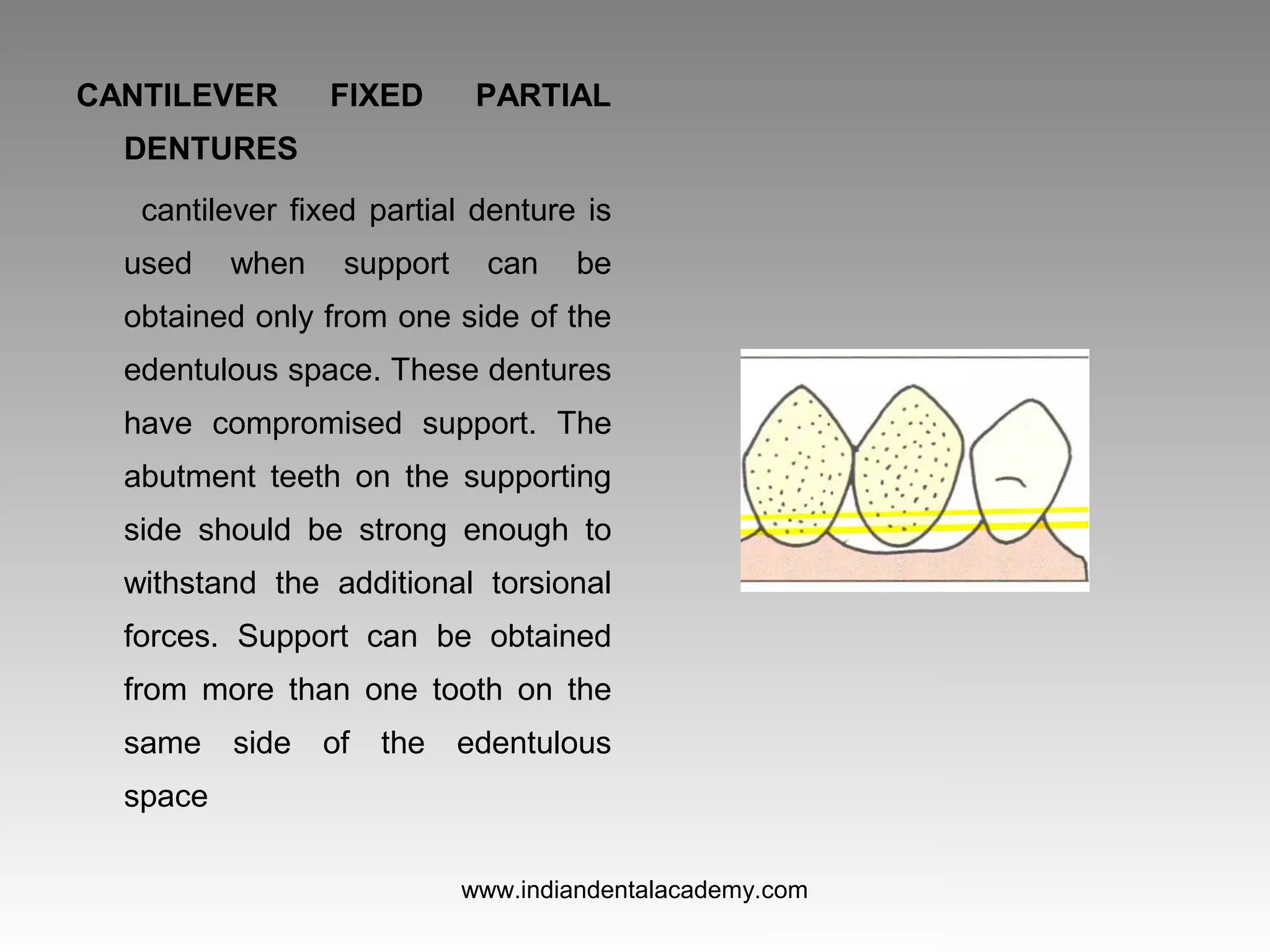
