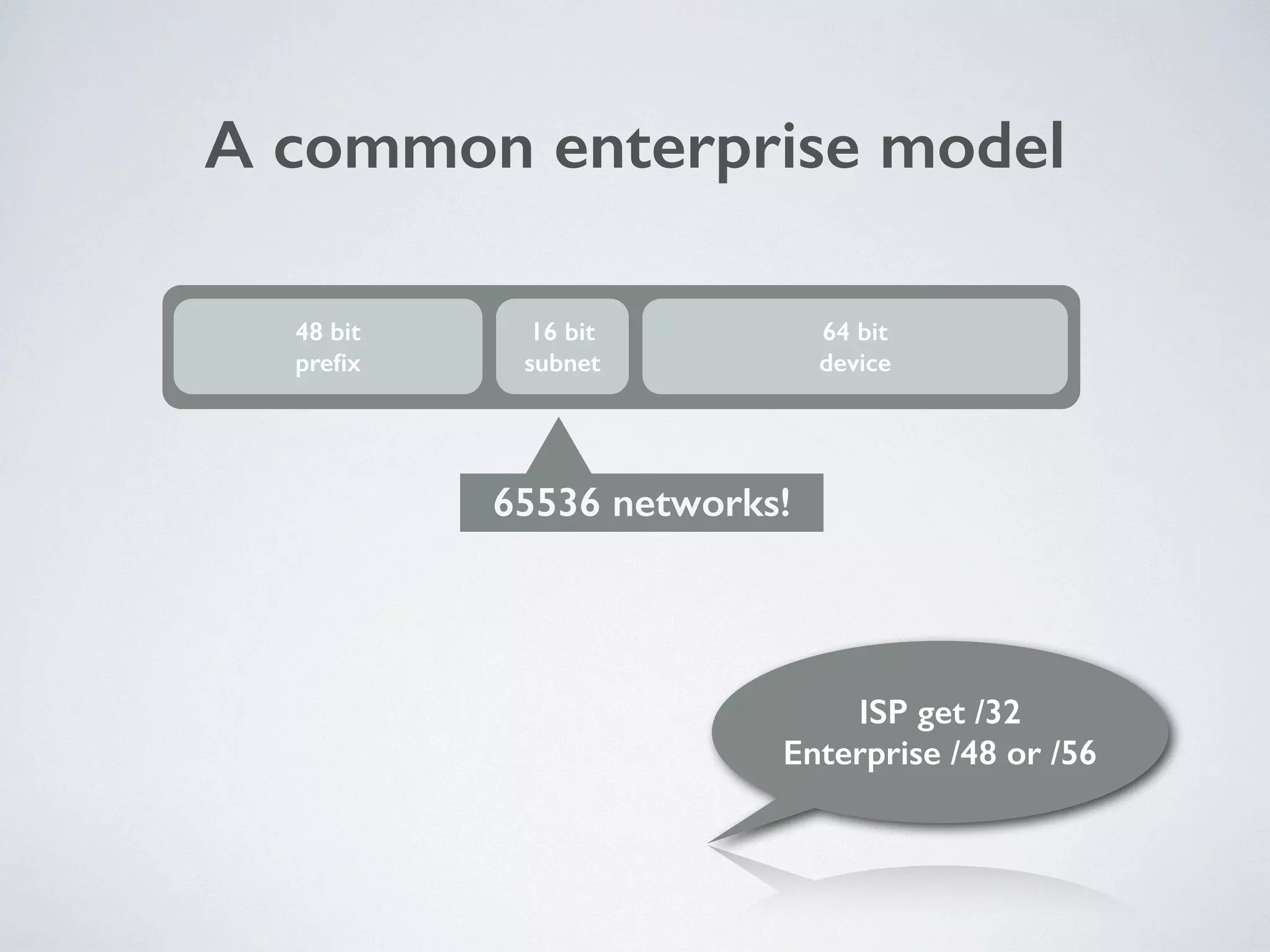
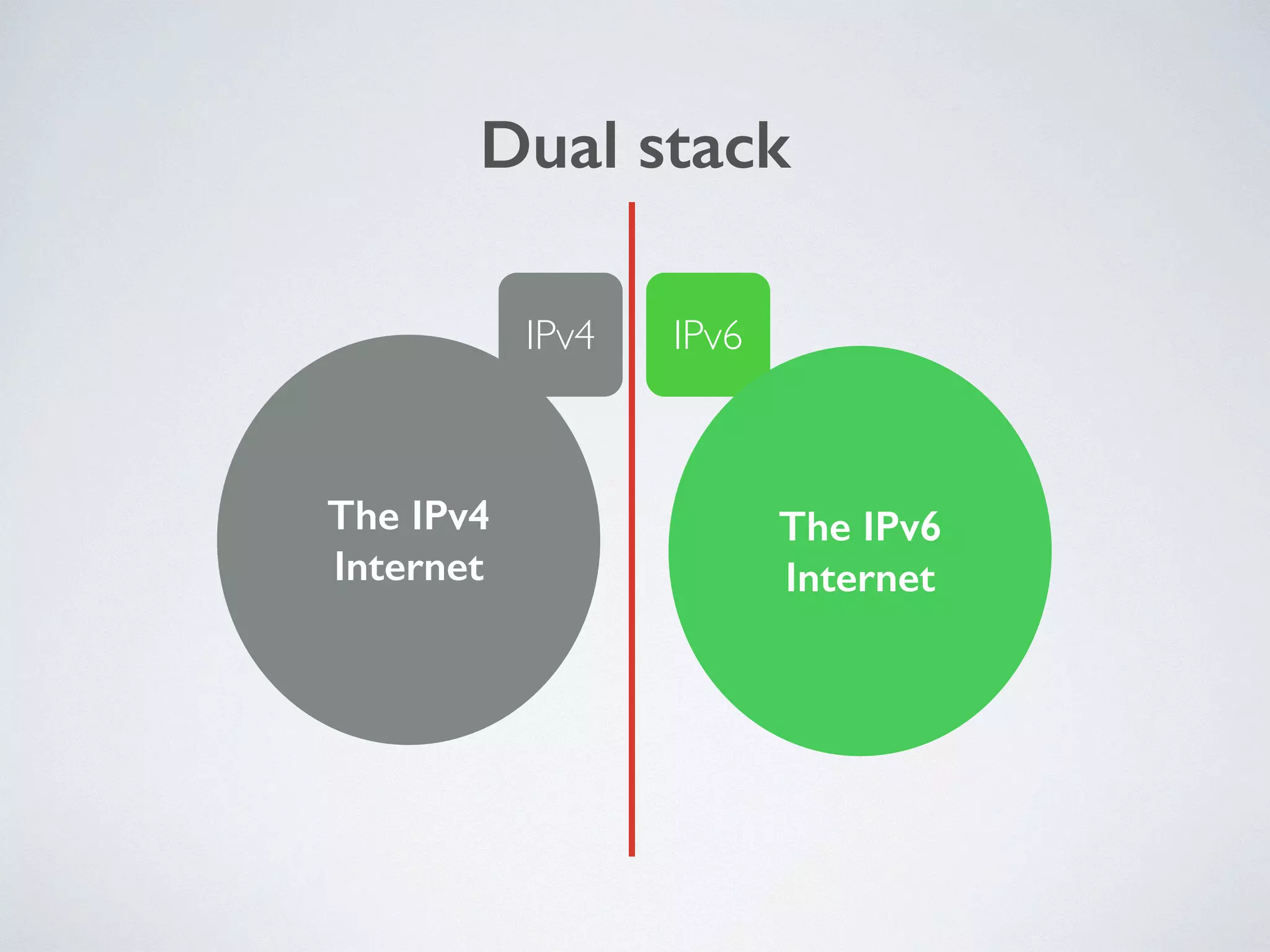
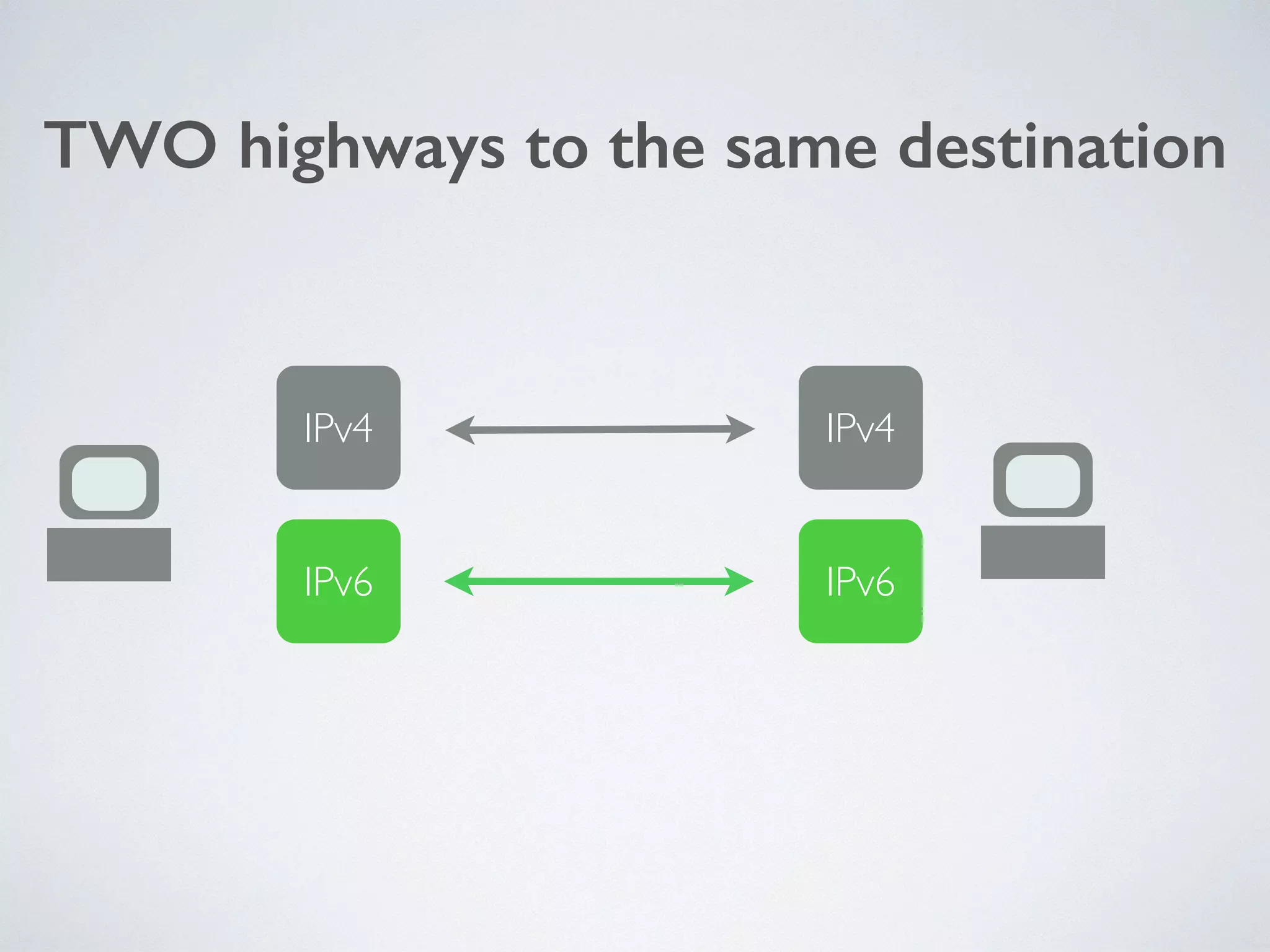
