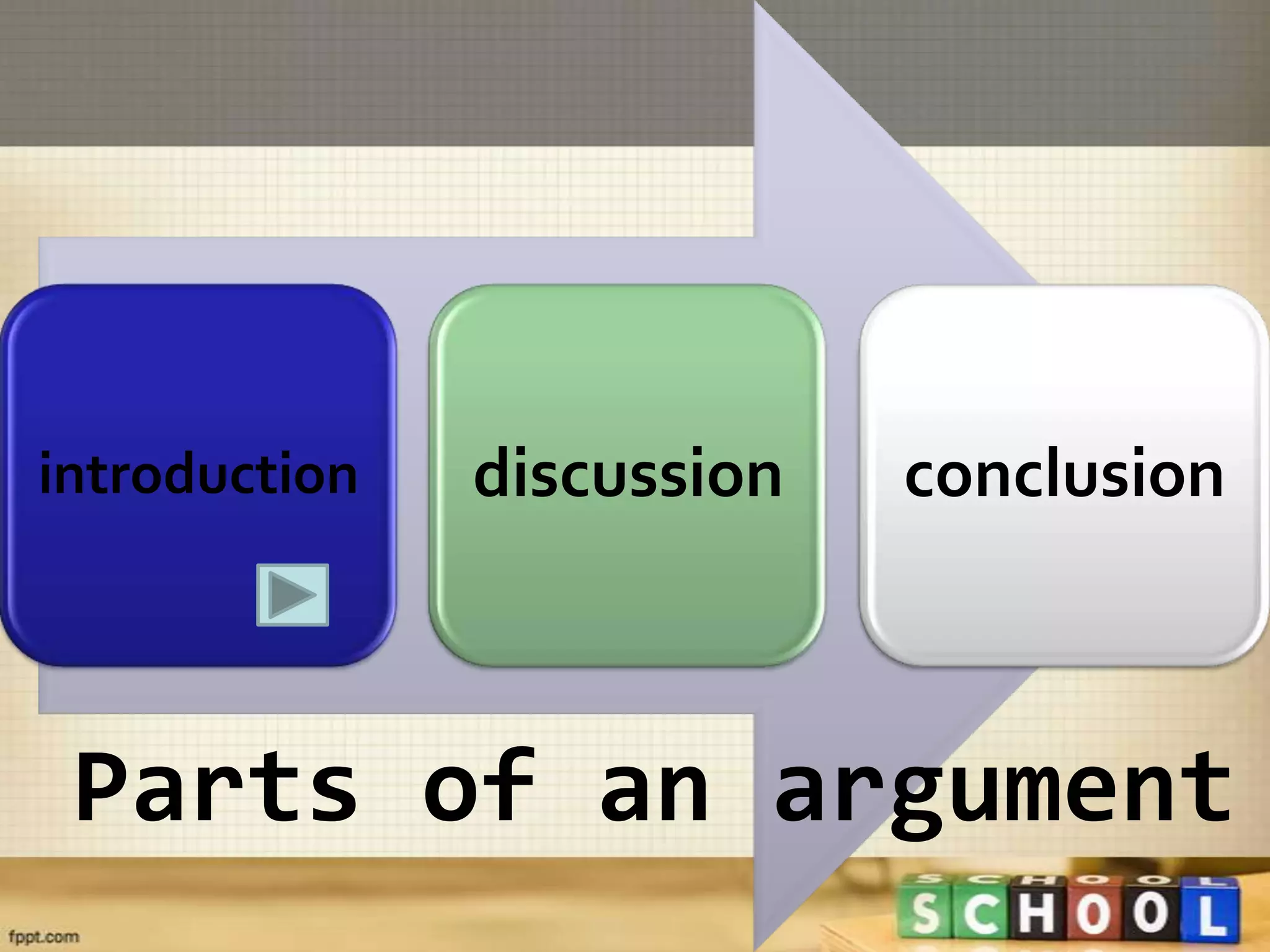
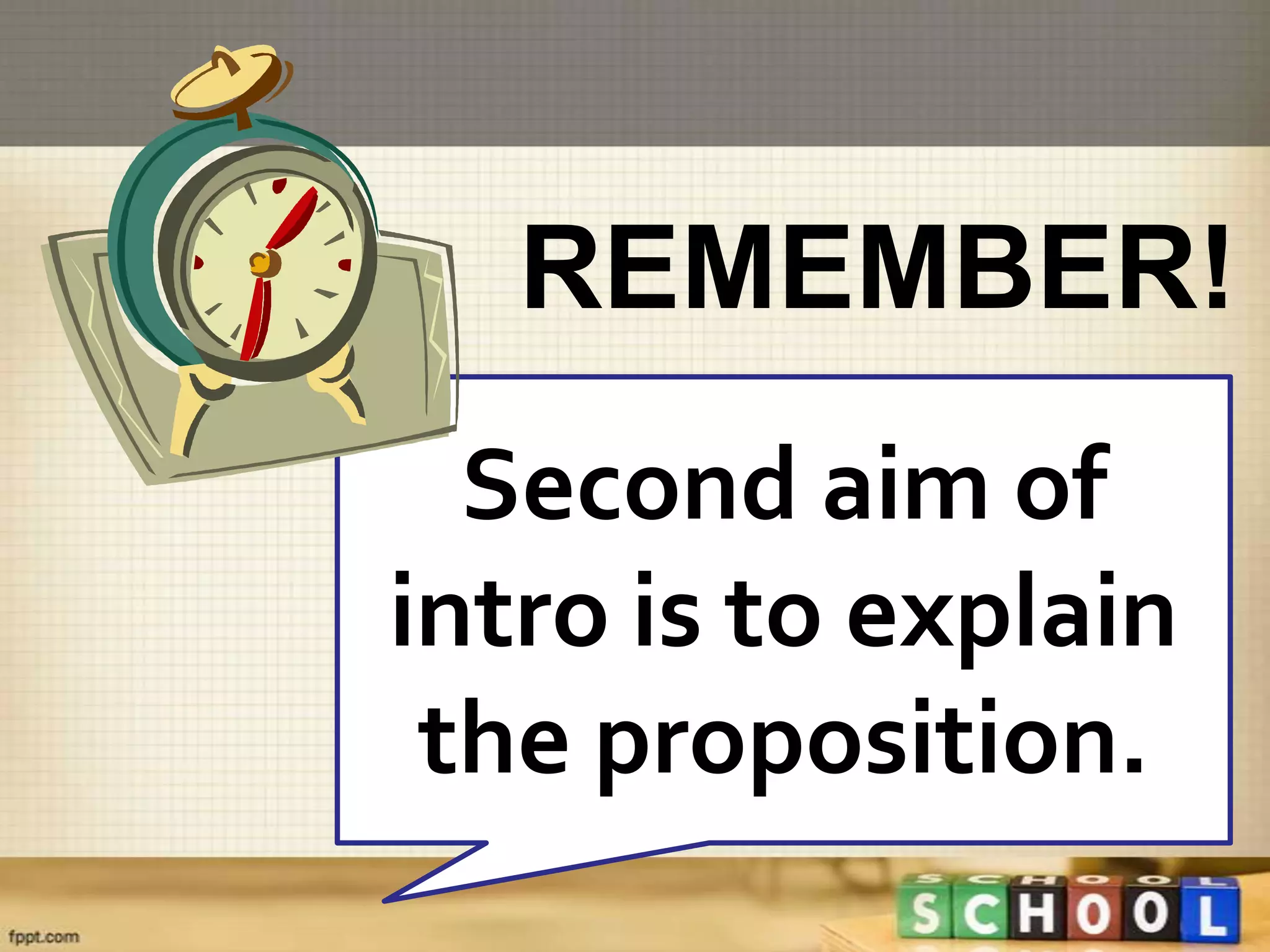
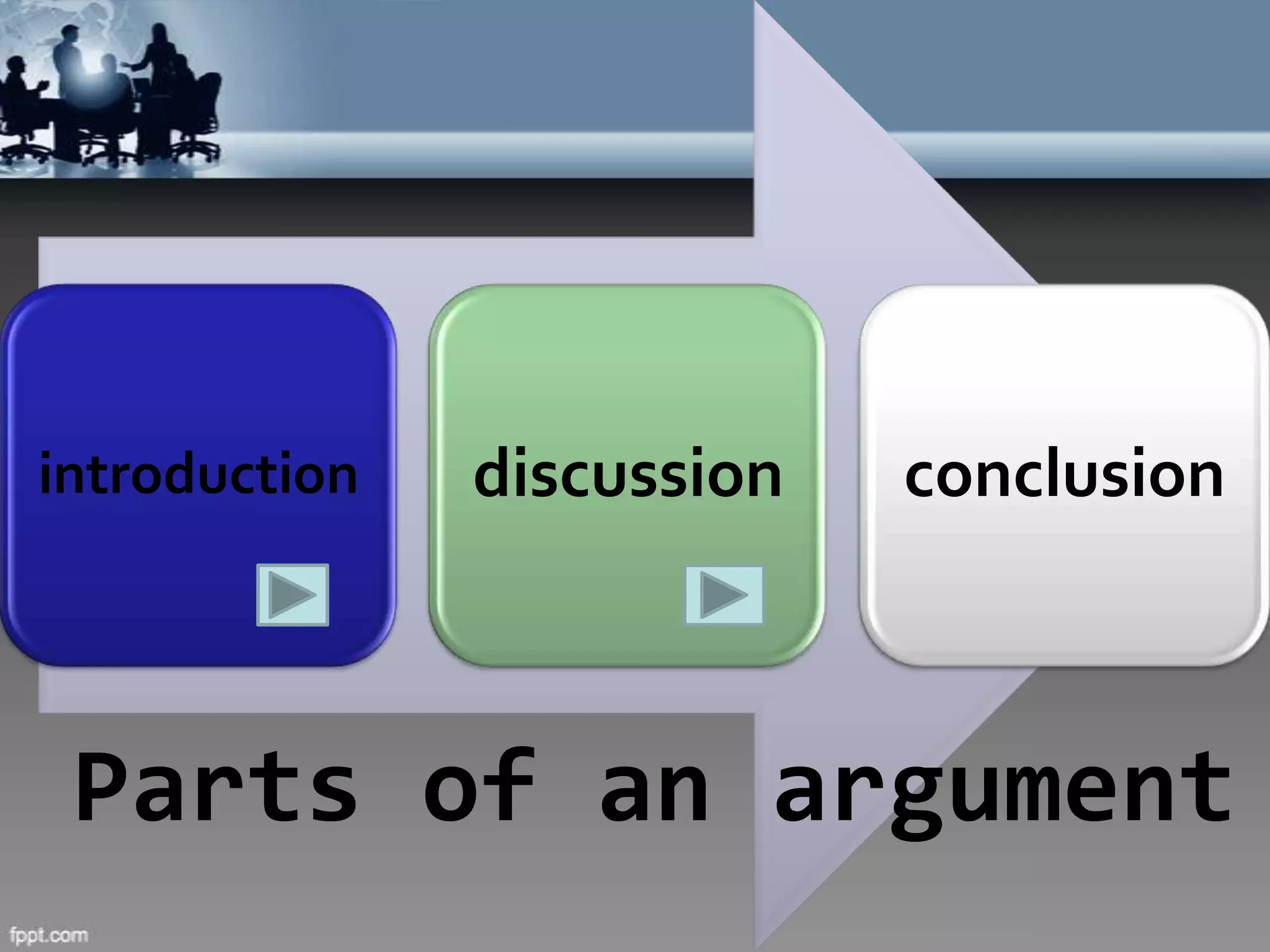
This document provides information about formal debate structure and processes. It discusses the key parts of an argument including the introduction, discussion, and conclusion. The introduction aims to arouse audience interest, explain the proposition, and state the issues being debated. The discussion includes the opposing affirmative and negative sides addressing the necessity, beneficiality, and practicability of the proposition. The conclusion summarizes each team's arguments and defenses. It also outlines the speaker roles and speech formats for the 1A, 1N, 2A, 2N, and 3A, 3N speakers.