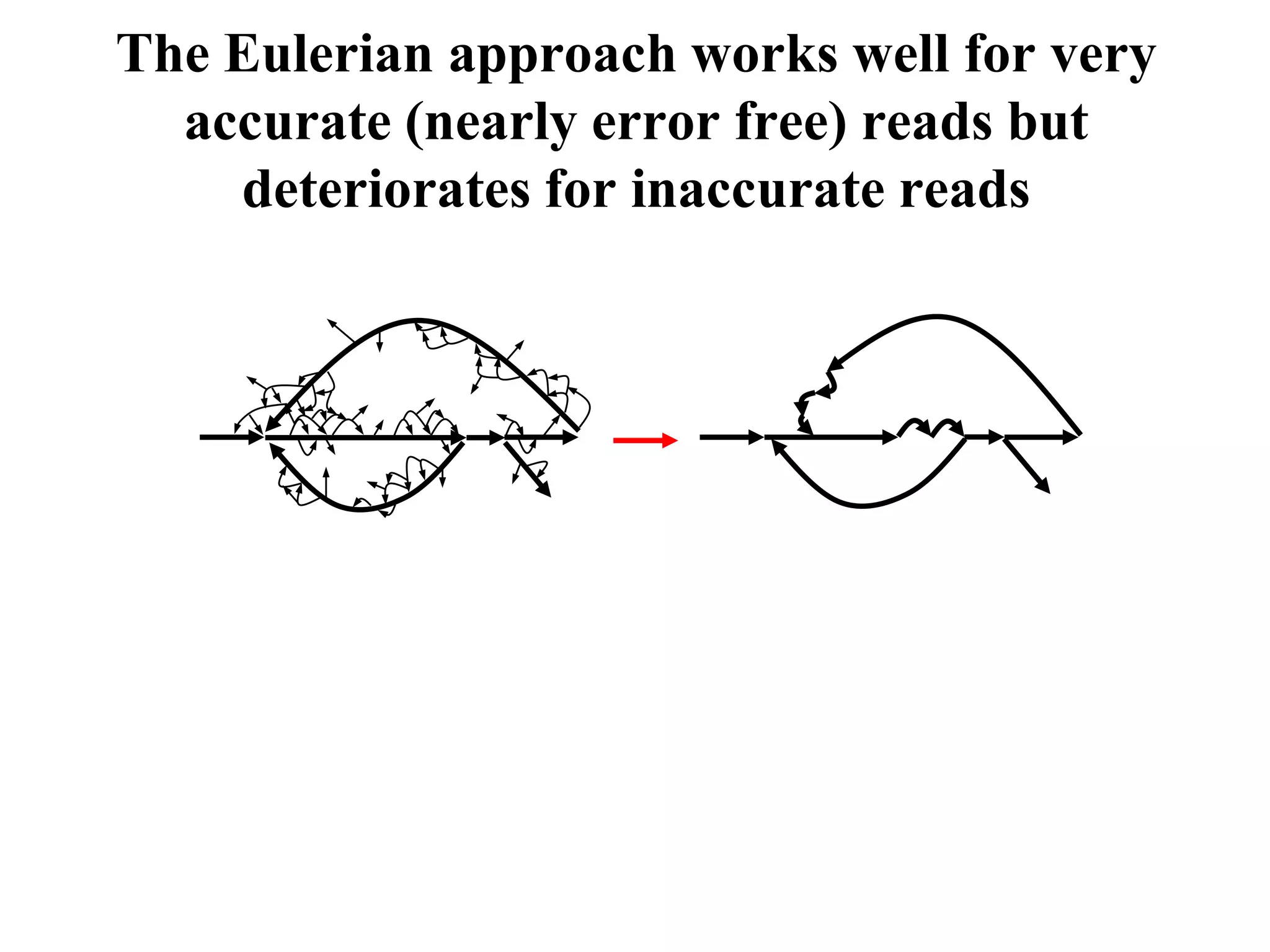
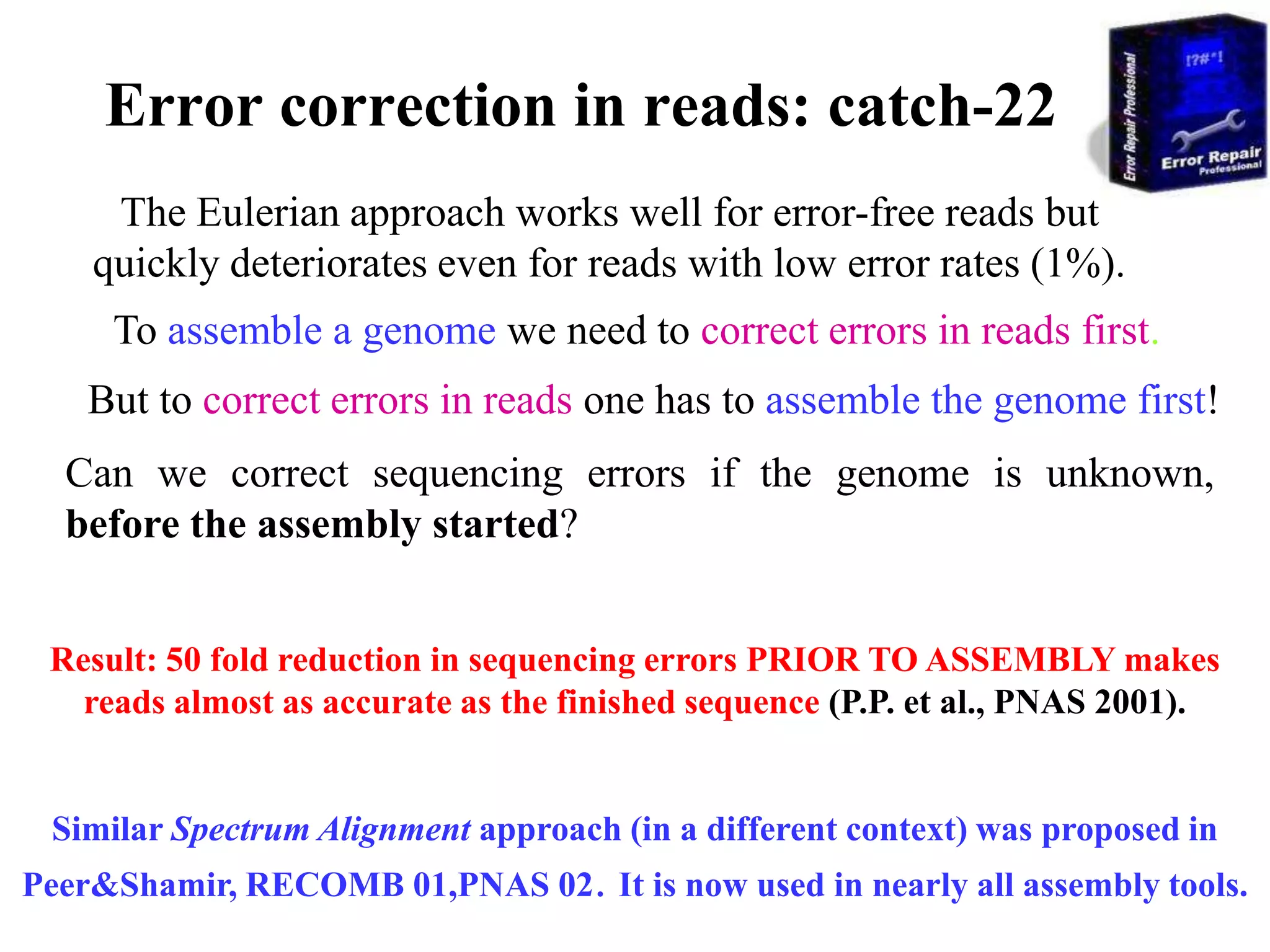
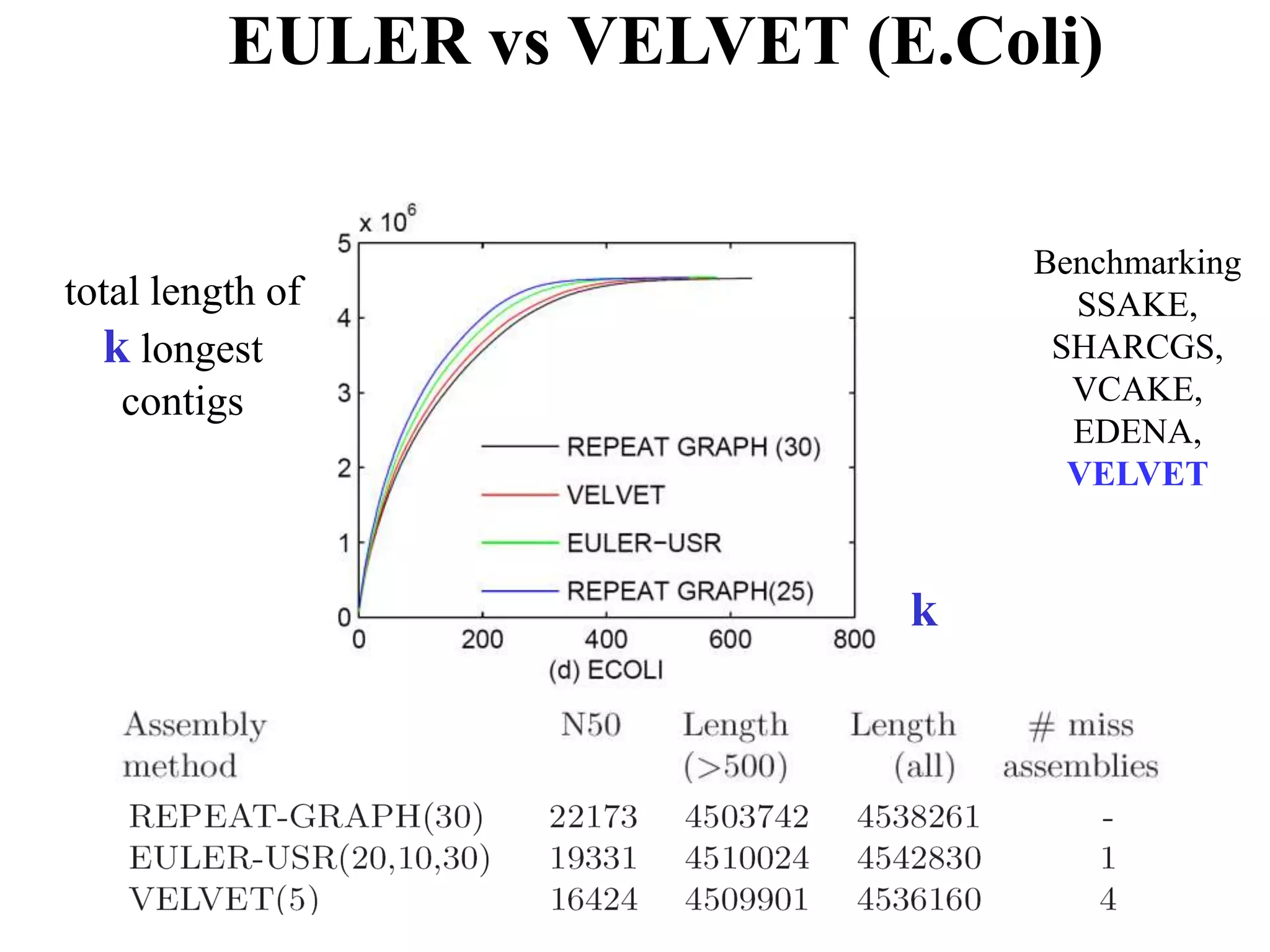
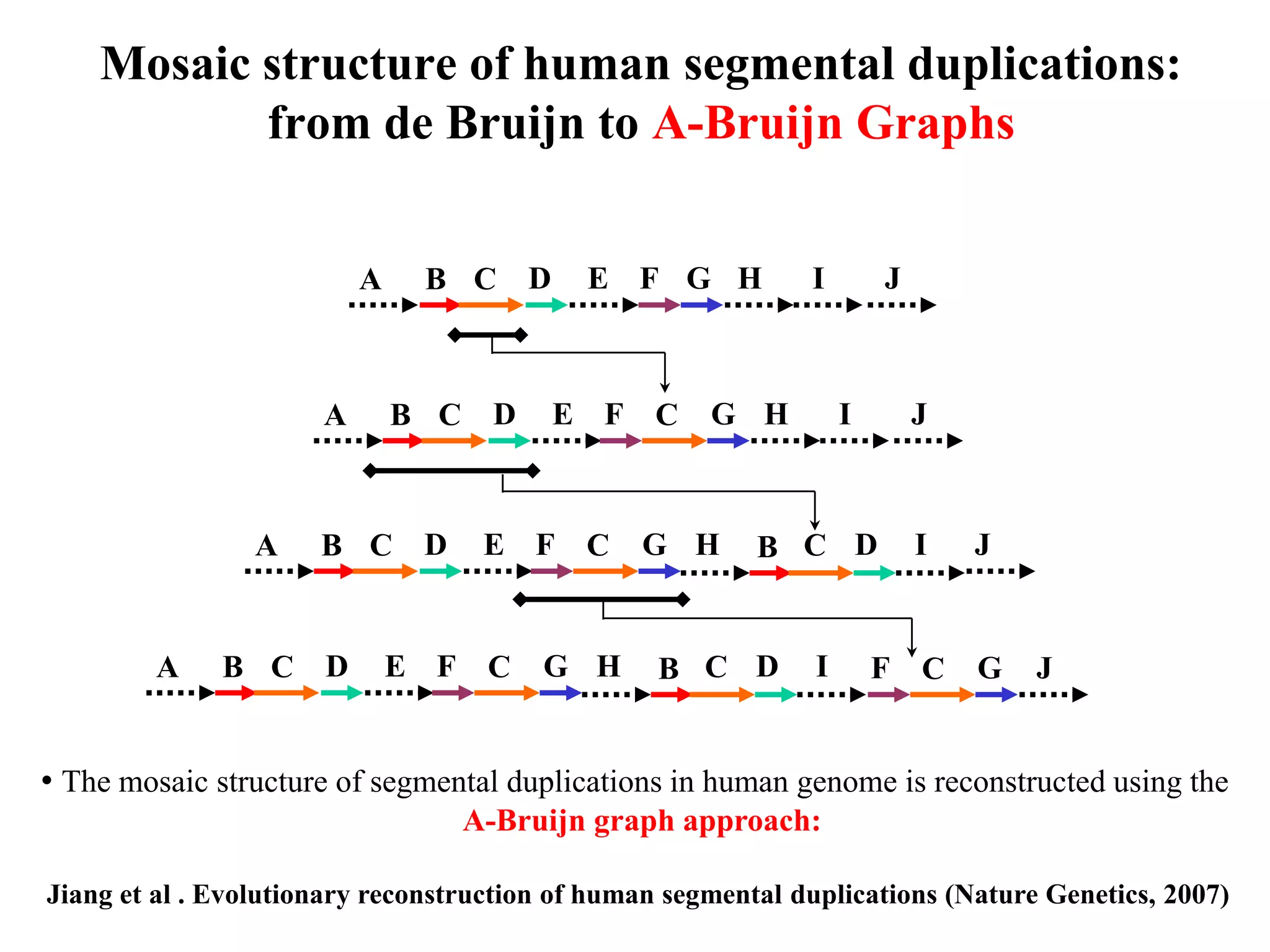
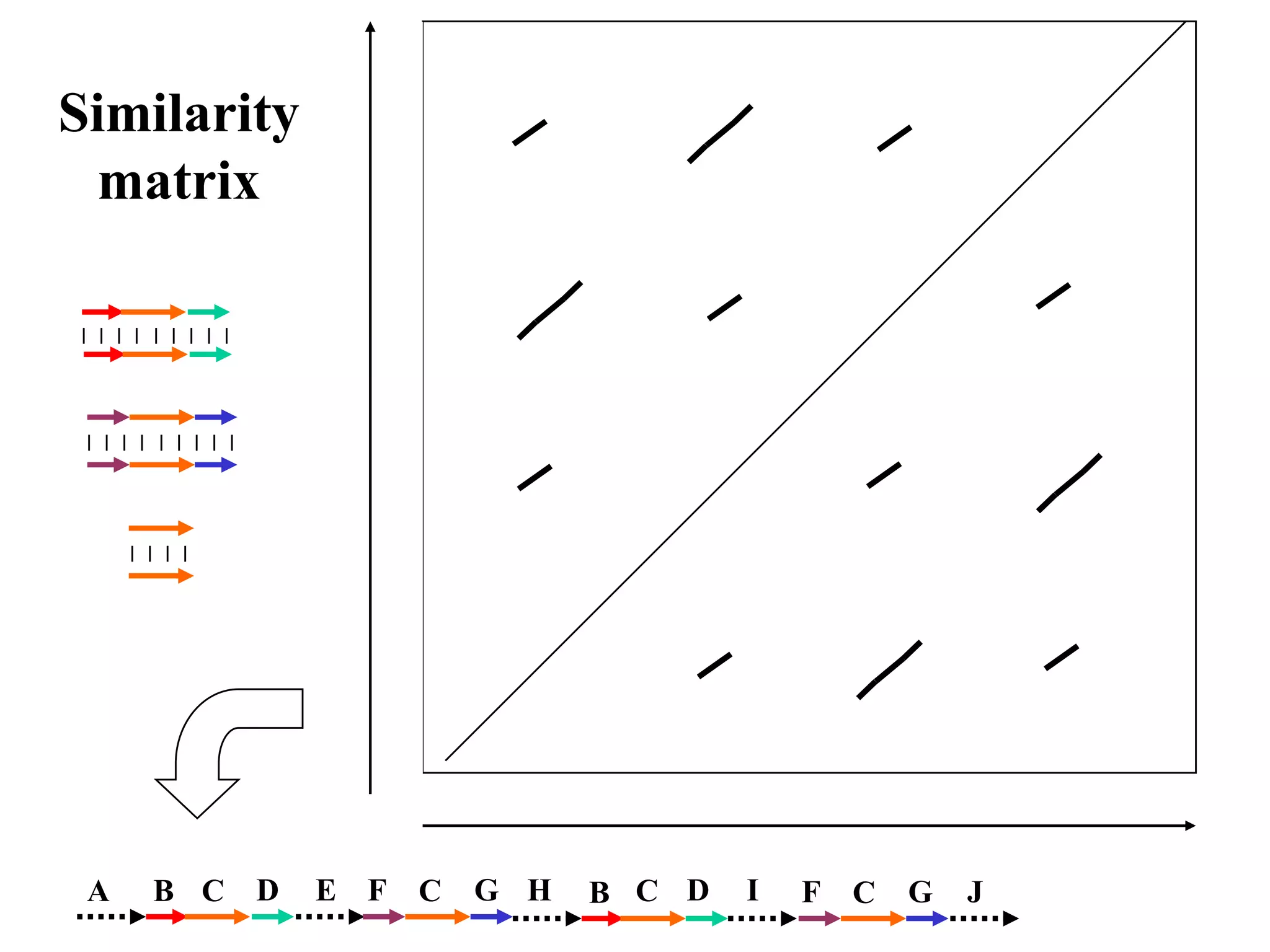
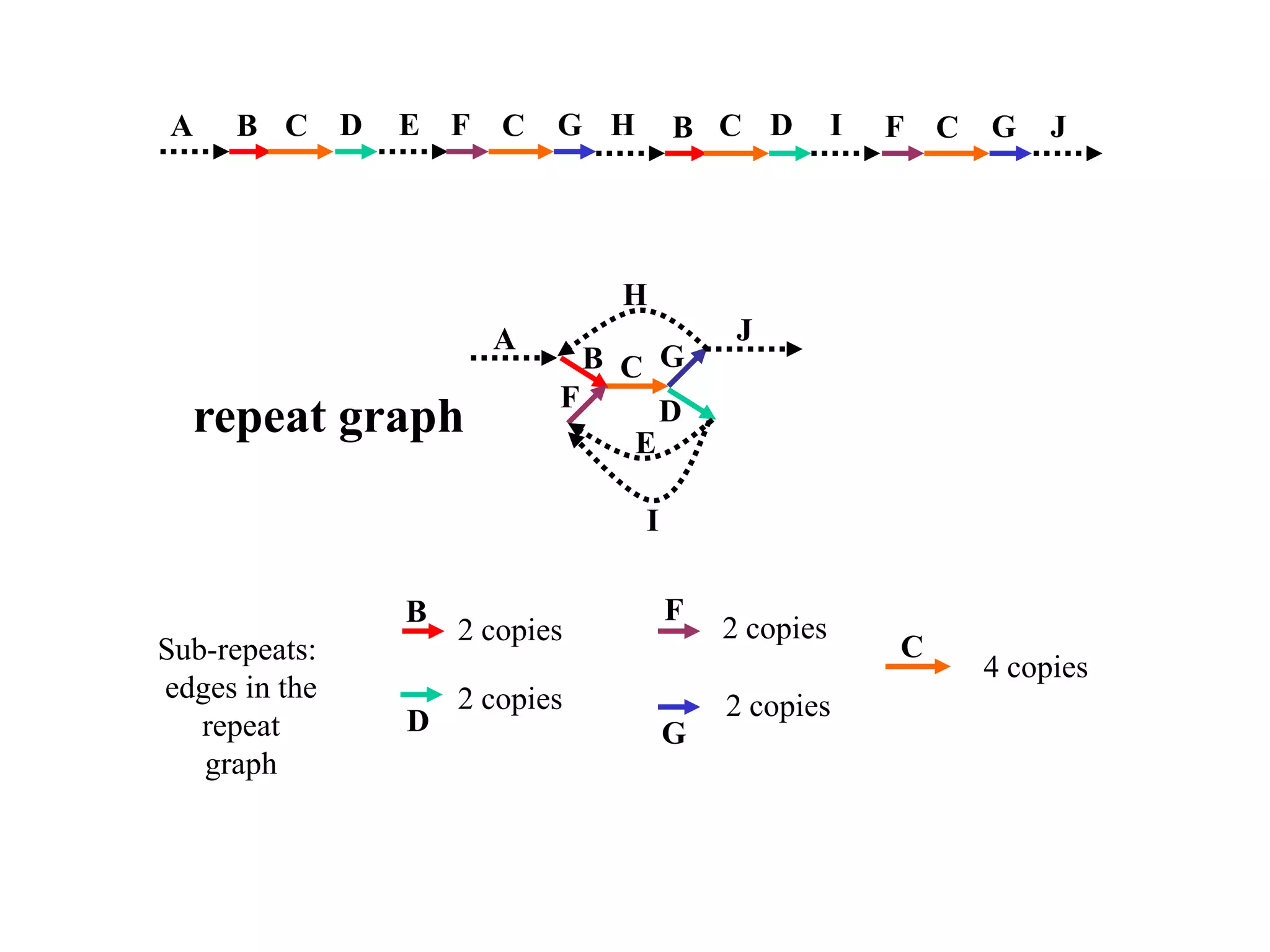
