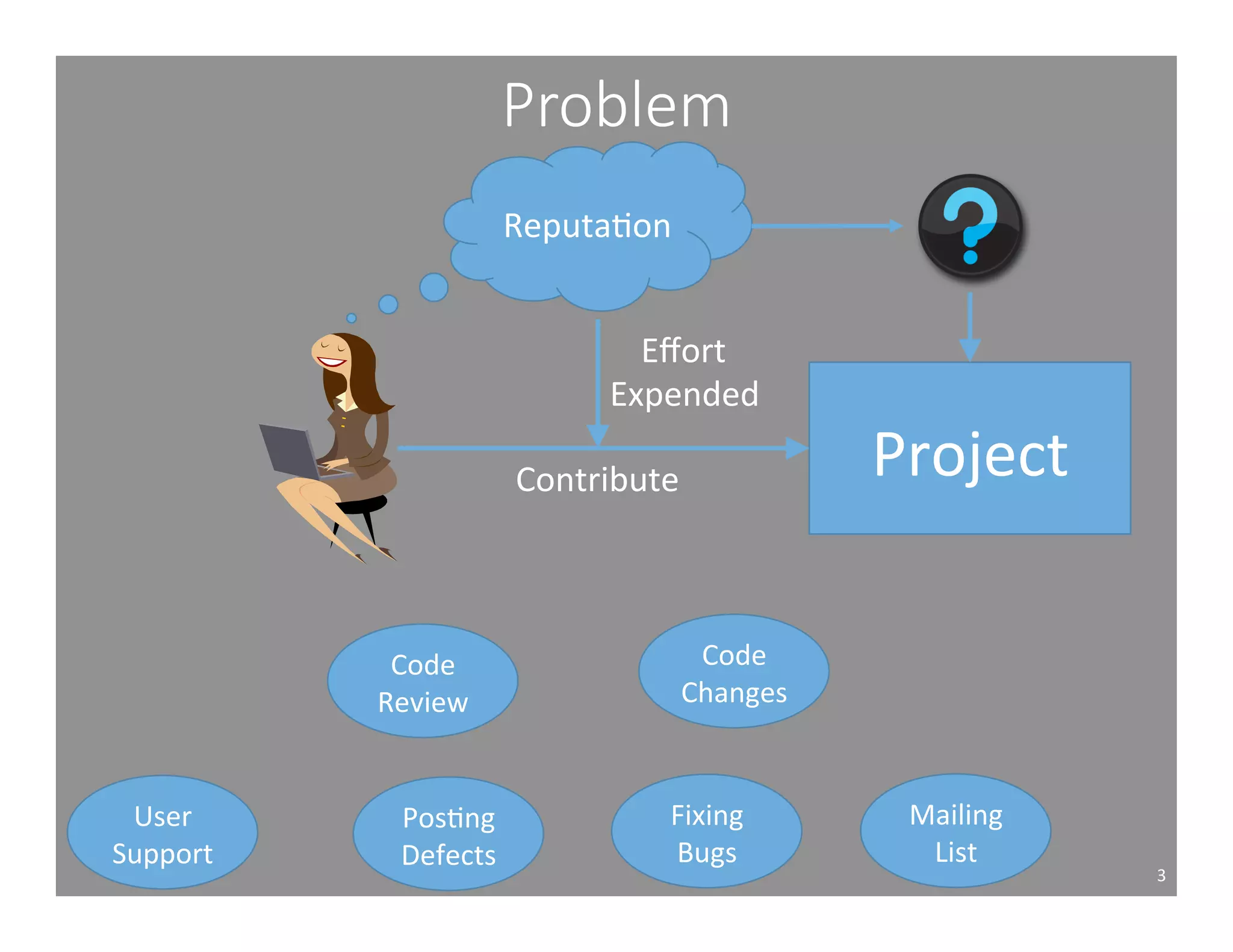
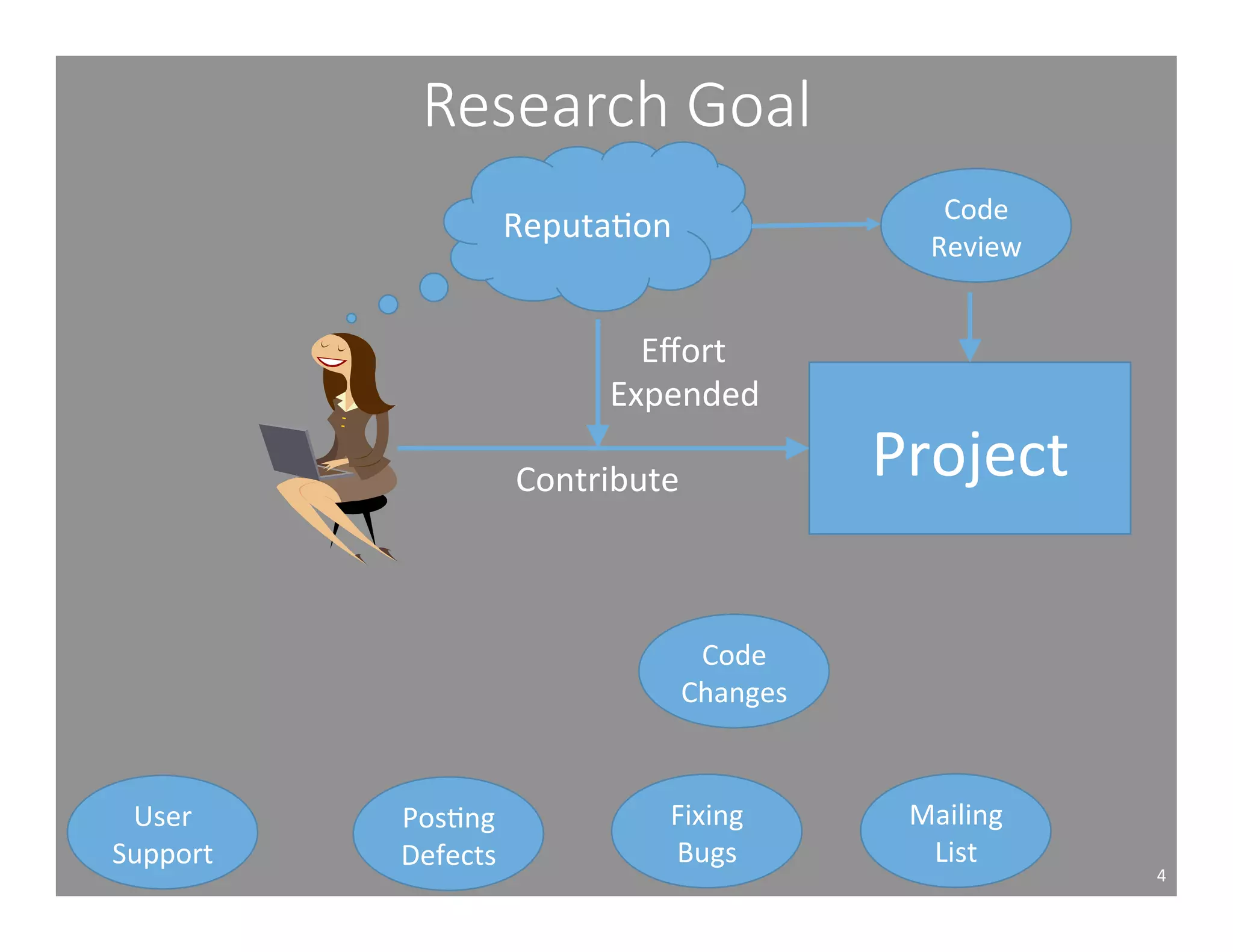
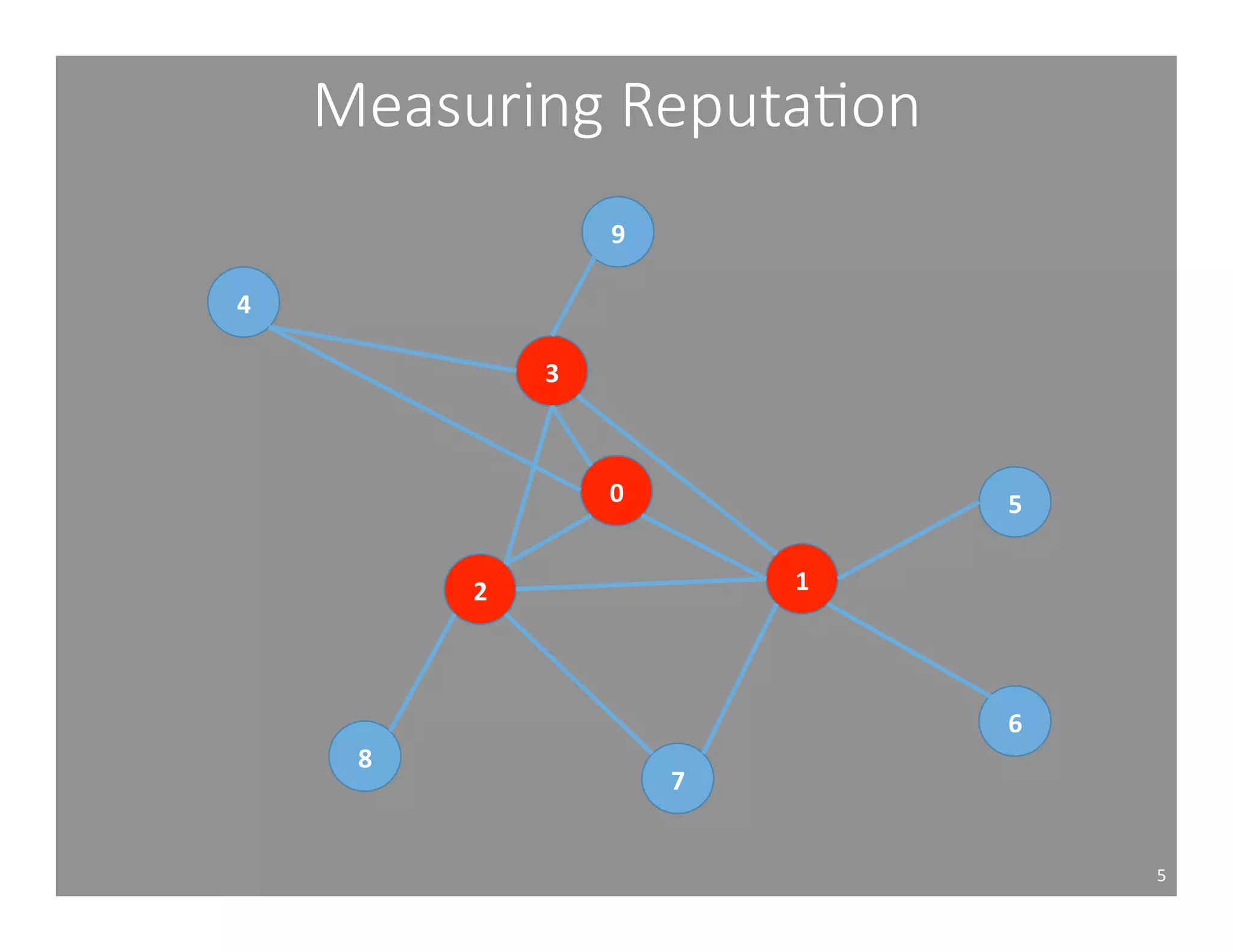
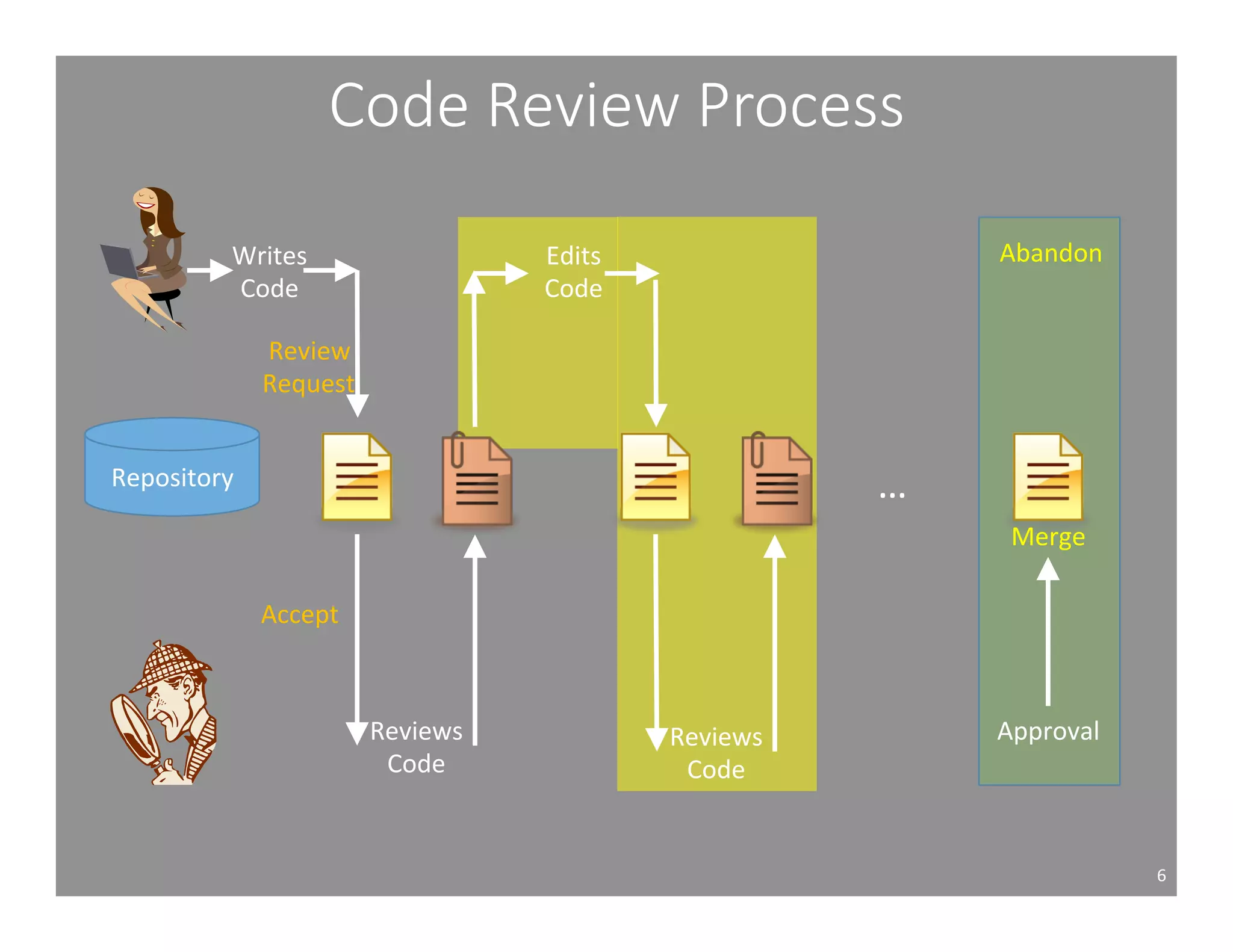
