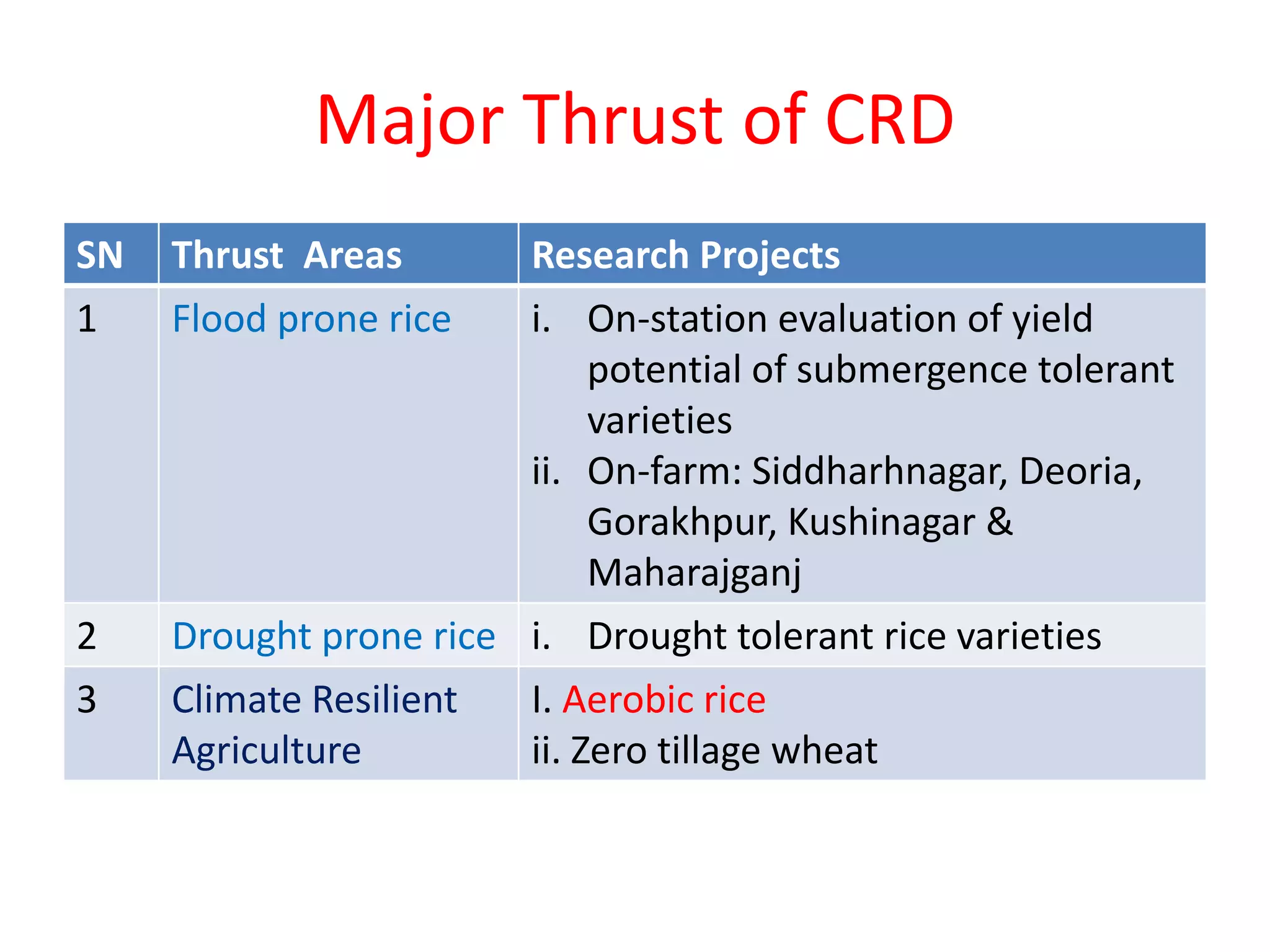
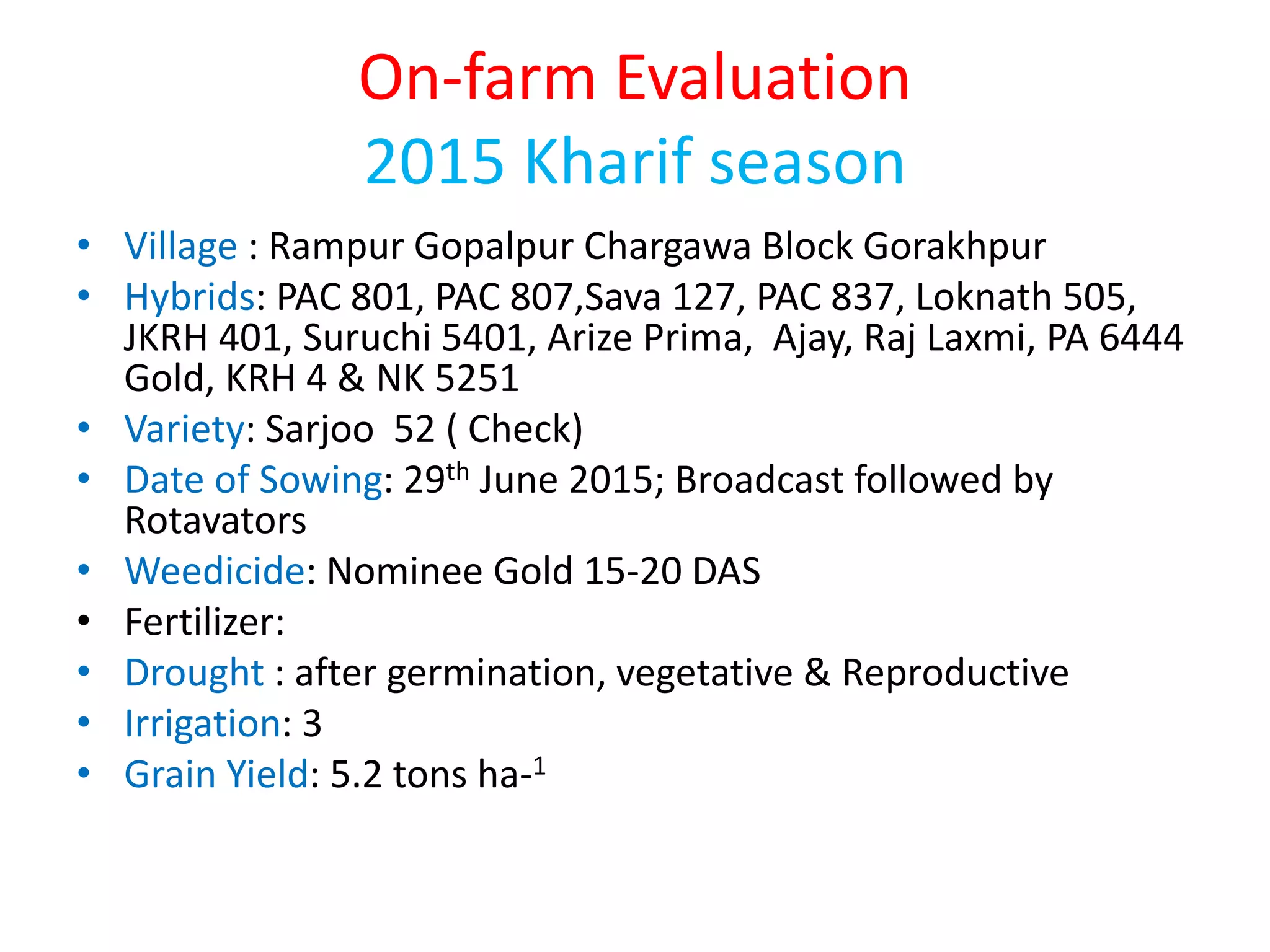
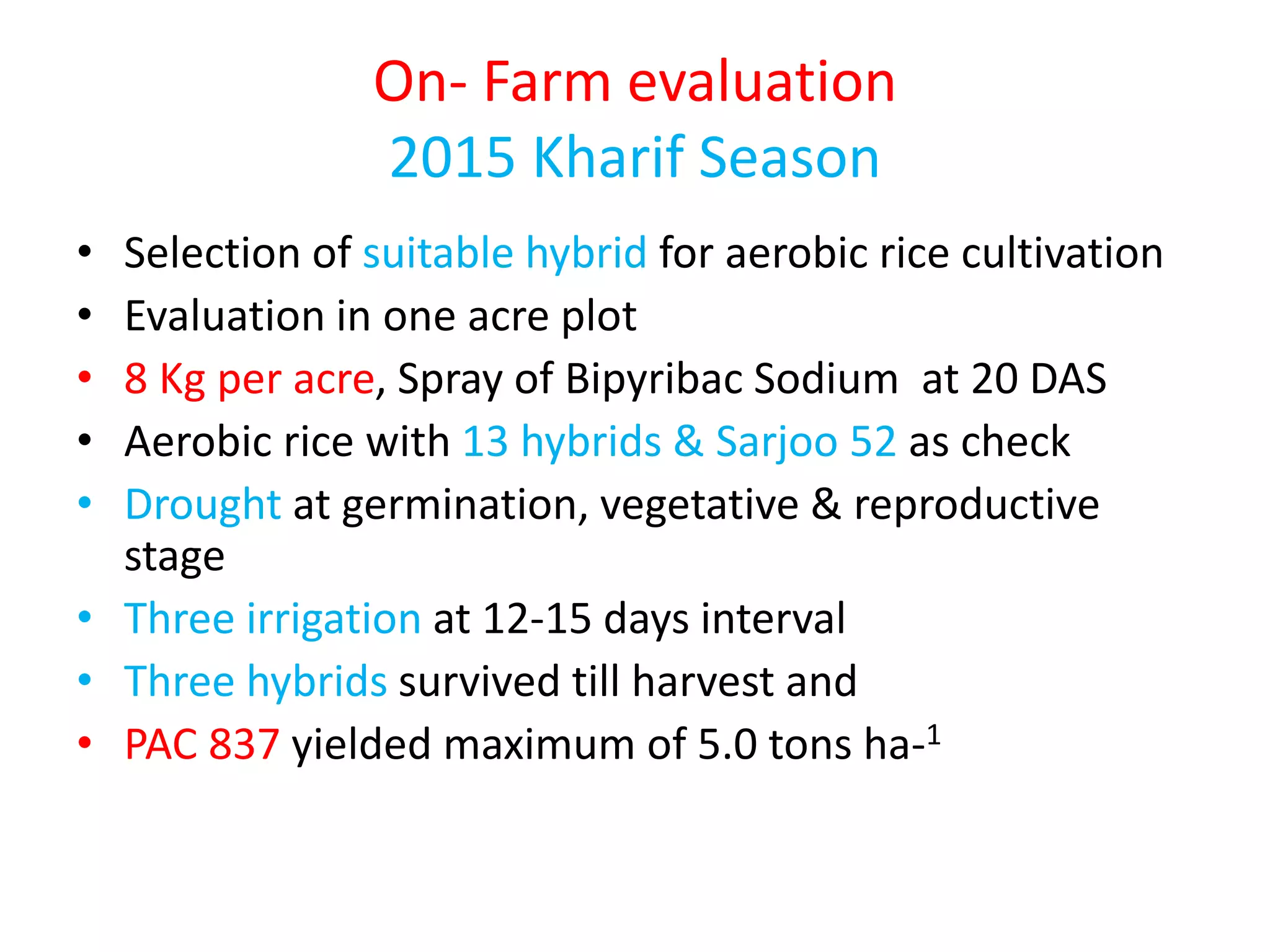