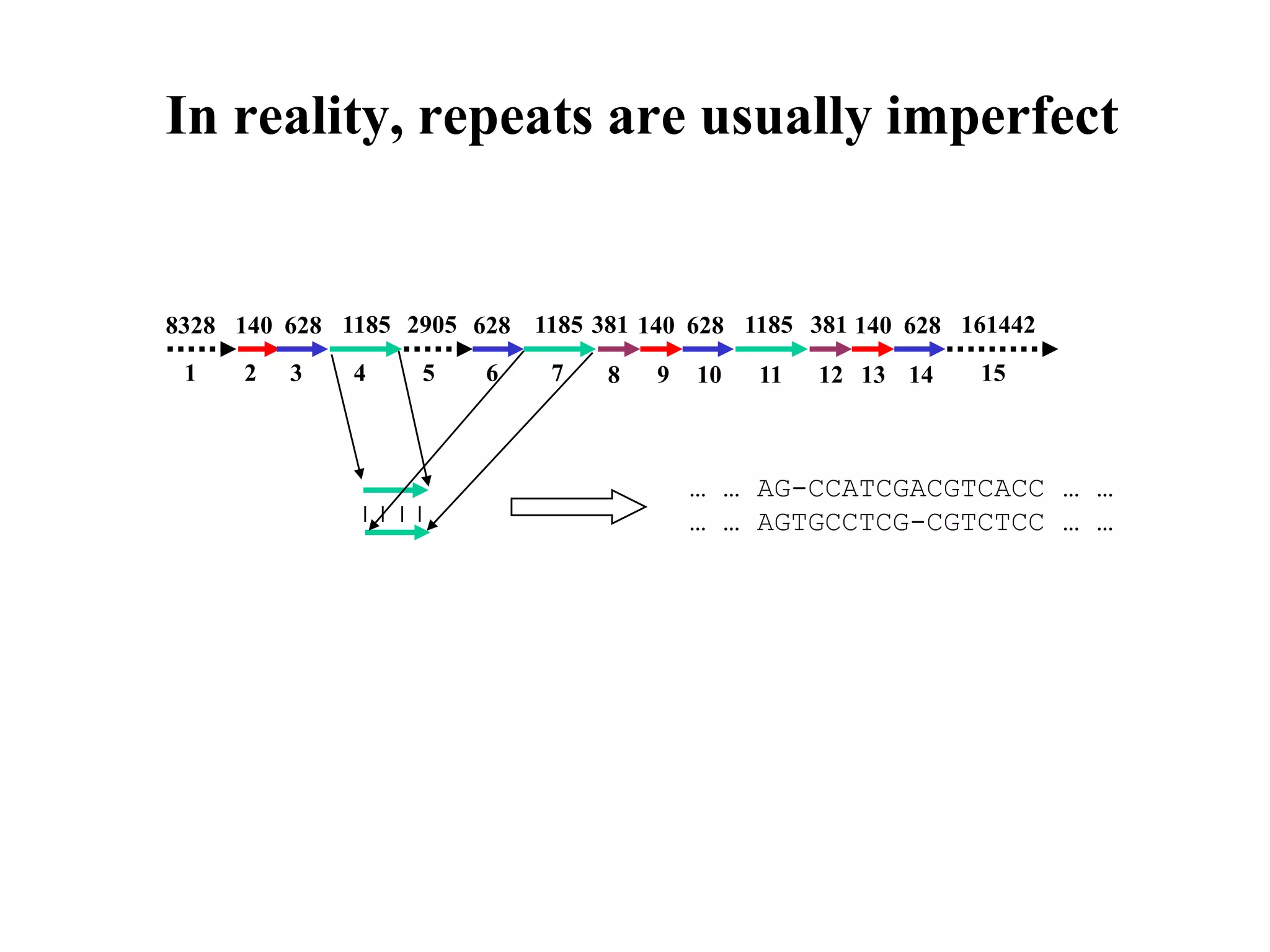
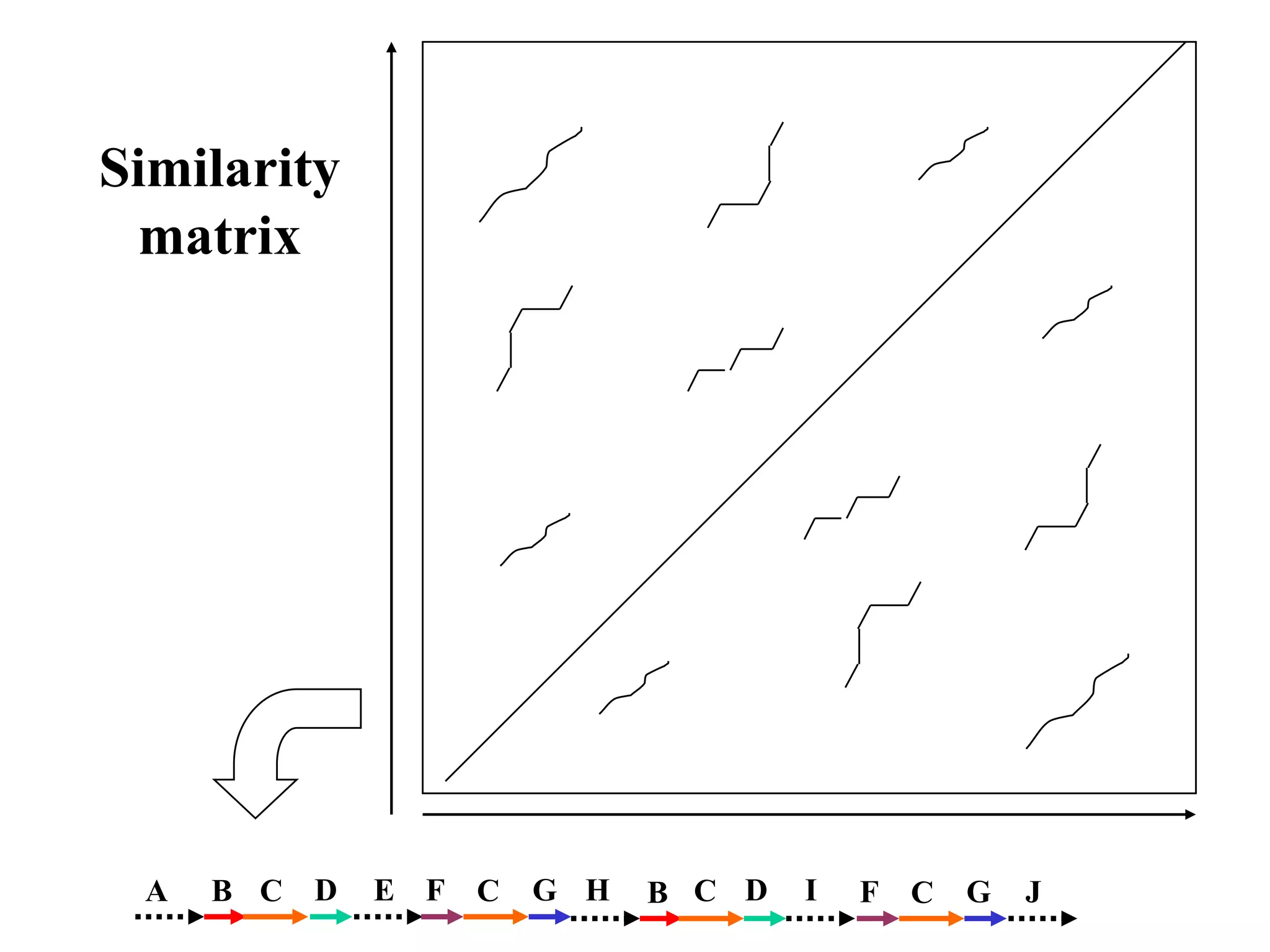
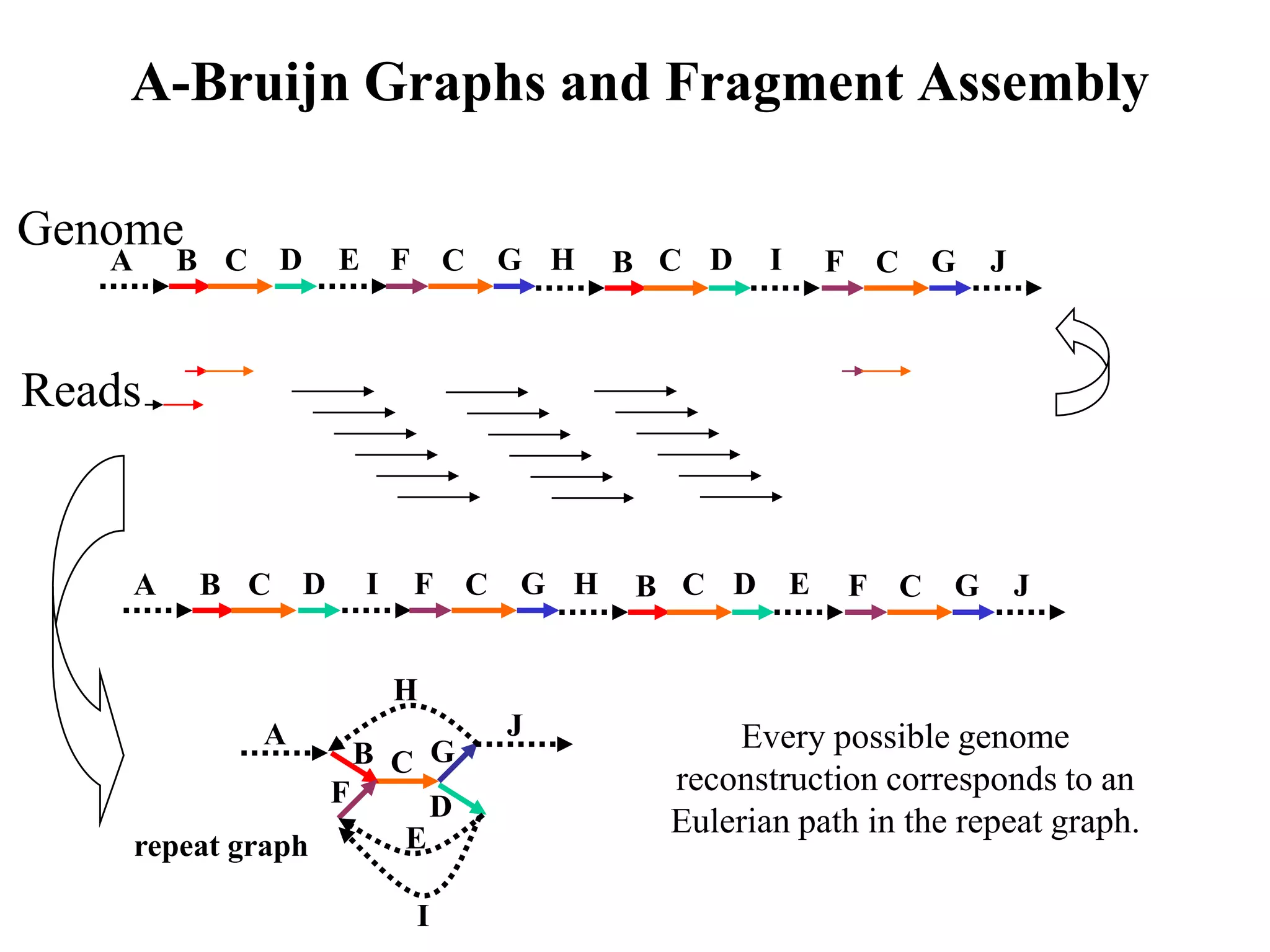
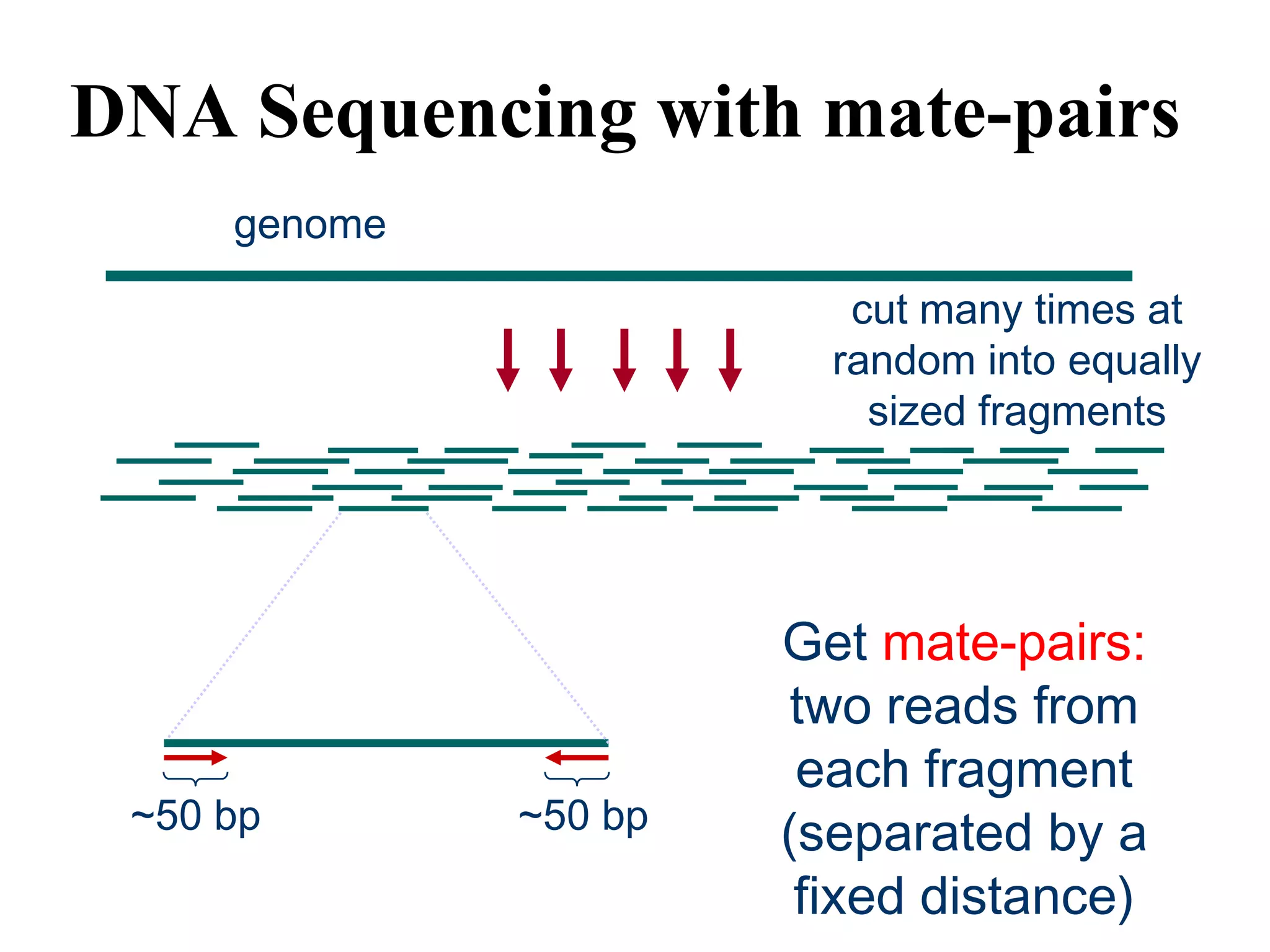
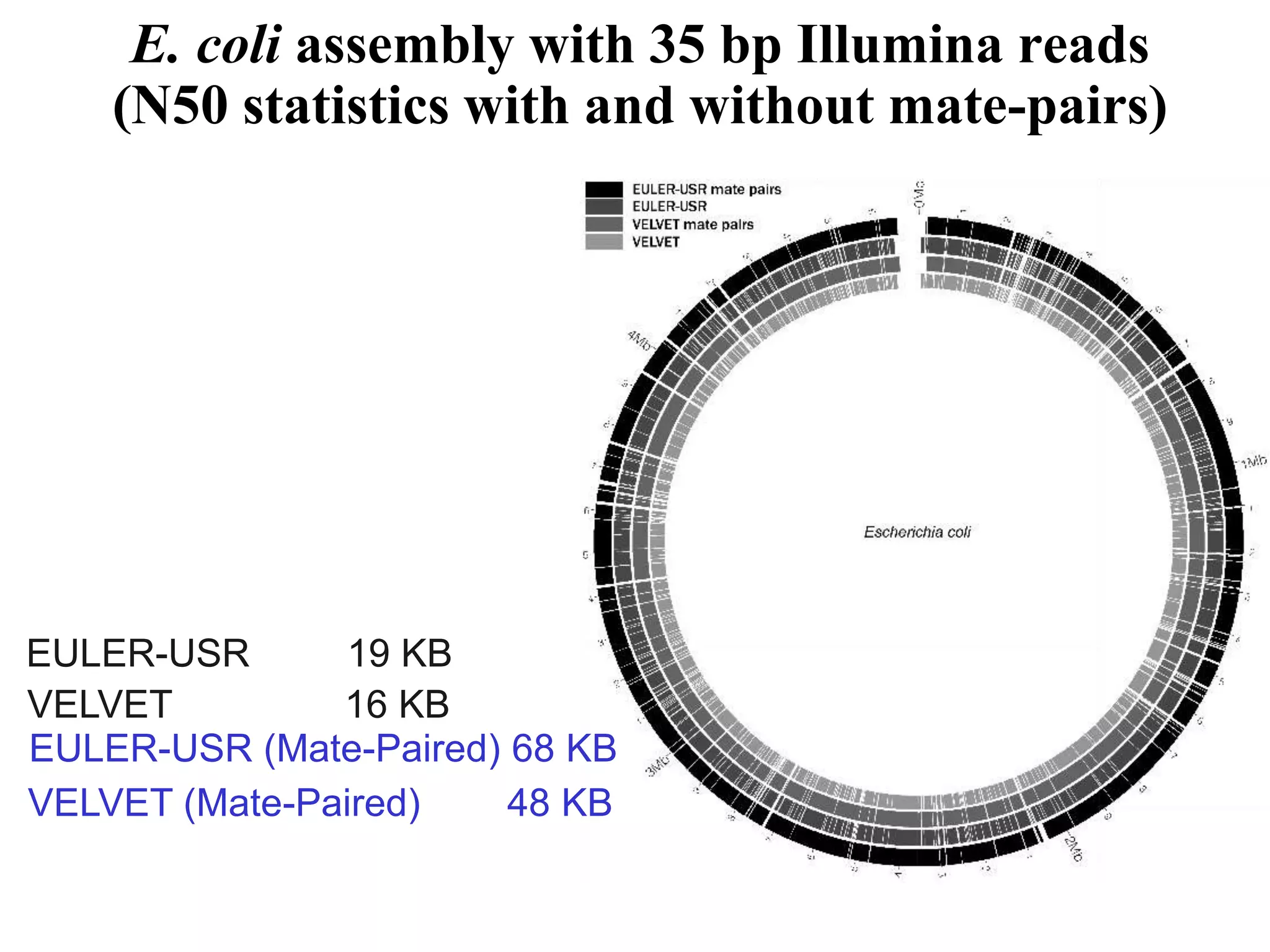
