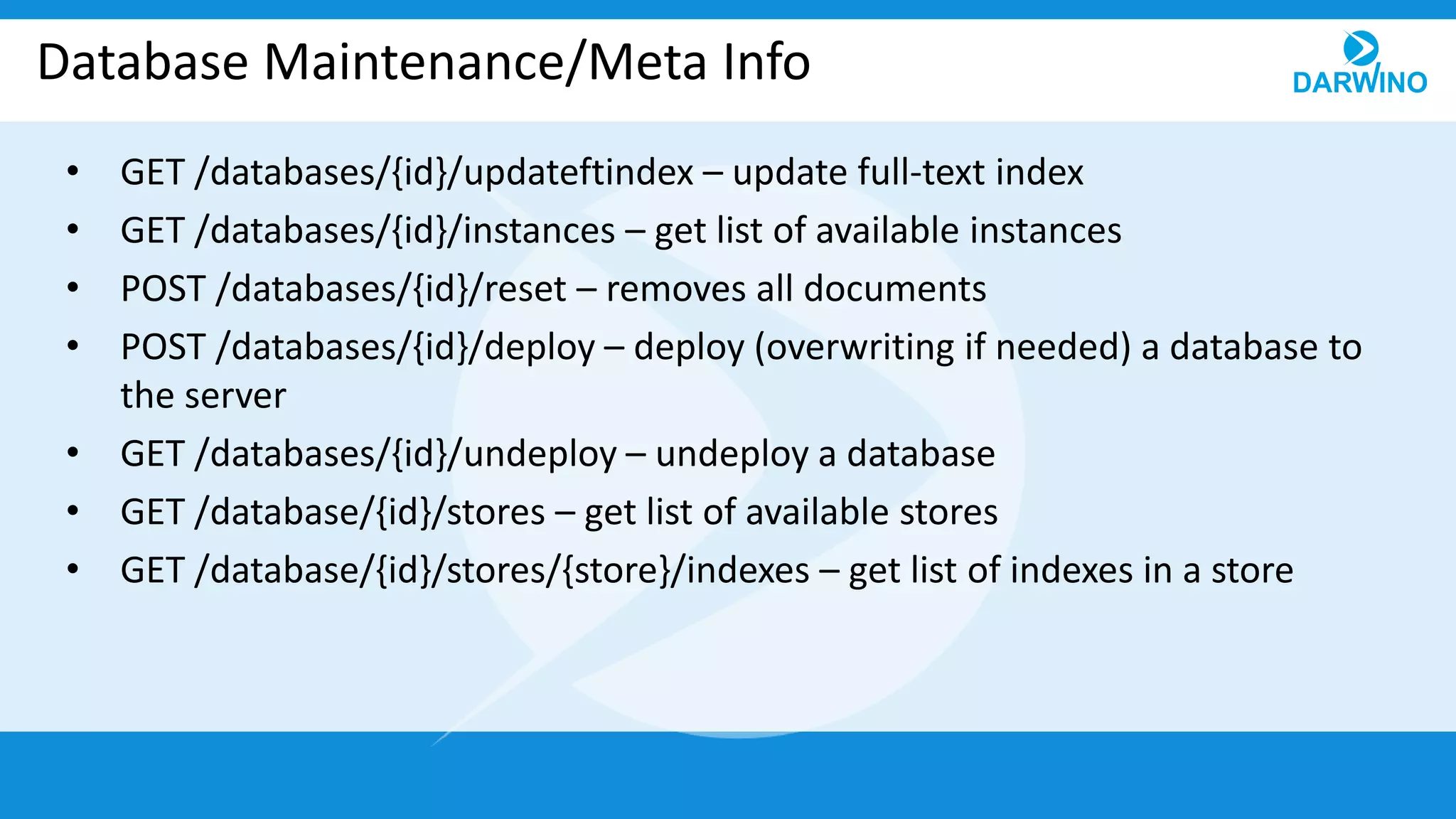
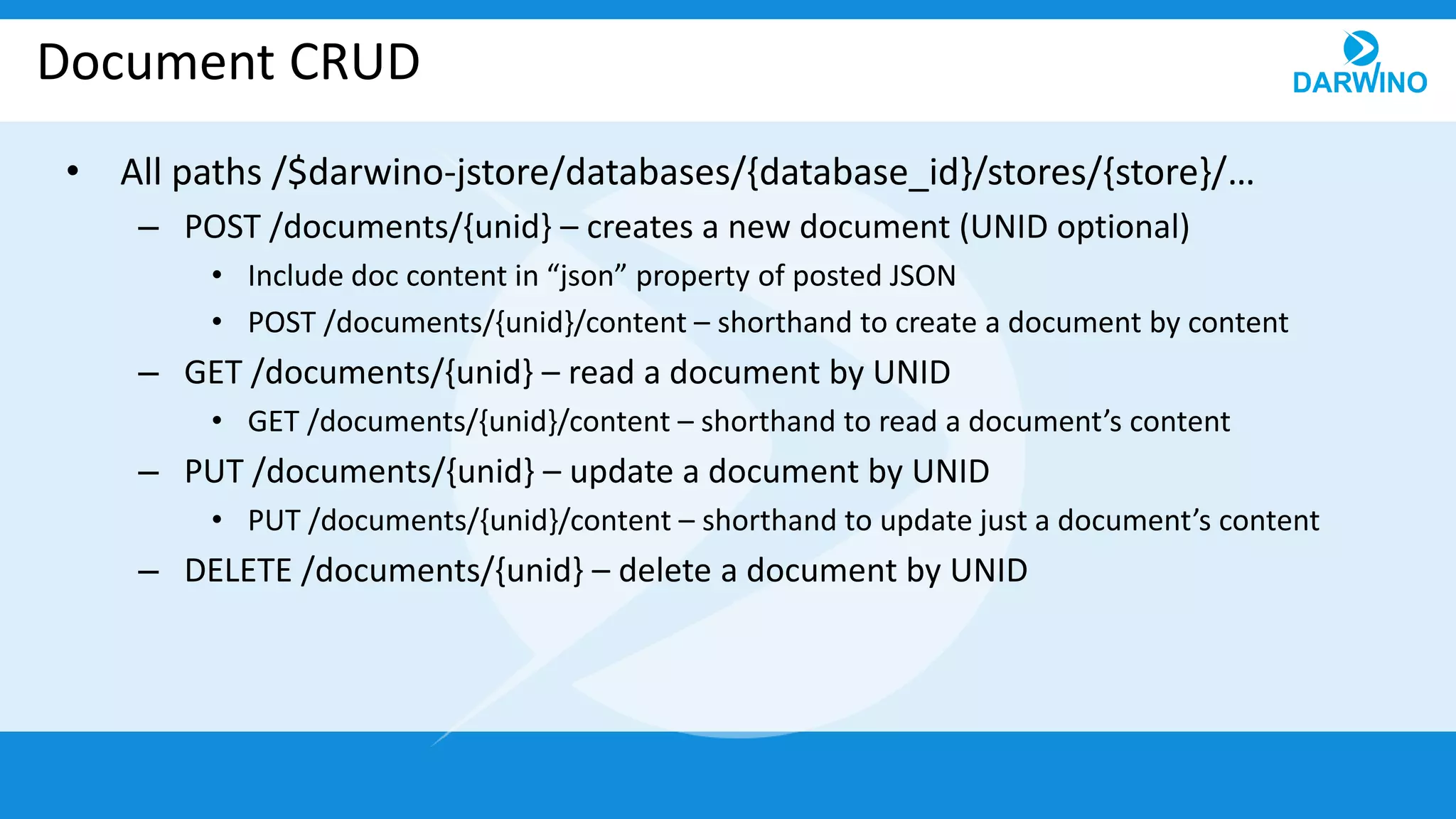
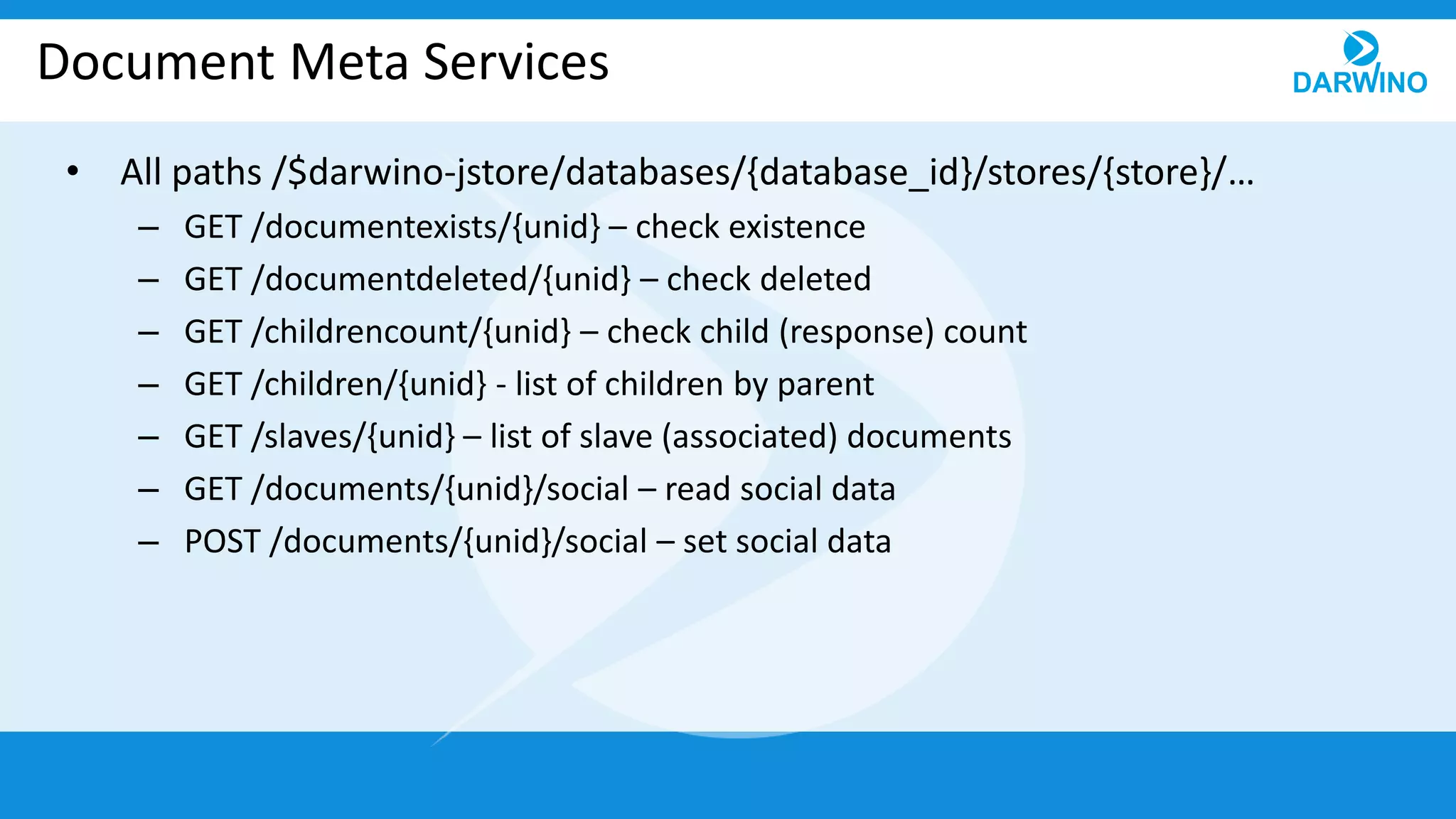
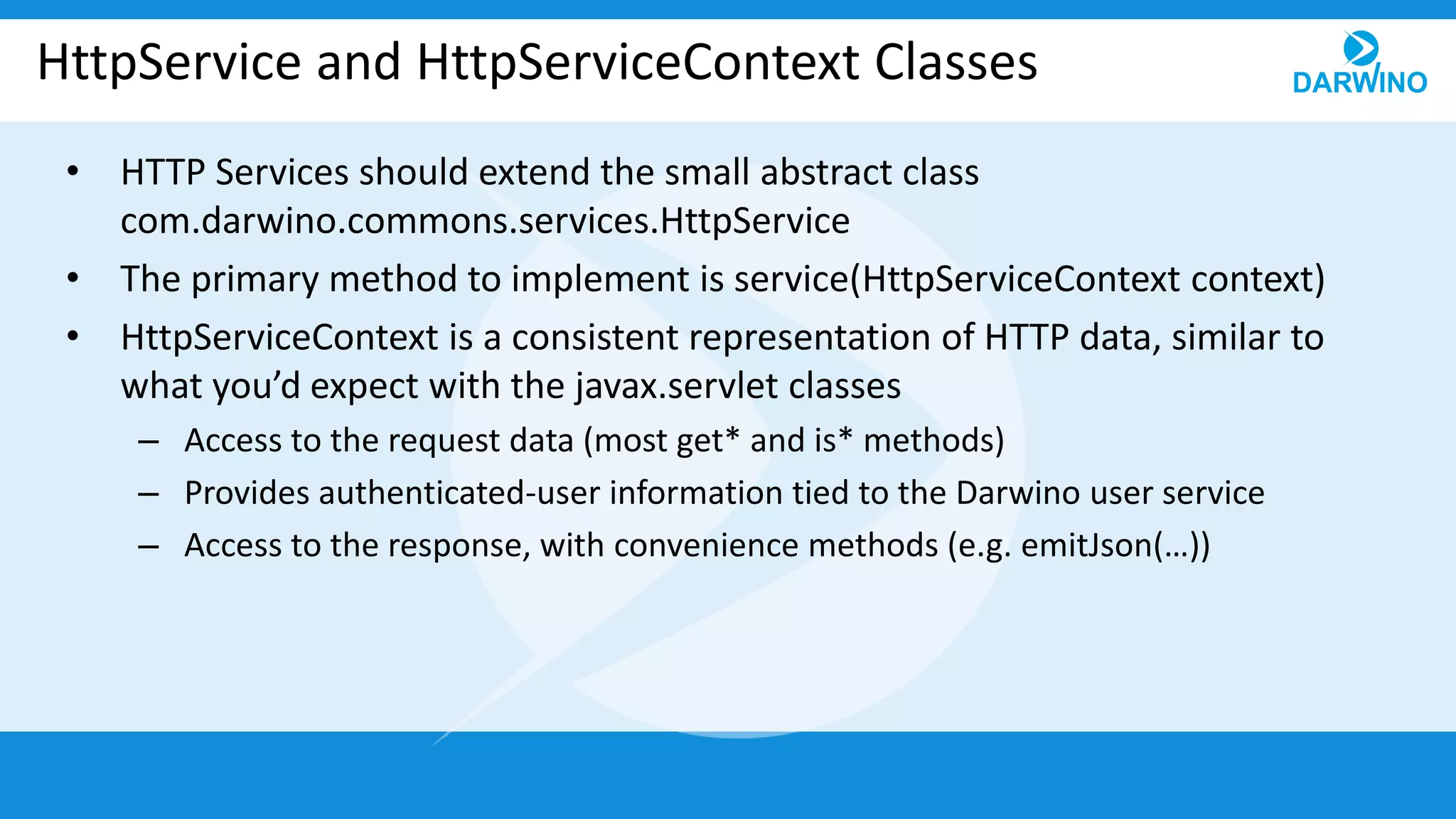
The document outlines the built-in REST services of Darwino, which are designed for managing databases, documents, and custom services. It details various operations such as retrieving databases, managing document CRUD operations, and handling attachments and indexes. Additionally, it describes the implementation of custom services using service factories for cross-platform consistency.





![Custom Services Example: Social Analyzer
binders.add(new RestServiceBinder("feeds") {
@Override public HttpService createService(HttpServiceContext context, String[] parts) {
return new FeedsService();
}
});
binders.add(new RestServiceBinder("userActions", "assign") {
@Override public HttpService createService(HttpServiceContext context, String[] parts) {
return new AssignUserService();
}
});
binders.add(new RestServiceBinder("users", null) {
@Override public HttpService createService(HttpServiceContext context, String[] parts) {
return new UserInfoService(parts[1]);
}
});](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/07-darwinorestservices-161206160405/75/07-darwino-rest-services-13-2048.jpg)