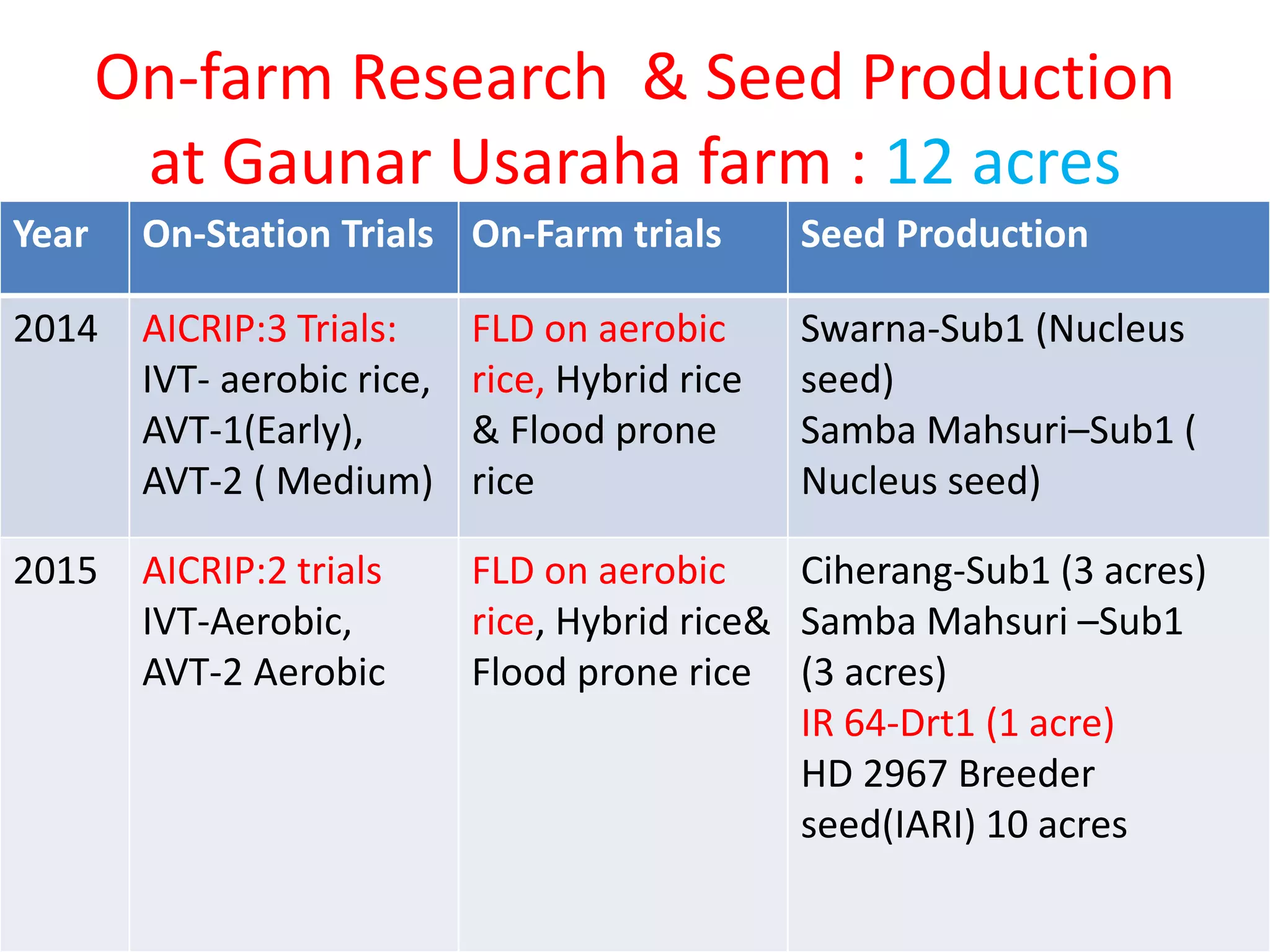
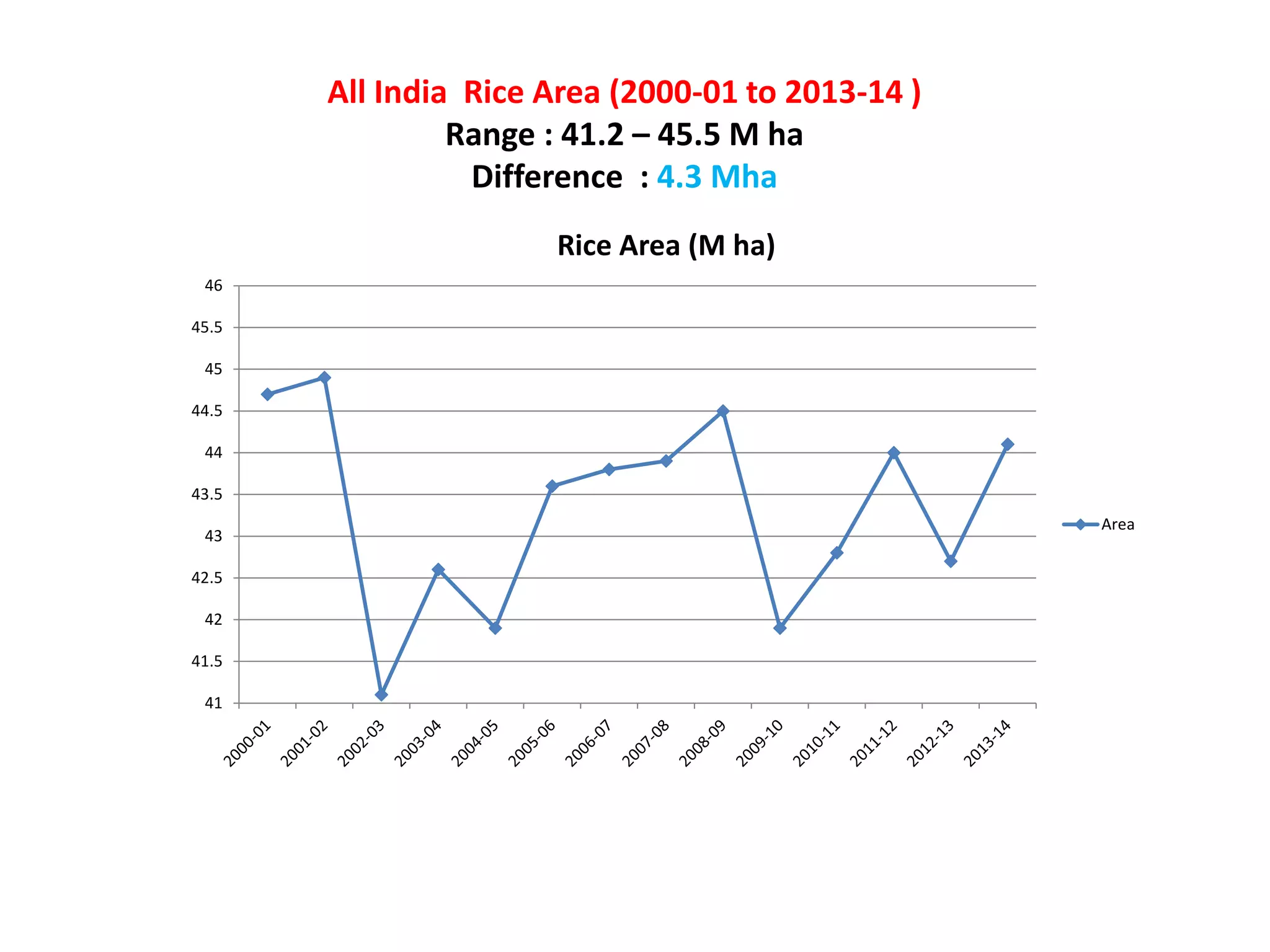
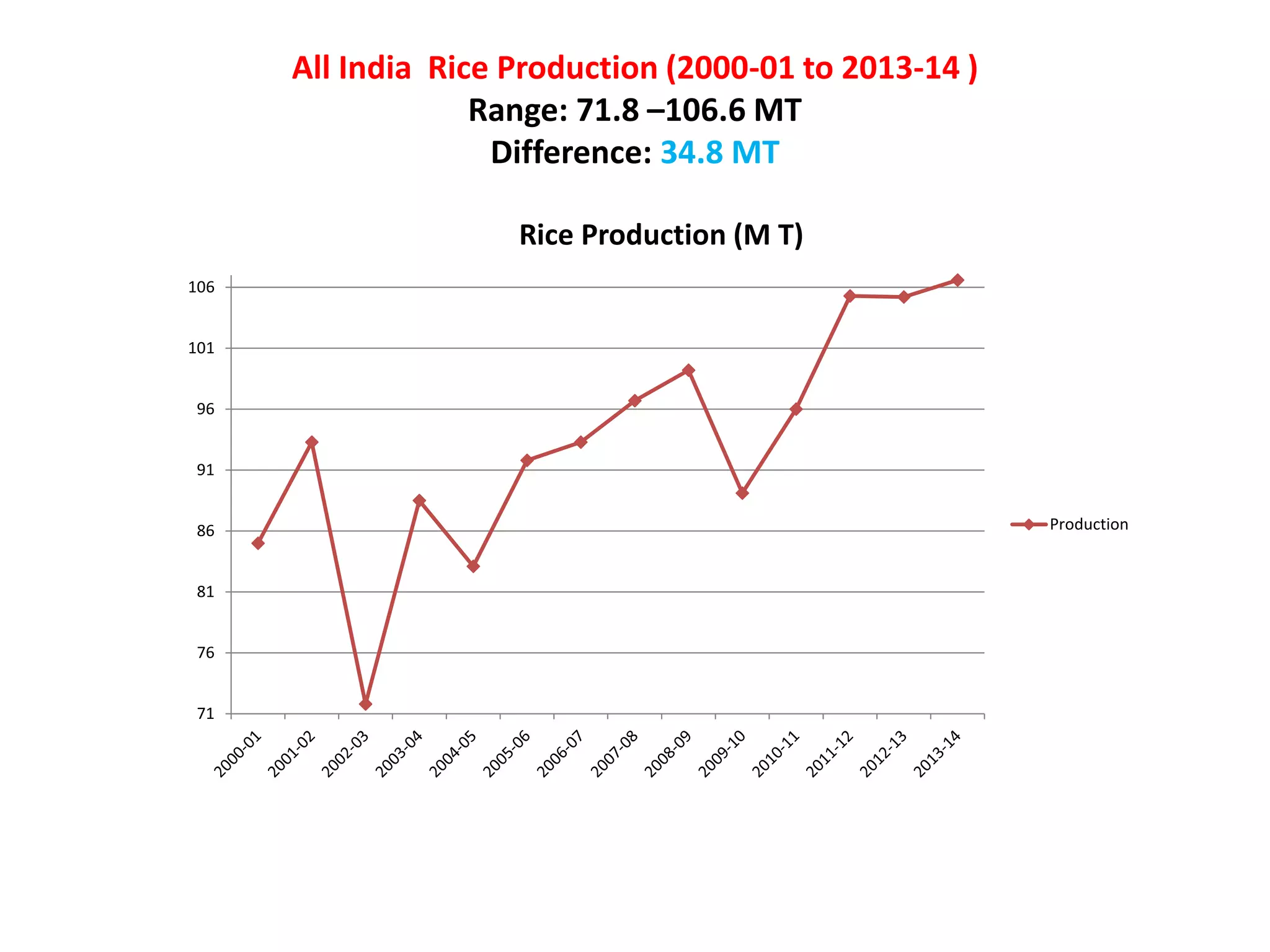