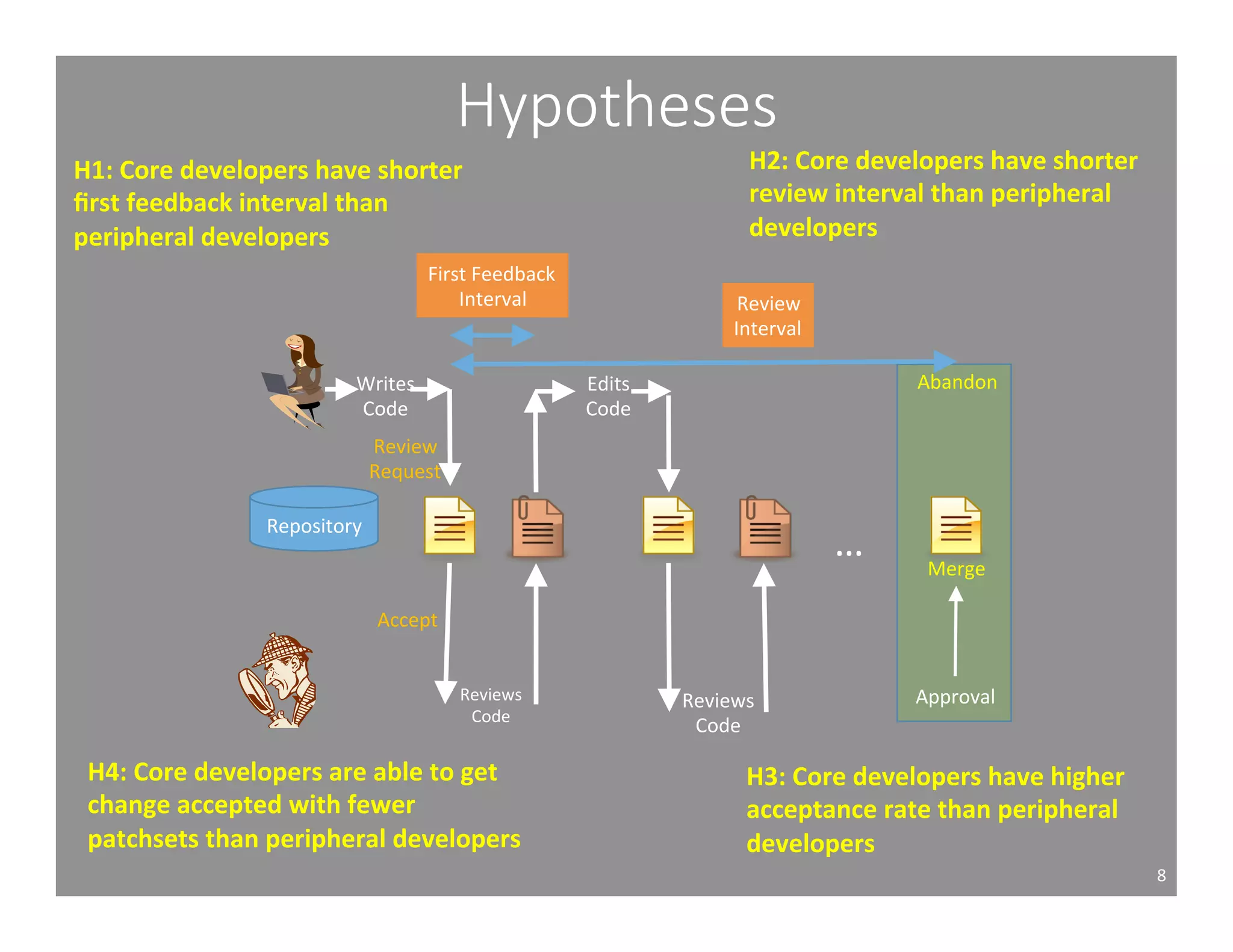
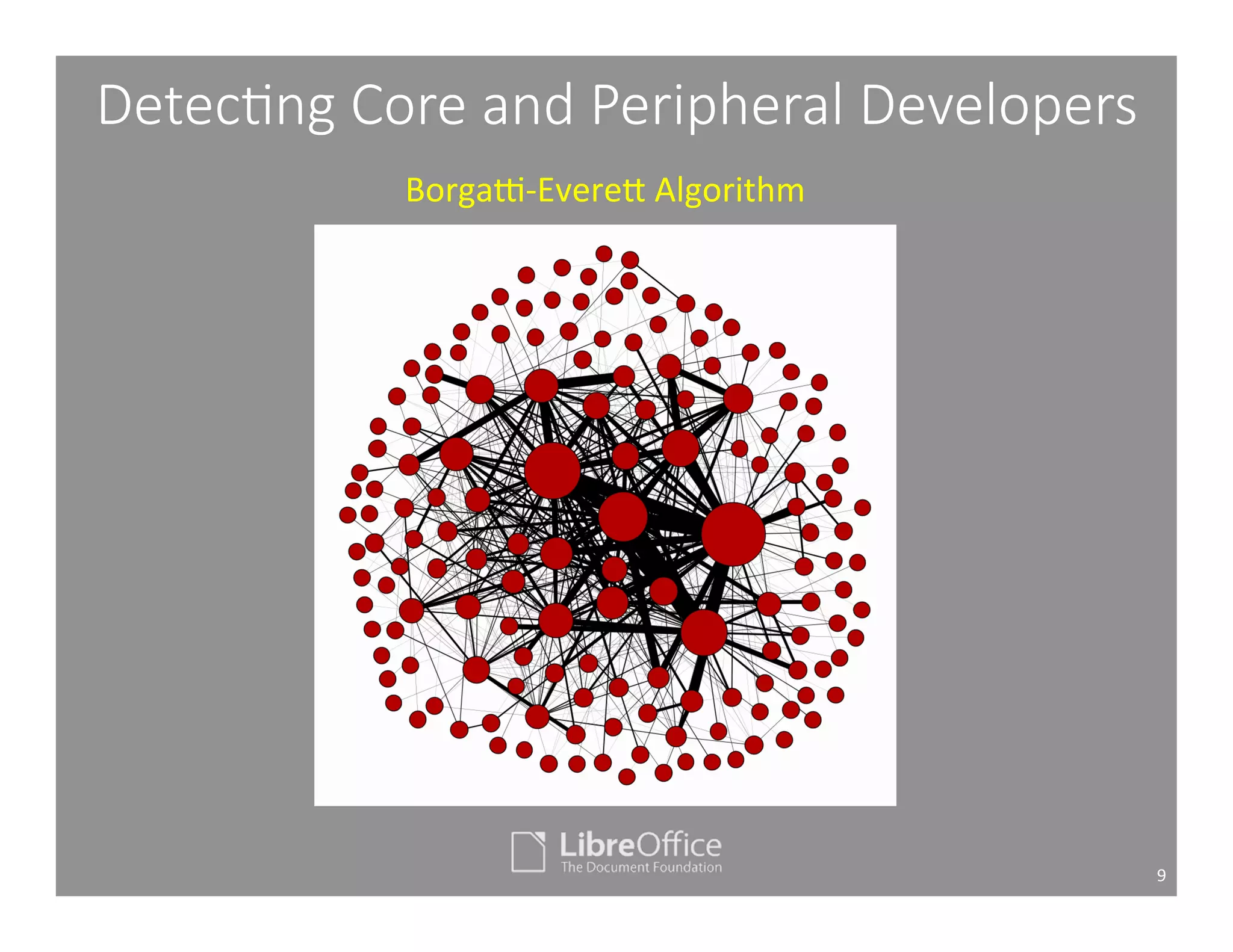
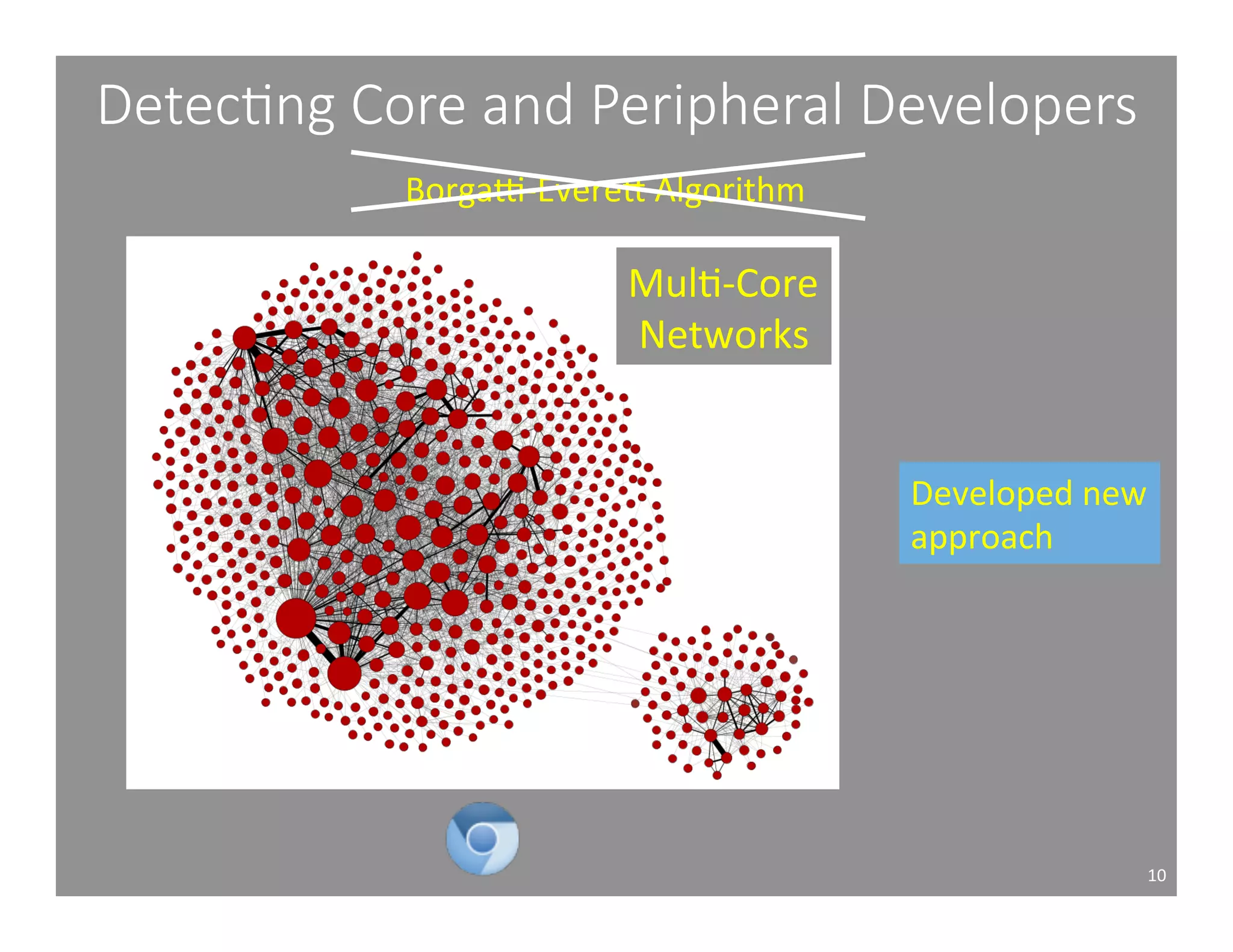
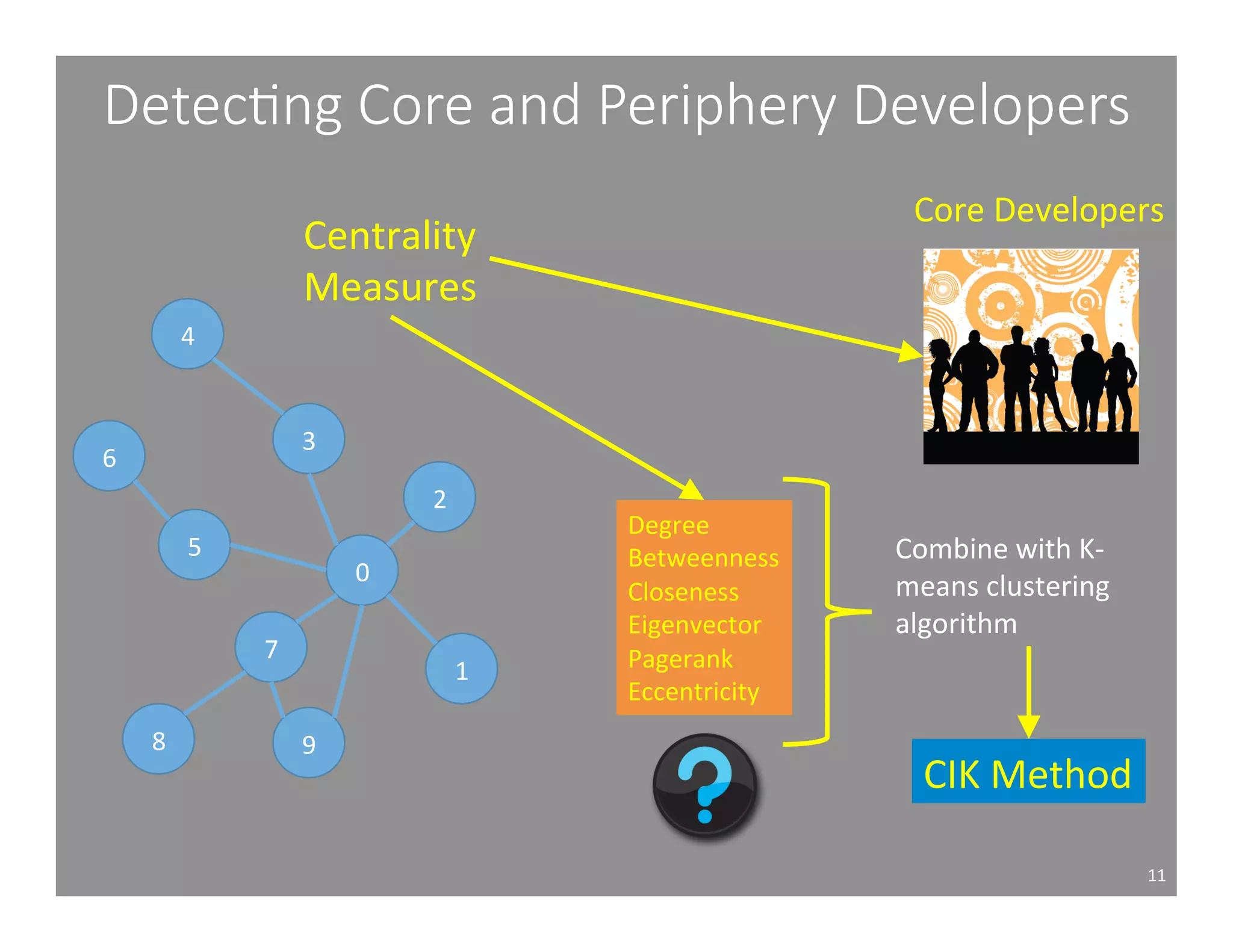
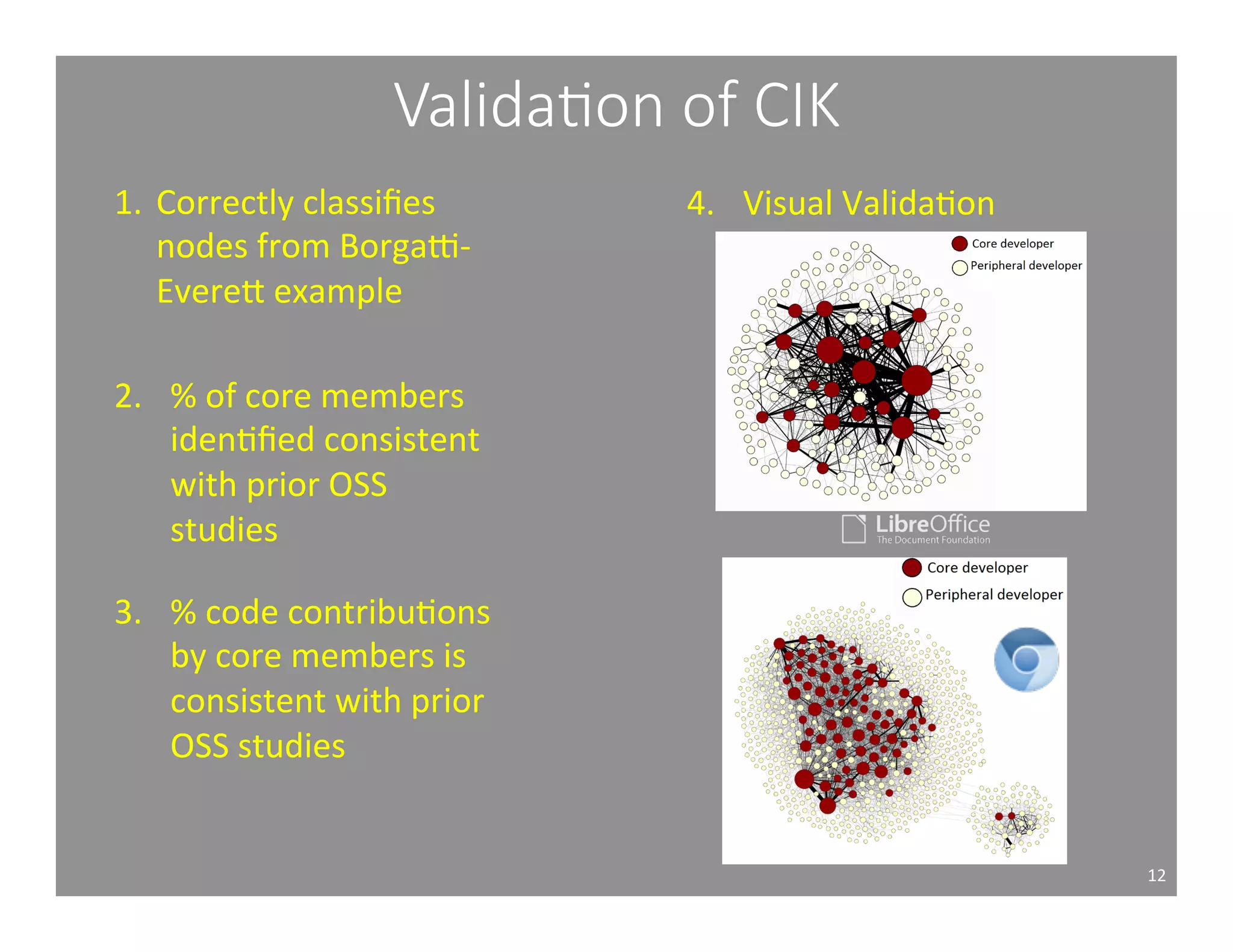
