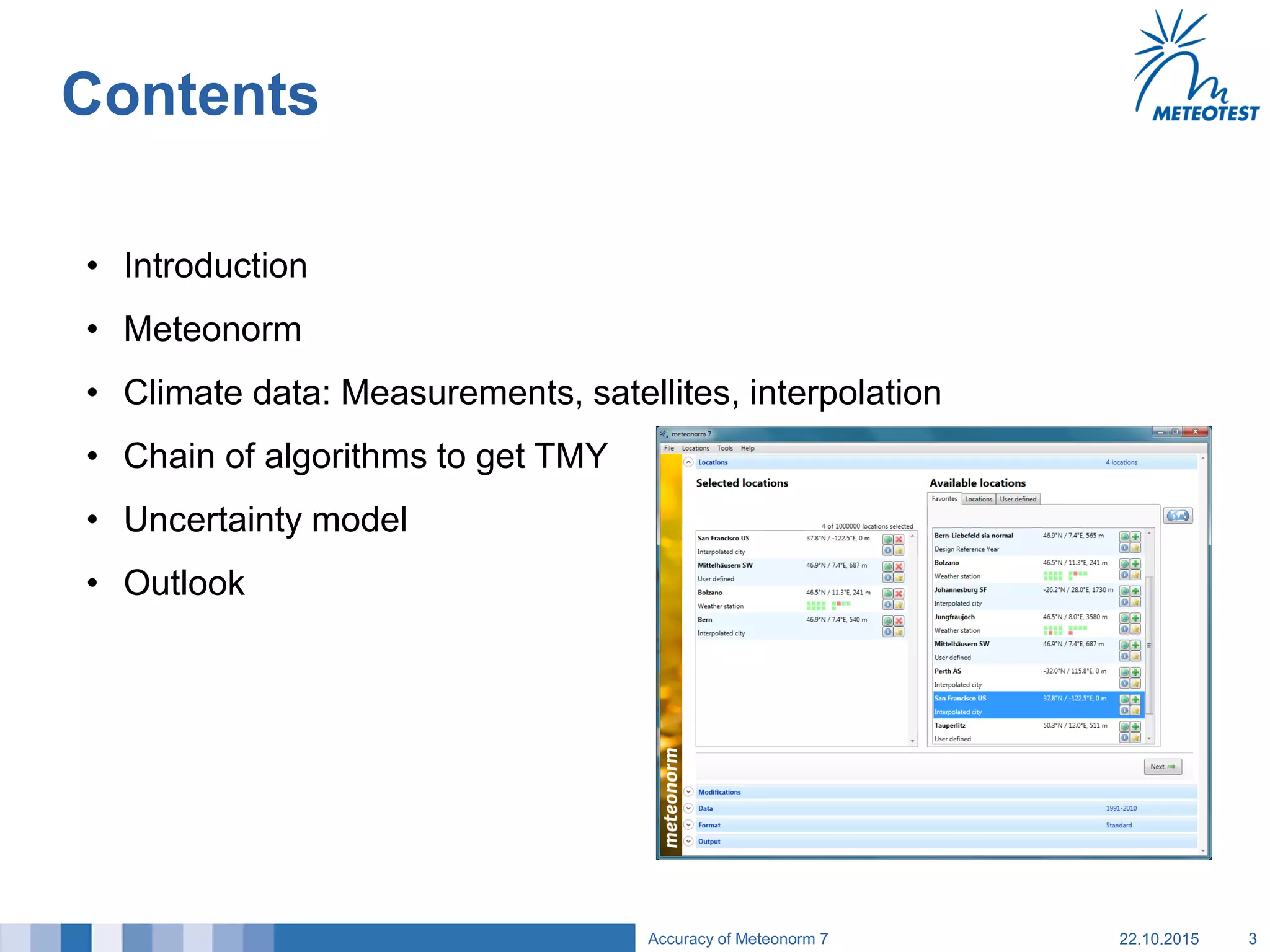
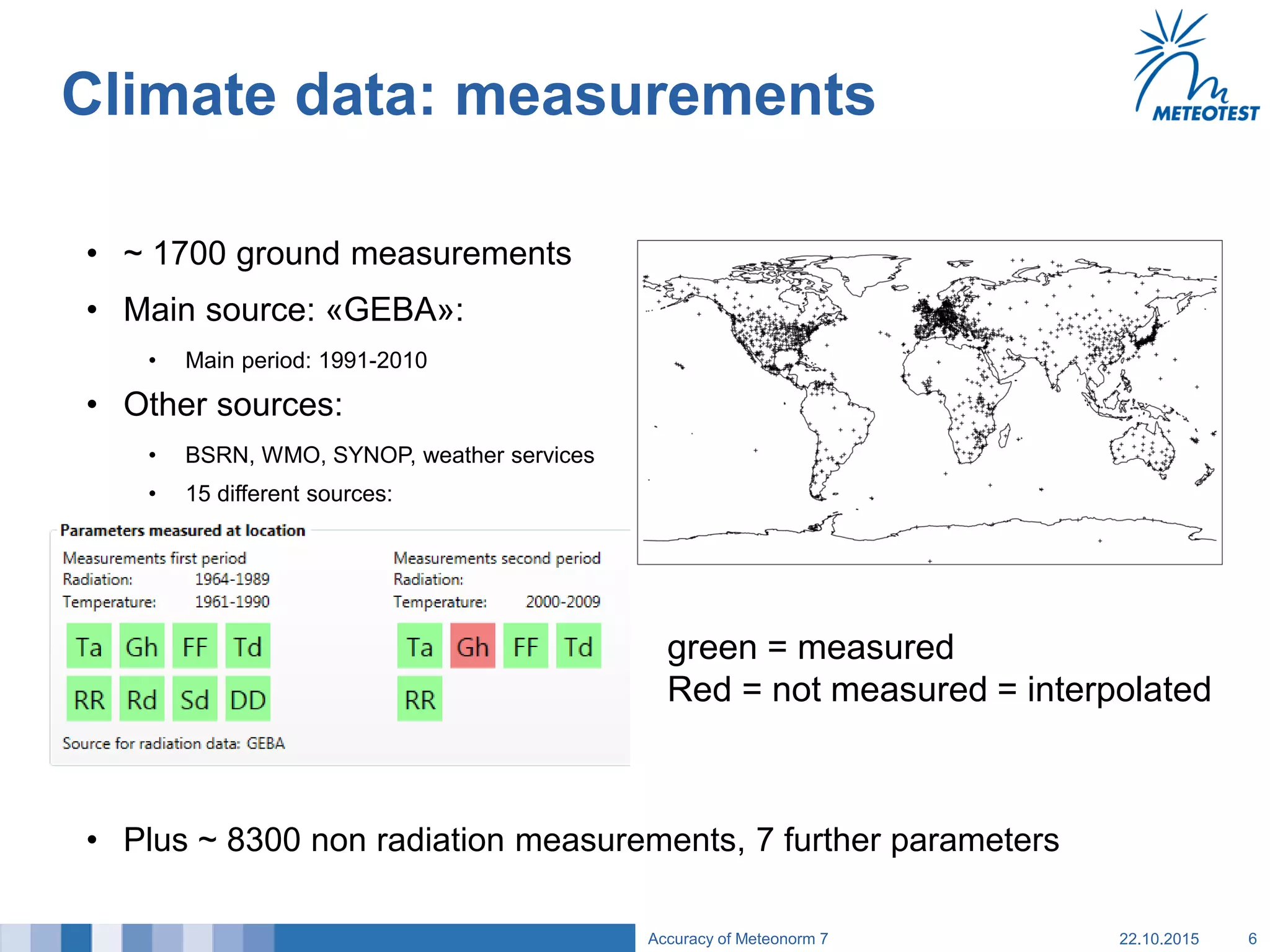
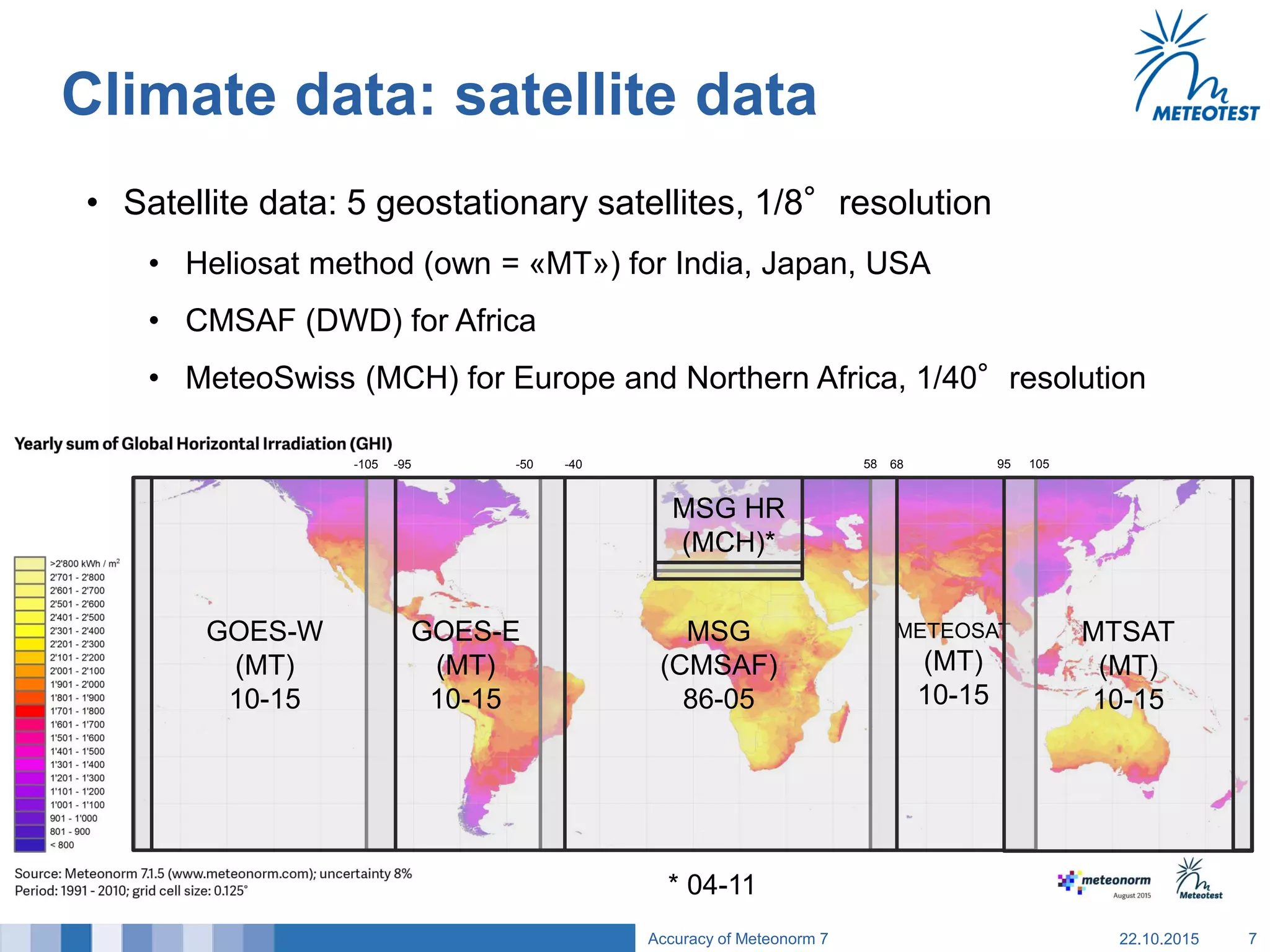