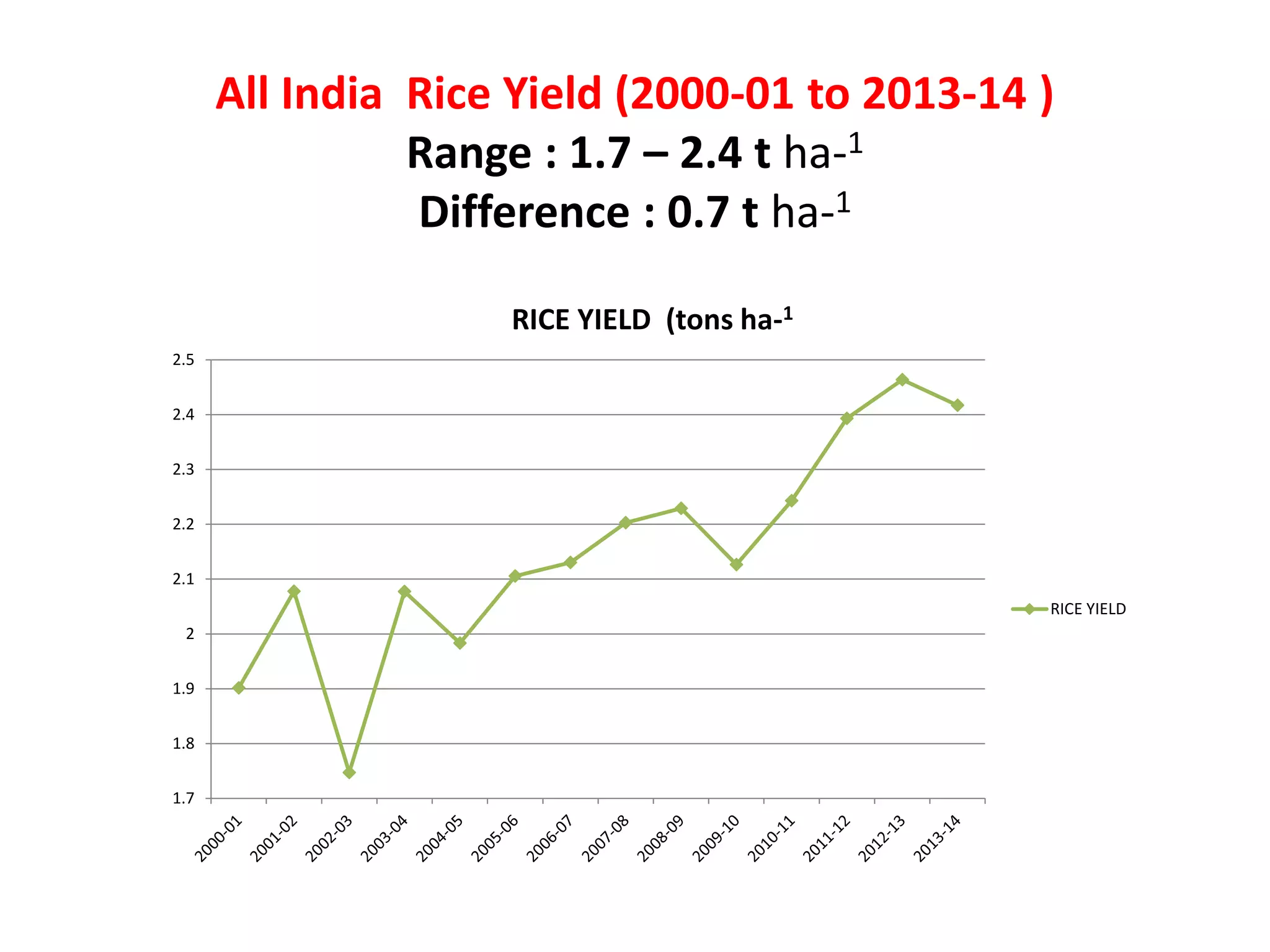
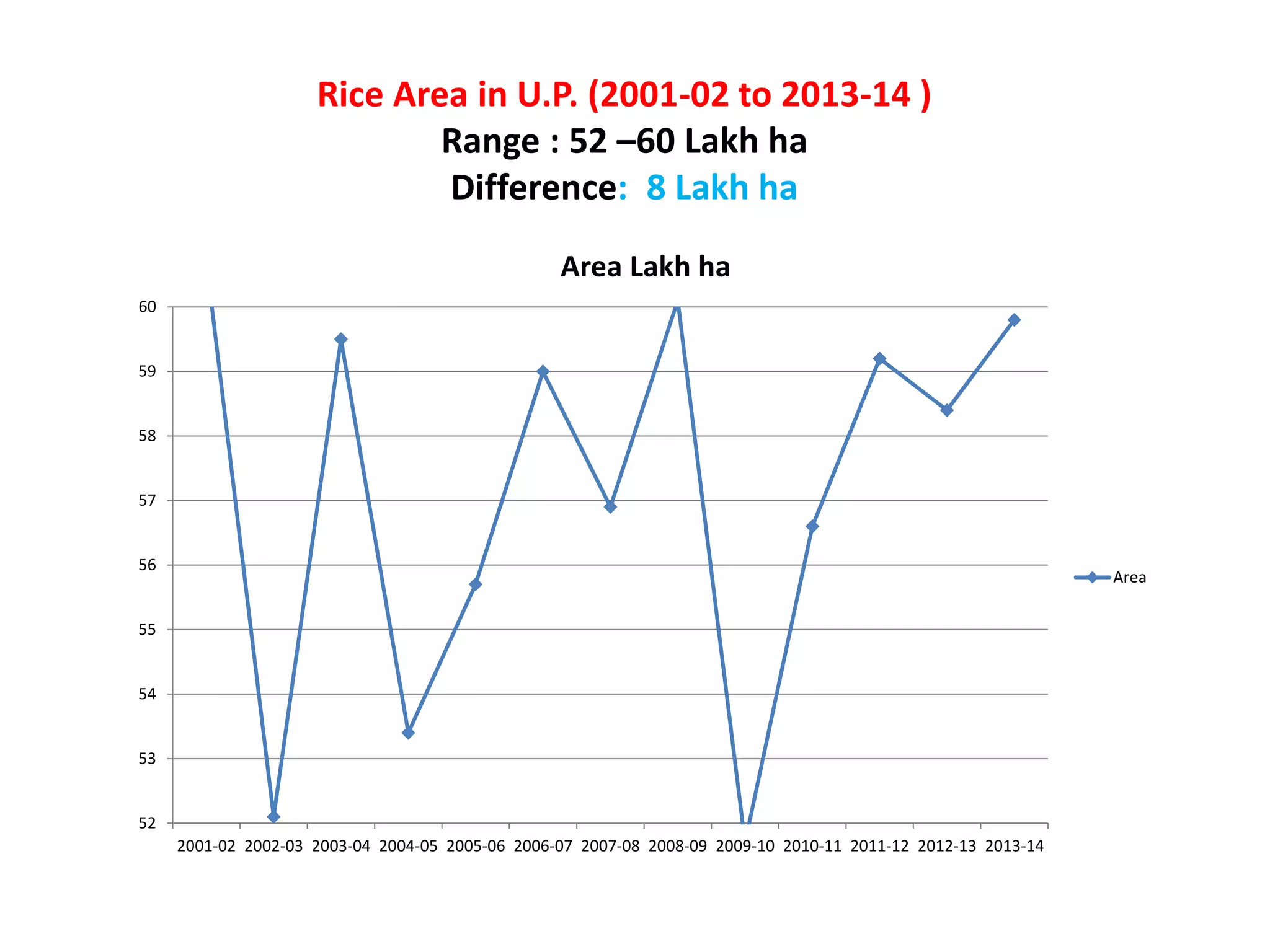
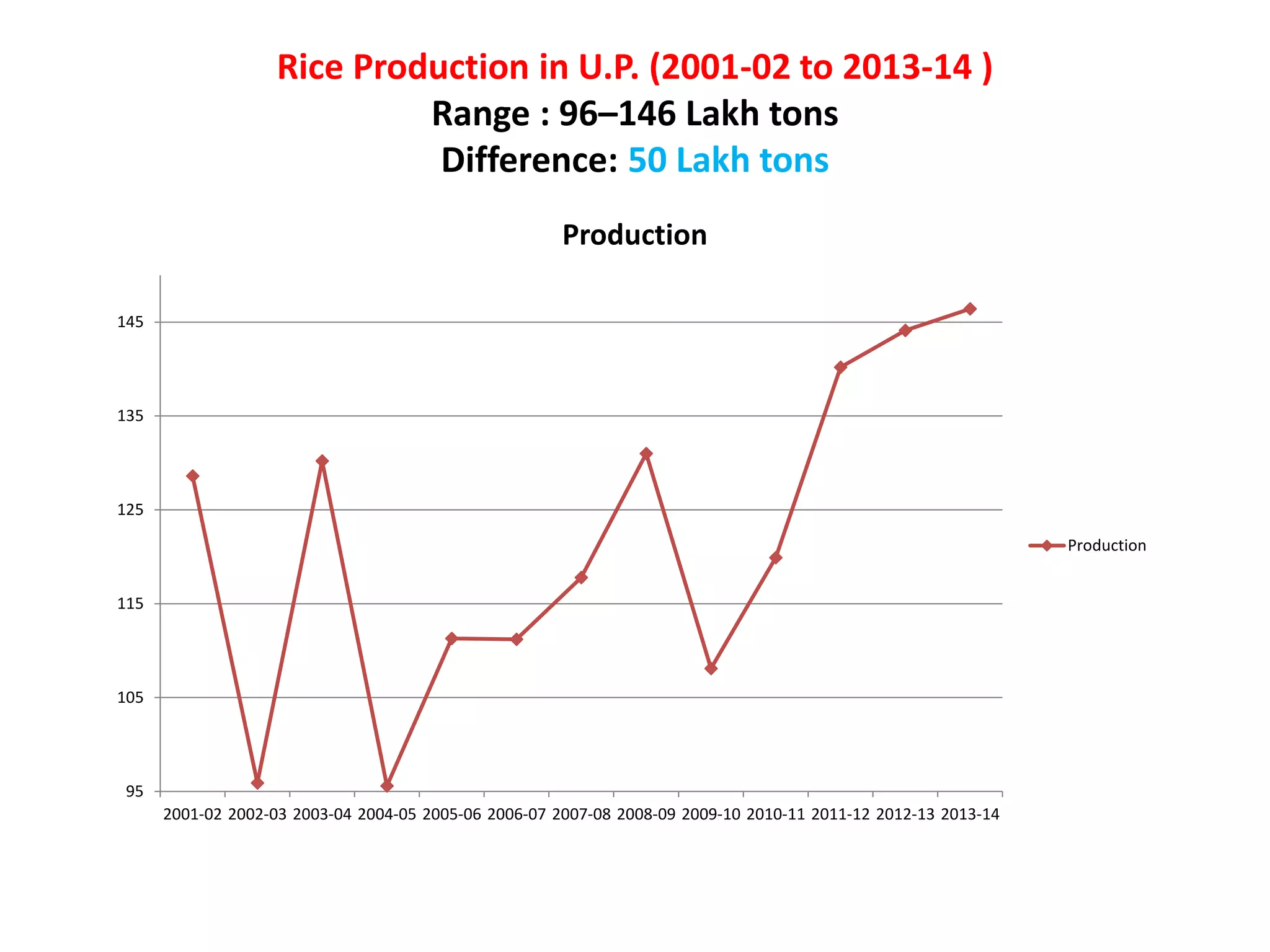
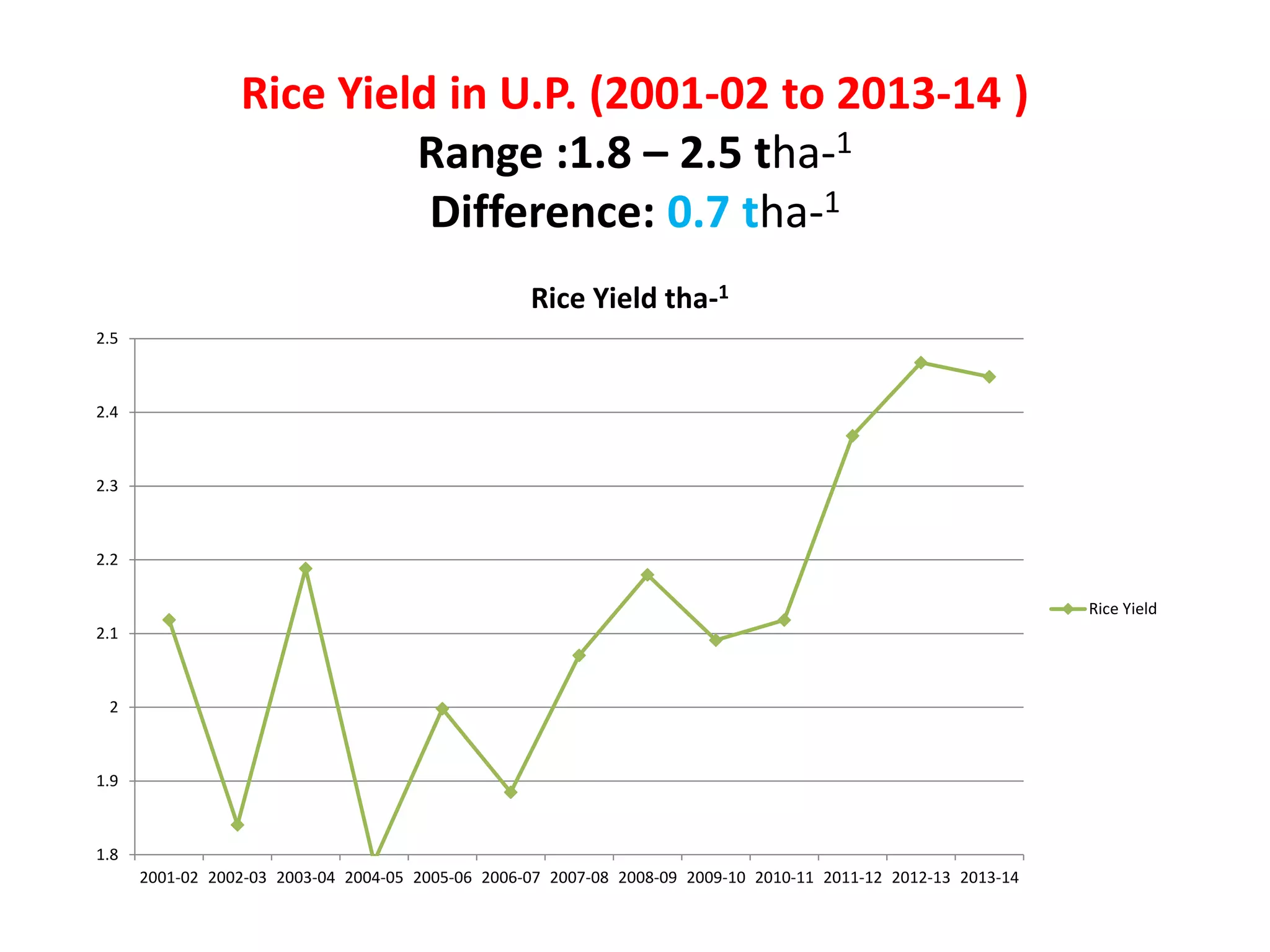