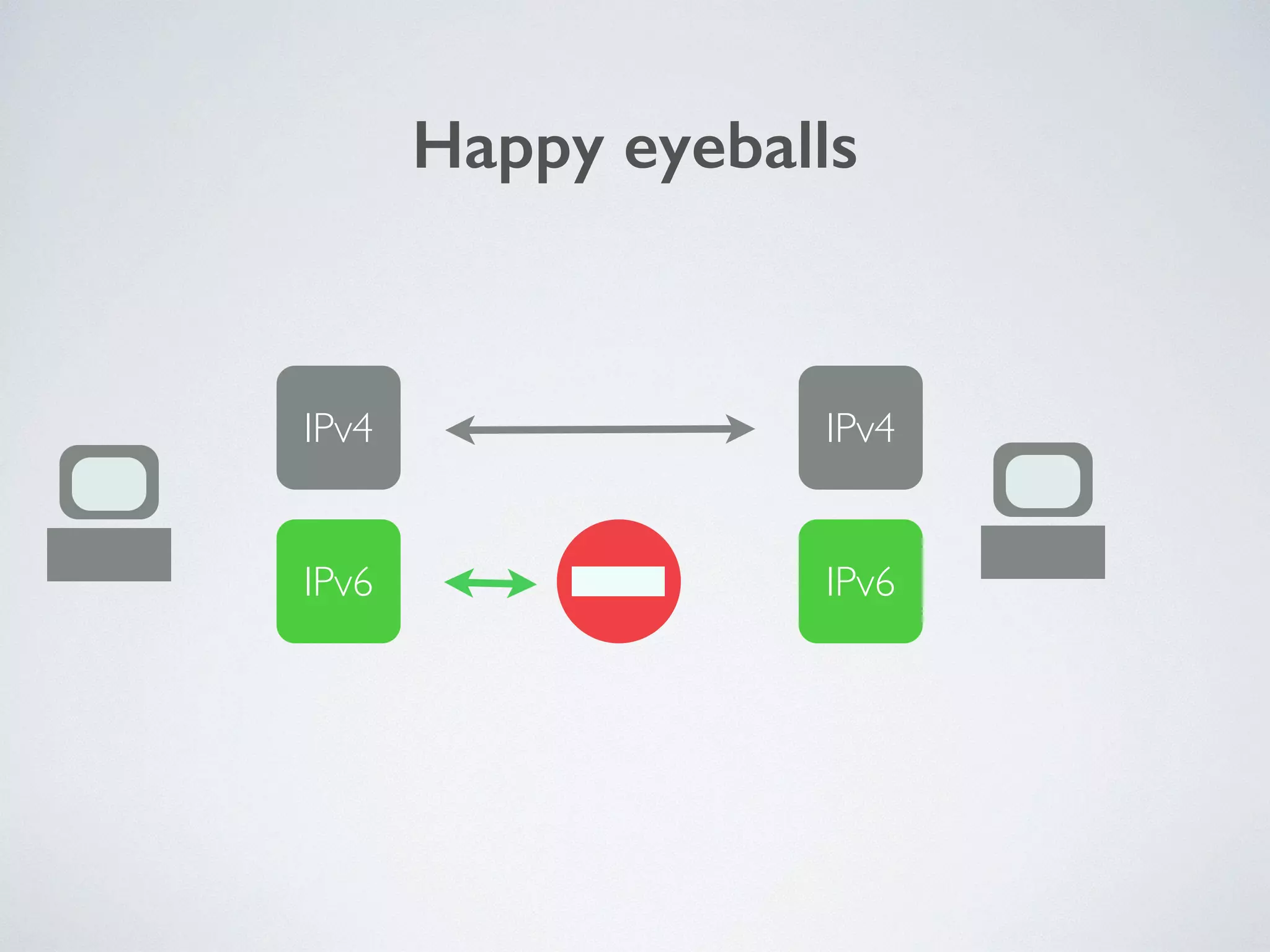
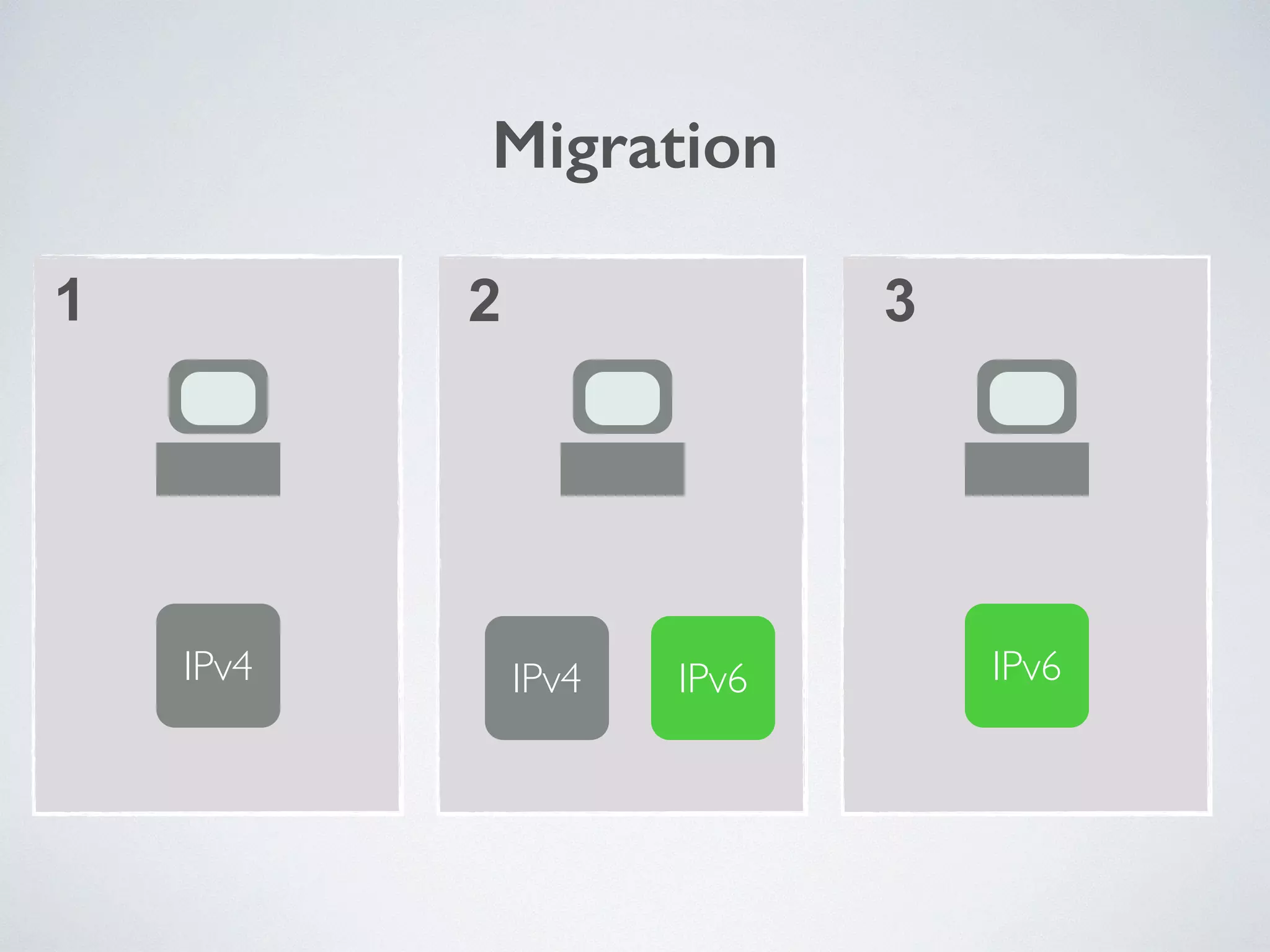