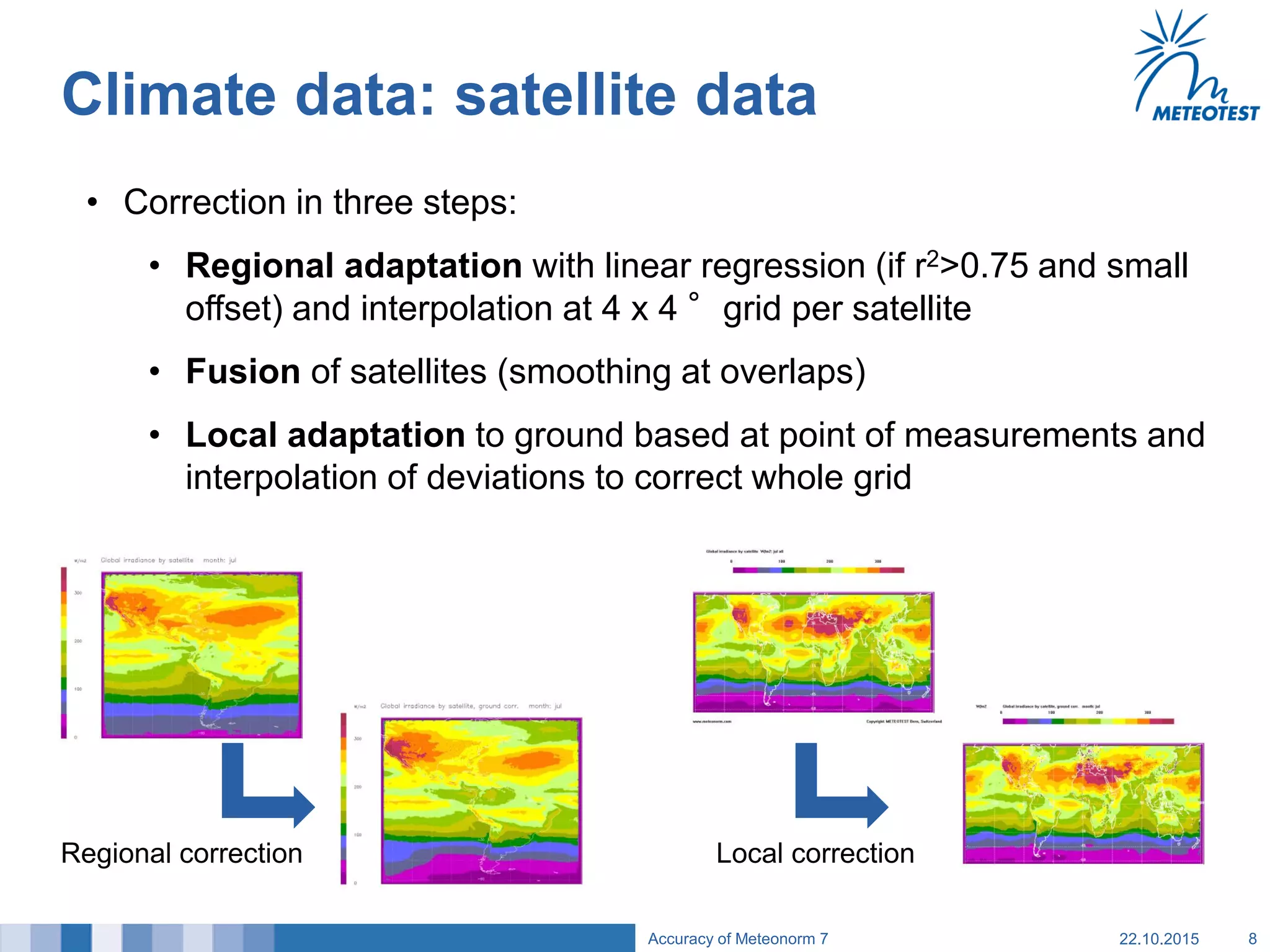
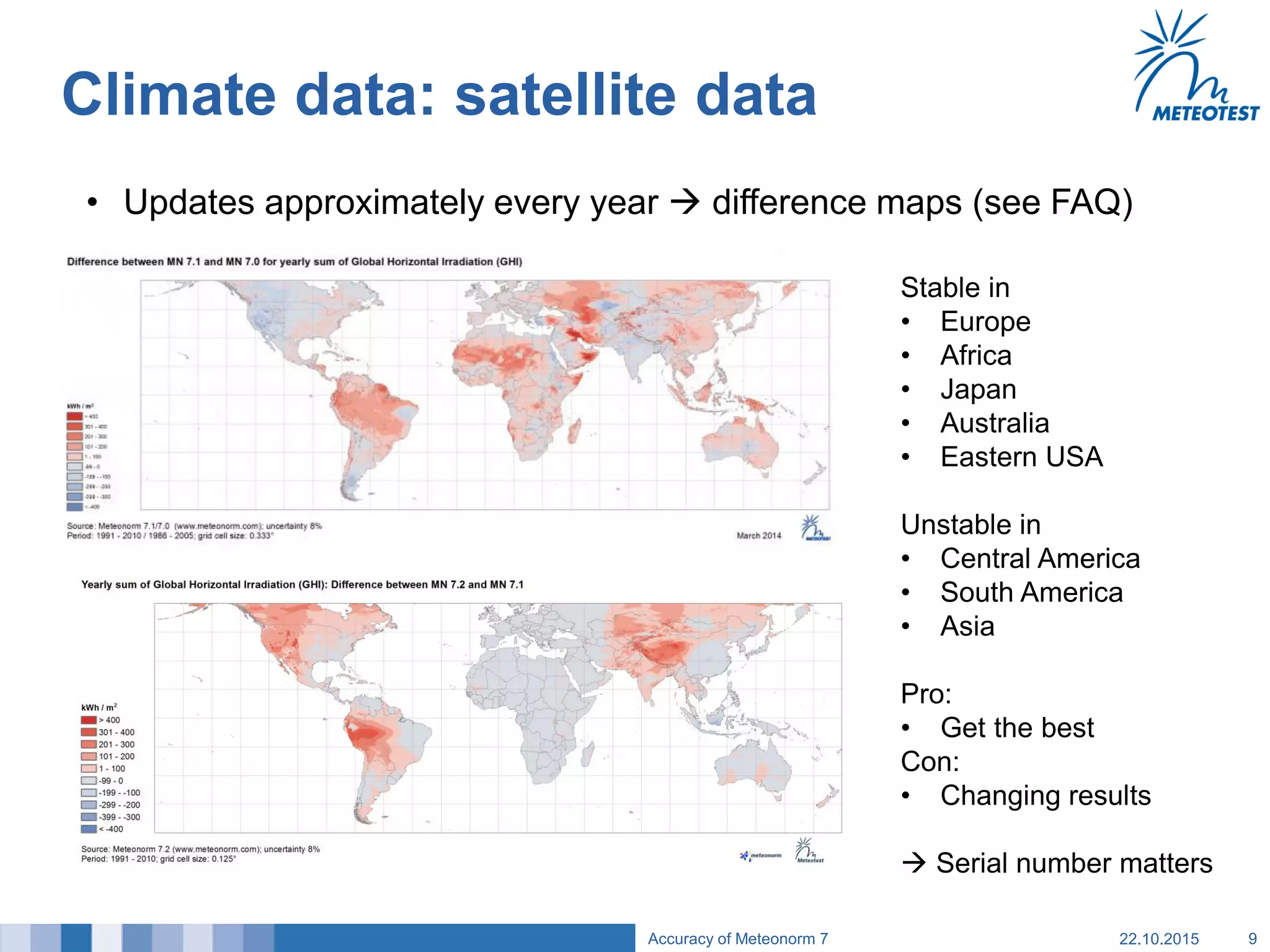
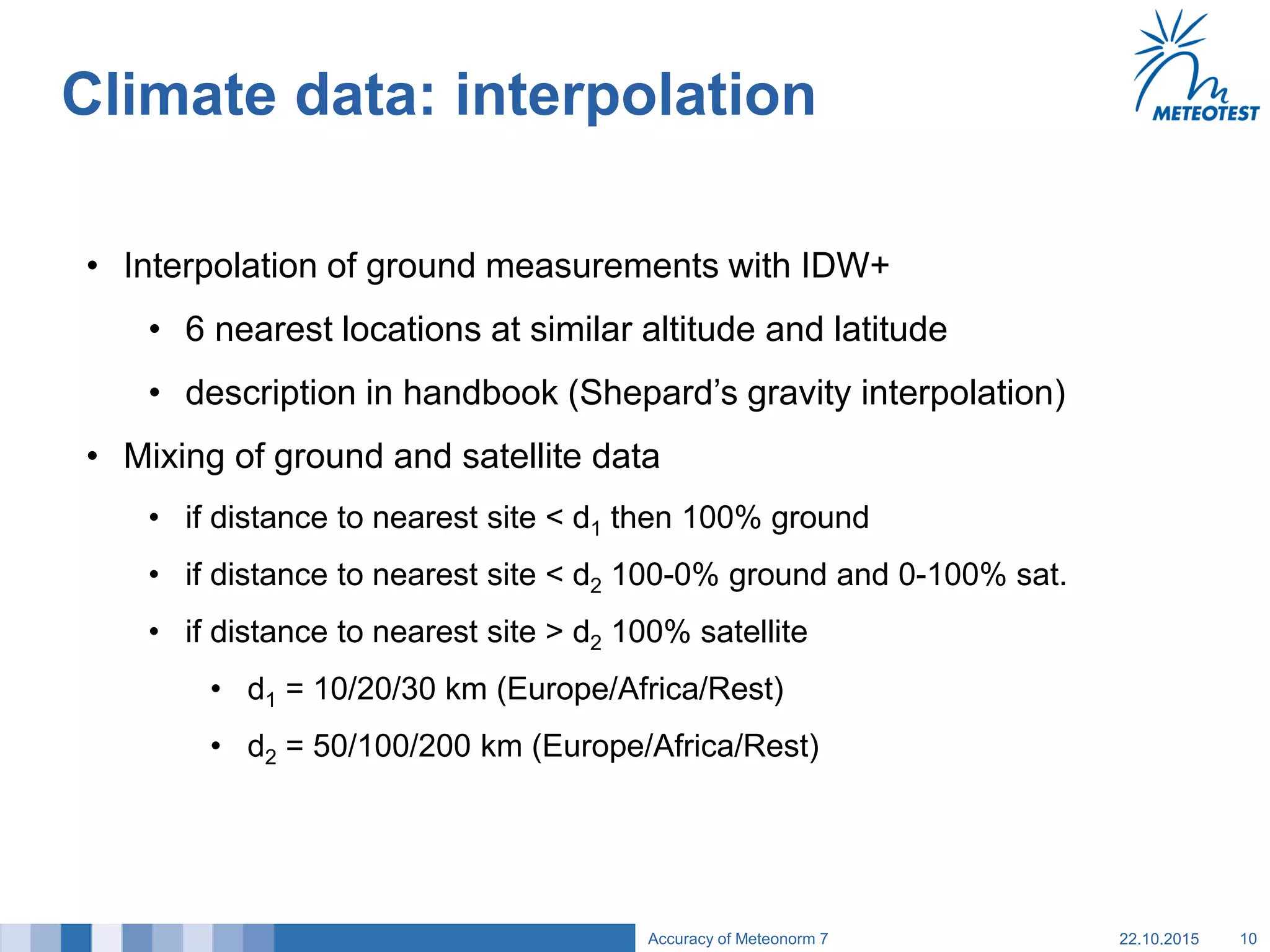
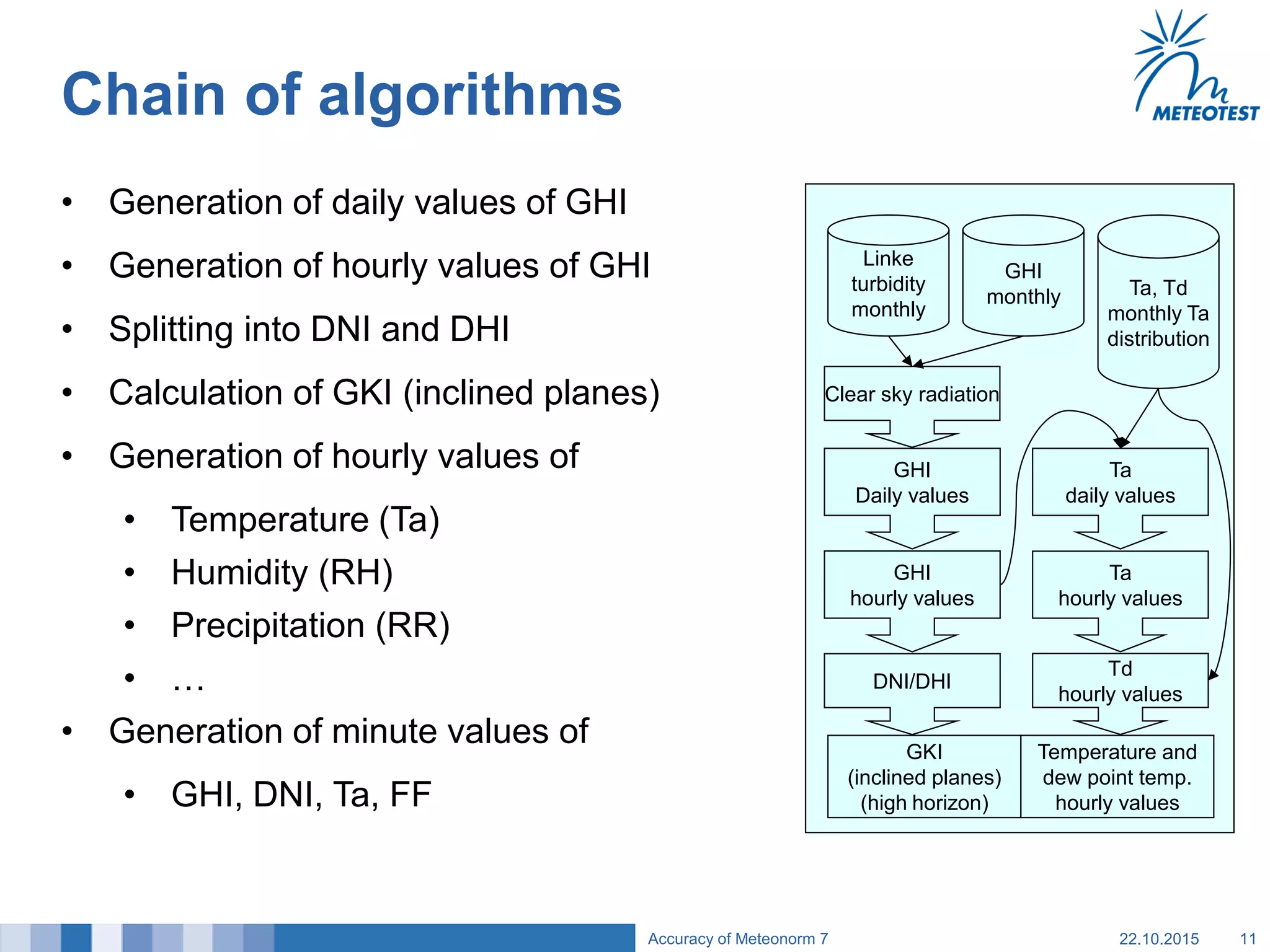
