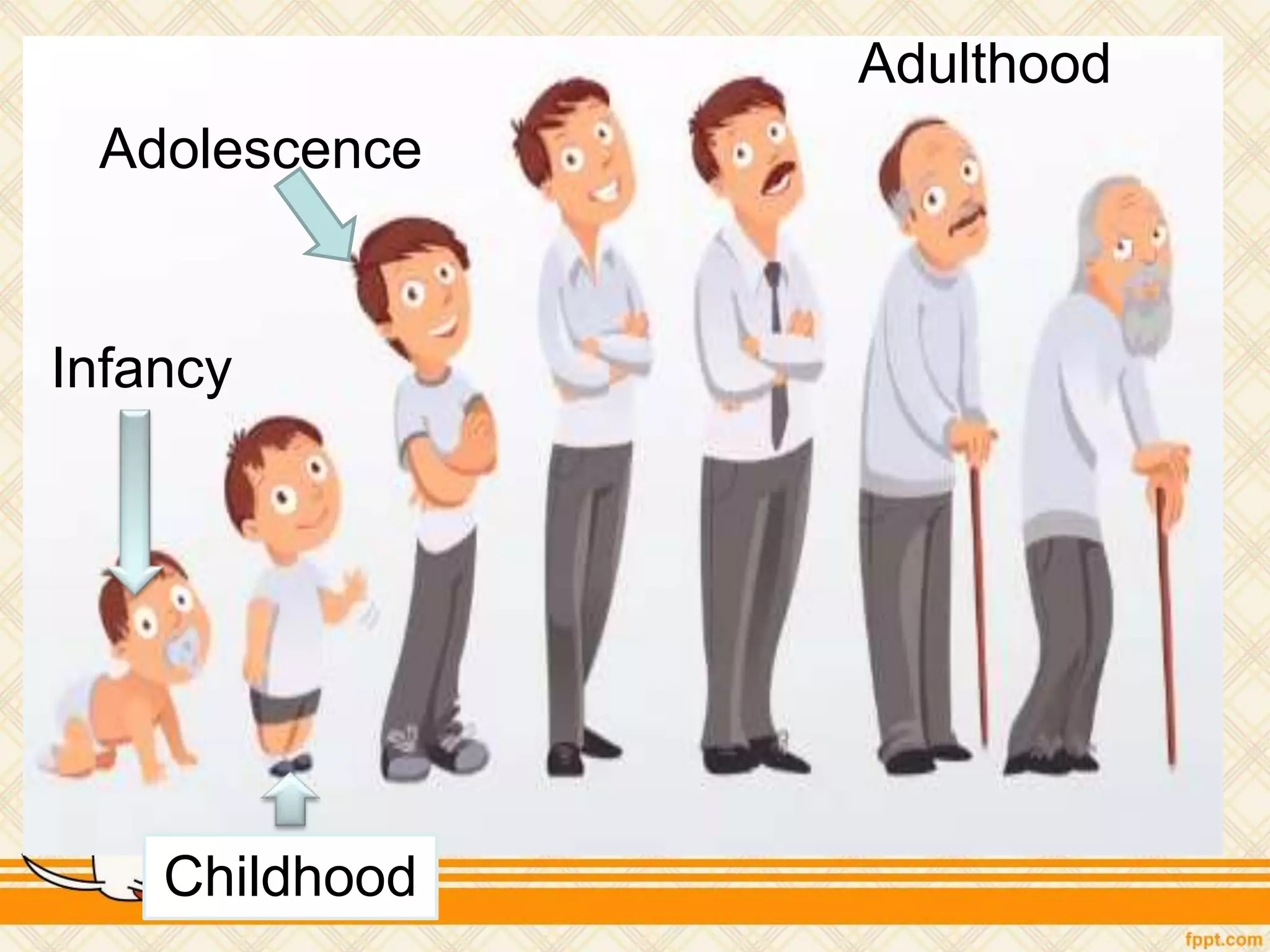
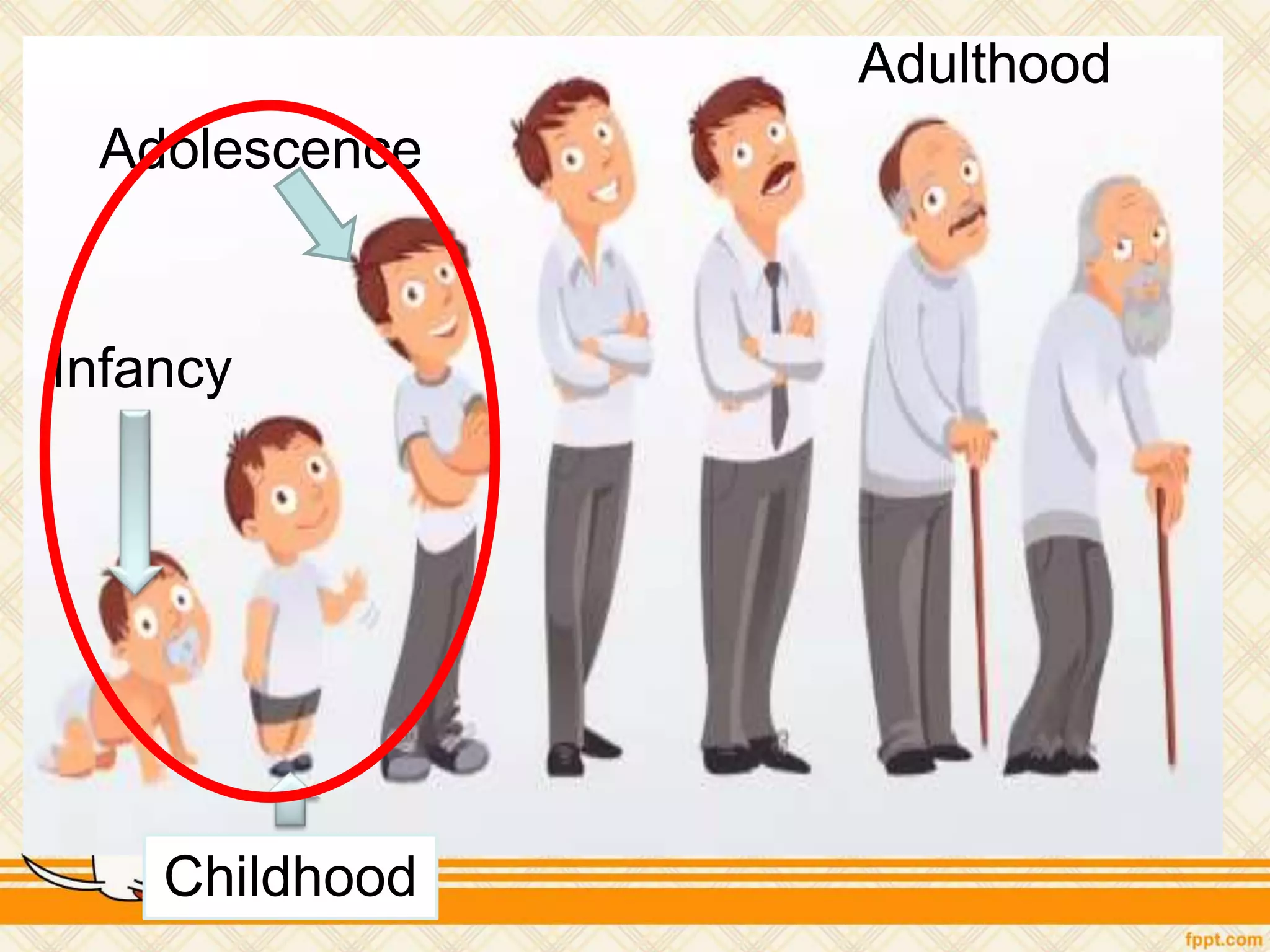
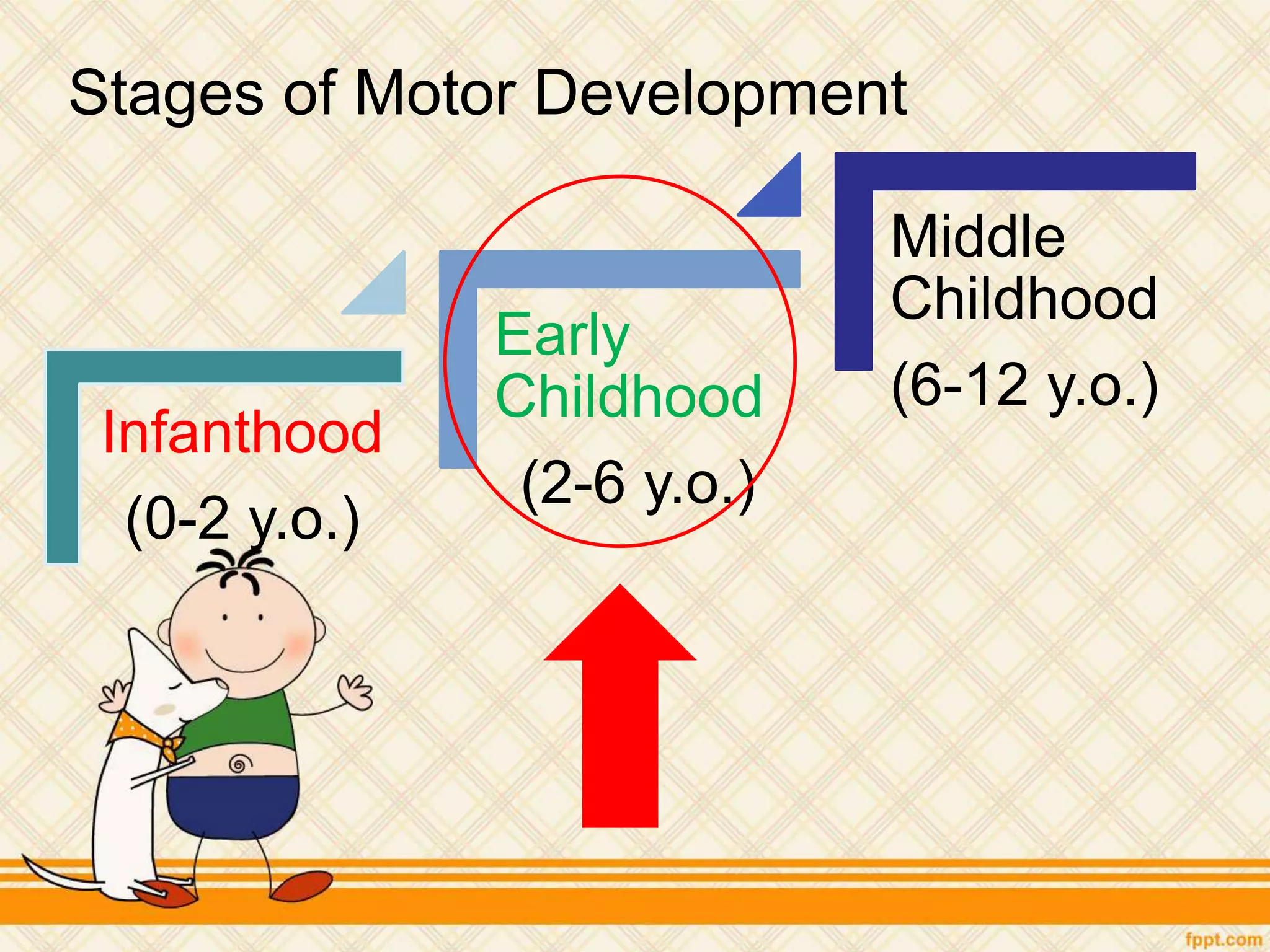
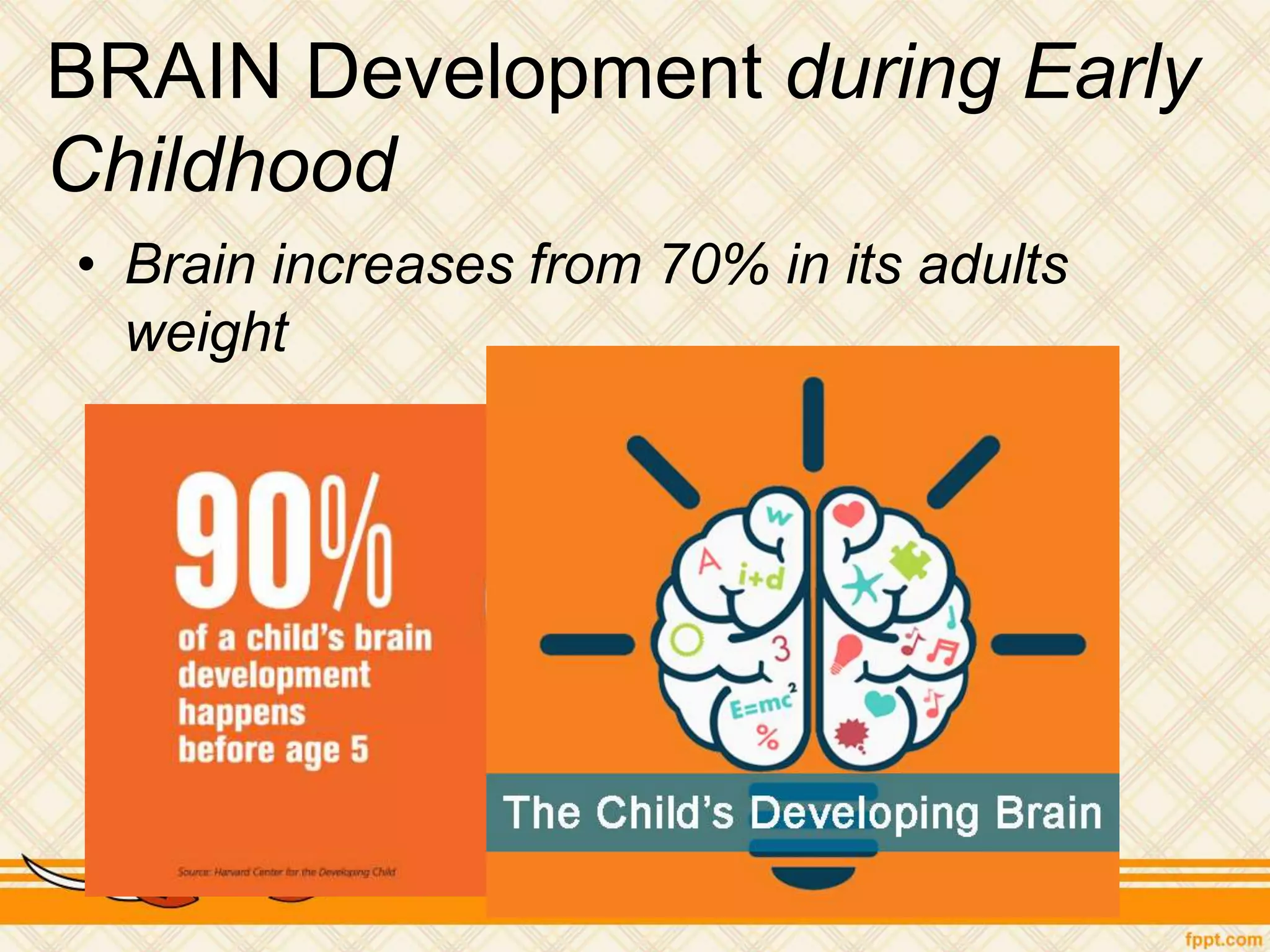