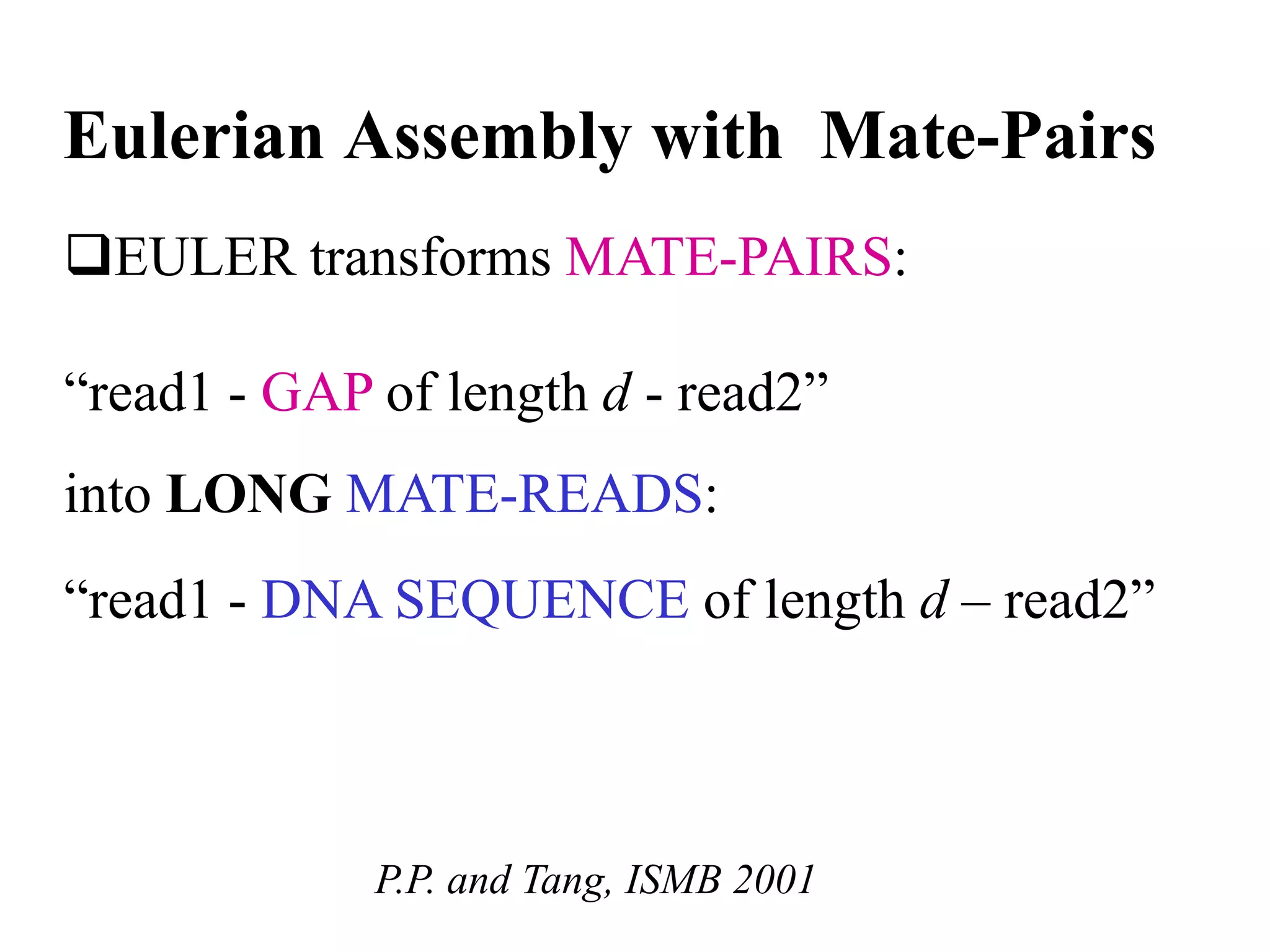
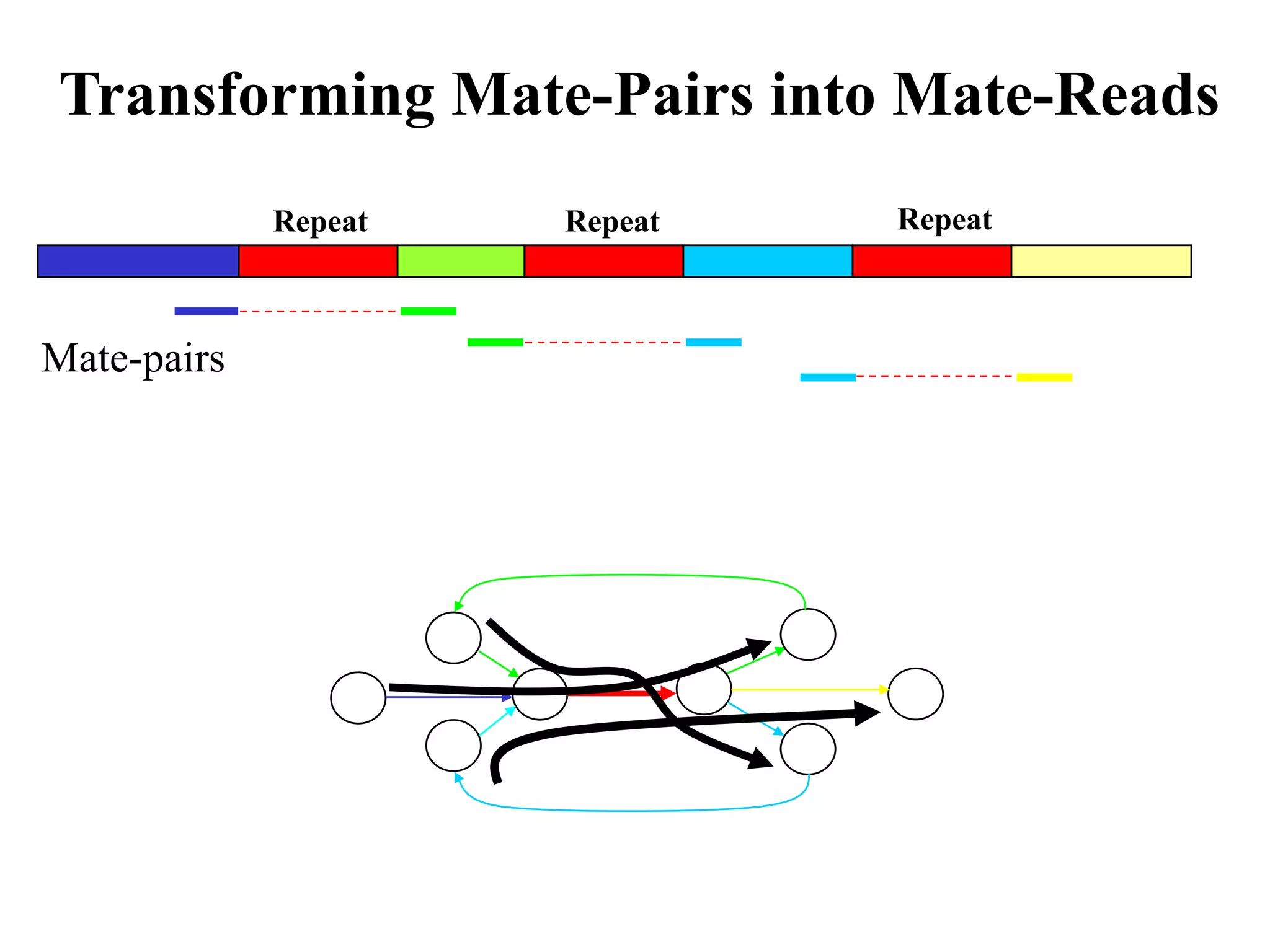
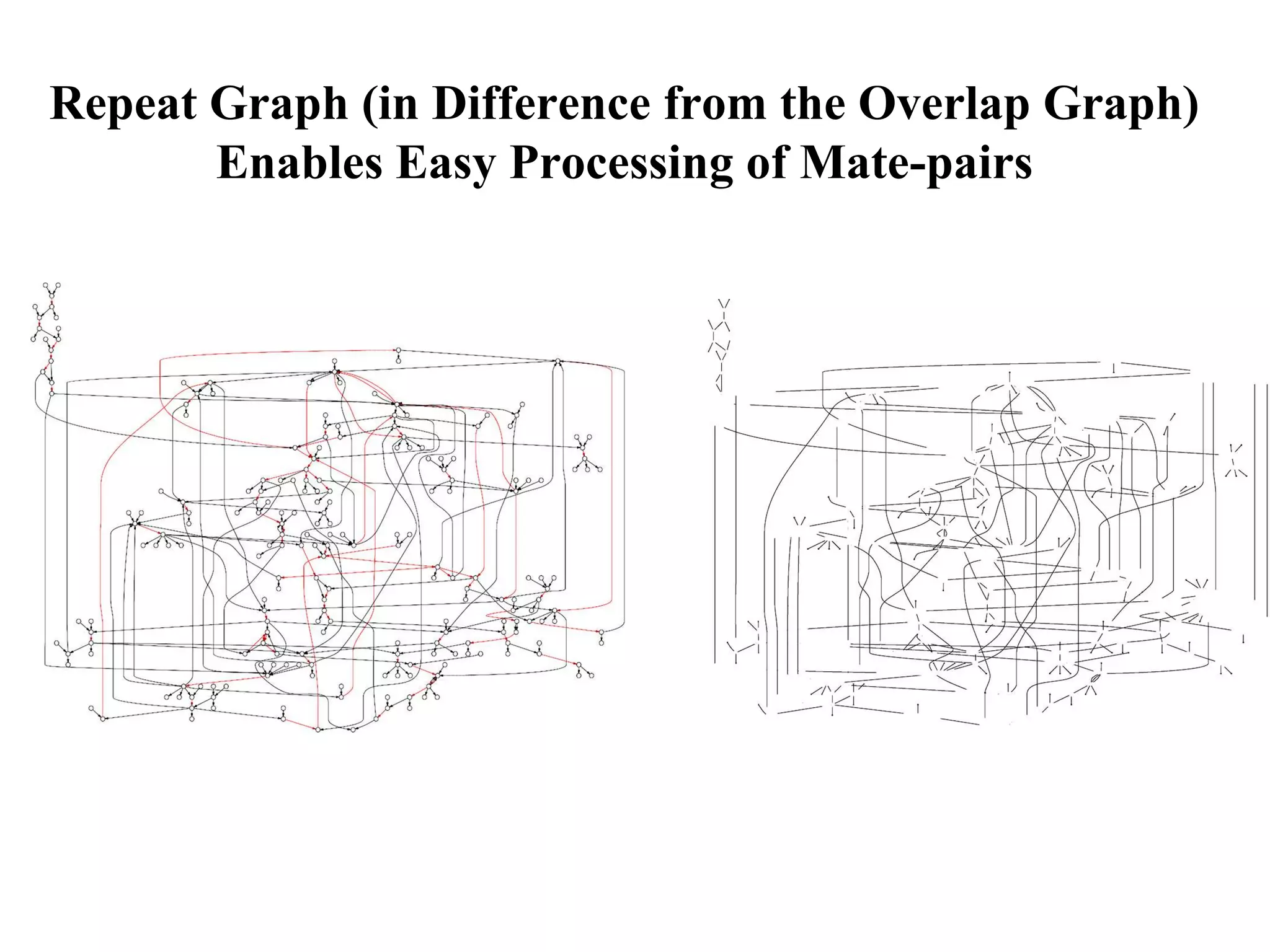
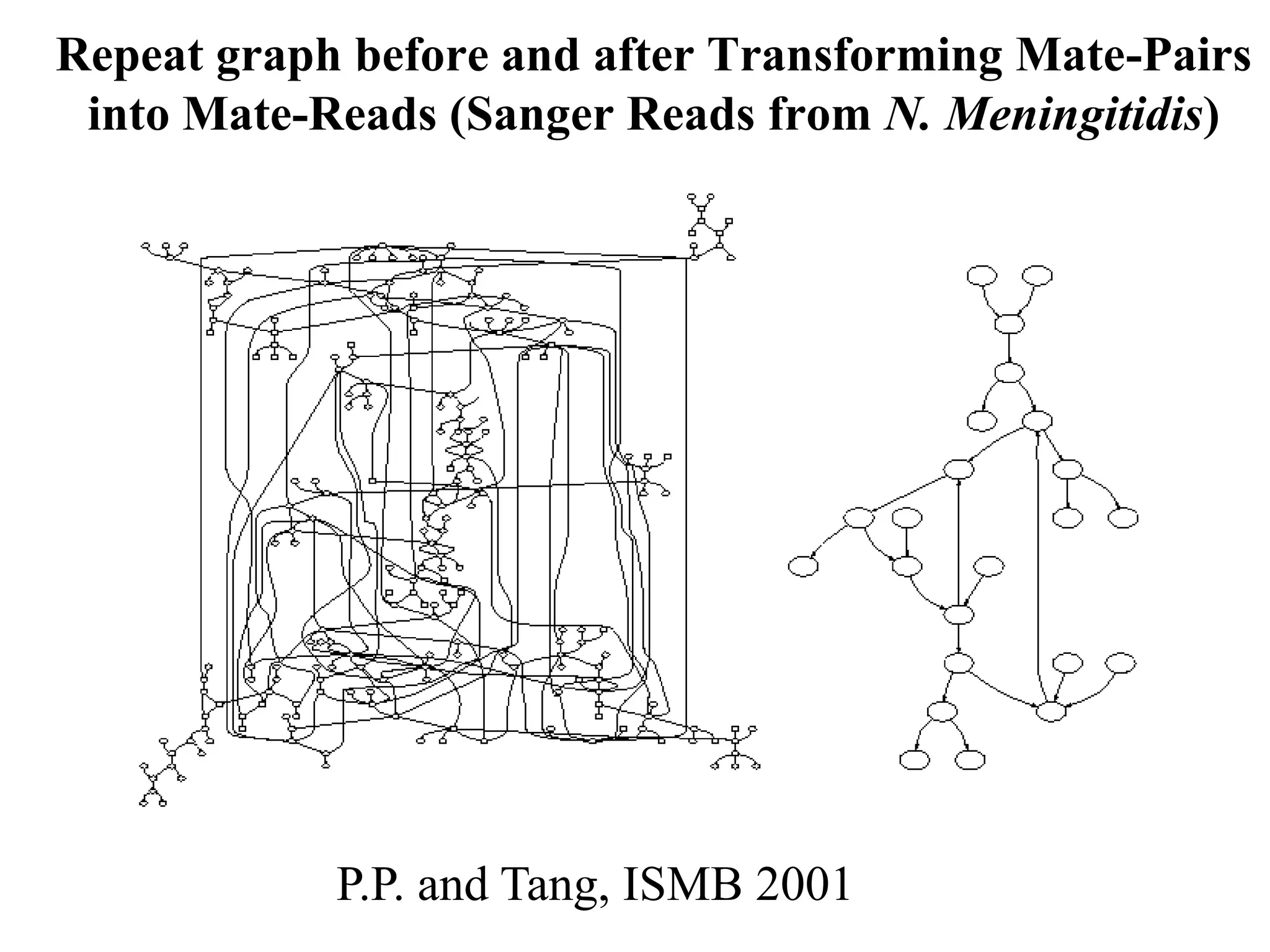
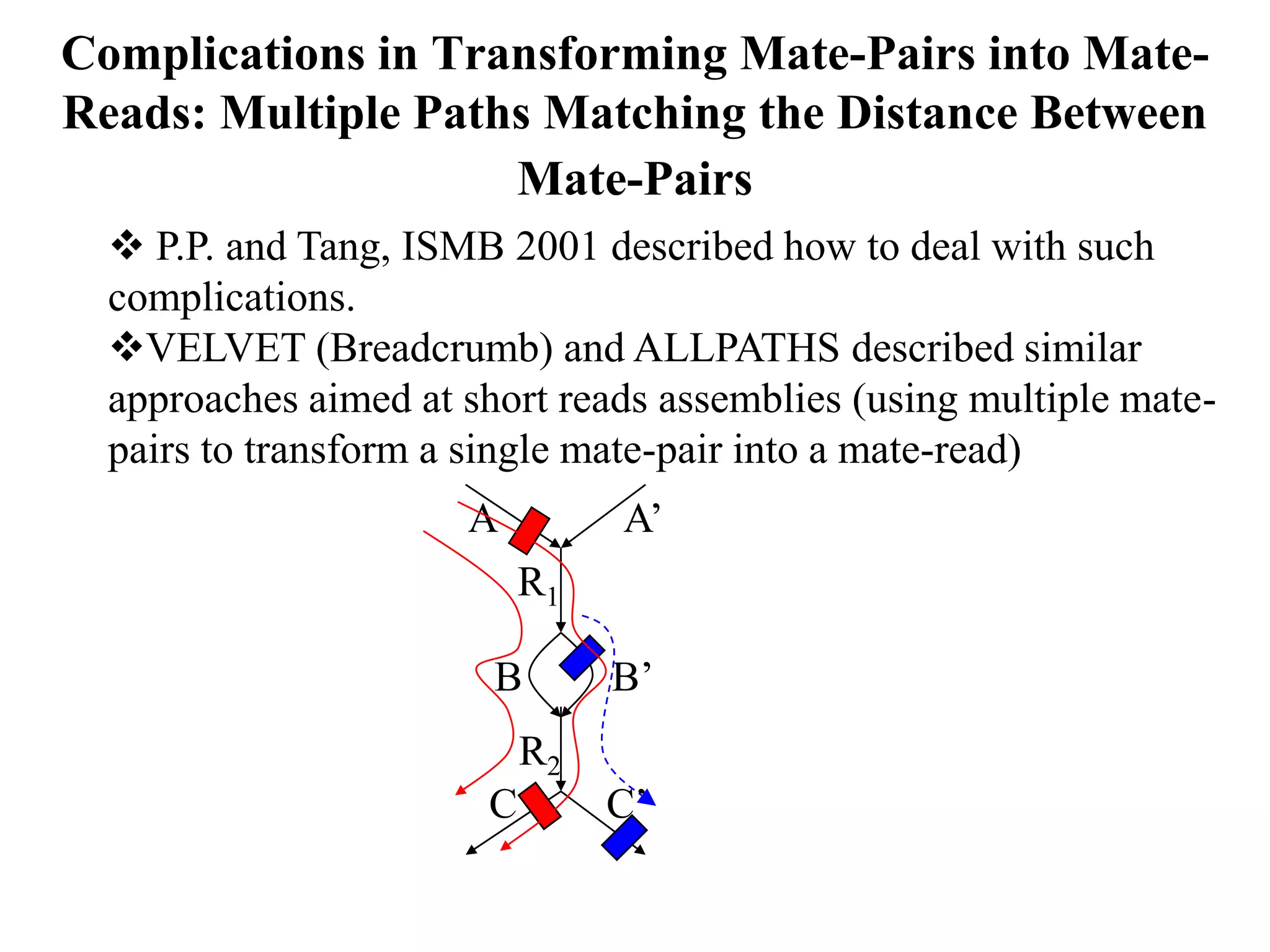
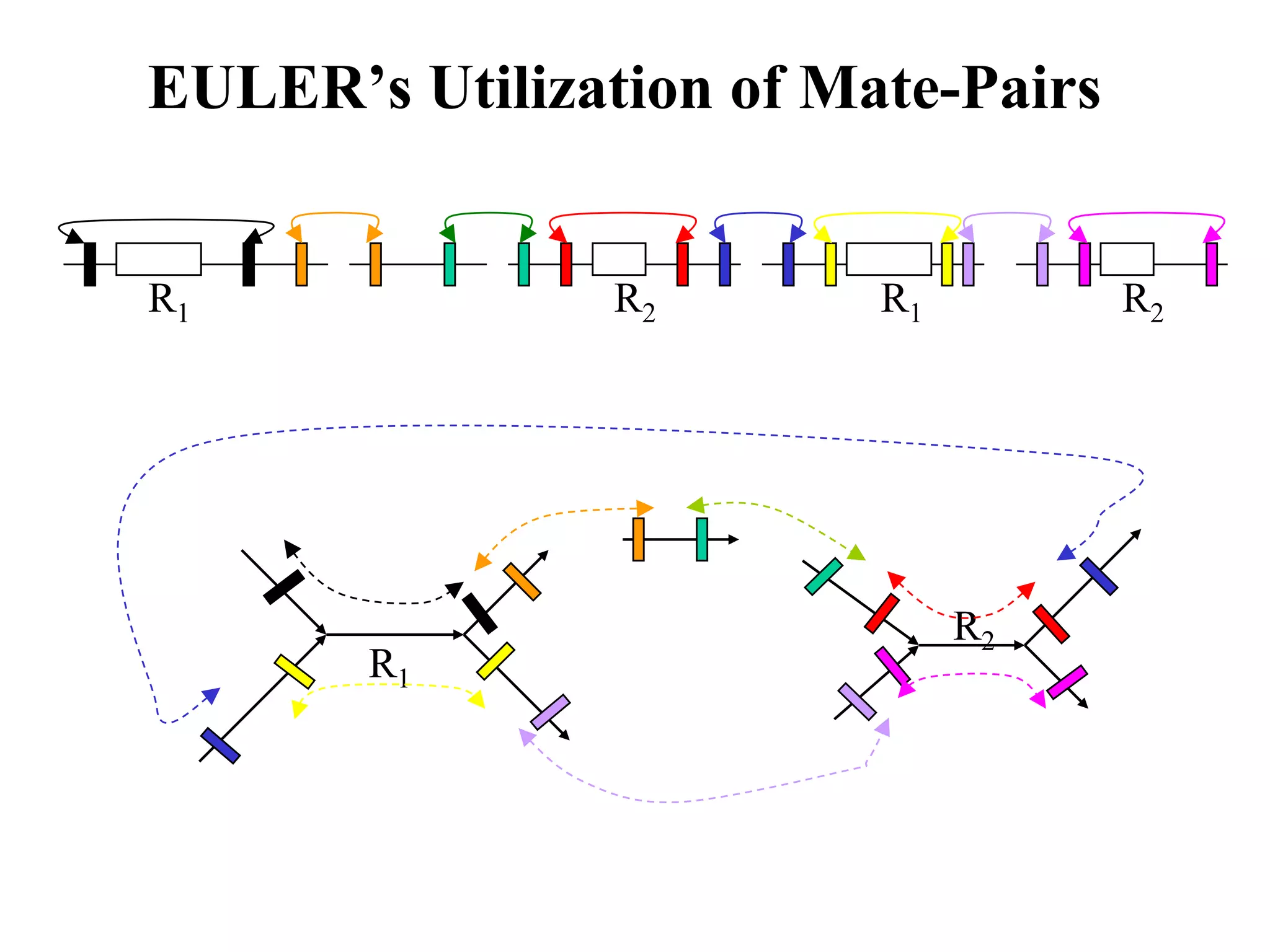