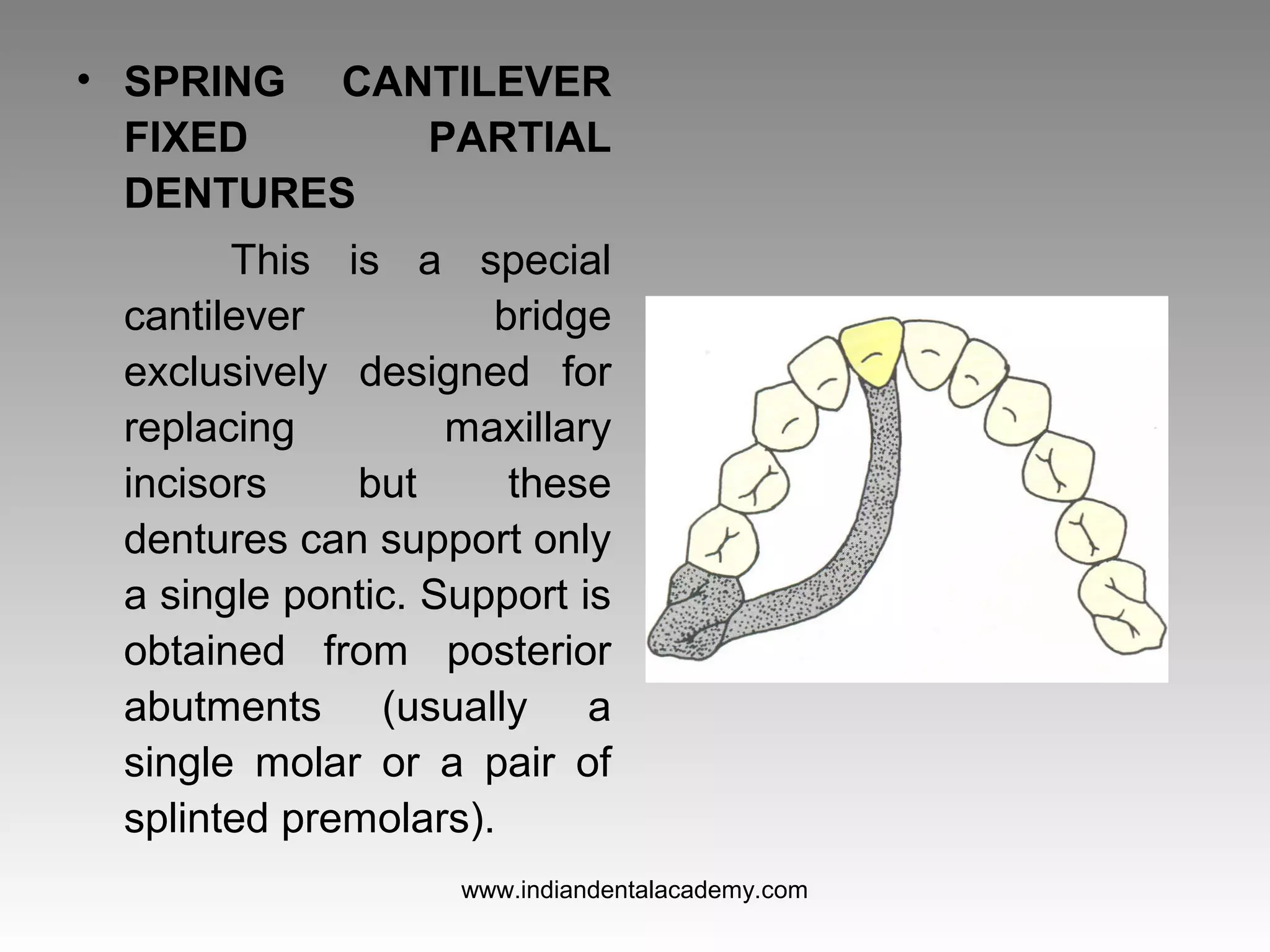