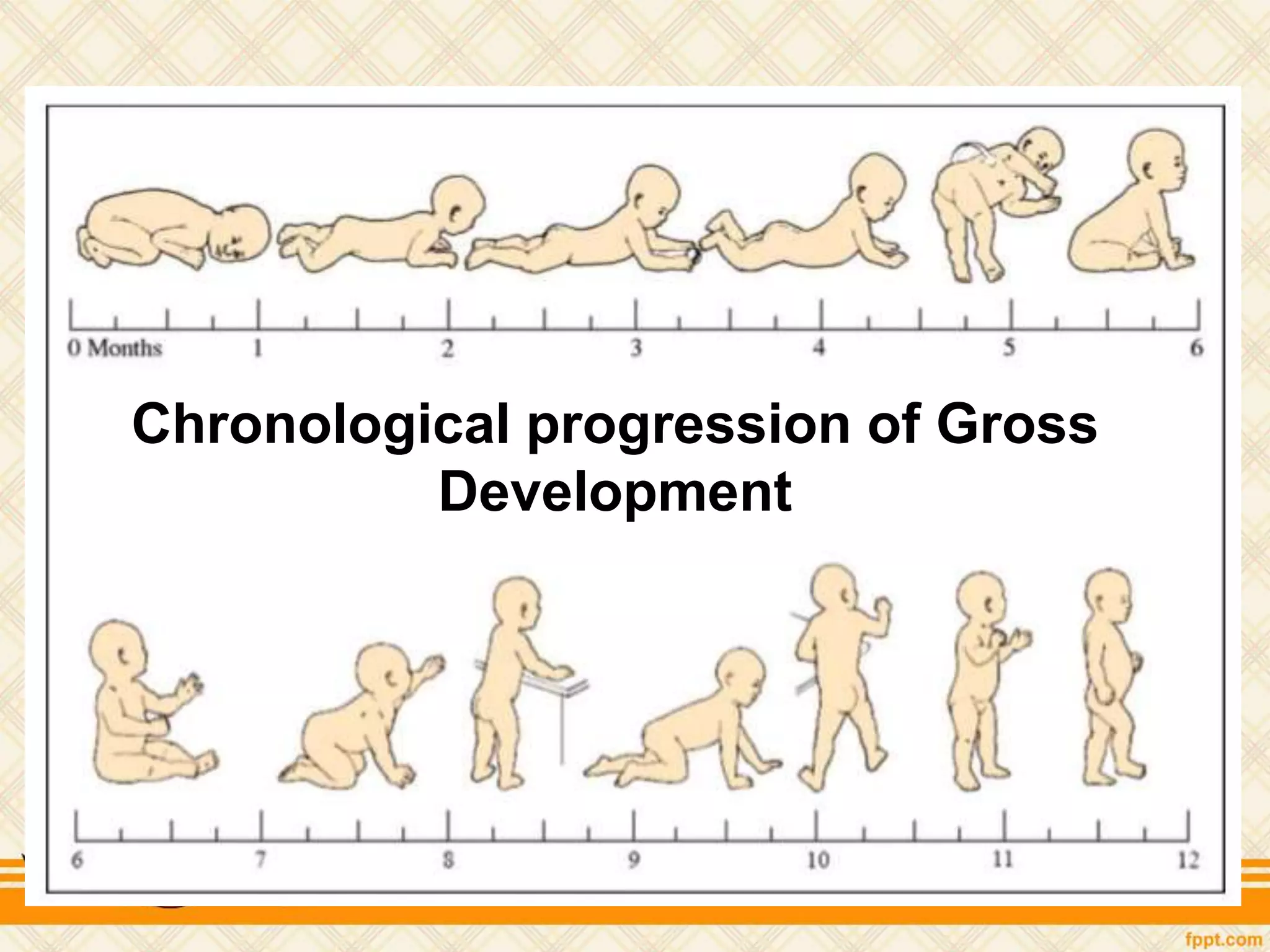
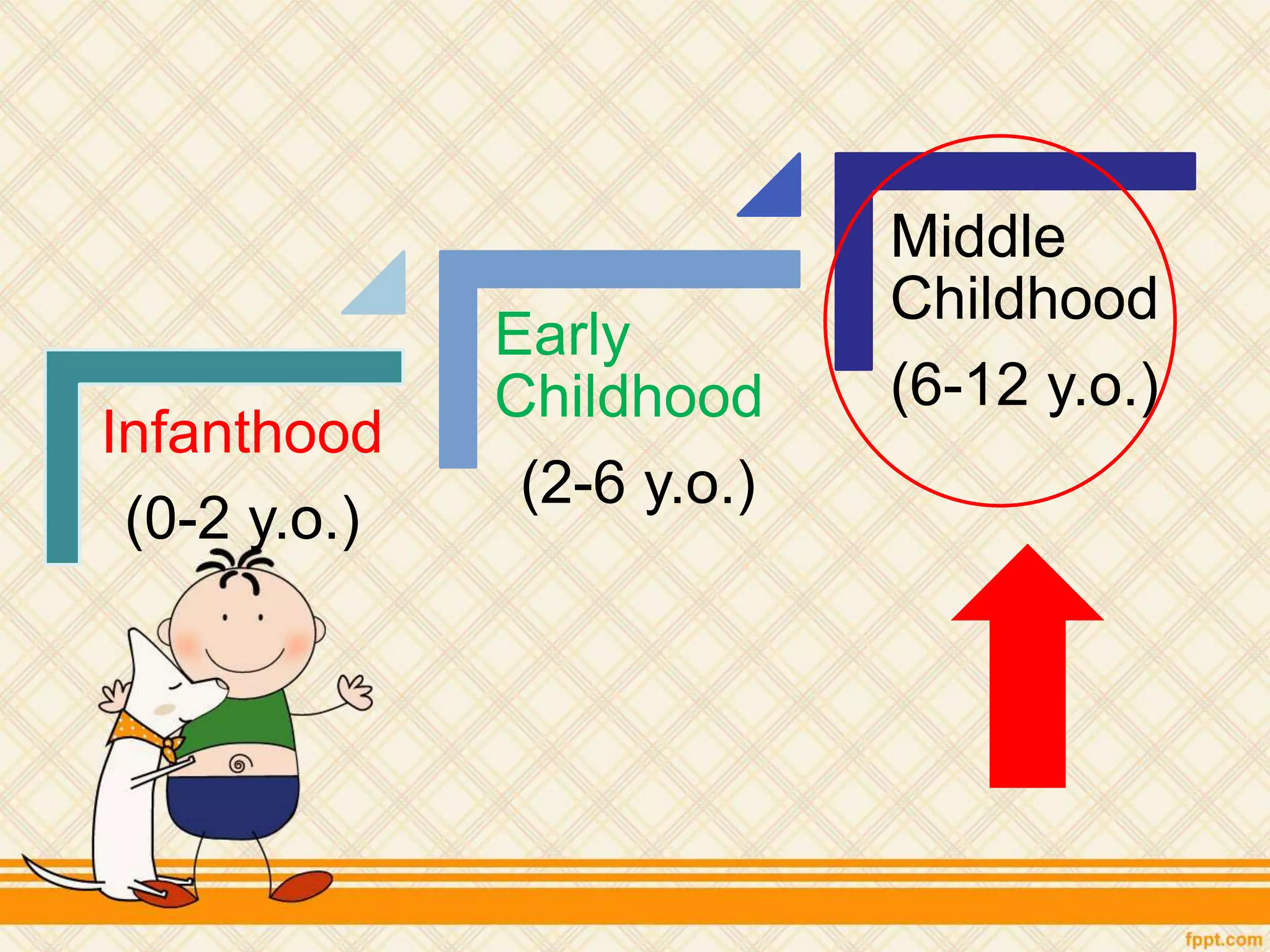
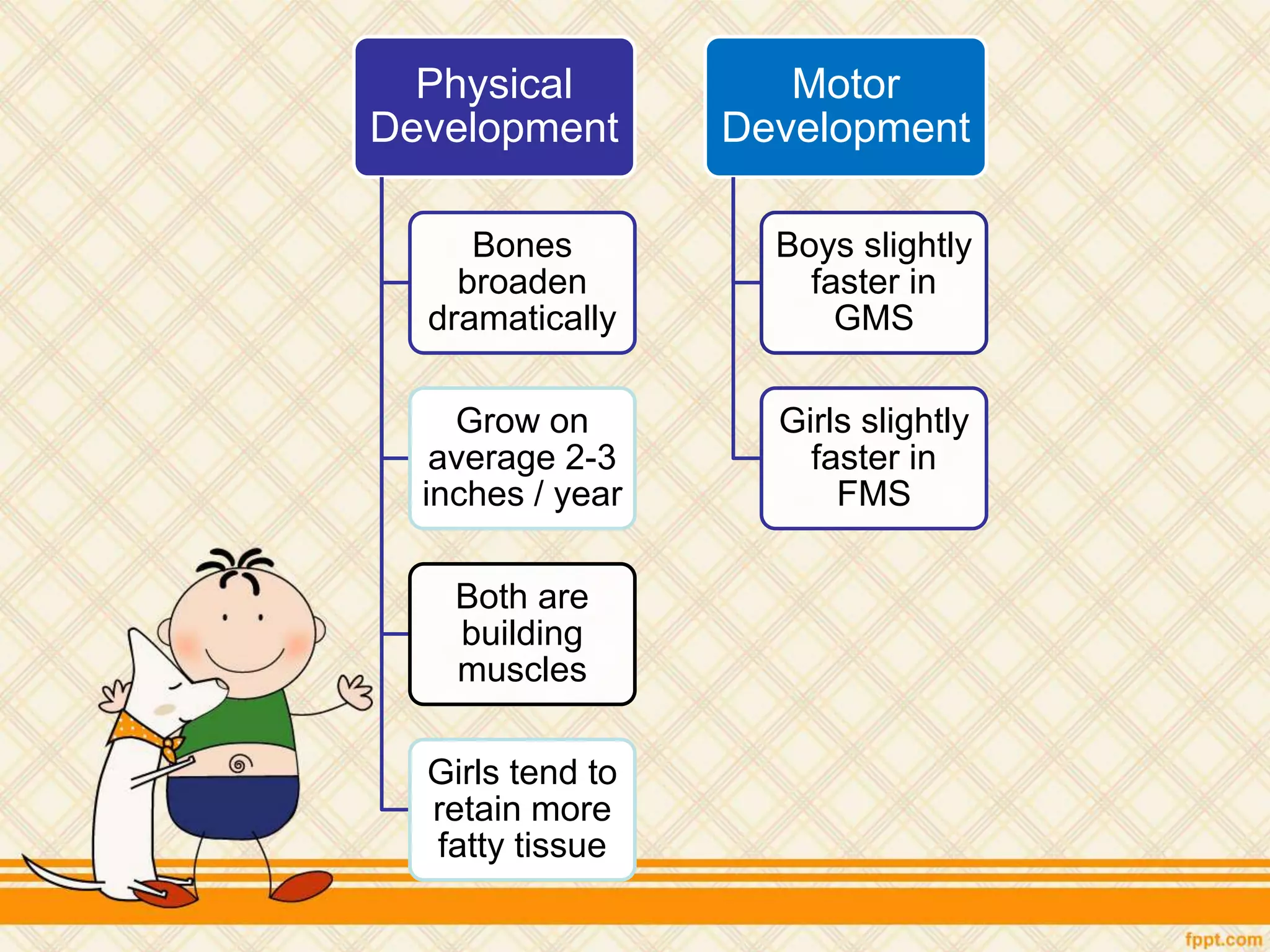