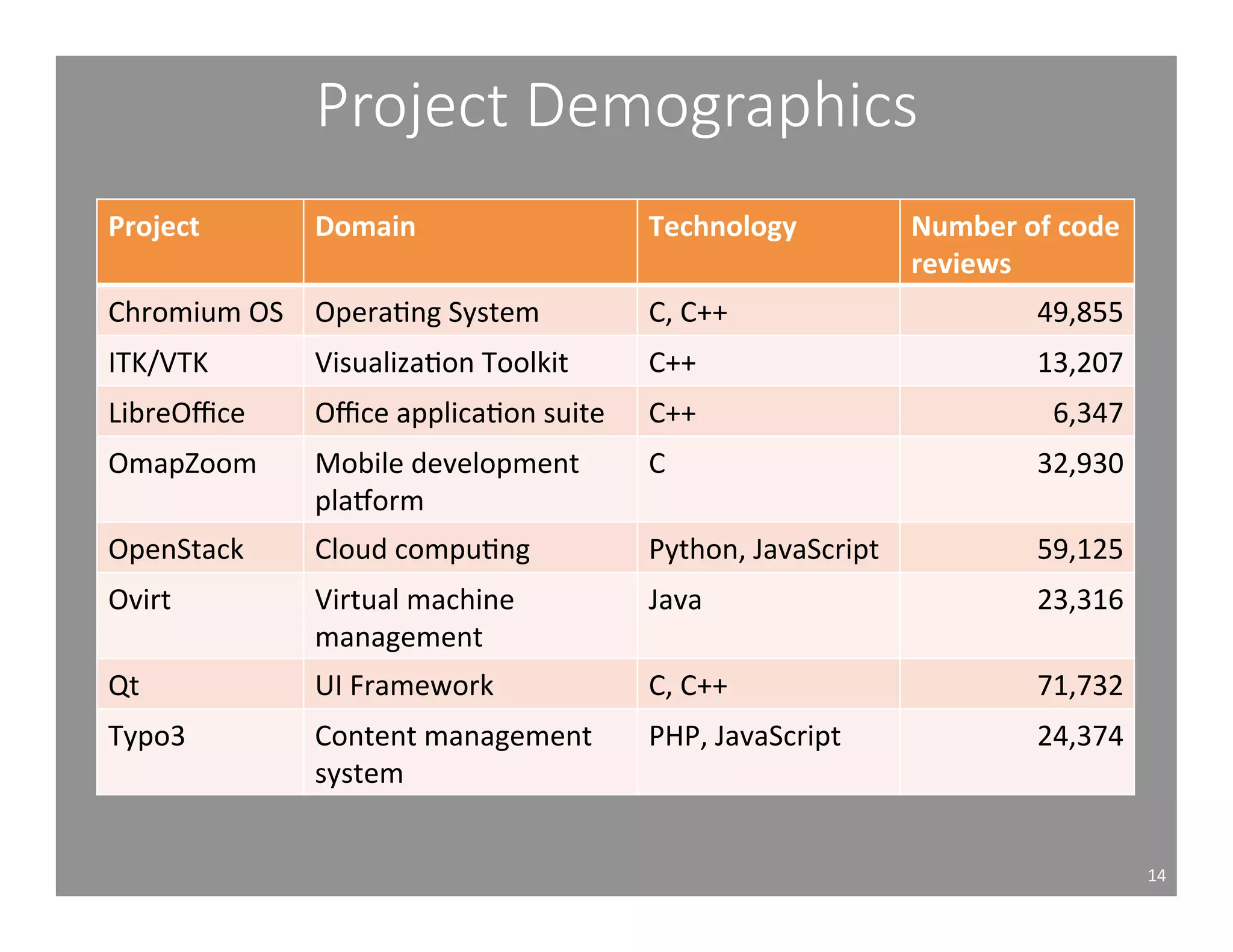
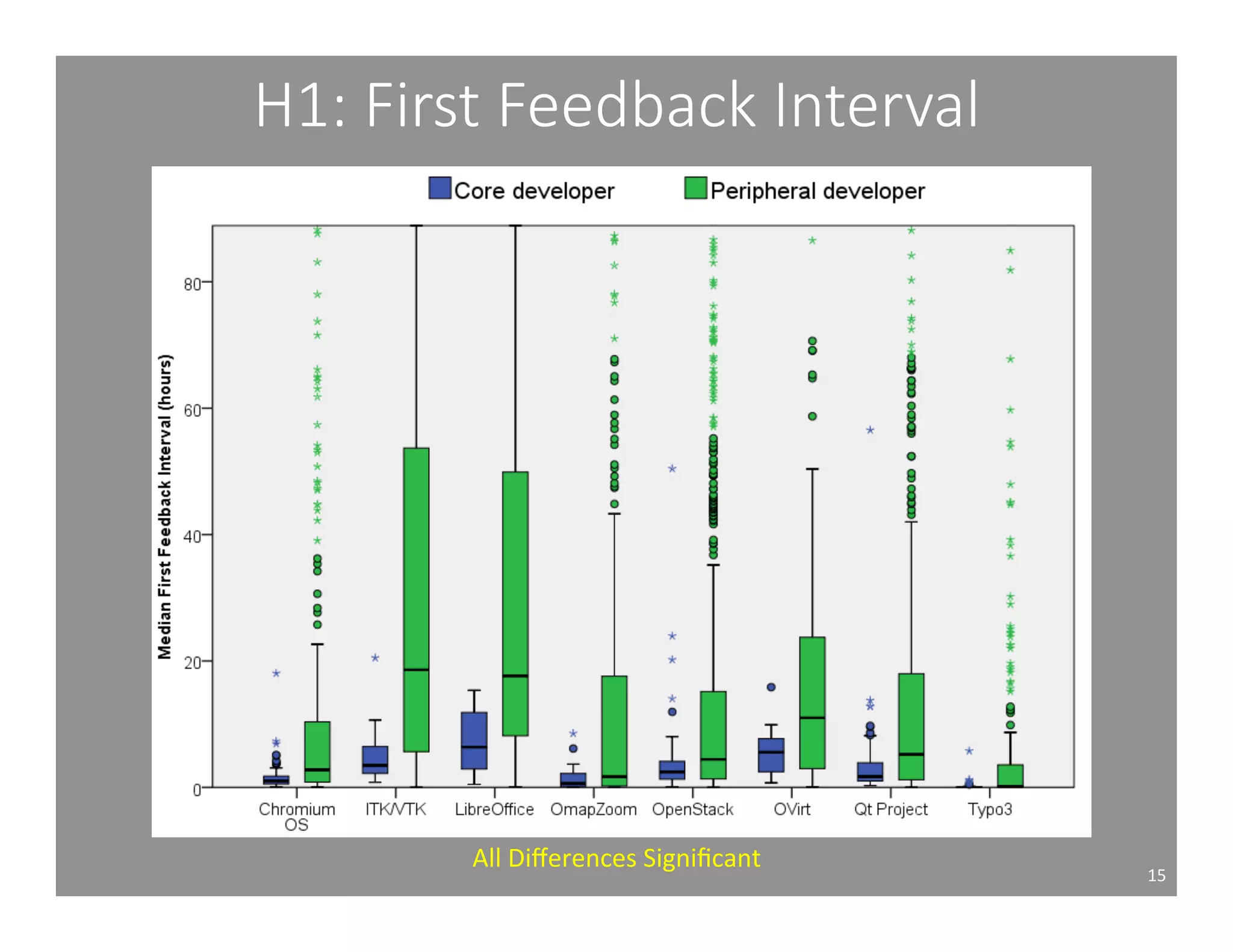
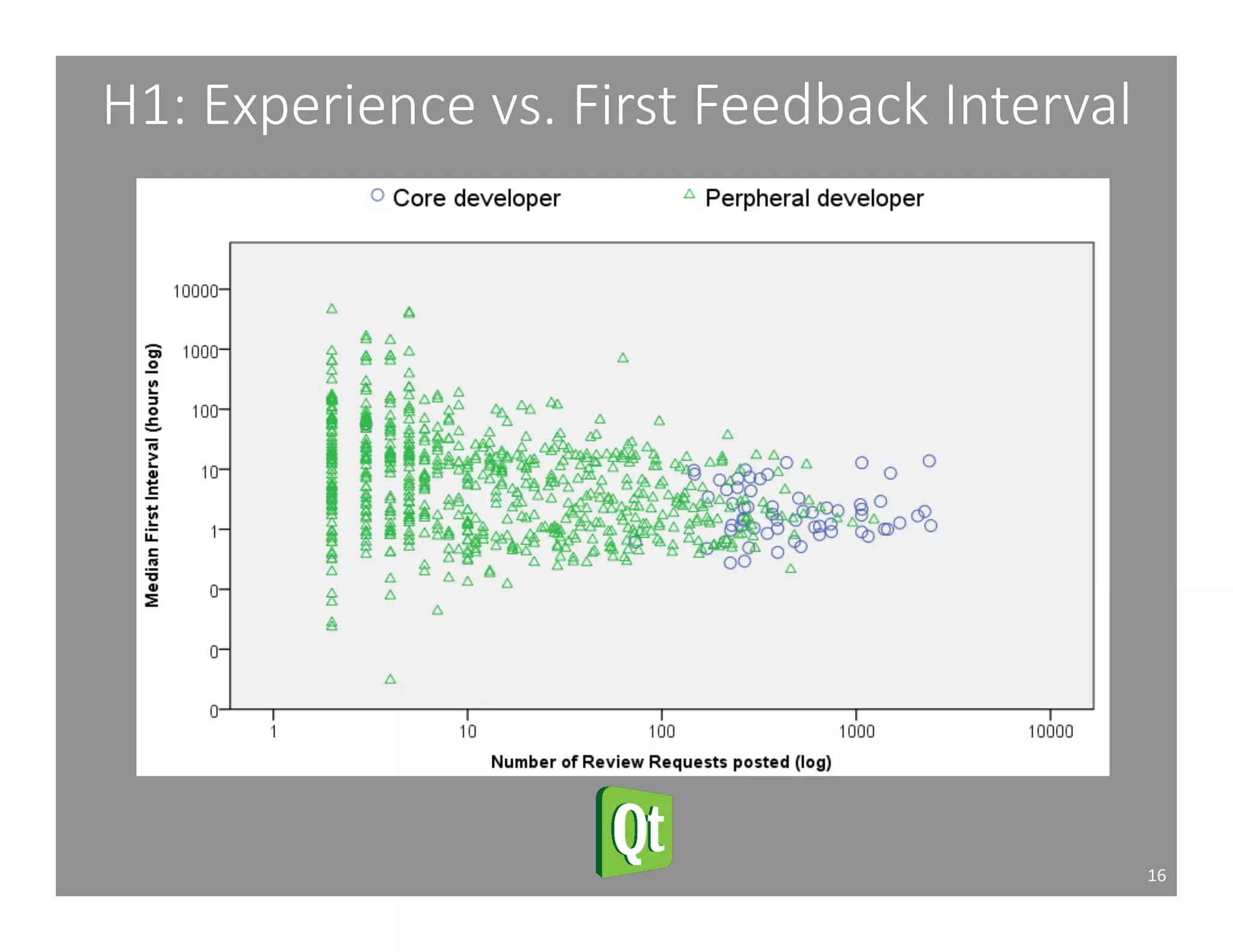
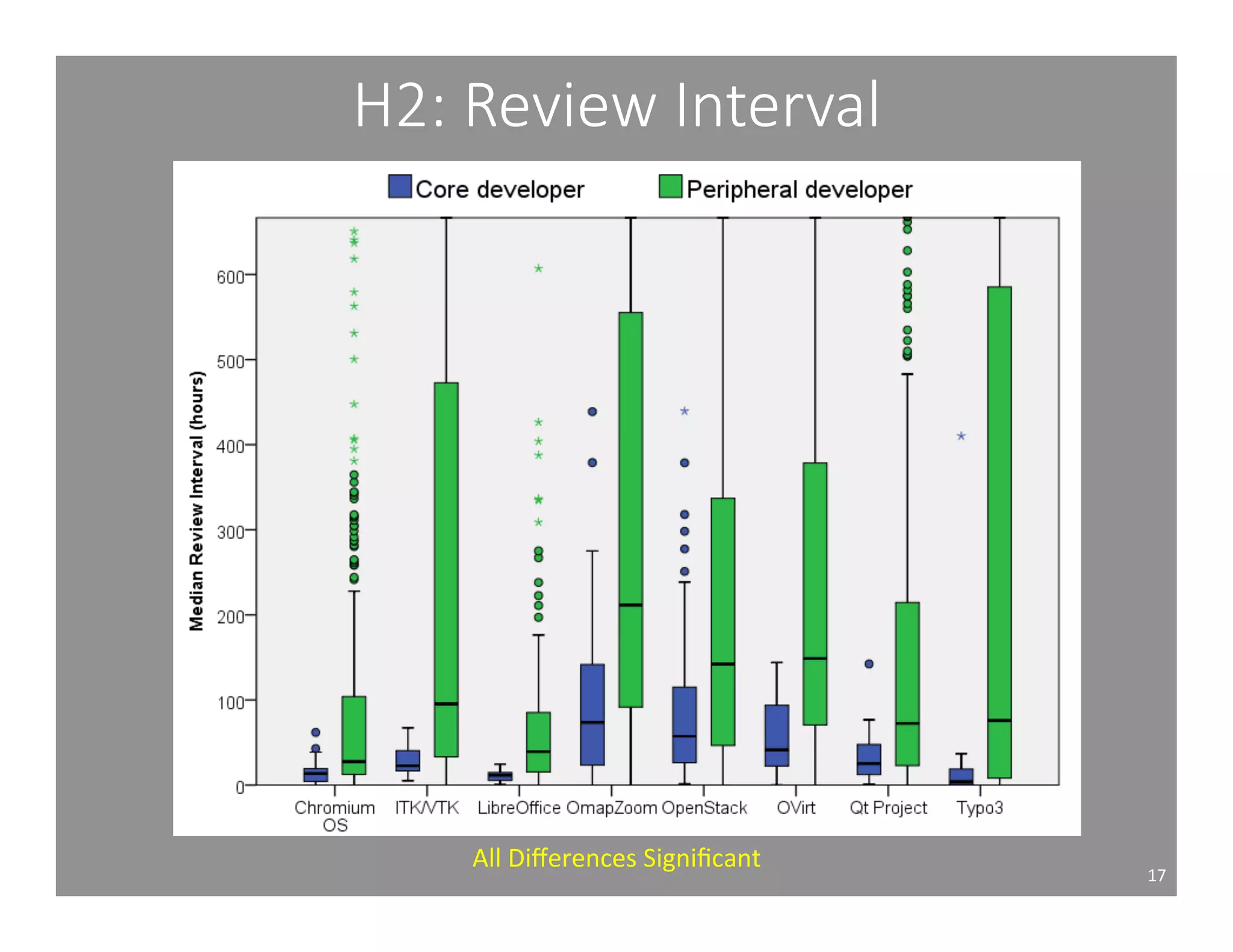