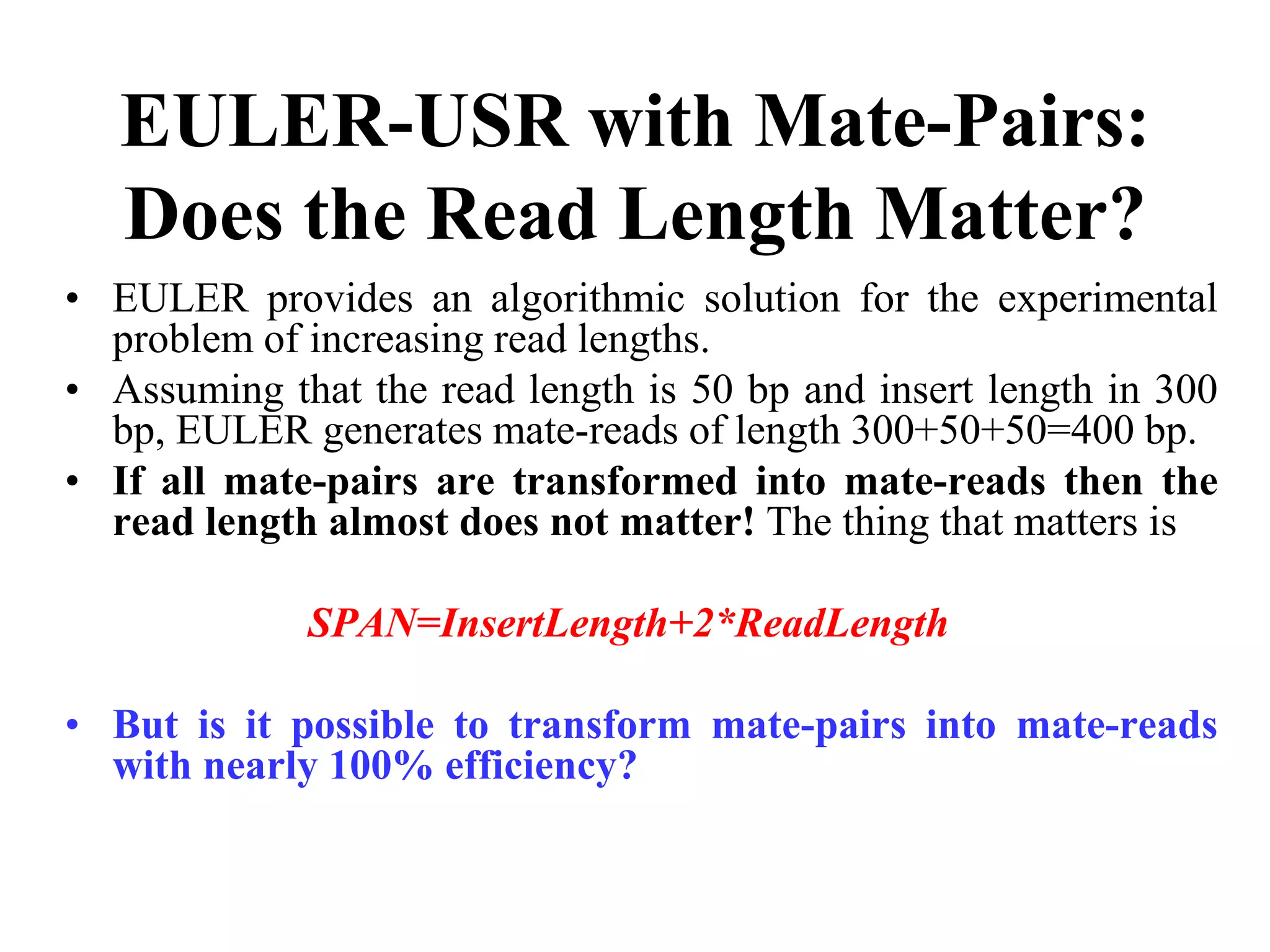
This document discusses how mate-pair information can be used to effectively increase read lengths and overcome challenges posed by short read lengths in de novo genome assembly. It describes