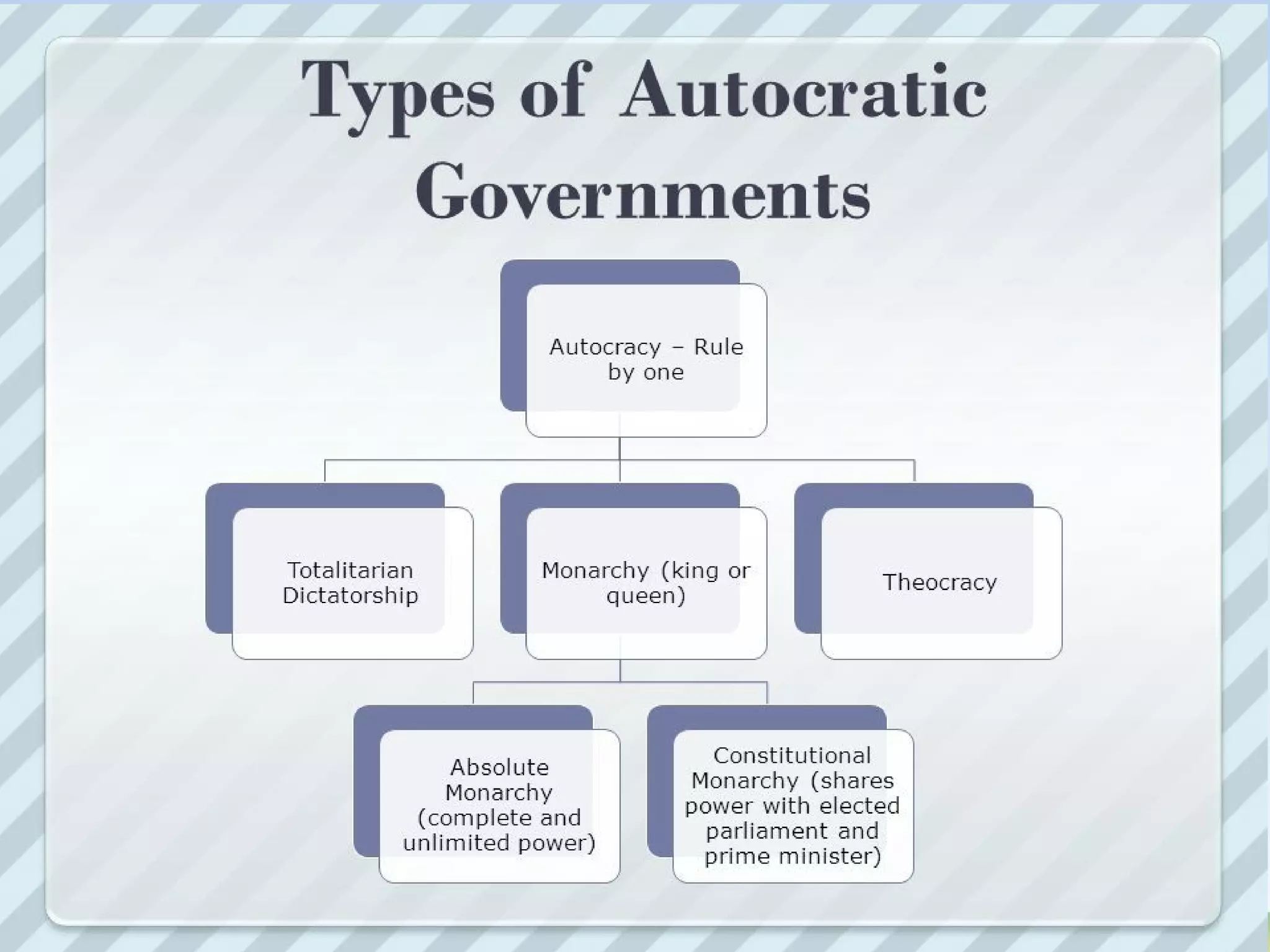
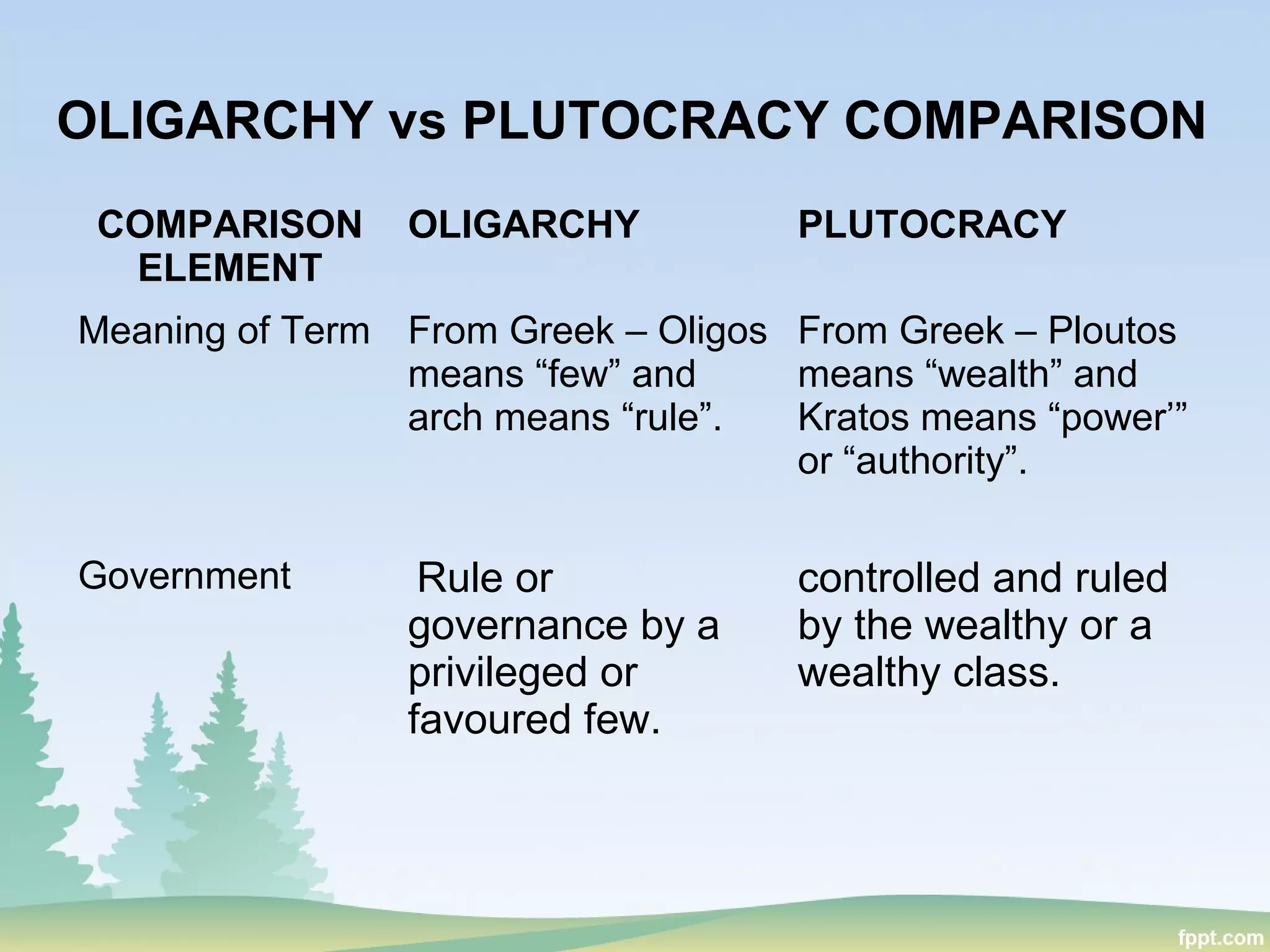
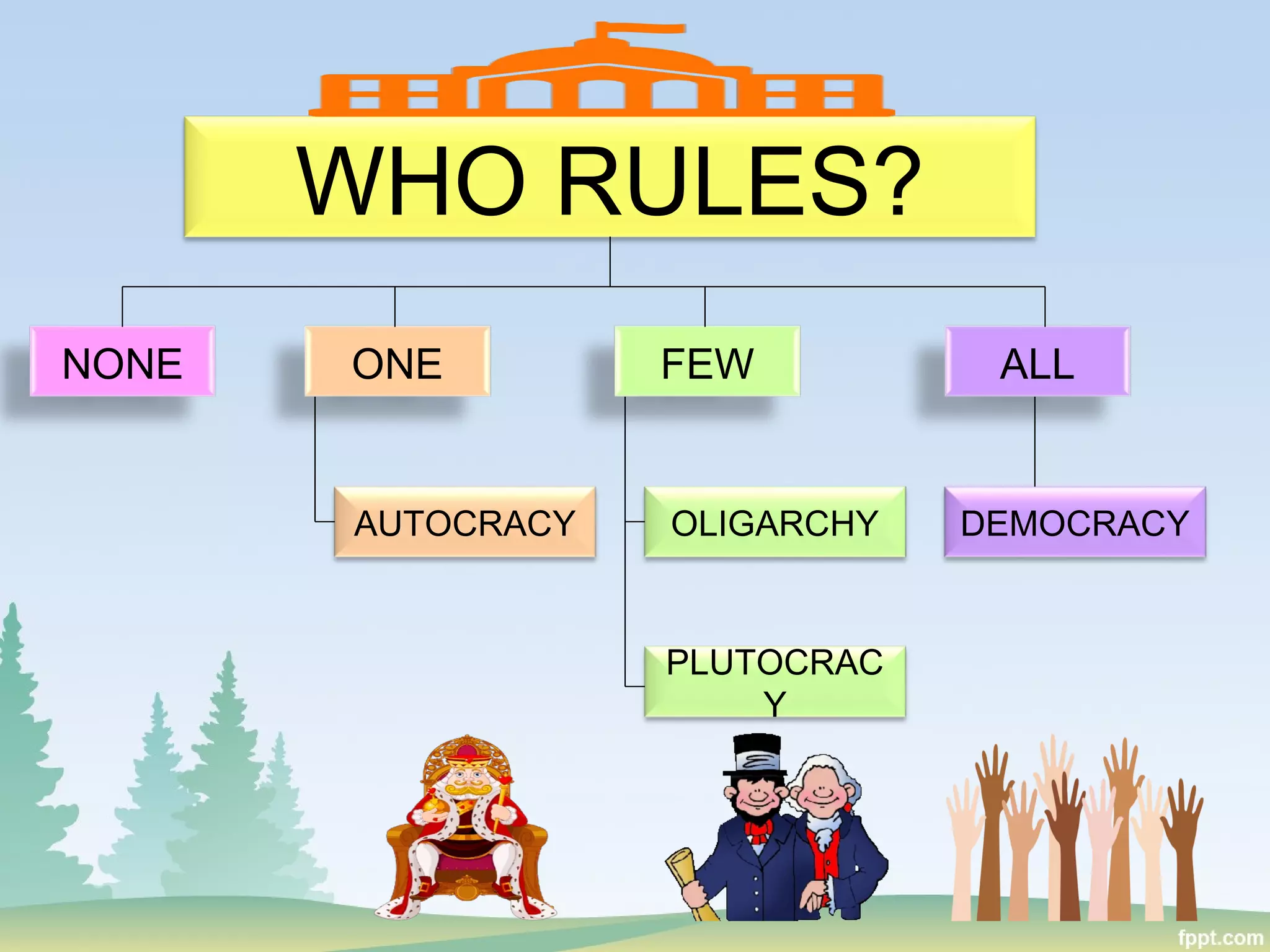
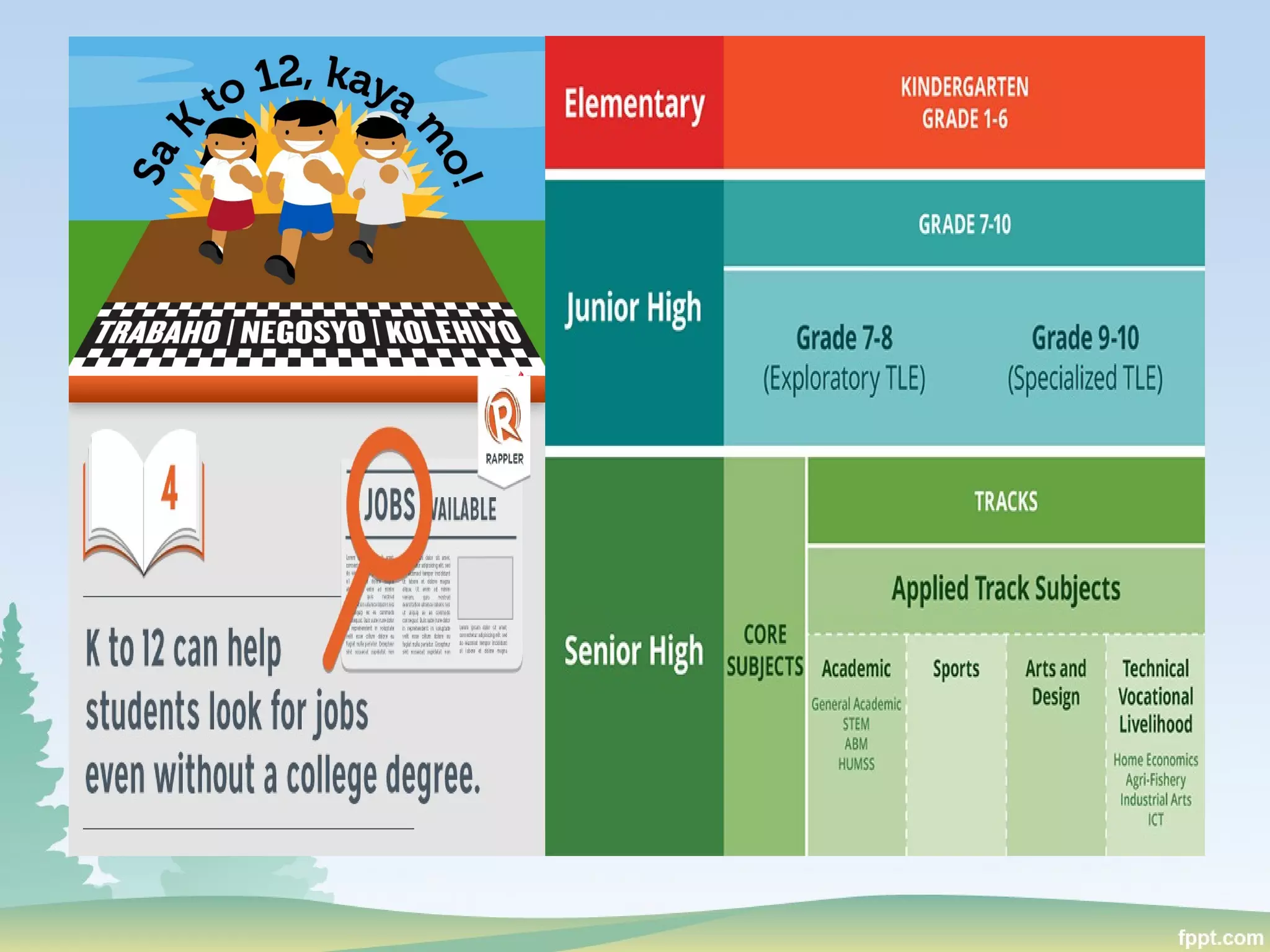