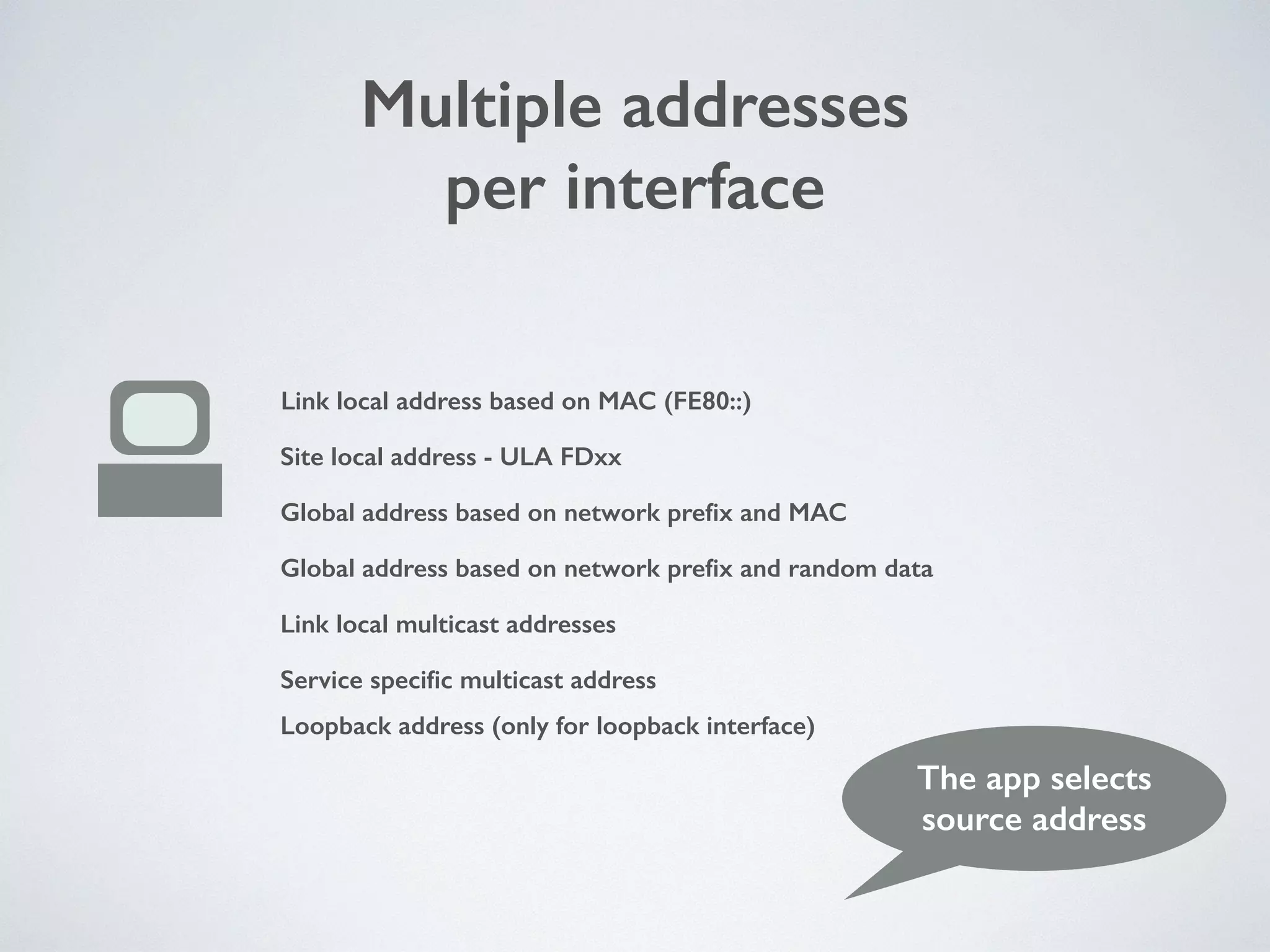
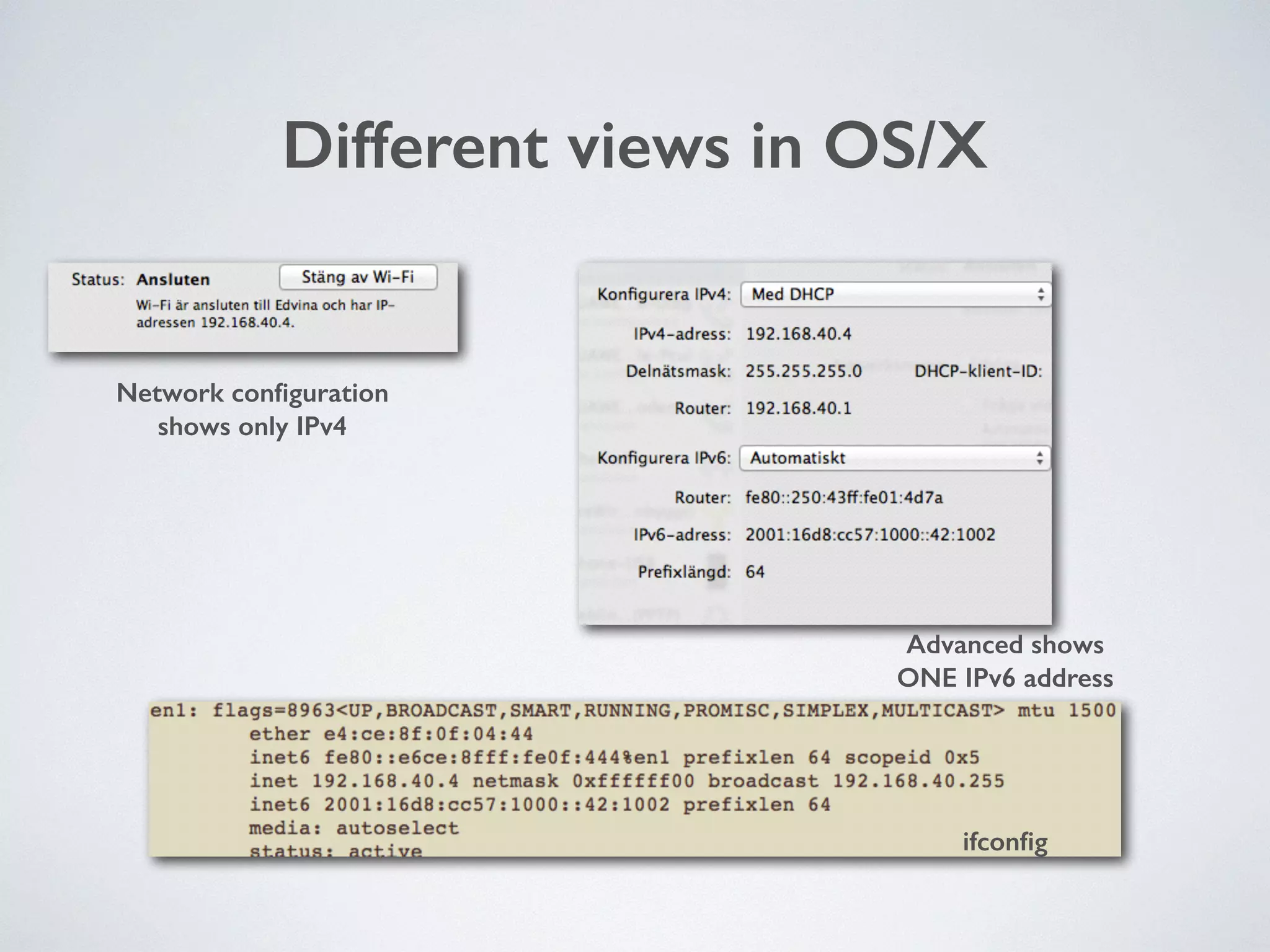
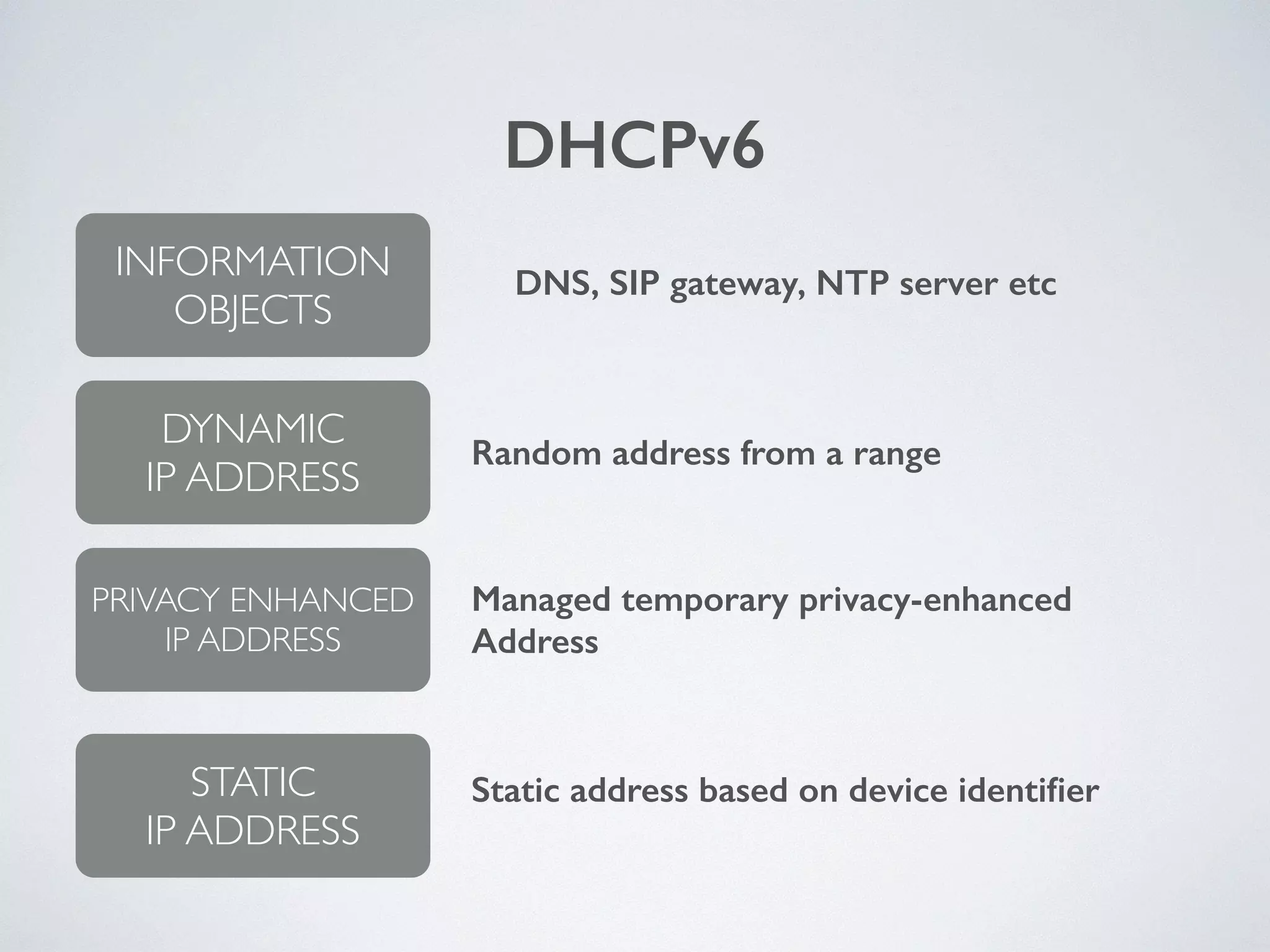