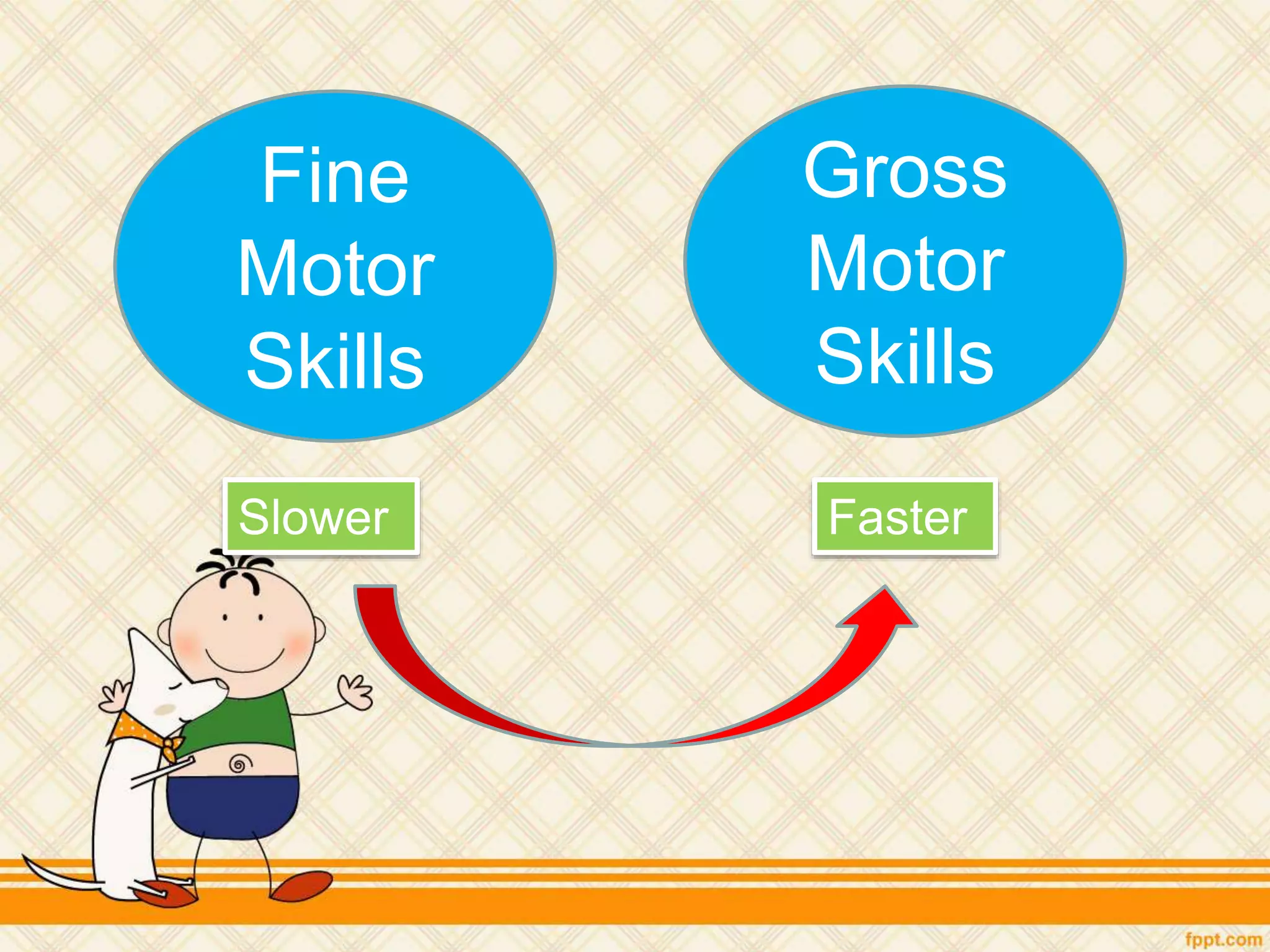
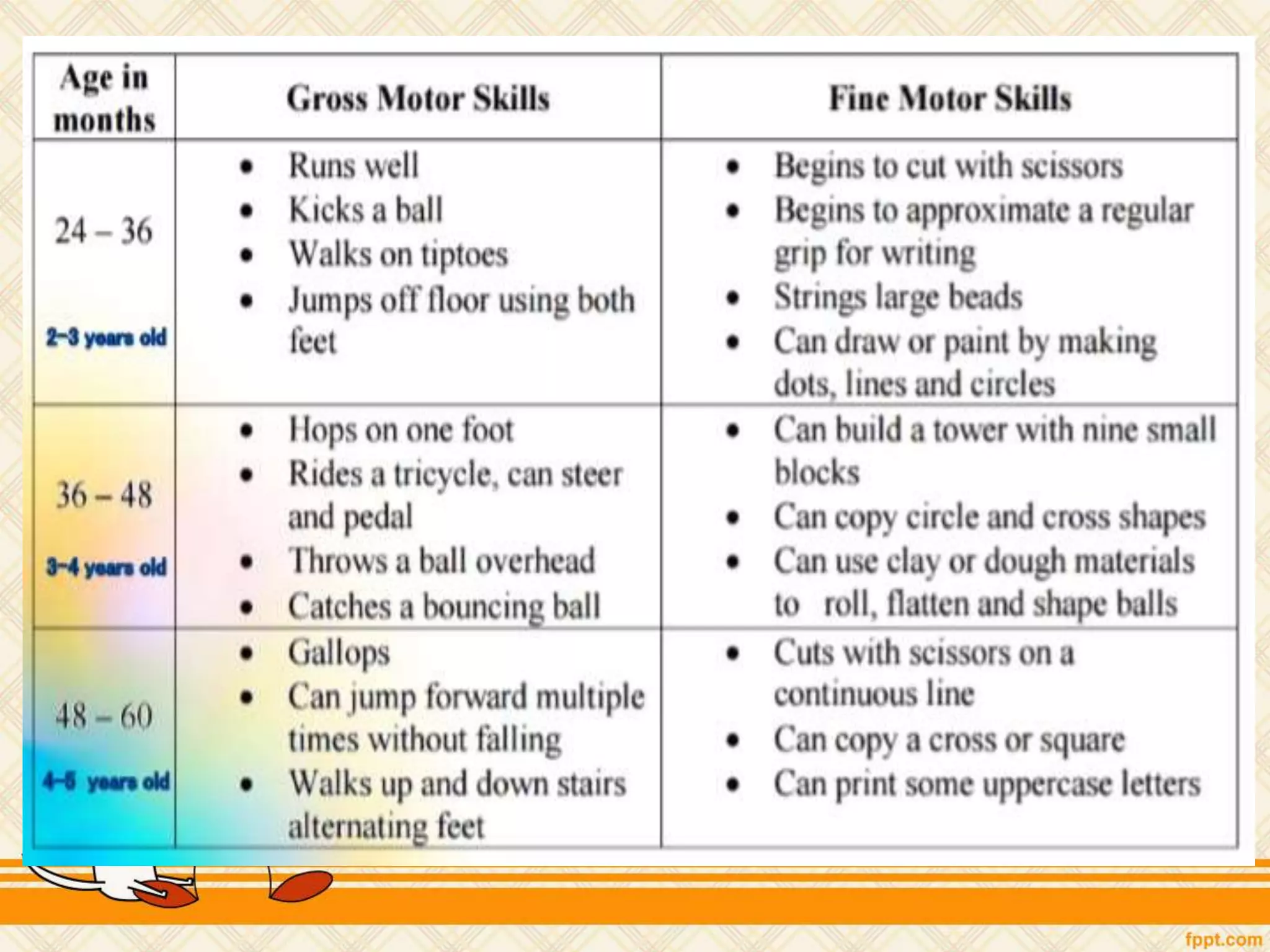
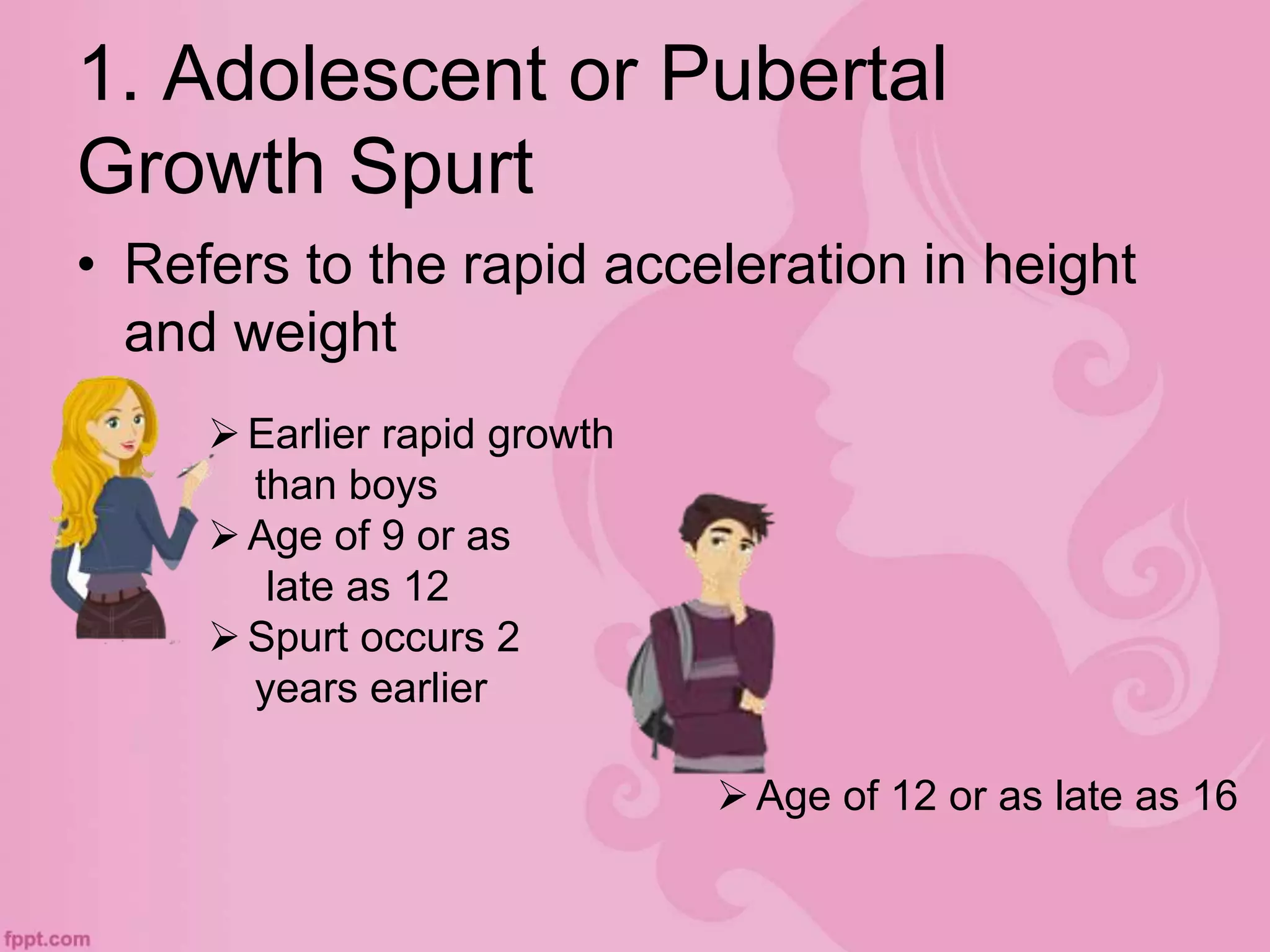
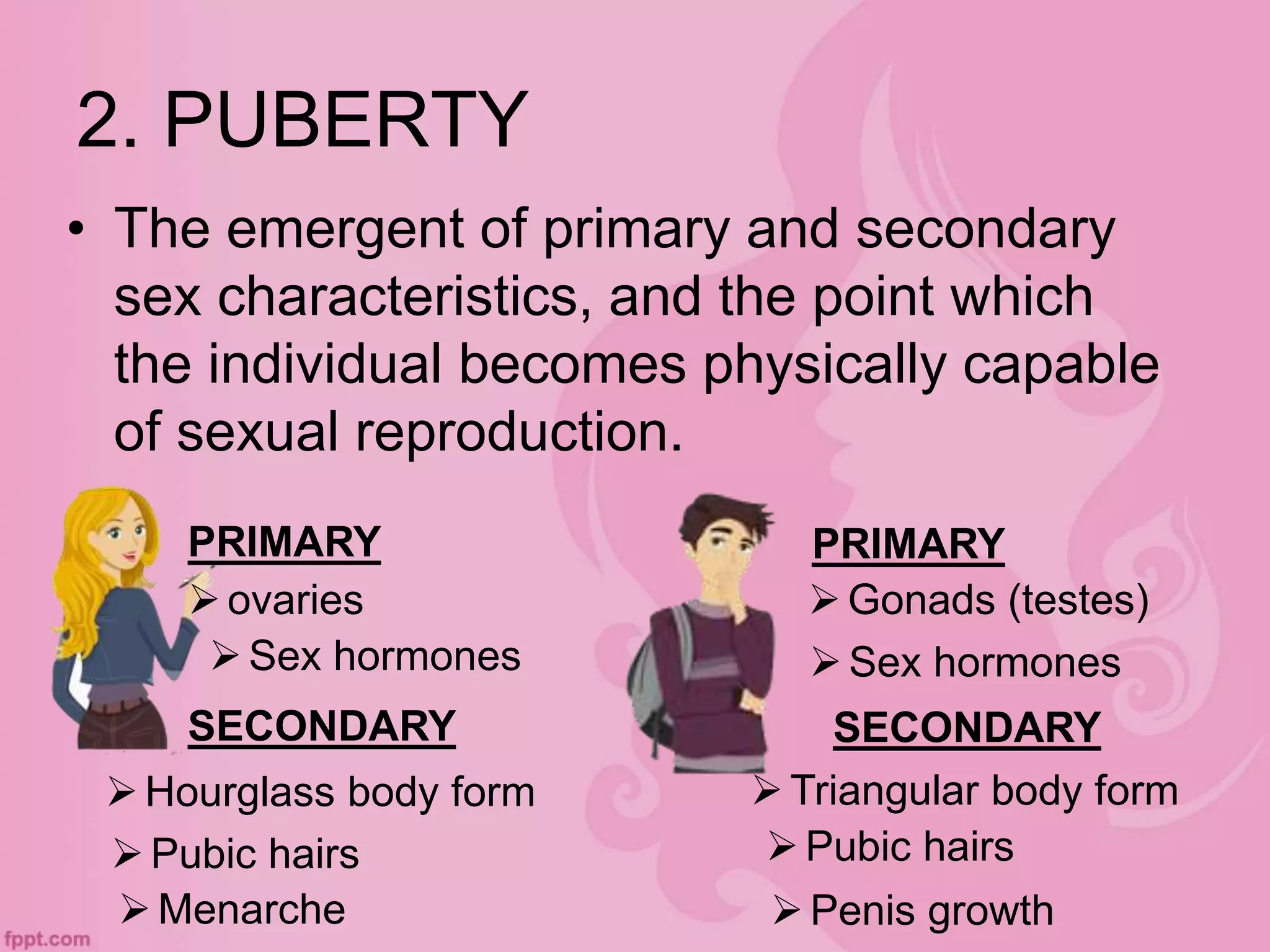