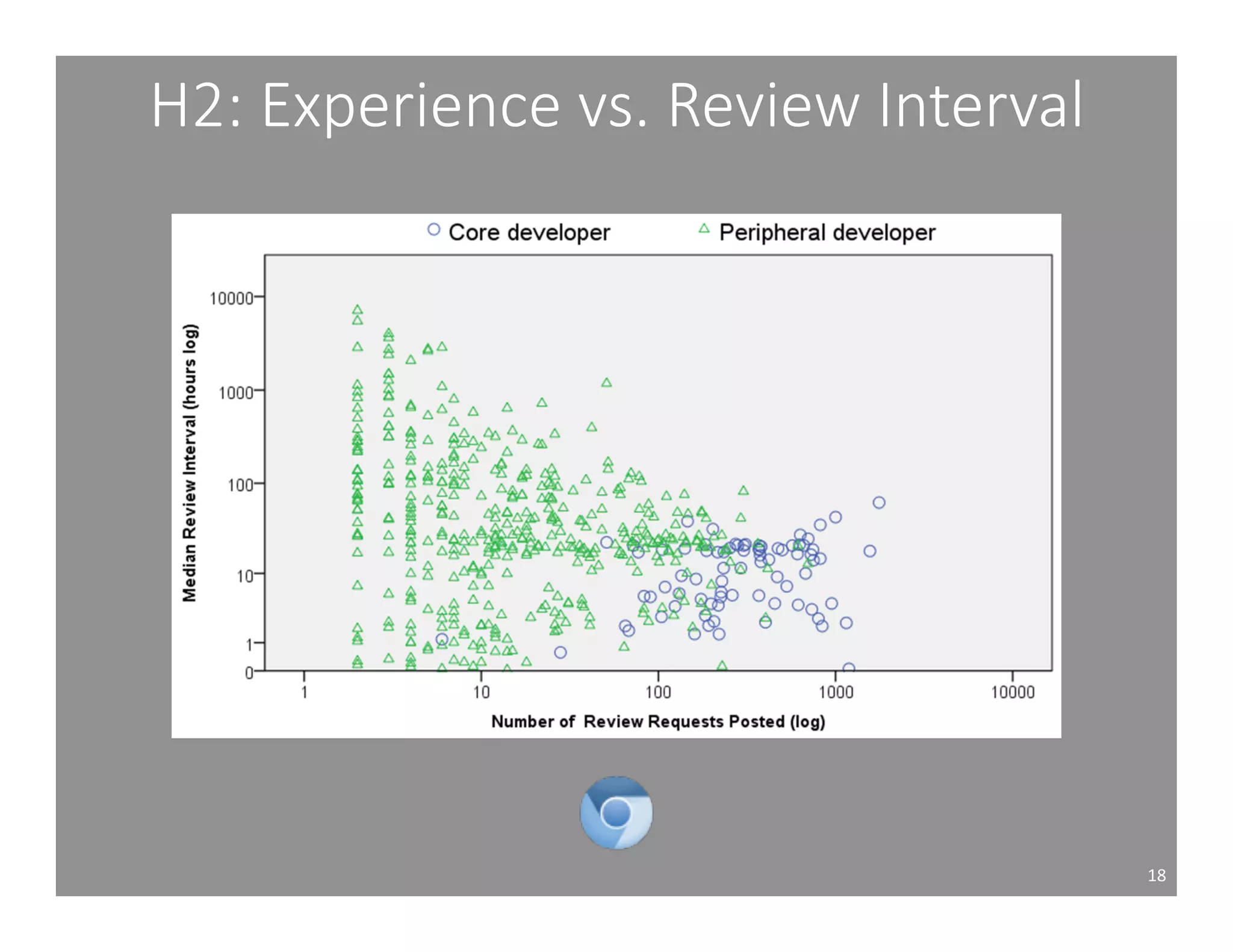
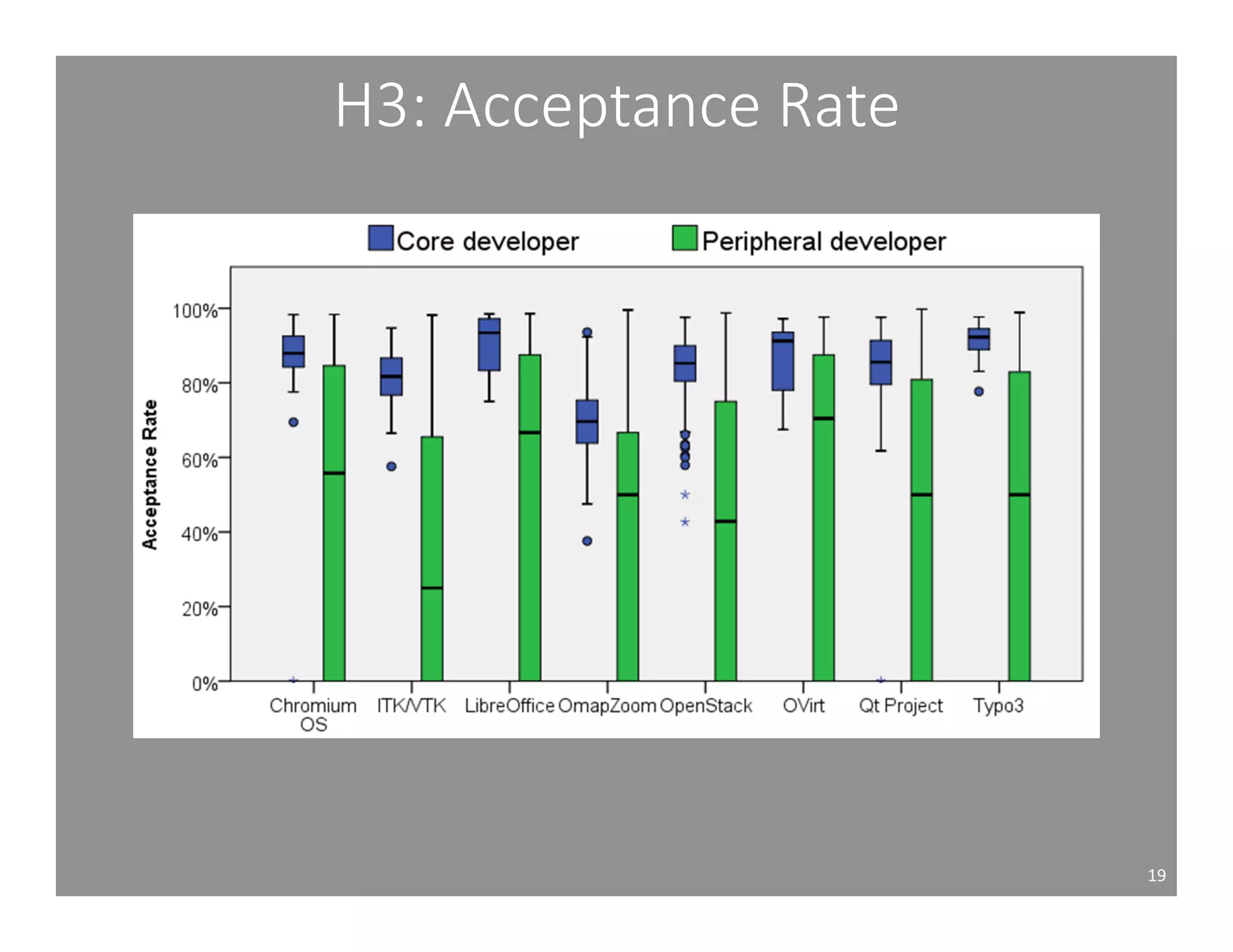
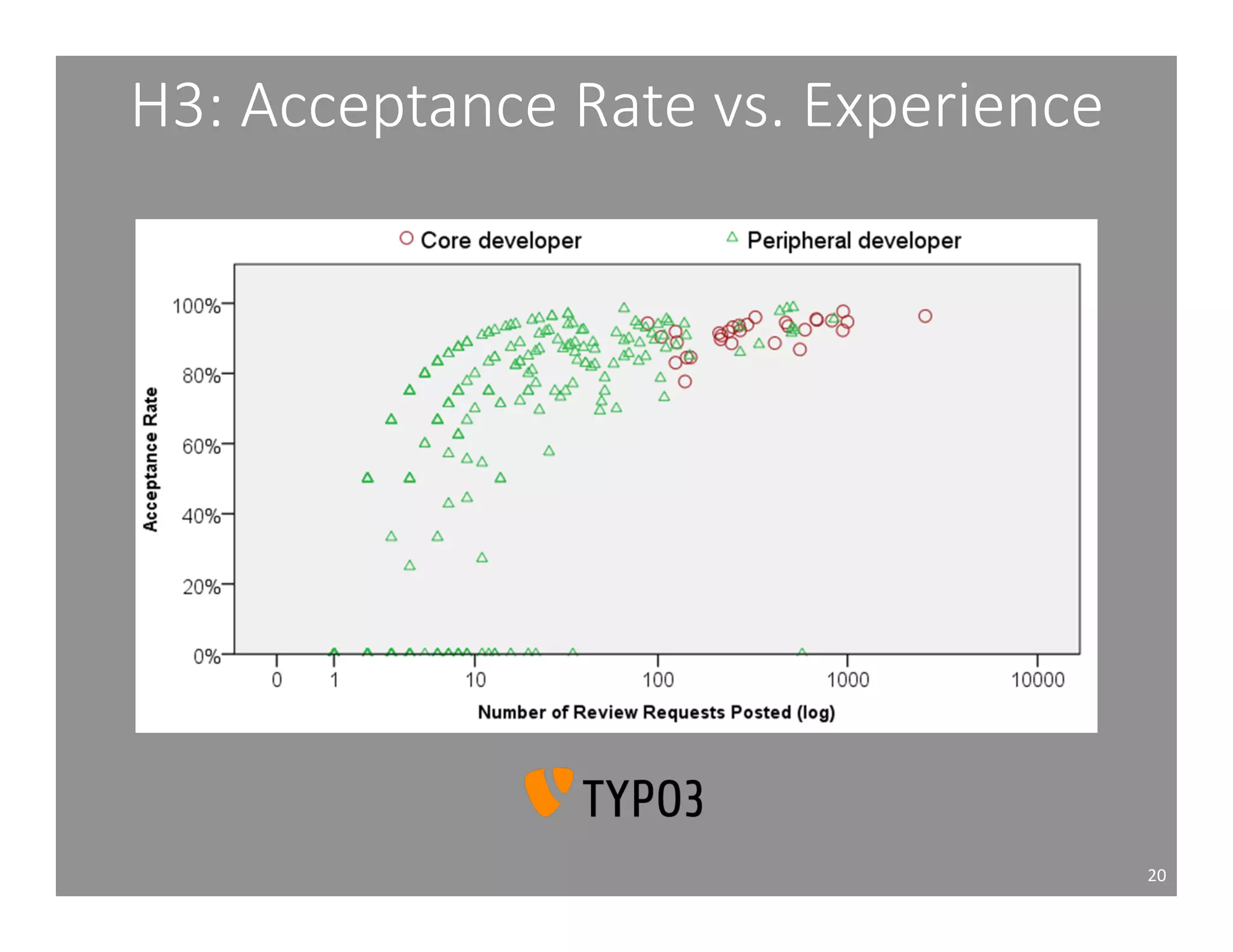
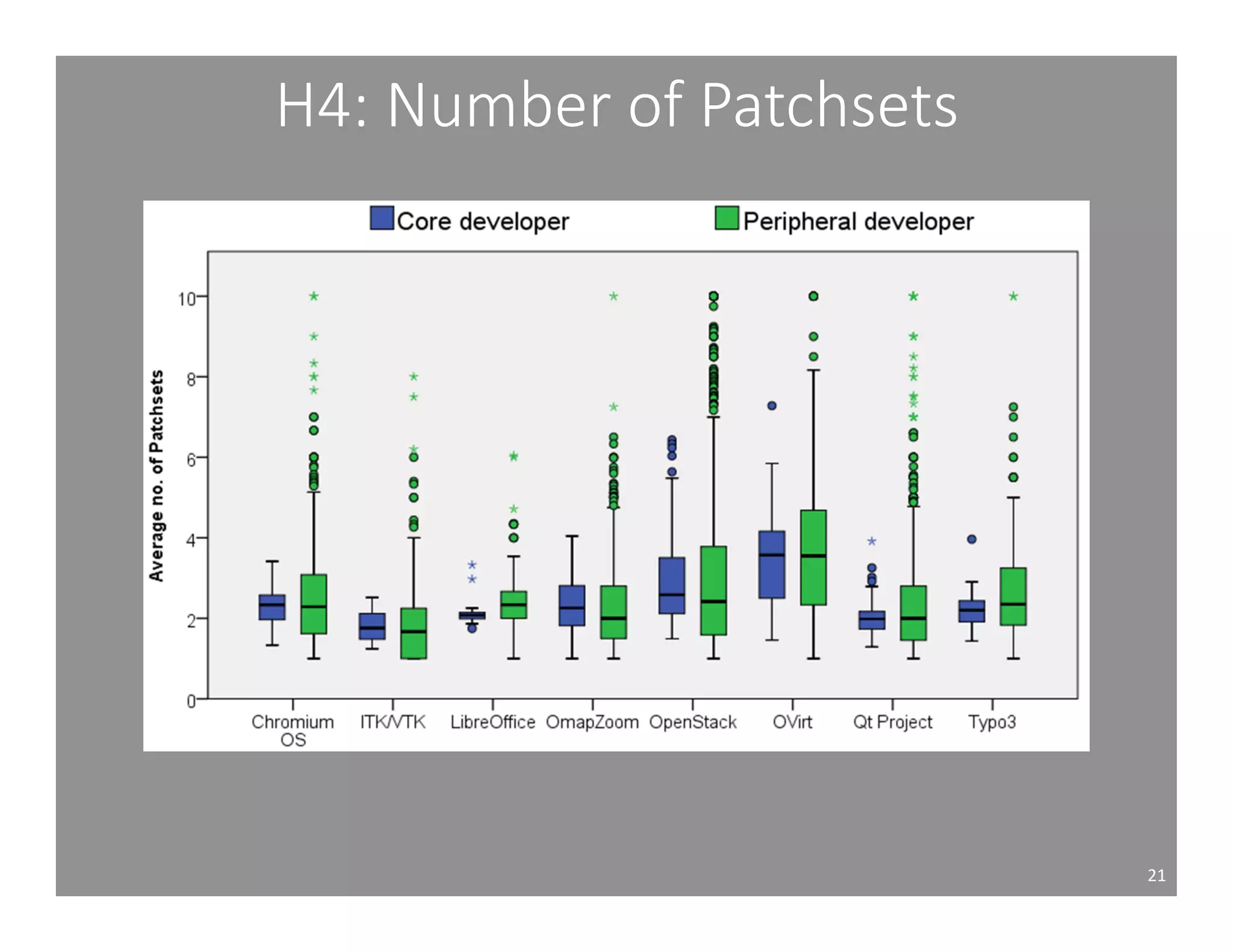