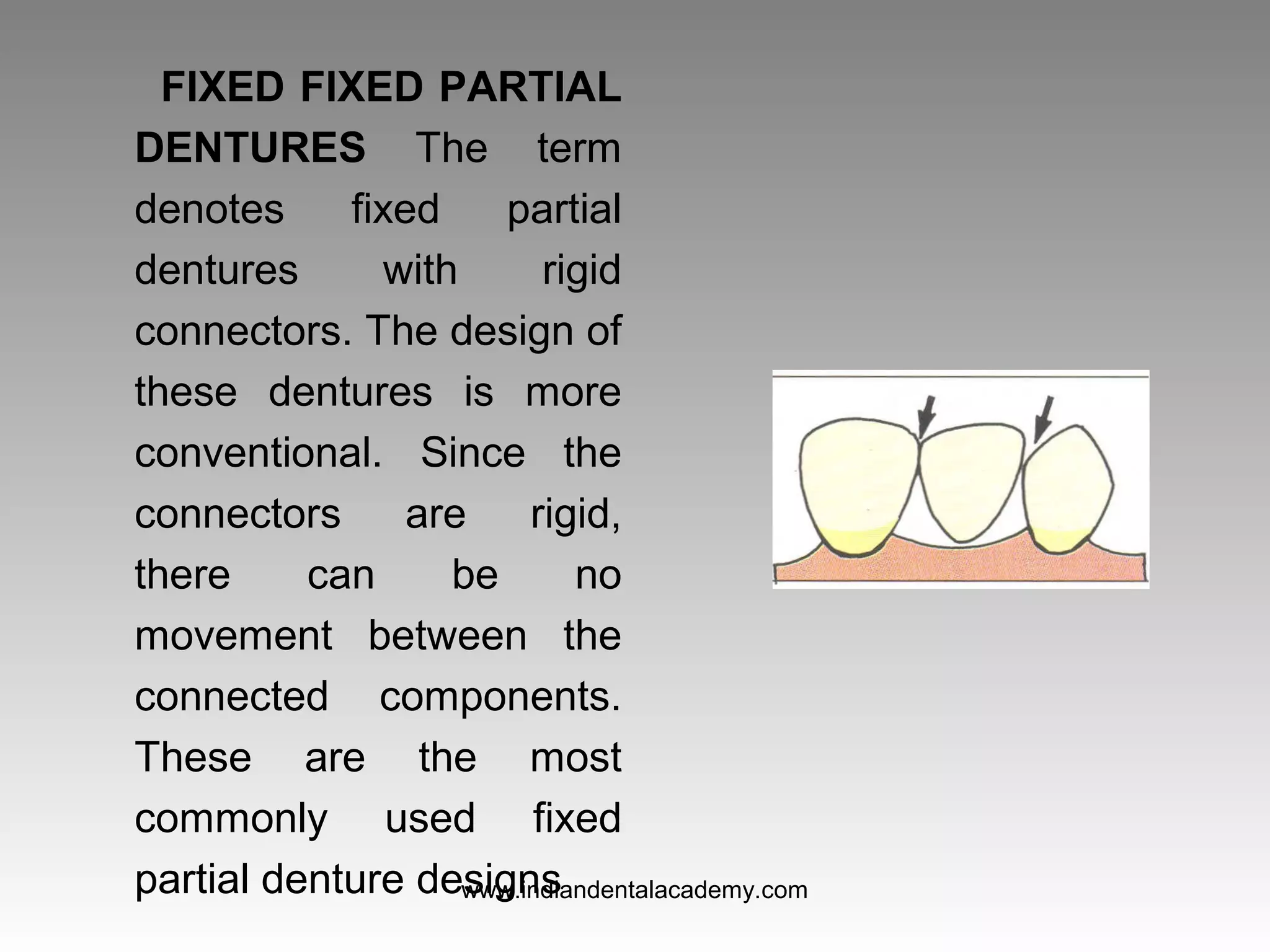
