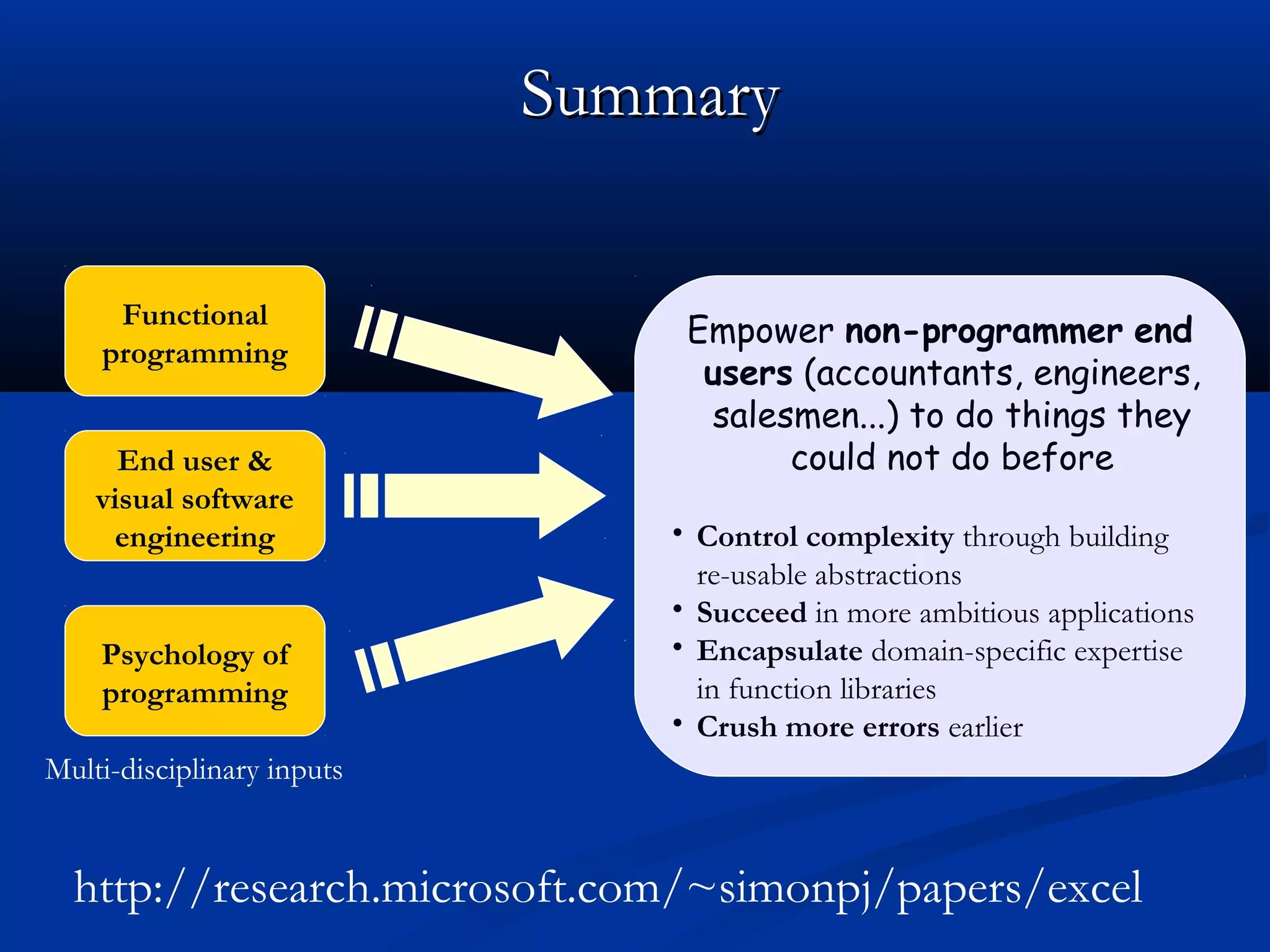
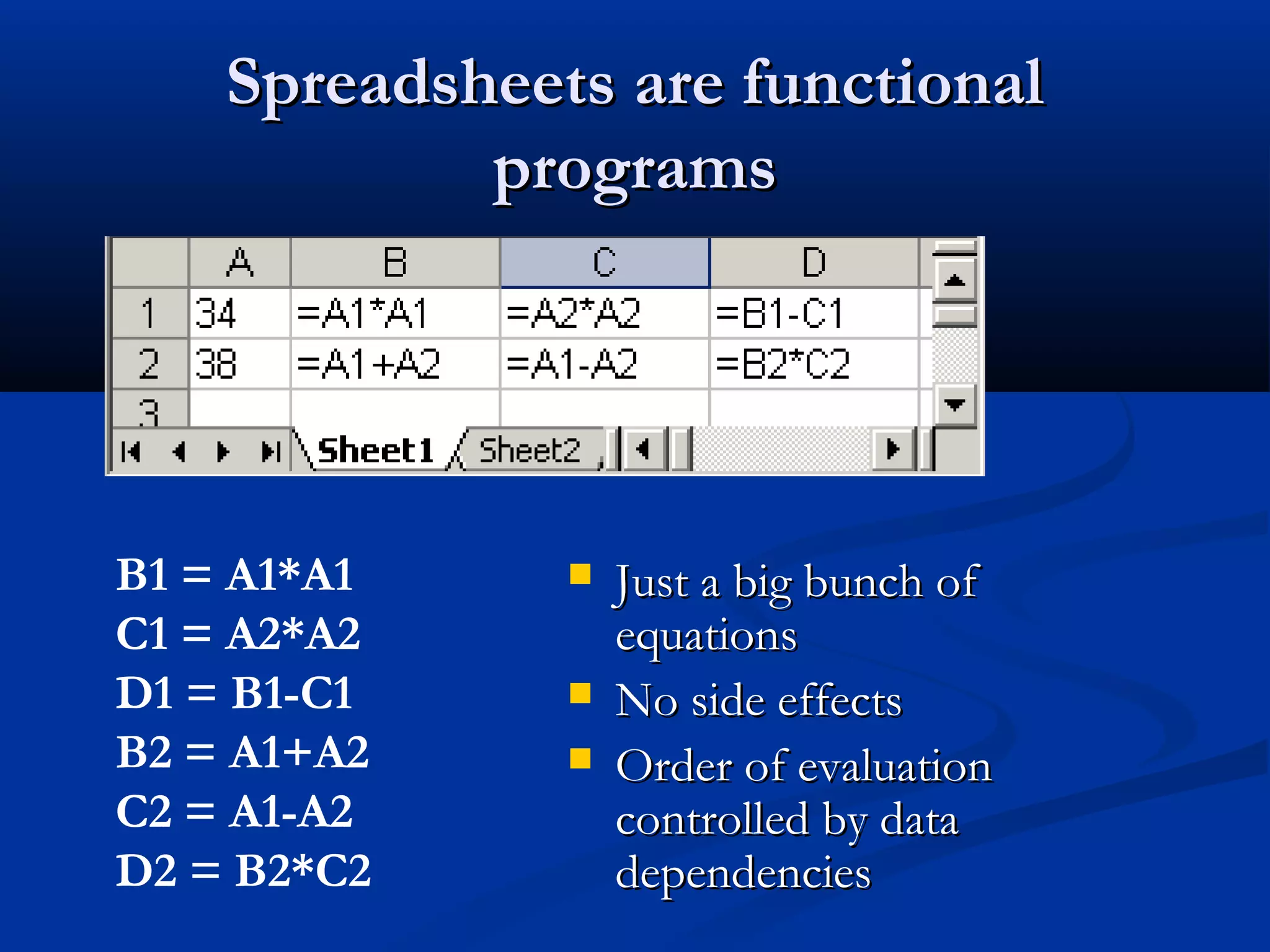
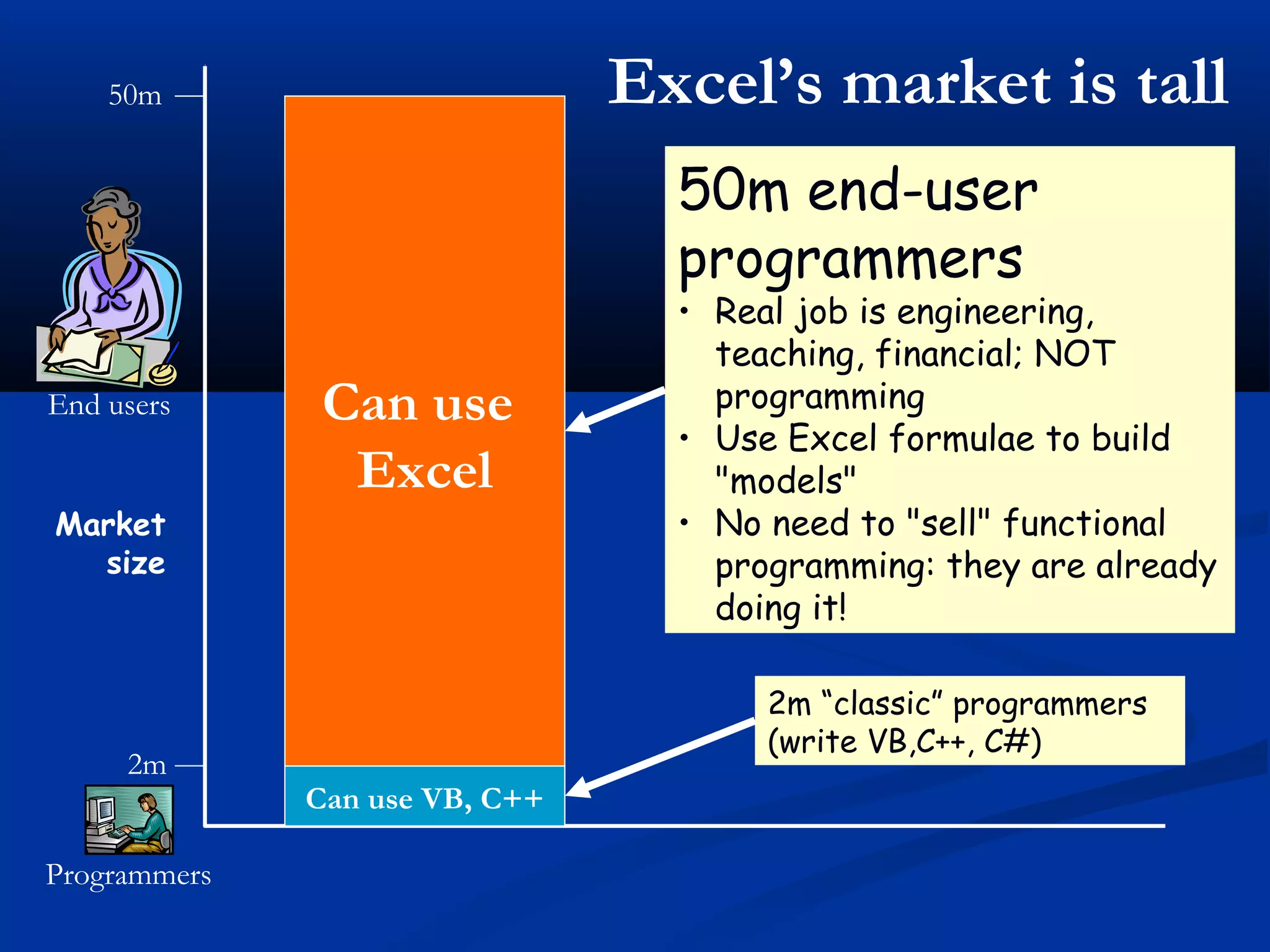
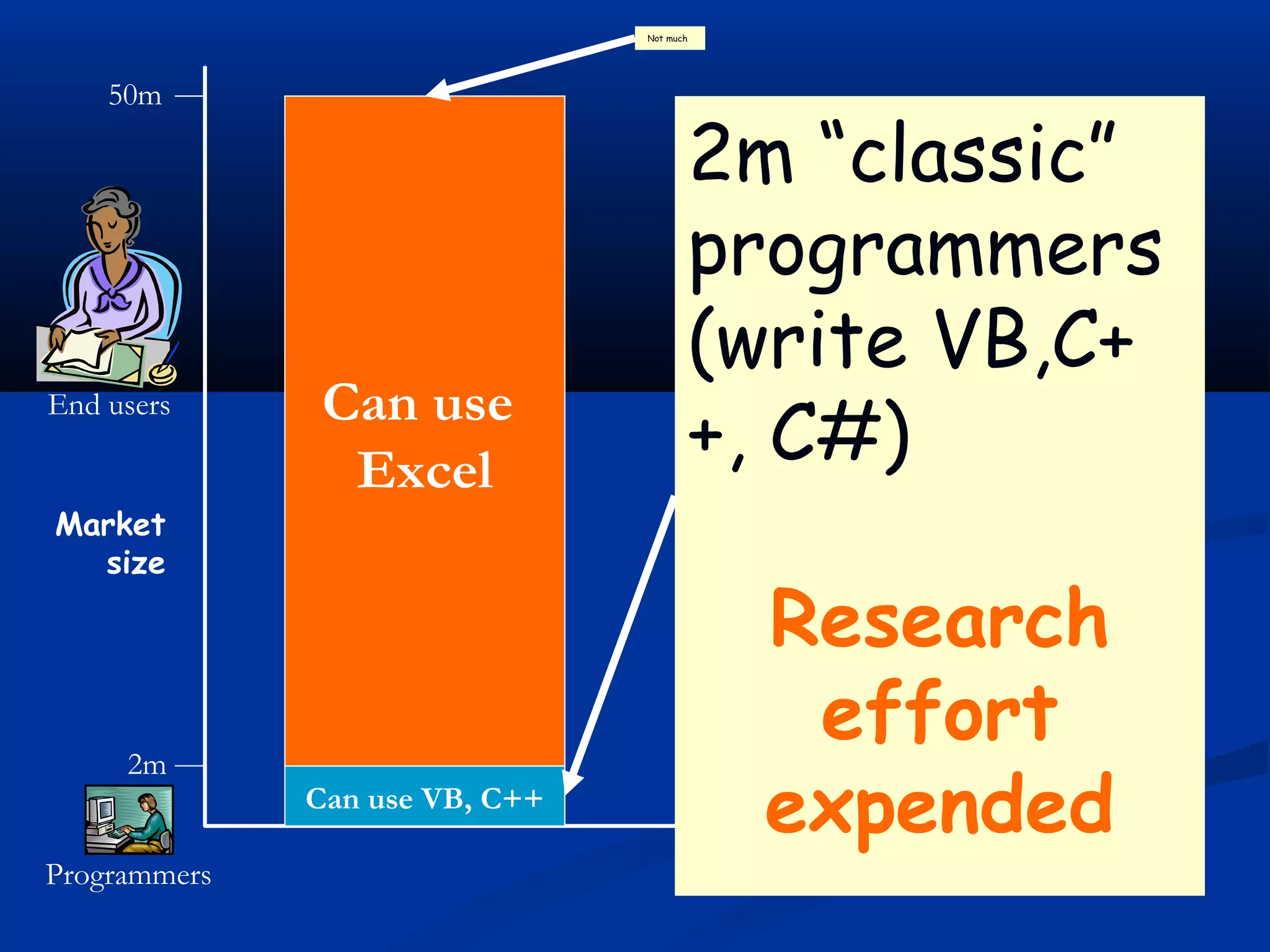
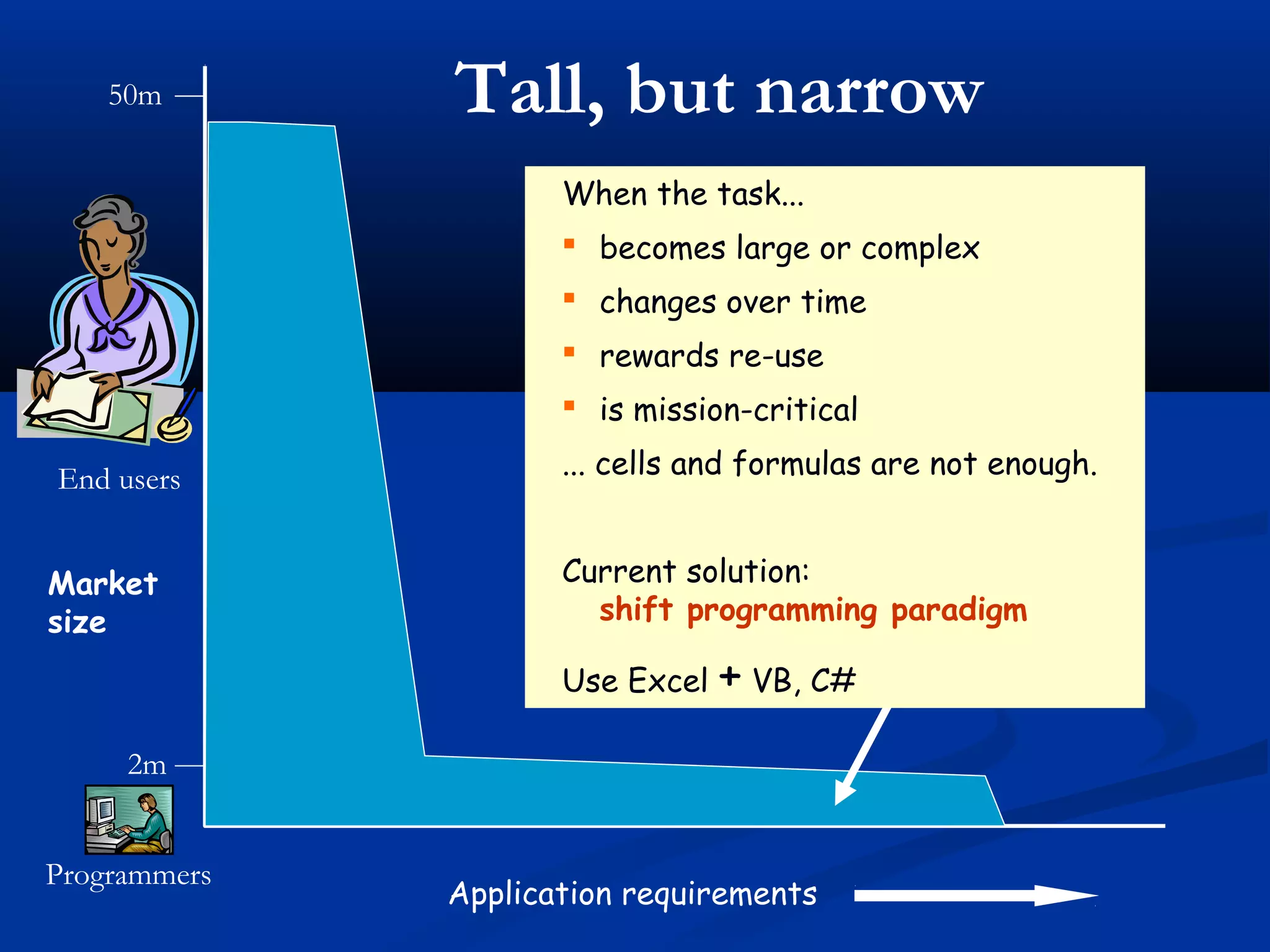
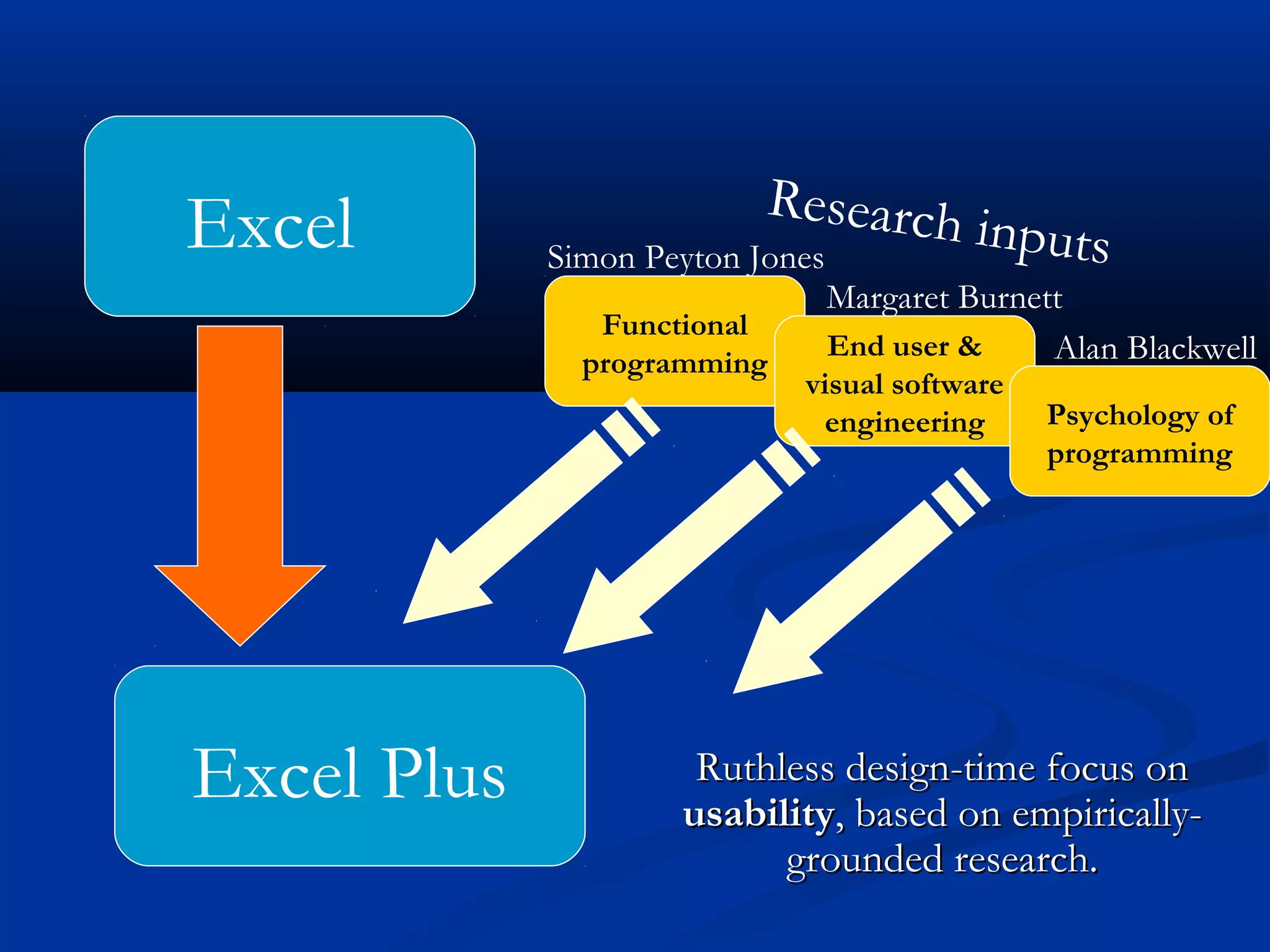
