Photosynthesis and Respiration Explained
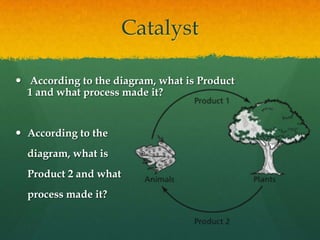
- 1. Catalyst According to the diagram, what is Product 1 and what process made it? According to the diagram, what is Product 2 and what process made it?
- 2. So what happens when you breathe? Oxygen (O2) goes in Carbon dioxide (CO2) goes out BUT IT’S NOT THIS SIMPLE….
- 3. So where does all this oxygen come from?? PLANTS doing PHOTOSYNTHESIS!
- 4. What does photosynthesis mean? Photo = light Synthesis = putting things together Photosynthesis = putting things together with light
- 5. So What do Plants Need to Survive? Plants need: Water- H2O Carbon Dioxide Light- the Sun! Chlorophyll- the GREEN in plants
- 6. What does the Reaction Look like?
- 7. What do Plants Make from Photosynthesis? Plants Make: 1. Glucose- sugar 2. Oxygen- the air
- 8. Guided Notes: Photosynthesis Photosynthesis is how plants use sunlight to make oxygen and sugar. Water + Carbon Dioxide Oxygen + Sugar (H2O) (CO2) (O2) (C6H12O6) + ENERGY from sunlight Reactants (what goes in) Products (what comes out)
- 10. What is cellular respiration? The processes that cells use to get energy from molecules
- 12. Does it require oxygen? Aerobic Anaerobic YES! NO!
- 13. Where does it happen? Aerobic Anaerobic Mostly Cytoplasm mitochondria
- 14. How much ATP does it make? Aerobic Anaerobic 38 ATP for 2 ATP for every every glucose glucose
- 15. What are the steps? Aerobic Anaerobic 1. Glycolysis 1. Glycolysis 2. Krebs Cycle 2. Fermentation (2 3. Electron types) Transport Chain
- 16. Is it sustainable? Aerobic Anaerobic YES! NO! It can continue We can only do indefinitely this short term
- 17. What types of cells use this? Aerobic Anaerobic Most cells Yeast Prokaryotes Muscle cells
- 18. Photosynthesis Respiration Make sugar (glucose) Make ATP by Purpose breaking down sugar from sunlight (glucose) Who does Plants, some Plants AND animals it? bacteria (all living things) chloroplast Mitochondria & Organelle cytoplasm CO2 + H2O sugar + O2 Equation sugar + O2 CO2 + H2O
- 19. Equations Photosynthesis: CO2 + H2O C6H12O6 + O2 Respiration: C6H12O6 + O2 H2O + CO2
- 20. Overview of the process Photosynthesis was about making energy which means making bonds. Respiration is about releasing energy which means breaking bonds.
- 21. Why do we need photosynthesis? • This process is how almost all of our planet gets its energy--almost all living things rely on the plants to capture energy from the sun and convert it into the bonds of glucose. Then we either eat the plants or things that eat only plants to get energy • They make all the oxygen on our plant so we couldn’t go through aerobic respiration without the plants making oxygen
- 22. Why do all living things need Respiration? All living things need to be able to get energy for their cells! Even the plants go through respiration so they can break down the glucose into ATP and use that energy in their cells REMEMBER: 1 glucose = 38 ATP
- 23. What happens in each step? Light-reaction: Take energy from the sun and store it in the bonds of ATP, release oxygen Dark-Reaction: use the ATP to make glucose from carbon dioxide and water Glycolysis: Split glucose into two pyruvate molecules Kreb’s Cycle: Break pyruvate down into carbon dioxides and steal the electrons Electron Transport Chain: Use the electrons to make ATP
- 24. Where does each take place? Photosynthesis: CHLOROPLAST Light Reaction: Thylakoid Dark Reaction: Stroma Respiration: MITOCHONDRIA Glycolysis: Cytoplasm Kreb’s Cycle: Matrix of Mitochondria ETC: Cristae of the Mitochondria