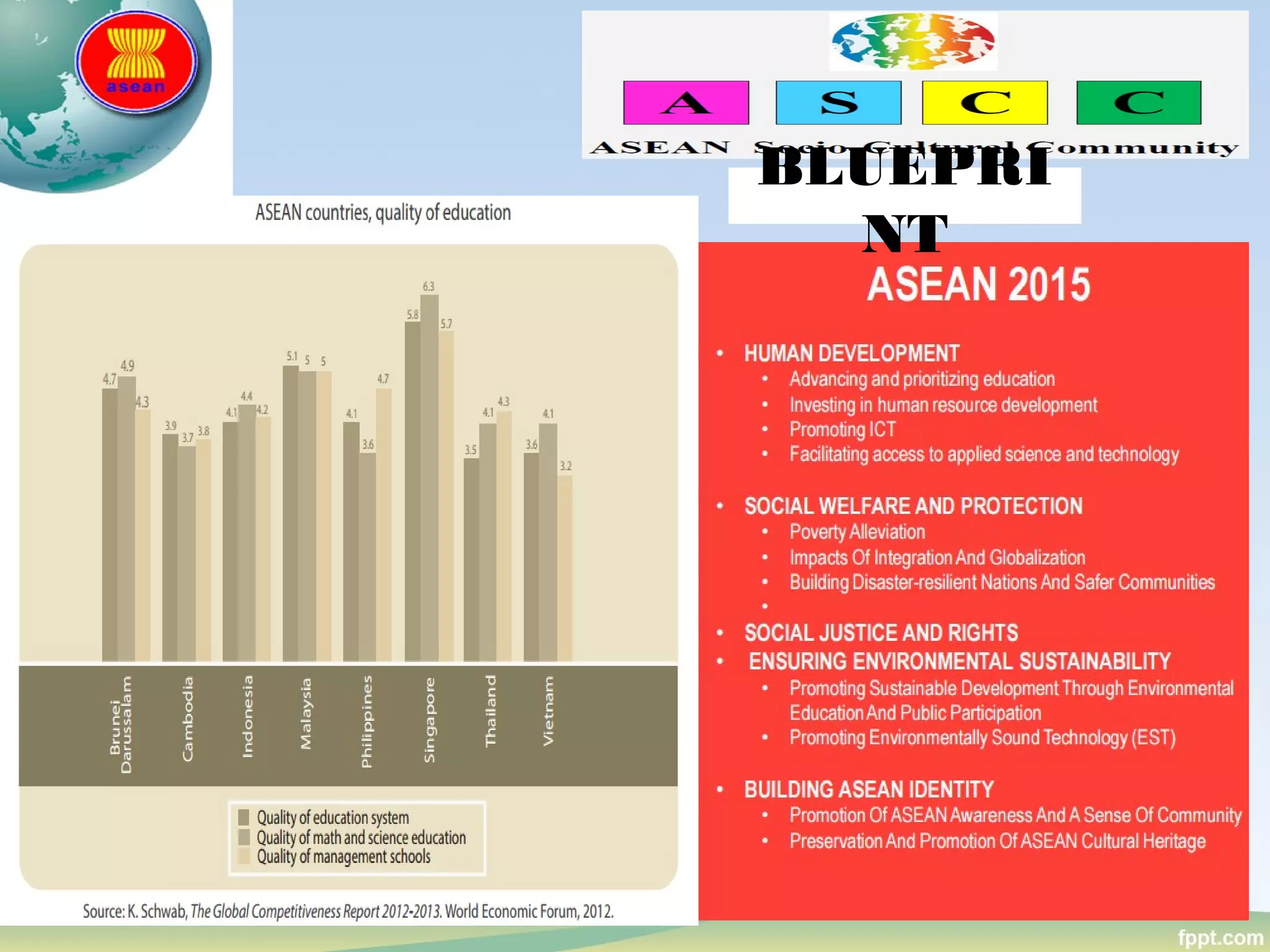
This document discusses politics and education in the Philippines. It begins by defining different types of governments - autocracy, oligarchy, democracy - and comparing autocracy and democracy. Next, it defines and compares oligarchy and plutocracy. It then discusses examples of plutocrats in the Philippines. The roles of key education institutions in the Philippines are outlined, including the Department of Education, Technical Education and Skills Development Authority, and Commission on Higher Education. It concludes by discussing the roles of higher education in the Philippines and the higher education reform agenda, focusing on excellence, capacity, access, and ethical governance.