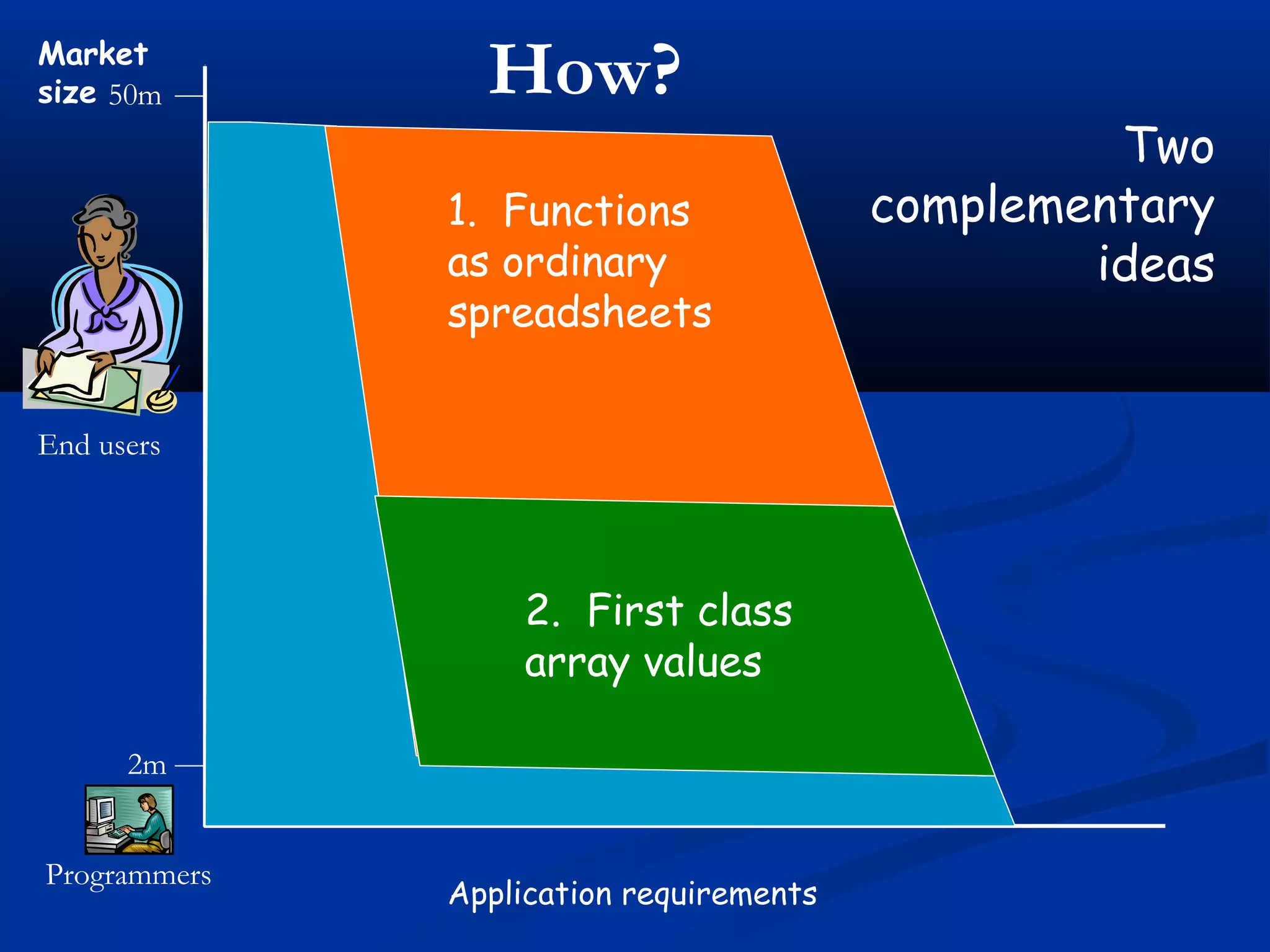
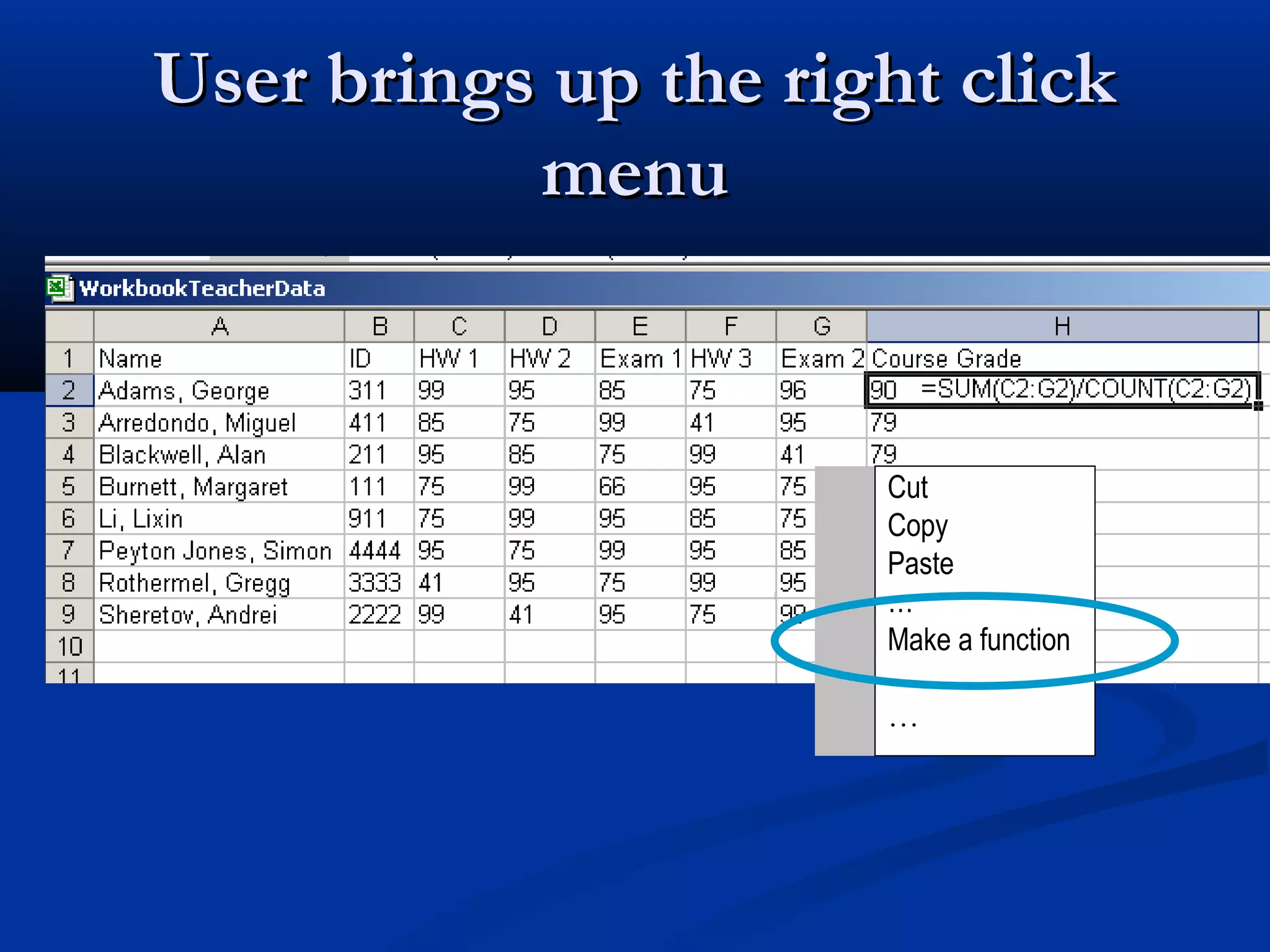
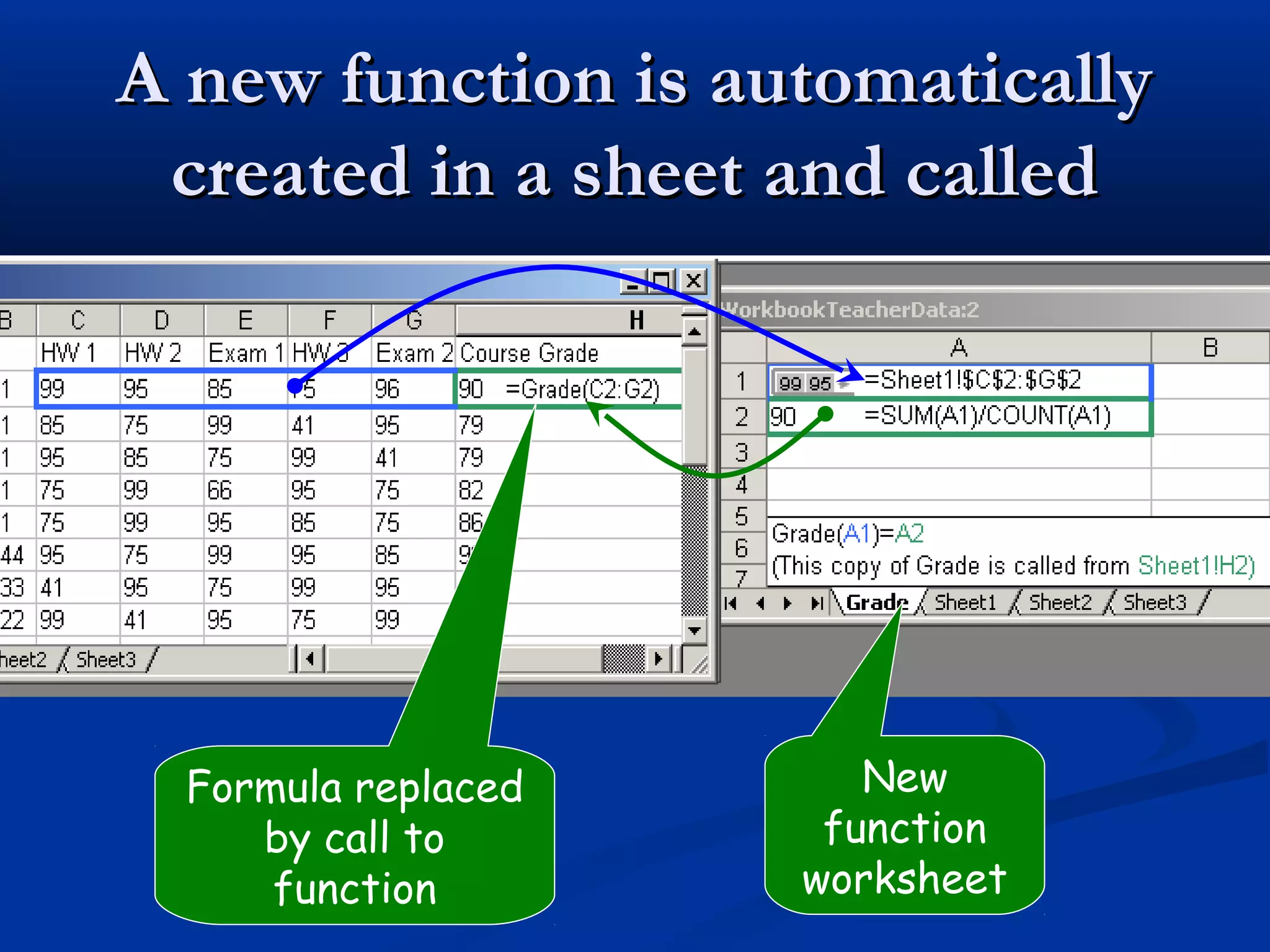
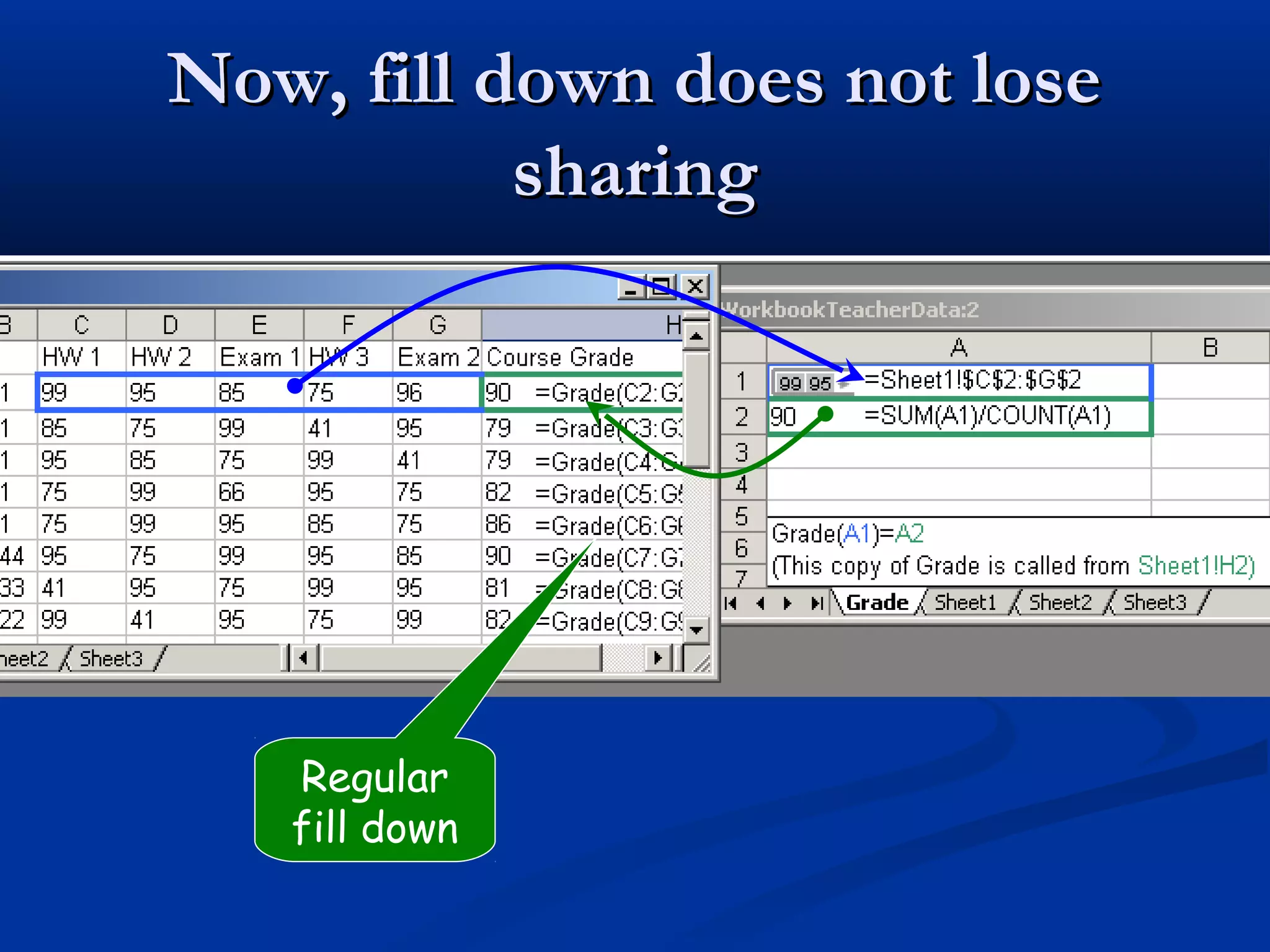
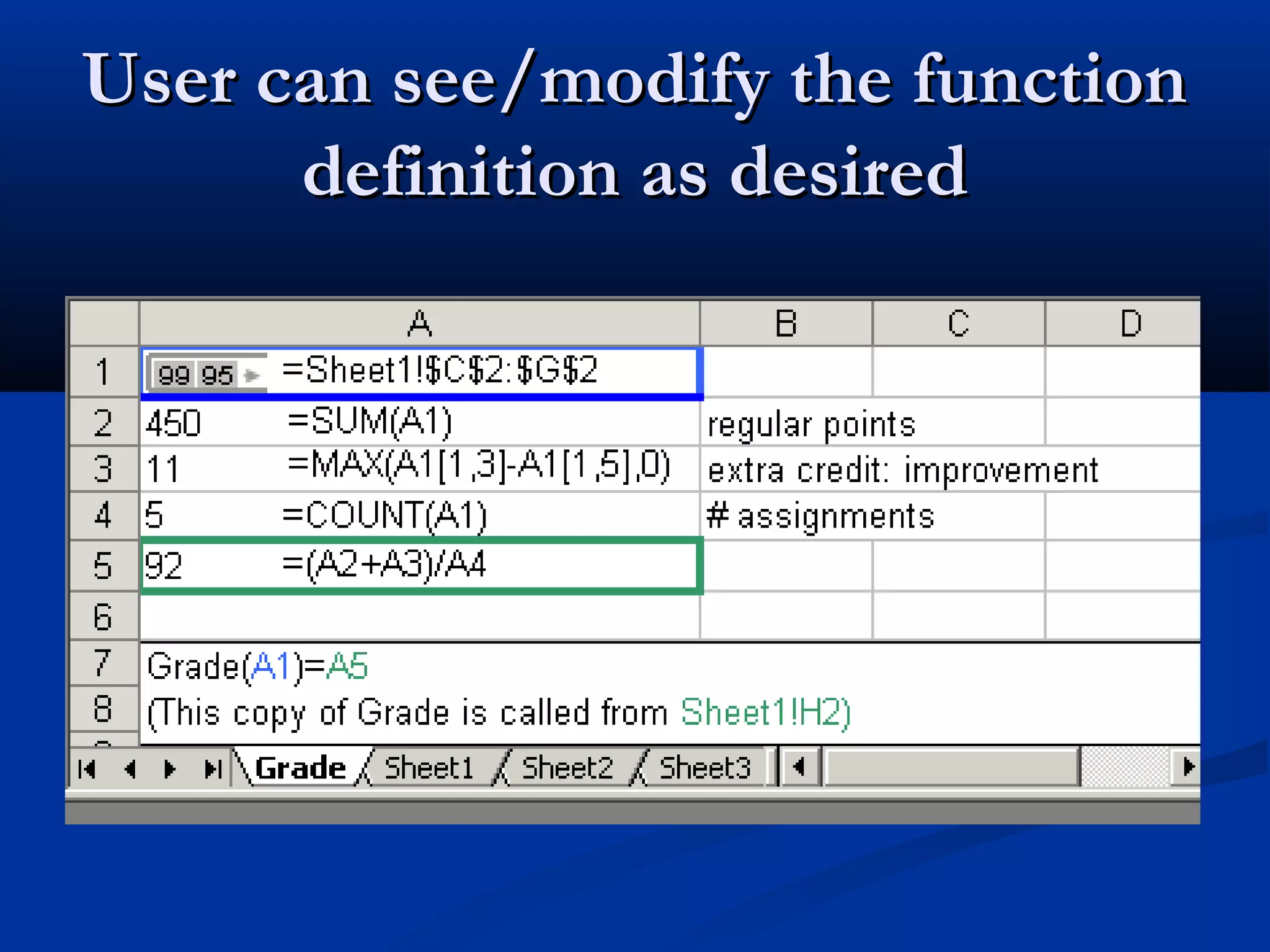