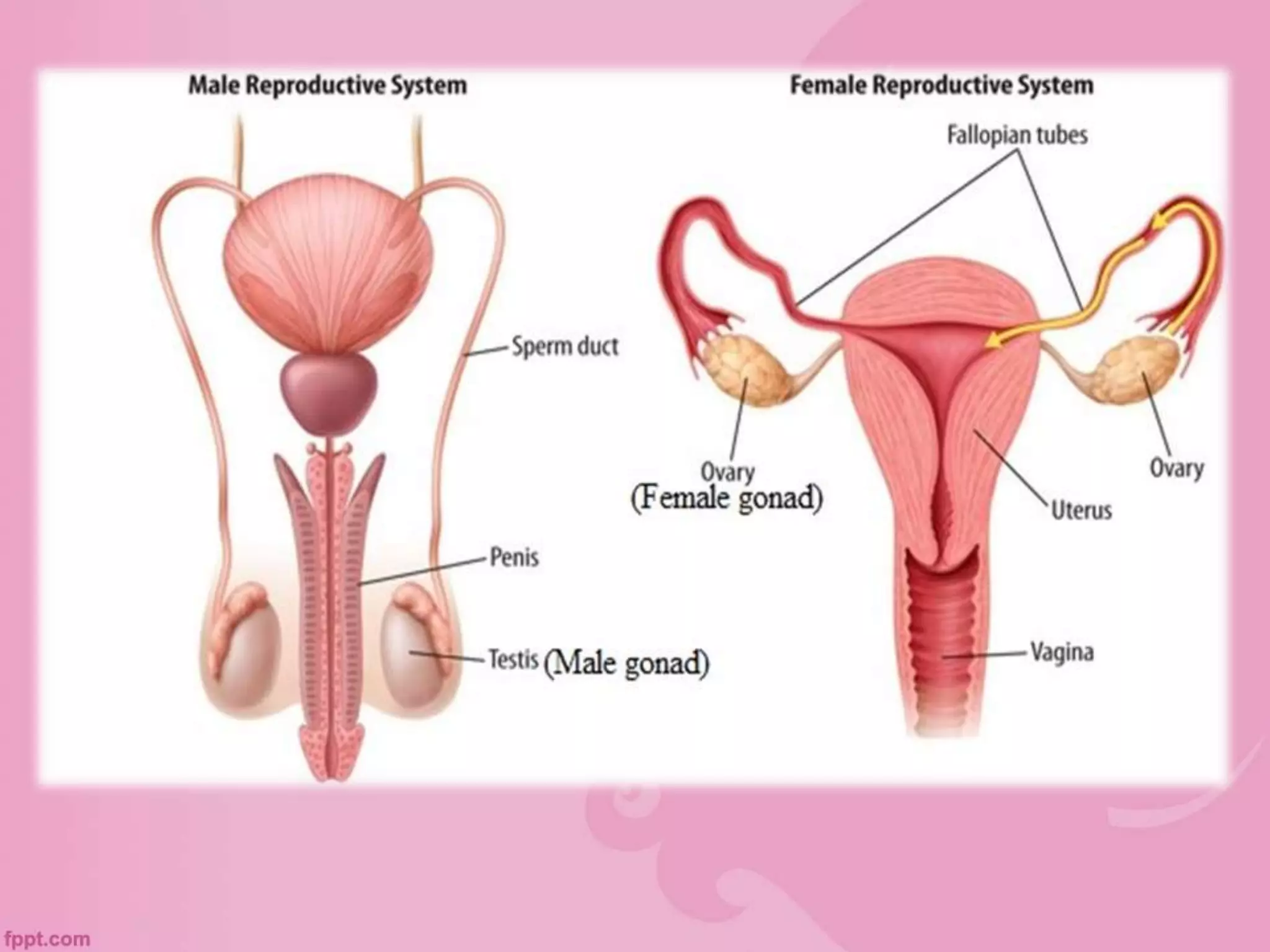
This document discusses physical and motor development in children and adolescents. It defines physical and motor skills and identifies stages of development from infancy to adulthood. During childhood, motor skills develop from large muscle movements to smaller, more refined movements. Fine motor skills involve smaller muscle groups while gross motor skills use larger muscle groups. The document provides examples of activities to develop both fine and gross motor skills. Physical development accelerates during adolescence through growth spurts and the onset of puberty bringing sexual maturity. Overall development follows predictable patterns but individuals vary in their needs and styles at each stage.