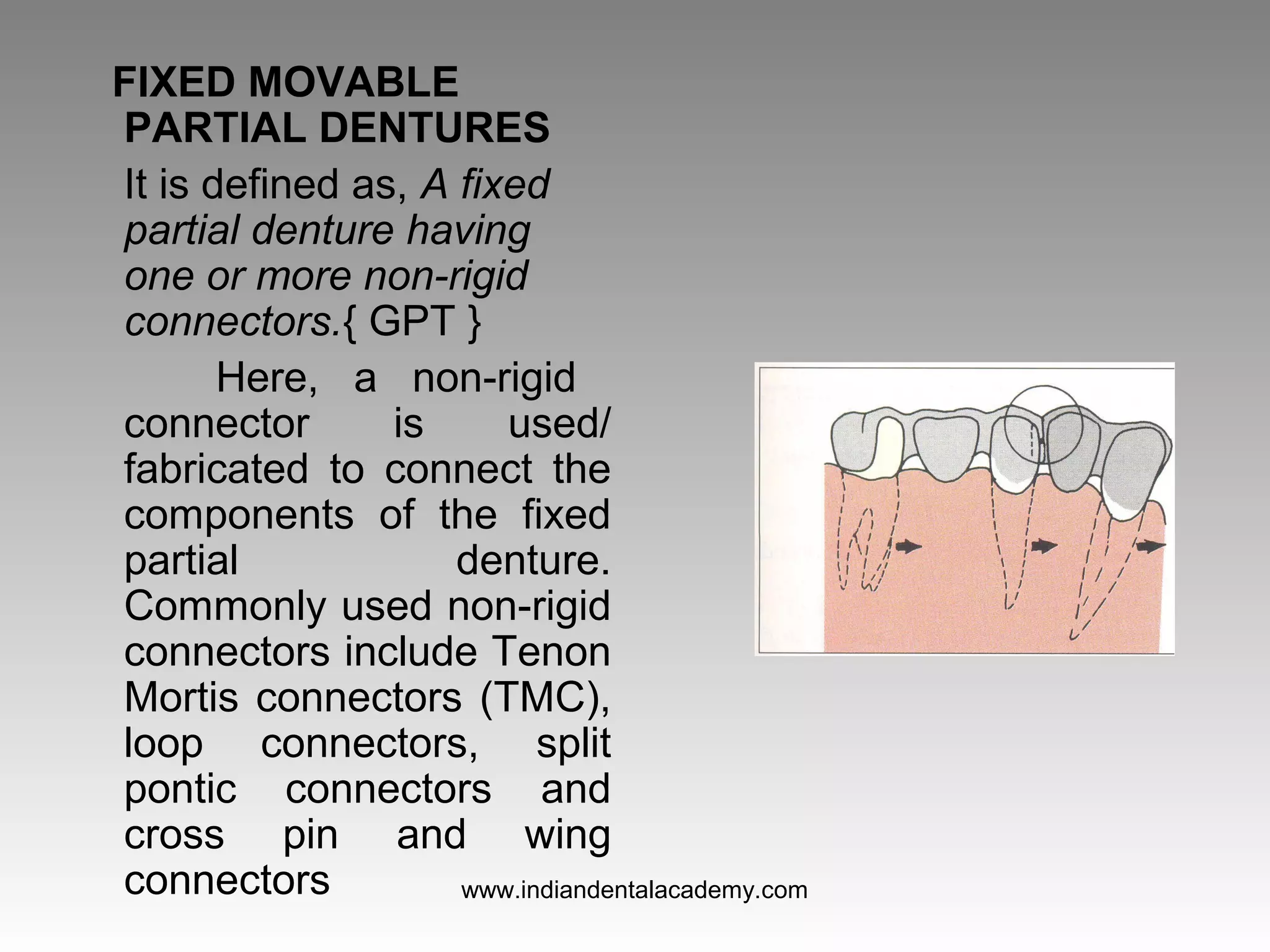