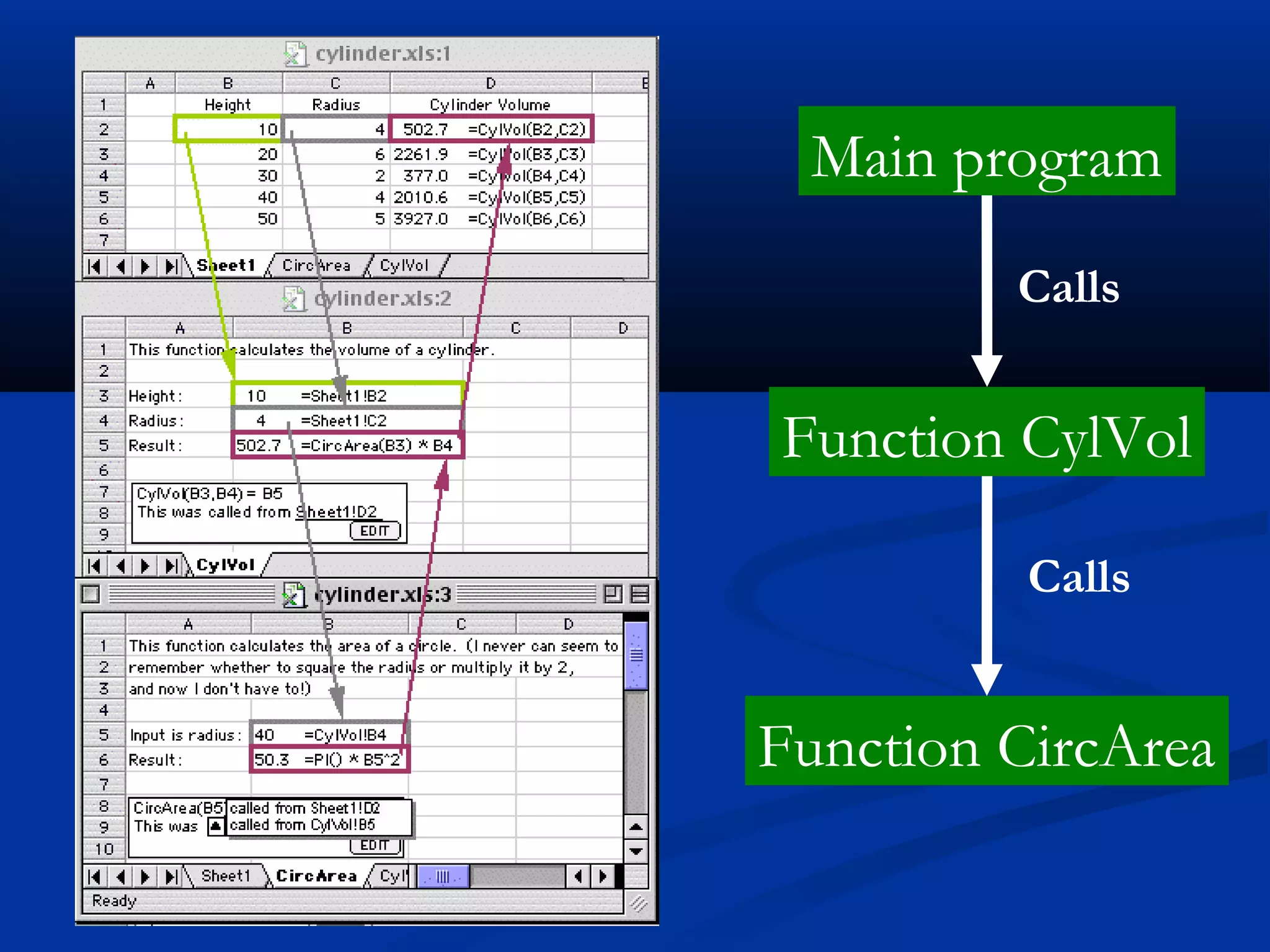
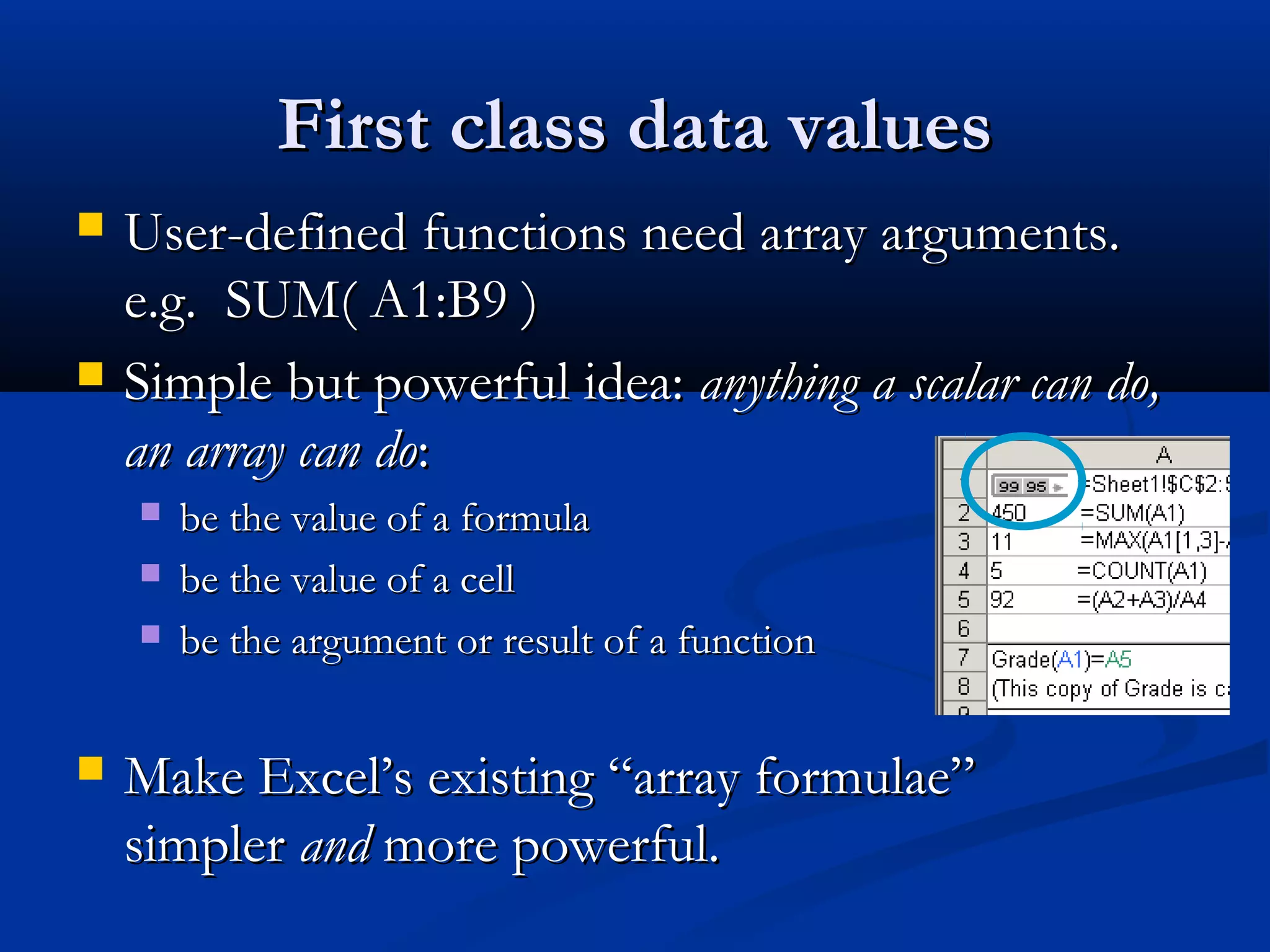
The document discusses bringing functional programming concepts to end users through Microsoft Excel. It proposes two main ideas: 1) Allowing users to define reusable functions like in other languages to reduce complexity and errors, and 2) Treating arrays as first-class values that can be used and returned from functions like scalars. The goal is to empower non-programmer end users to build more complex and robust models without needing to learn new programming paradigms by building on their existing skills in Excel.



















![Bulk data operationsBulk data operations
A1 = …connect to a database relation…A1 = …connect to a database relation…
A2 = EXTEND( A1, [First Name], GetFirst( [Name] ) )A2 = EXTEND( A1, [First Name], GetFirst( [Name] ) )
A3 = EXTEND( A1, [Last Name], GetLast( [Name] ) )A3 = EXTEND( A1, [Last Name], GetLast( [Name] ) )
A4 = FILTER( A3, AND( [Age] > 30, [Age] < 50 ) )A4 = FILTER( A3, AND( [Age] > 30, [Age] < 50 ) )
A5 = SELECT( A4, [First Name], [Last Name], [Age] )A5 = SELECT( A4, [First Name], [Last Name], [Age] )
This stuff can be done today, by hand (e.g.
Data/AutoFilter), but it can’t be automated
robustly](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/peytonjones-140510213628-phpapp01/75/Spreadsheets-Functional-Programming-for-the-Masses-33-2048.jpg)