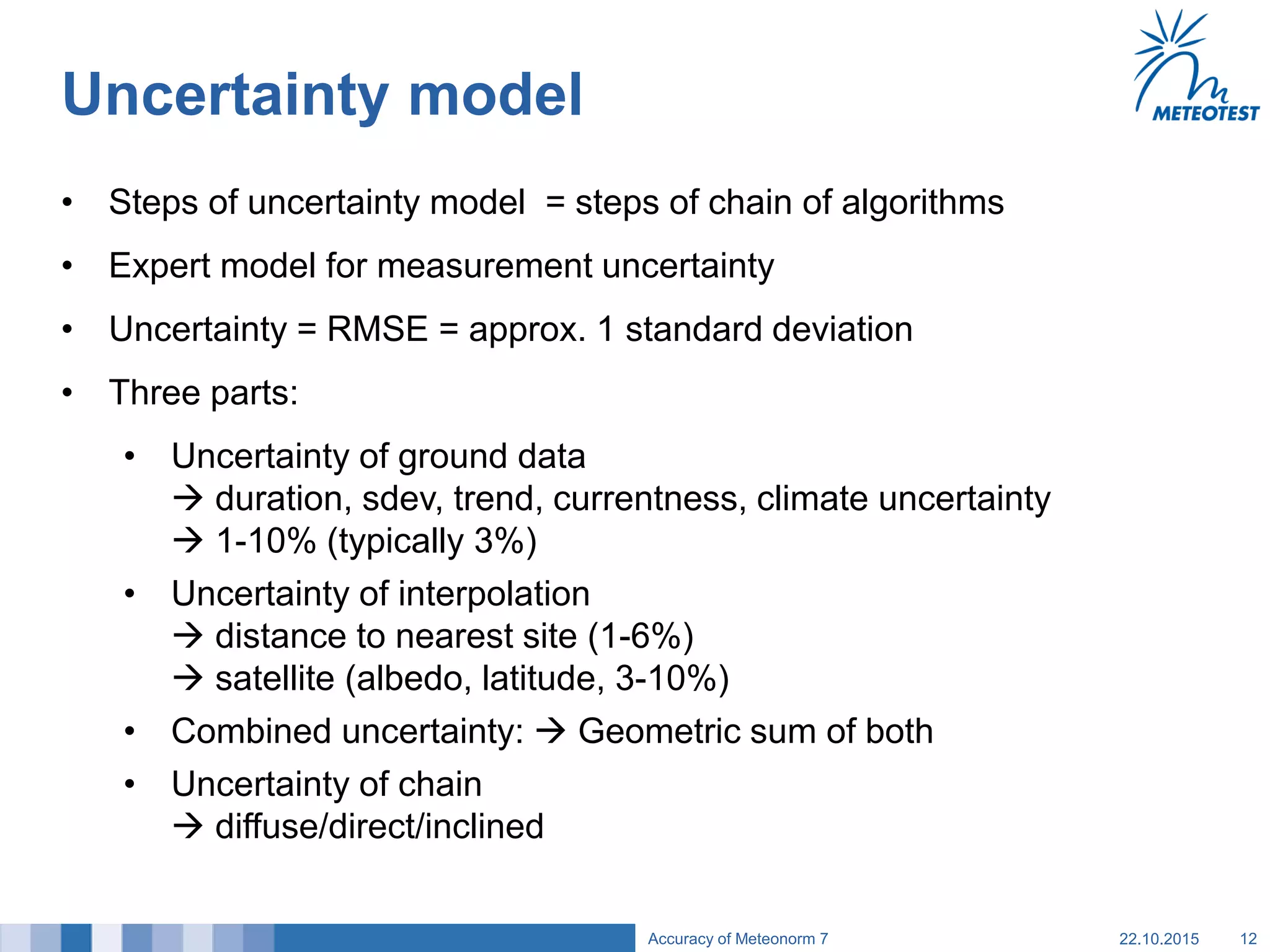
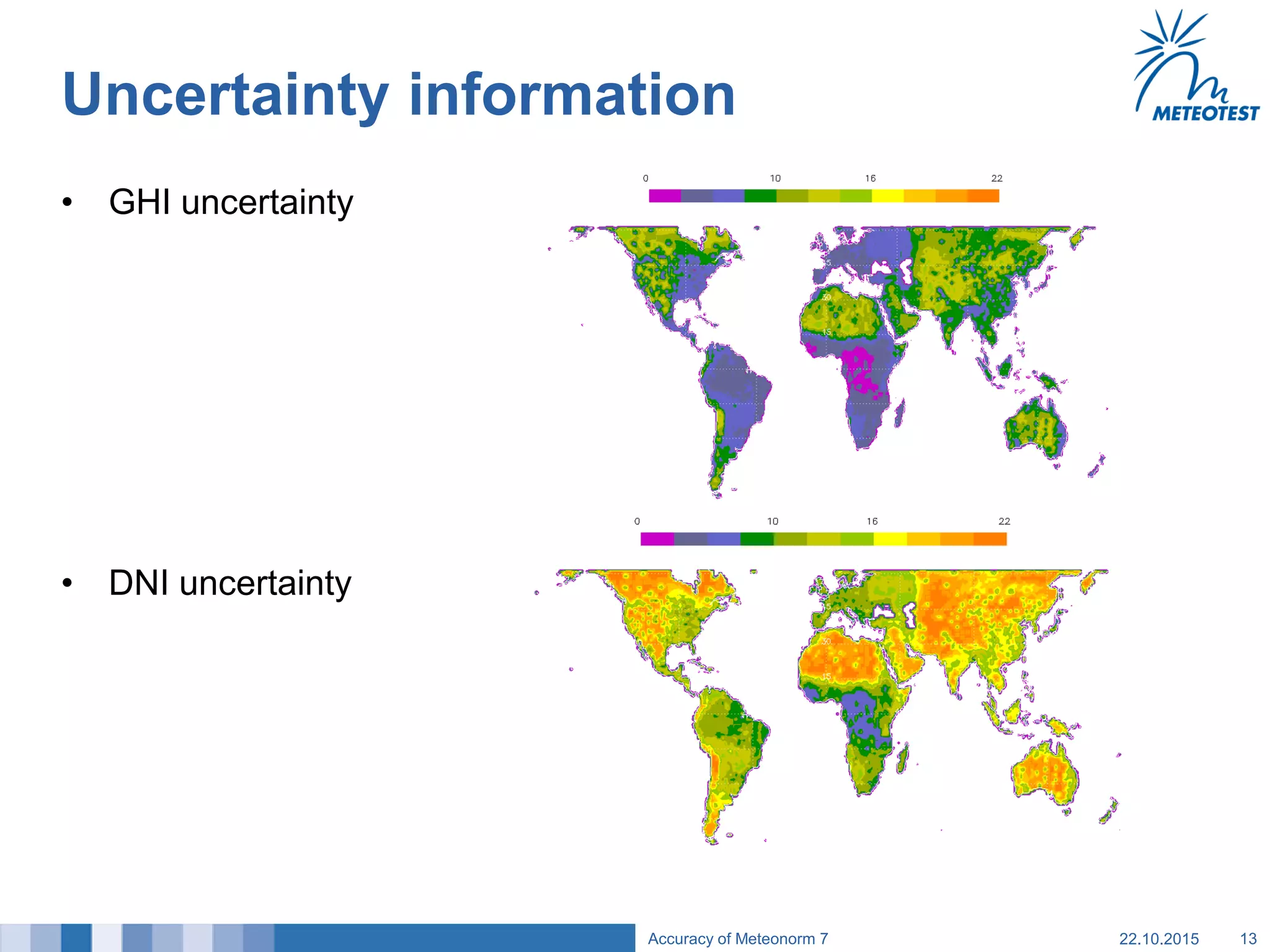
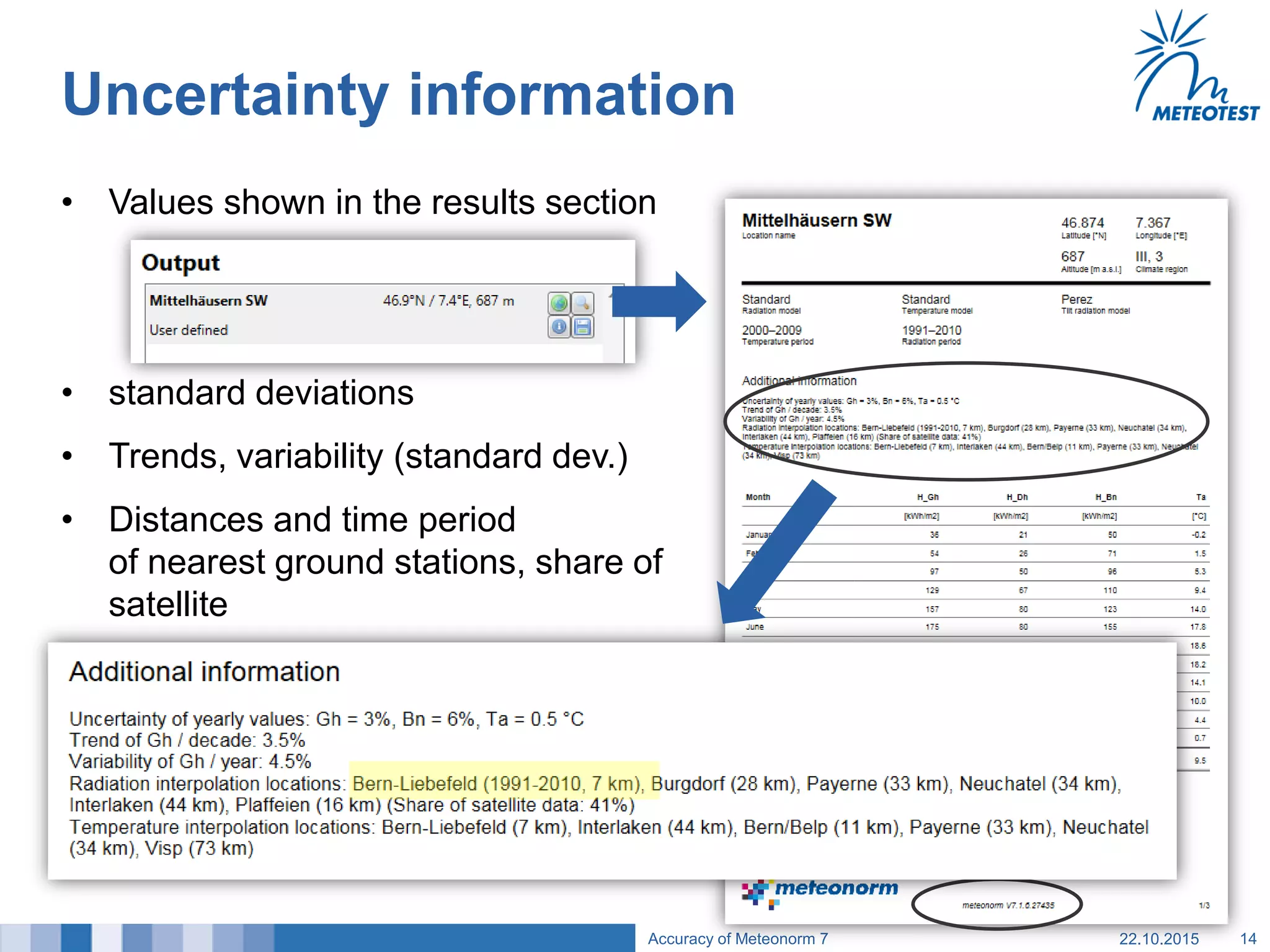
This document provides an overview of the Meteonorm software and its process for generating Typical Meteorological Year (TMY) climate data. It details how Meteonorm combines ground measurements from over 1700 stations with satellite data using interpolation algorithms to produce hourly climate values. It then describes Meteonorm's uncertainty model which estimates the uncertainty in the data to be between 2-10% based on factors like measurement accuracy, interpolation distance, and effects of using satellite data. The document concludes that Meteonorm provides a useful input for simulation tools despite its uncertainties and that its data archive can be enhanced in the future.