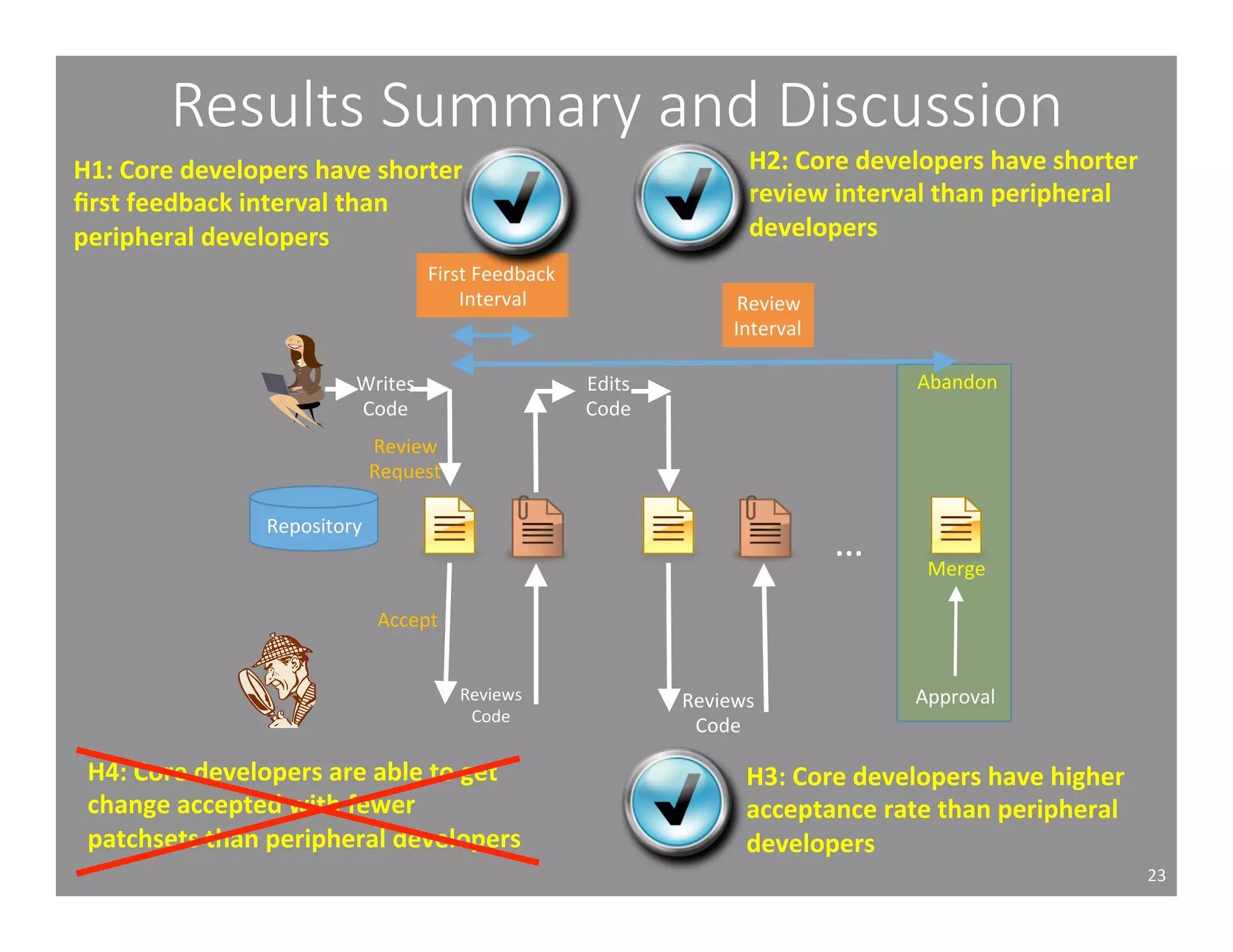
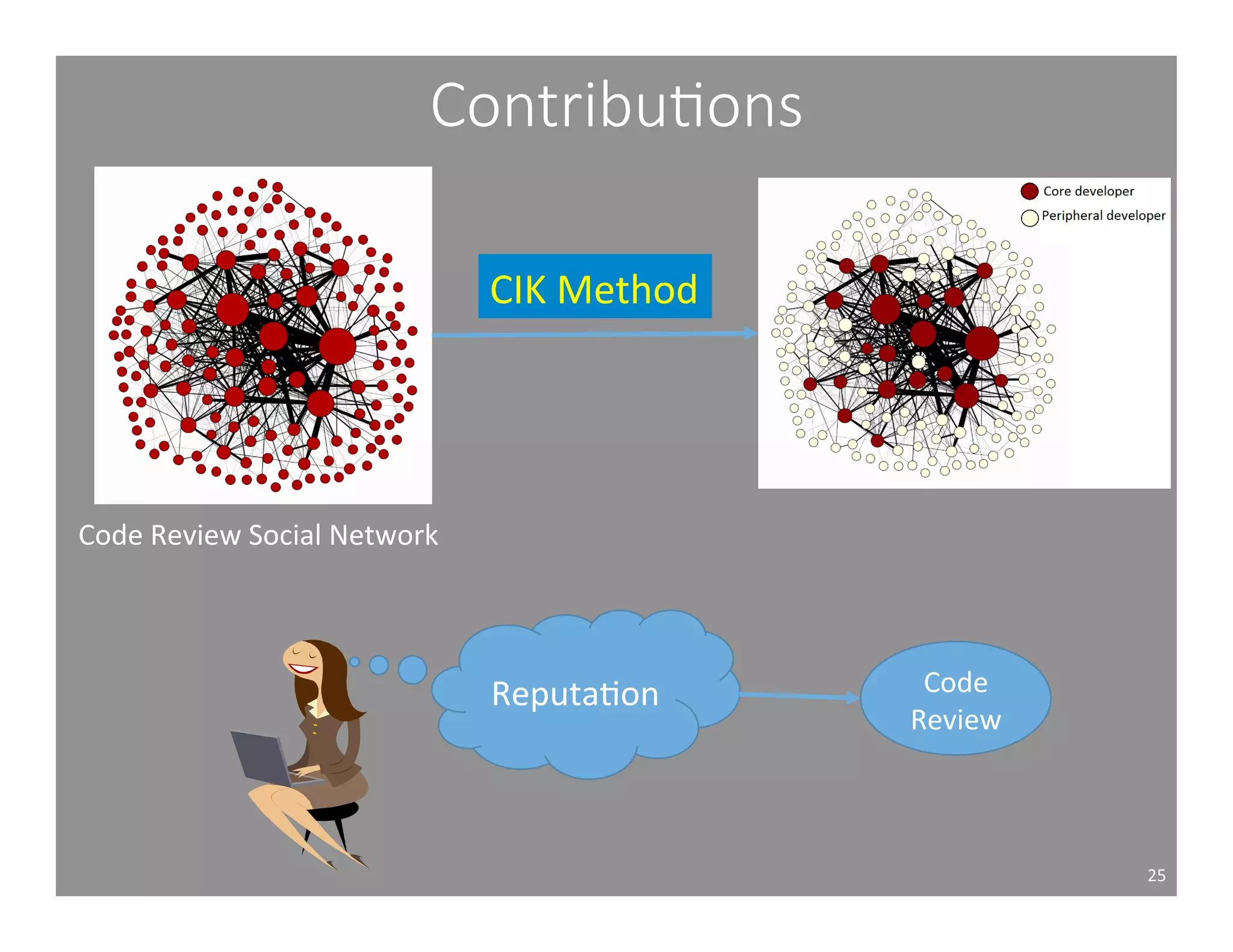
This document studies the impact of developer reputation on code review outcomes in open source software projects. It analyzes code review data from 8 open source projects to test hypotheses about whether core developers, who have higher reputation, have shorter feedback and review intervals, higher acceptance rates, and fewer required patchsets than peripheral developers. The results provide empirical evidence that core developers do receive preferential treatment in code reviews, supporting all the hypotheses. This suggests reputation influences code review behaviors and outcomes for developers in open source projects.