how the Eulerian assembly algorithm transforms mate-pair reads into long "mate-reads" by connecting the two reads in a pair via the estimated insert length. This has the effect of increasing the overall read length and improving assembly, to the point where read length may no longer be a major limitation as long as the span between mate-pairs is large enough. The repeat graph data structure enables easy processing of mate-pair information in this way.
















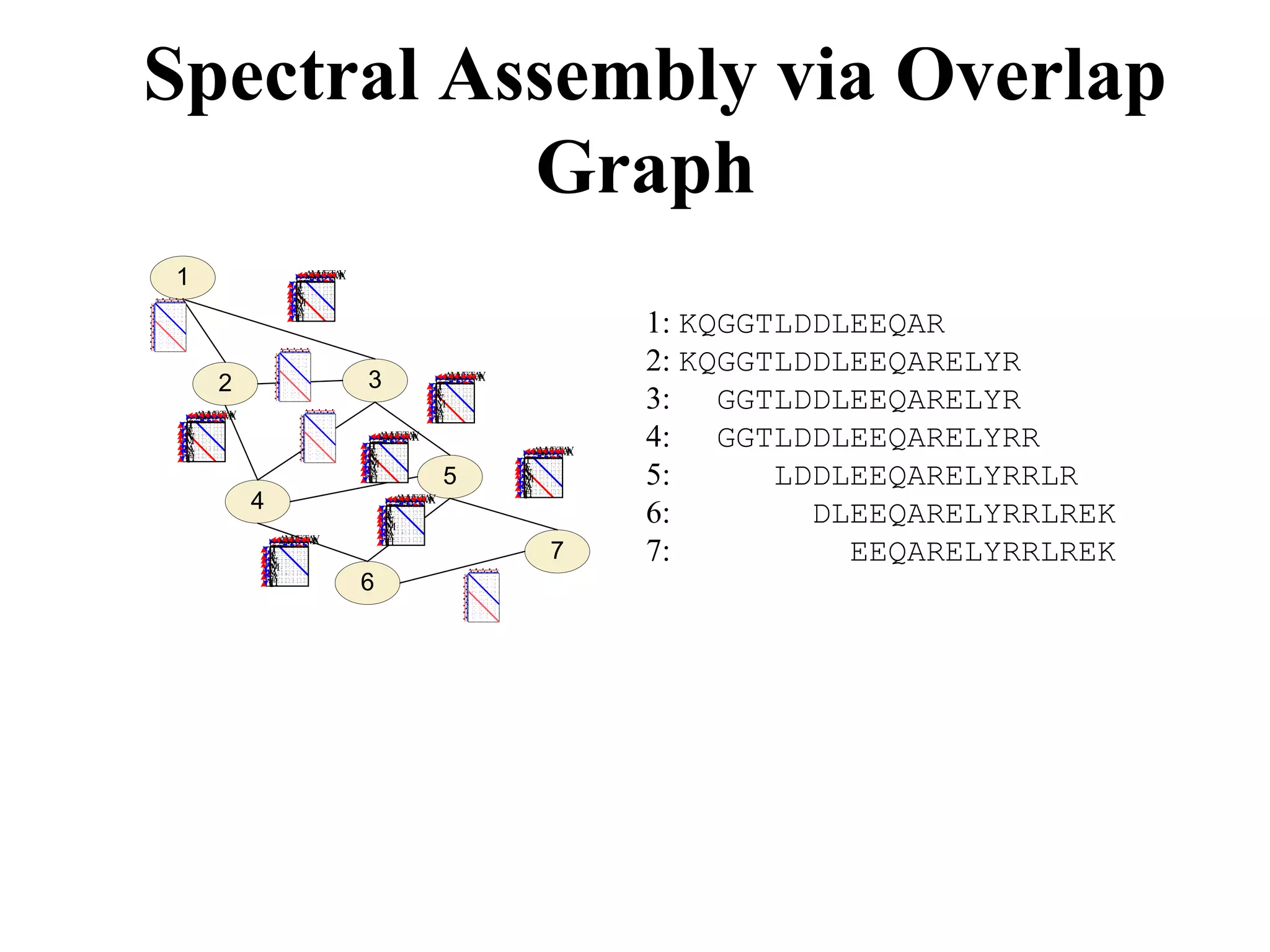
![28 aa protein contig, 24 spectra
[271.1] F (SK) S G T E C R A S M S E C D P A E H C T G Q S
GRHSLFHPEDTGKVFKVSHSFPHPLYDMSLLKNRFLRPGDDSSHDLMLLR
50 amino acids long protein contig of 92 assembled spectra
b-ions in each spectrum Mass difference between b-ions Oxidized Methionine](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20101209dnaseqpevzner-110425120311-phpapp01/75/20101209-dnaseq-pevzner-69-2048.jpg)