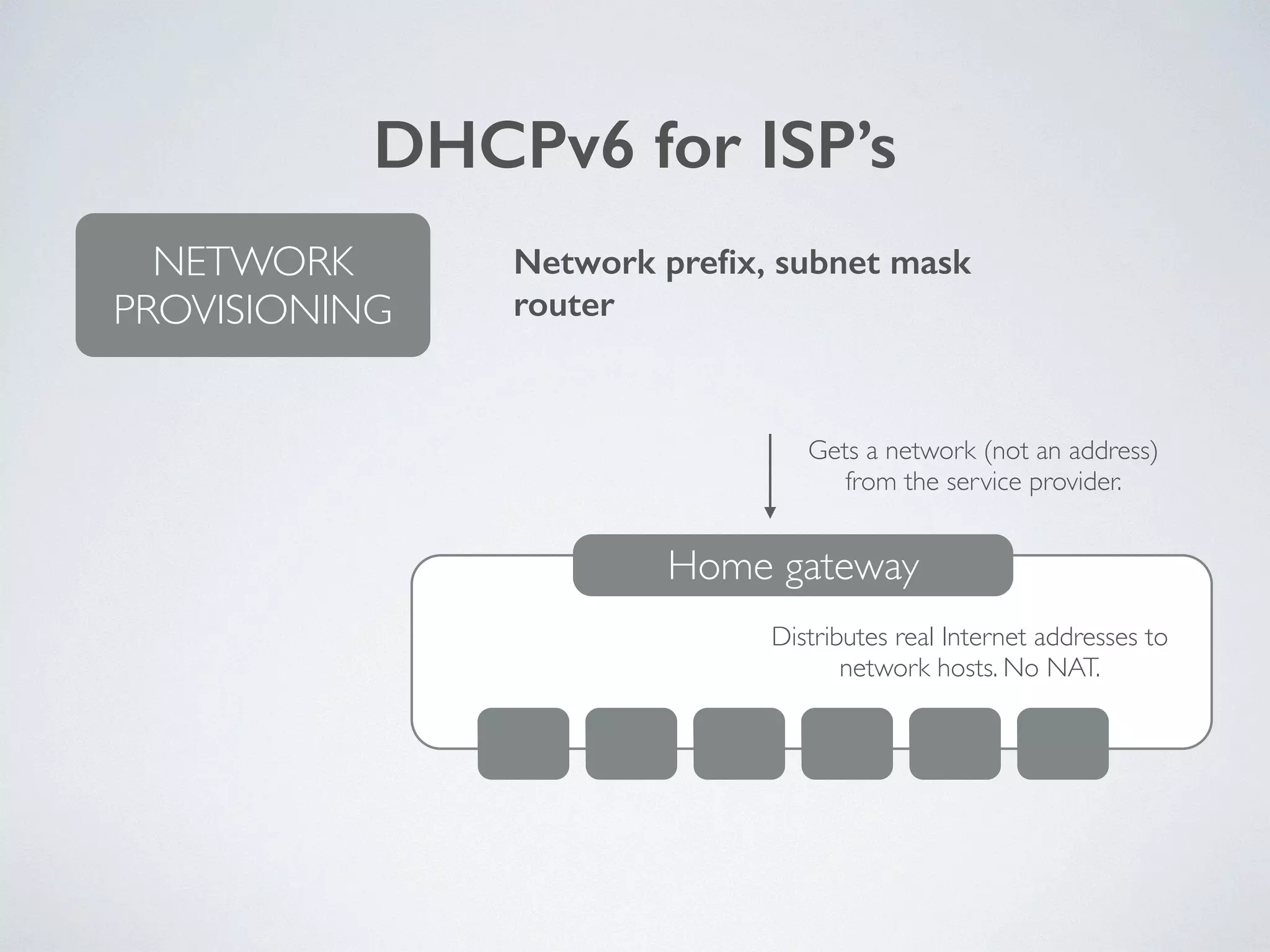
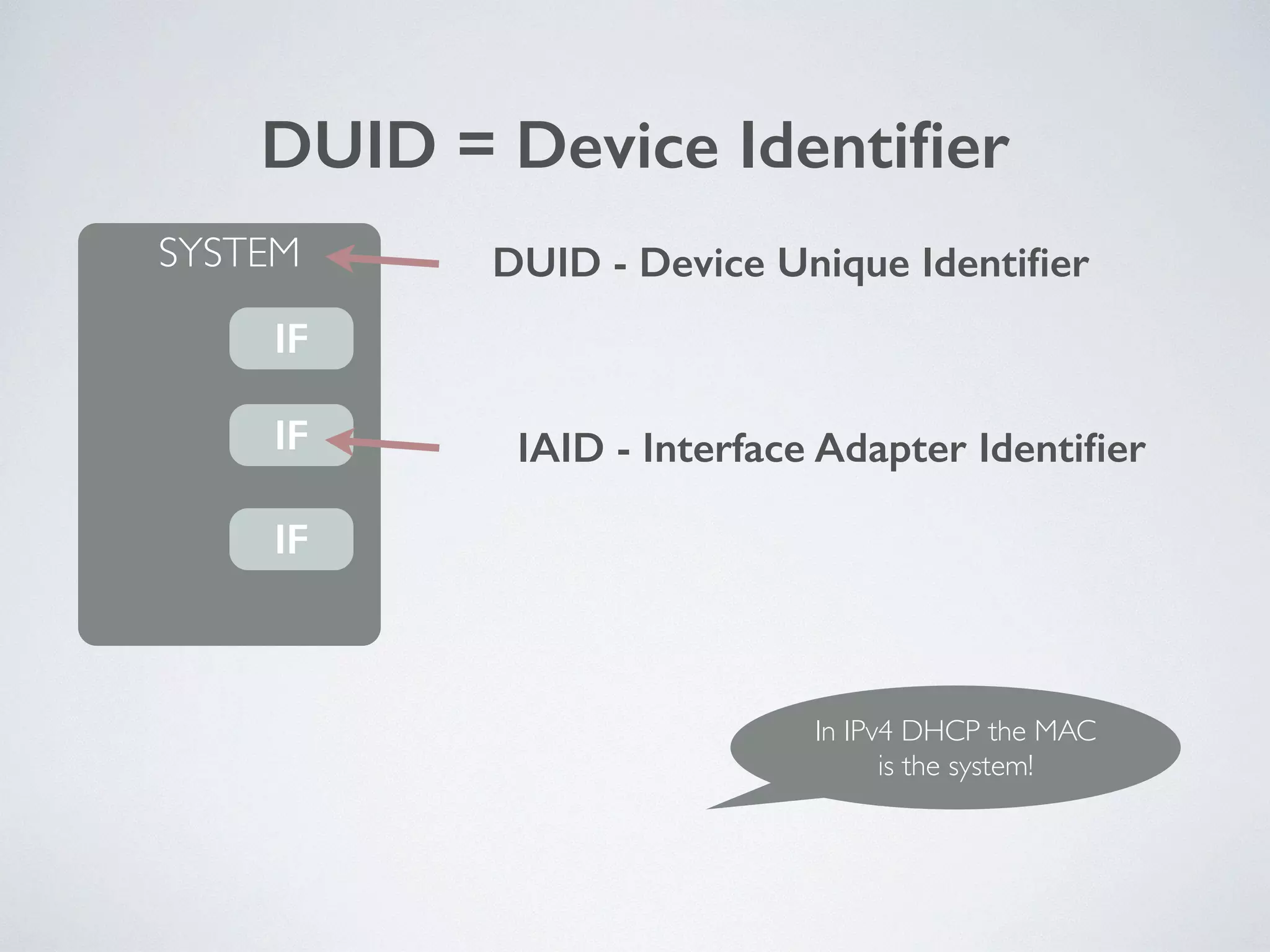
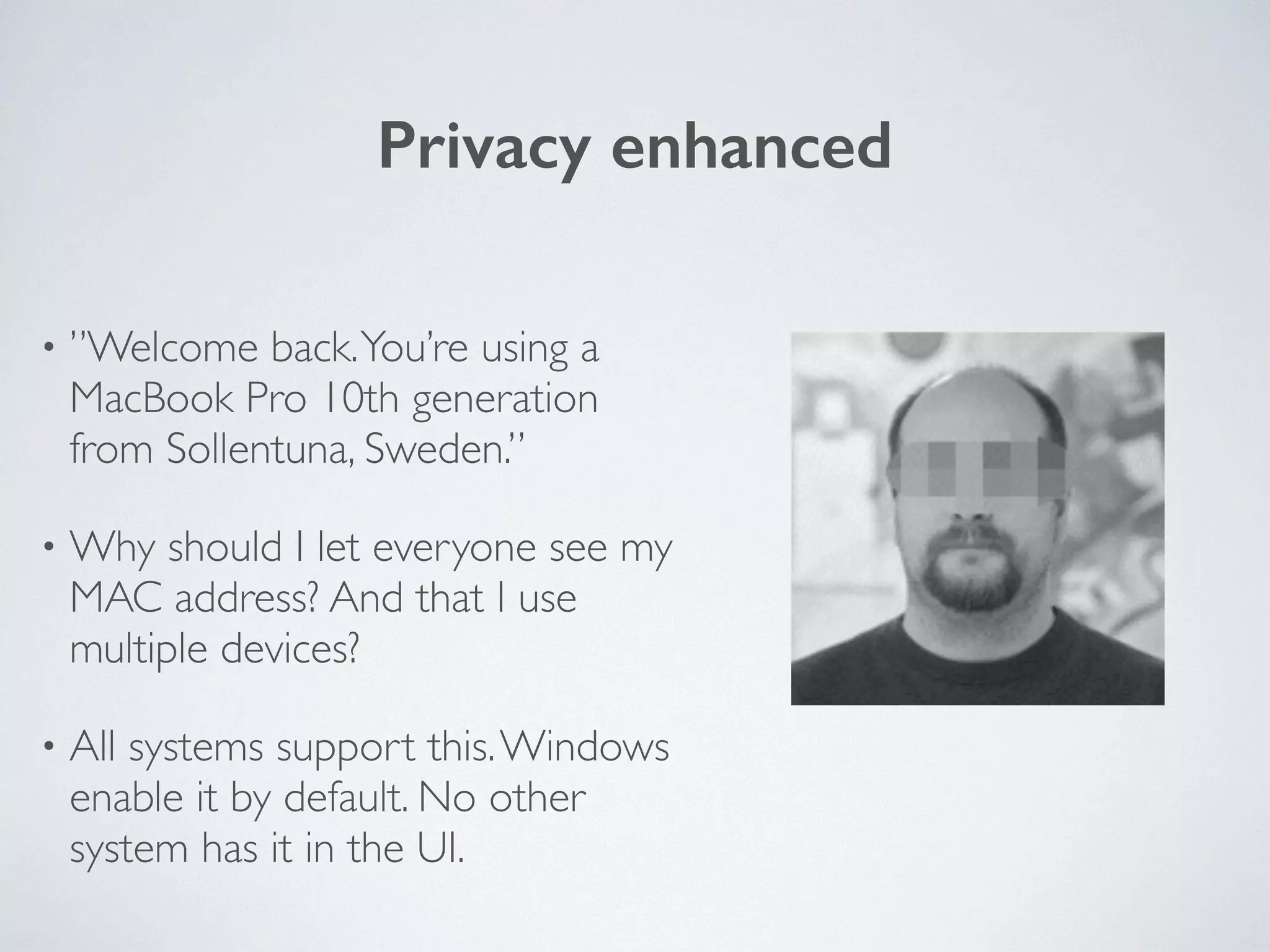
The document discusses the importance of transitioning to IPv6 due to the limitations of IPv4, especially as internet growth exceeds previous rates. It outlines a ten-step plan for organizations to adopt IPv6, ensuring future connectivity and addressing security issues associated with new protocols. The text emphasizes the urgent need for businesses to integrate IPv6 into all IT projects to avoid fragmentation of the internet.