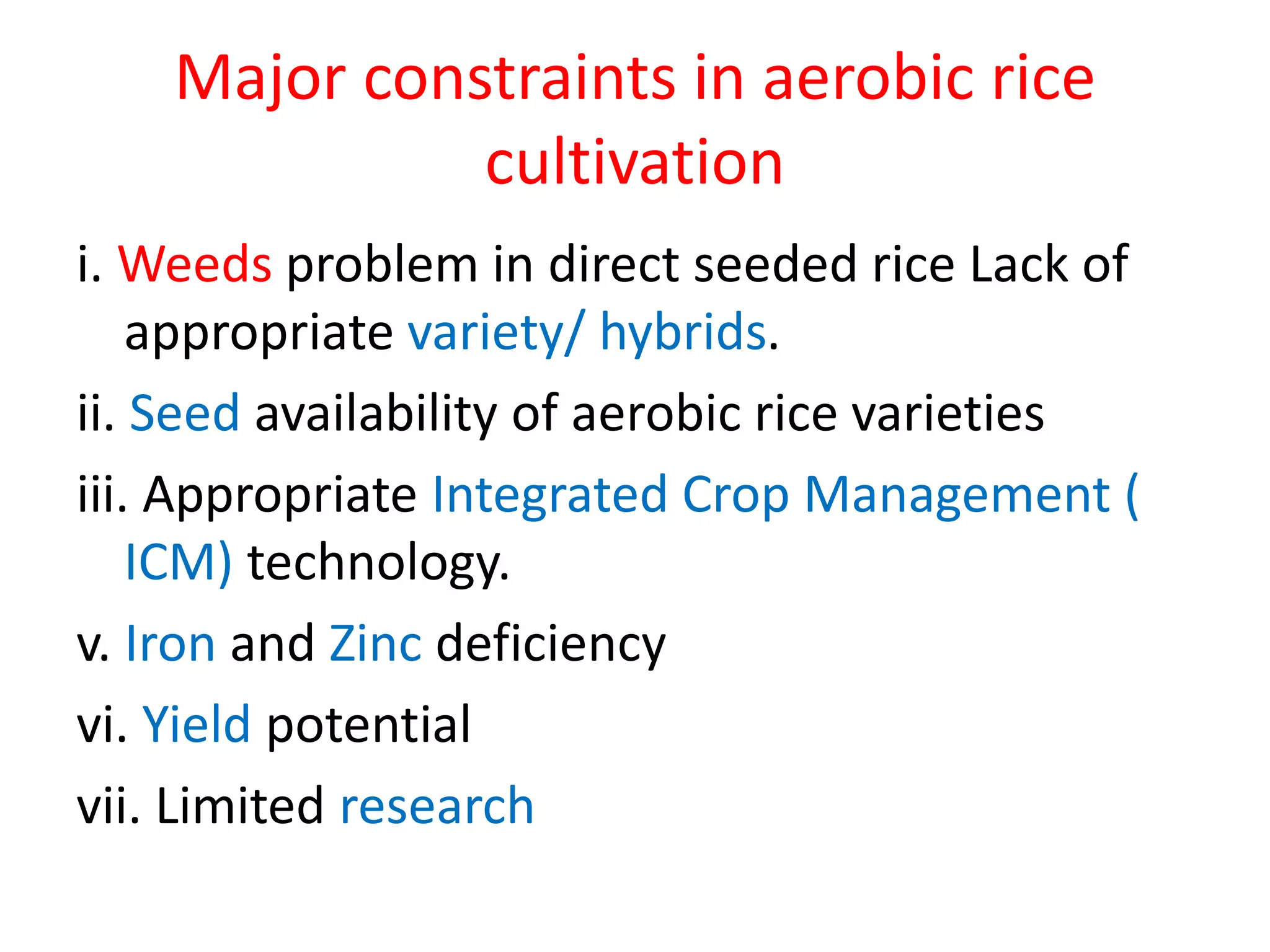
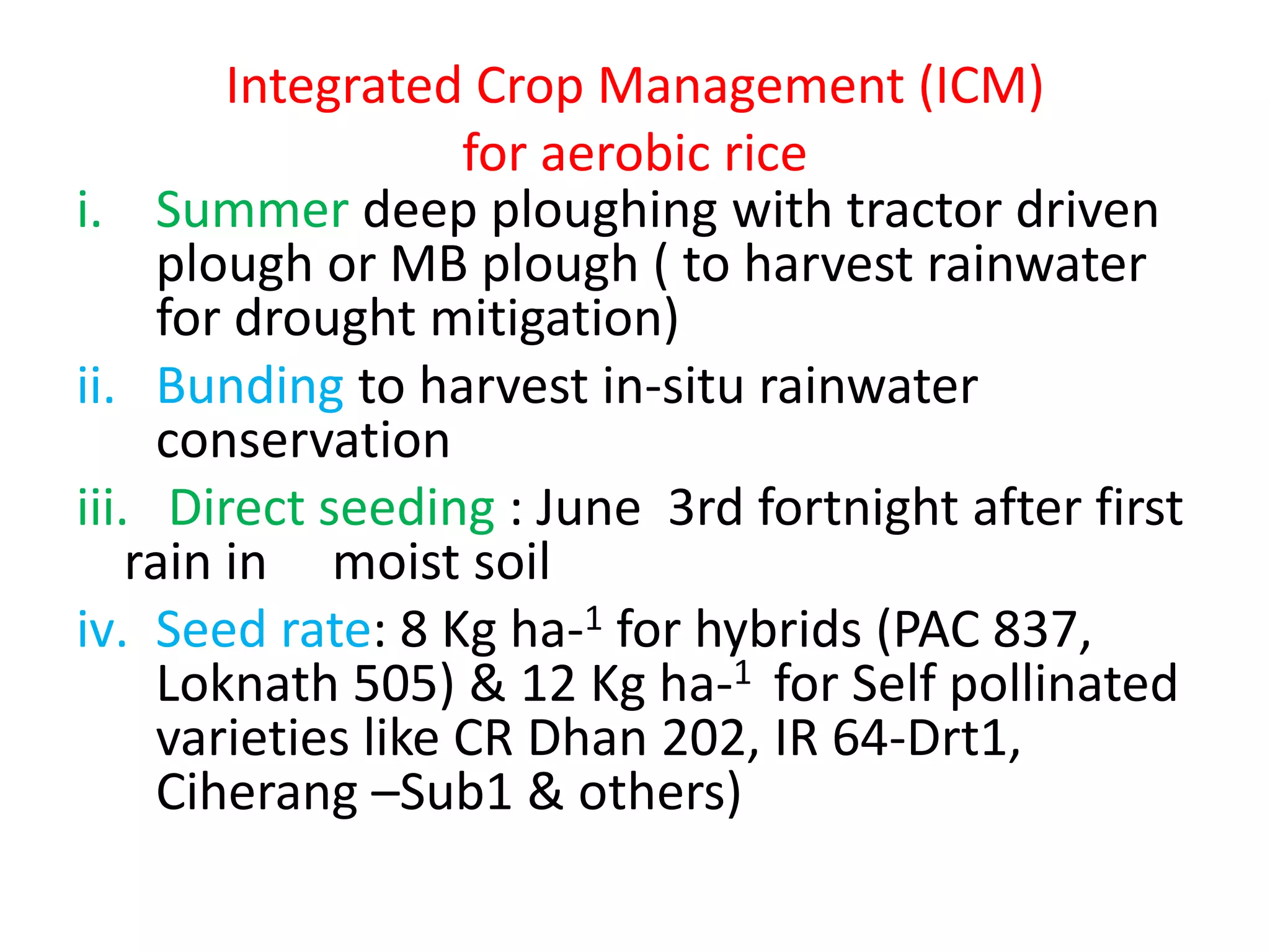
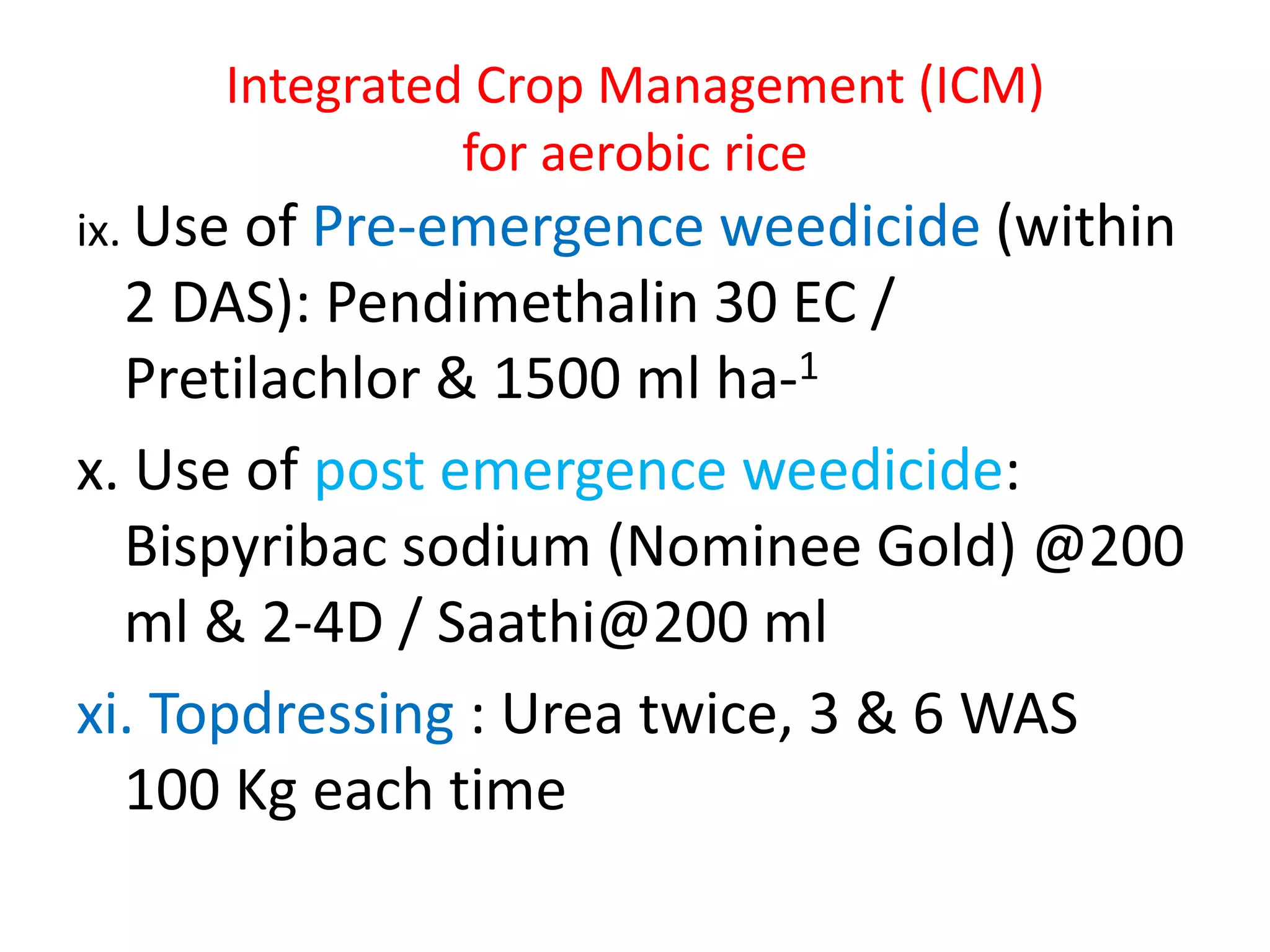
The document discusses on-farm research and trials on aerobic rice technology aimed at enhancing rice production under drought and flood-prone conditions in Uttar Pradesh, India. It highlights various hybrids' performance, integrated crop management practices, and the benefits of adopting aerobic rice cultivation, such as water conservation and improved yields. Key findings indicate that specific hybrids like pac 837 and loknath 505 show better performance in terms of drought tolerance and higher grain yield.