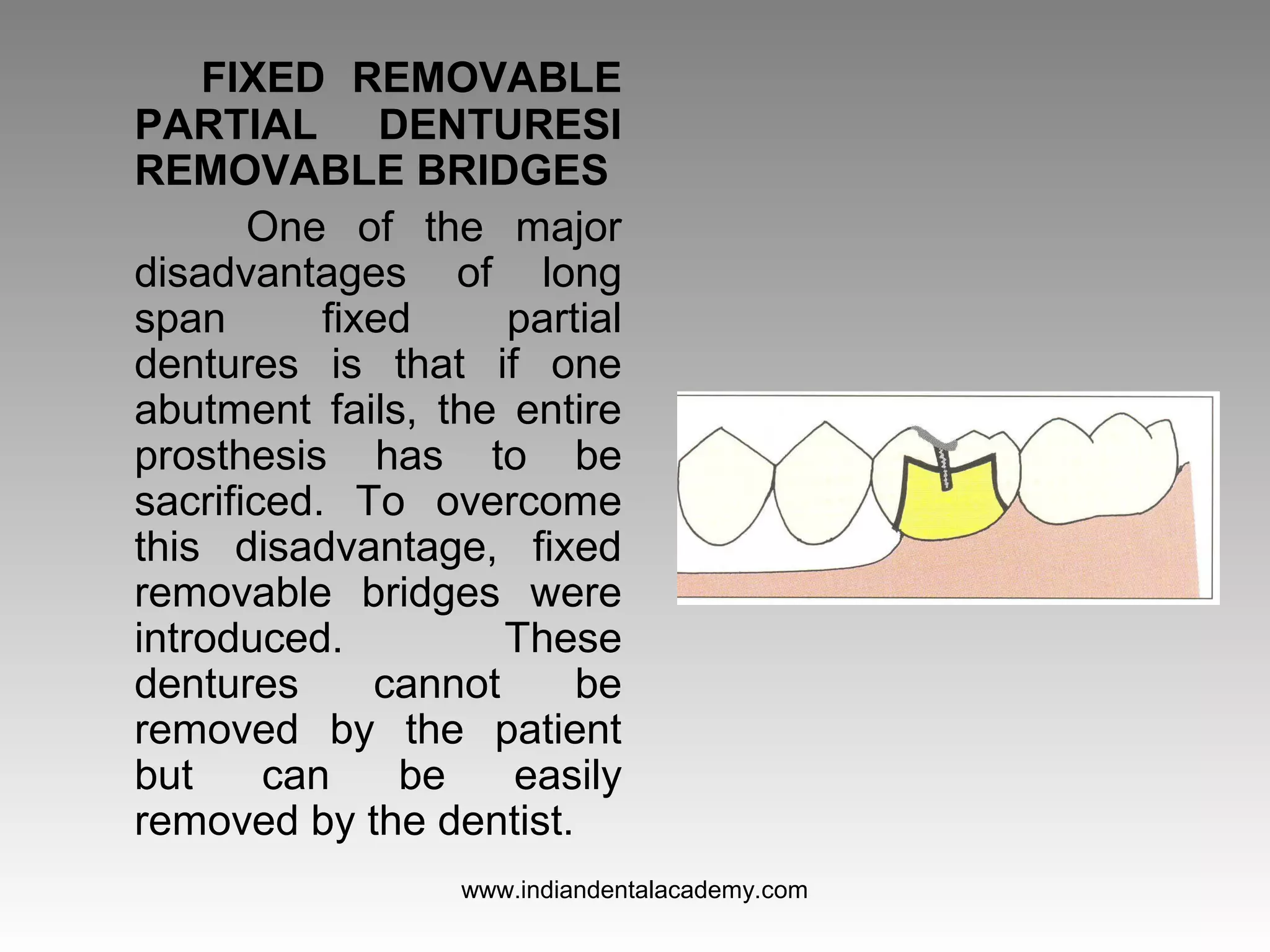
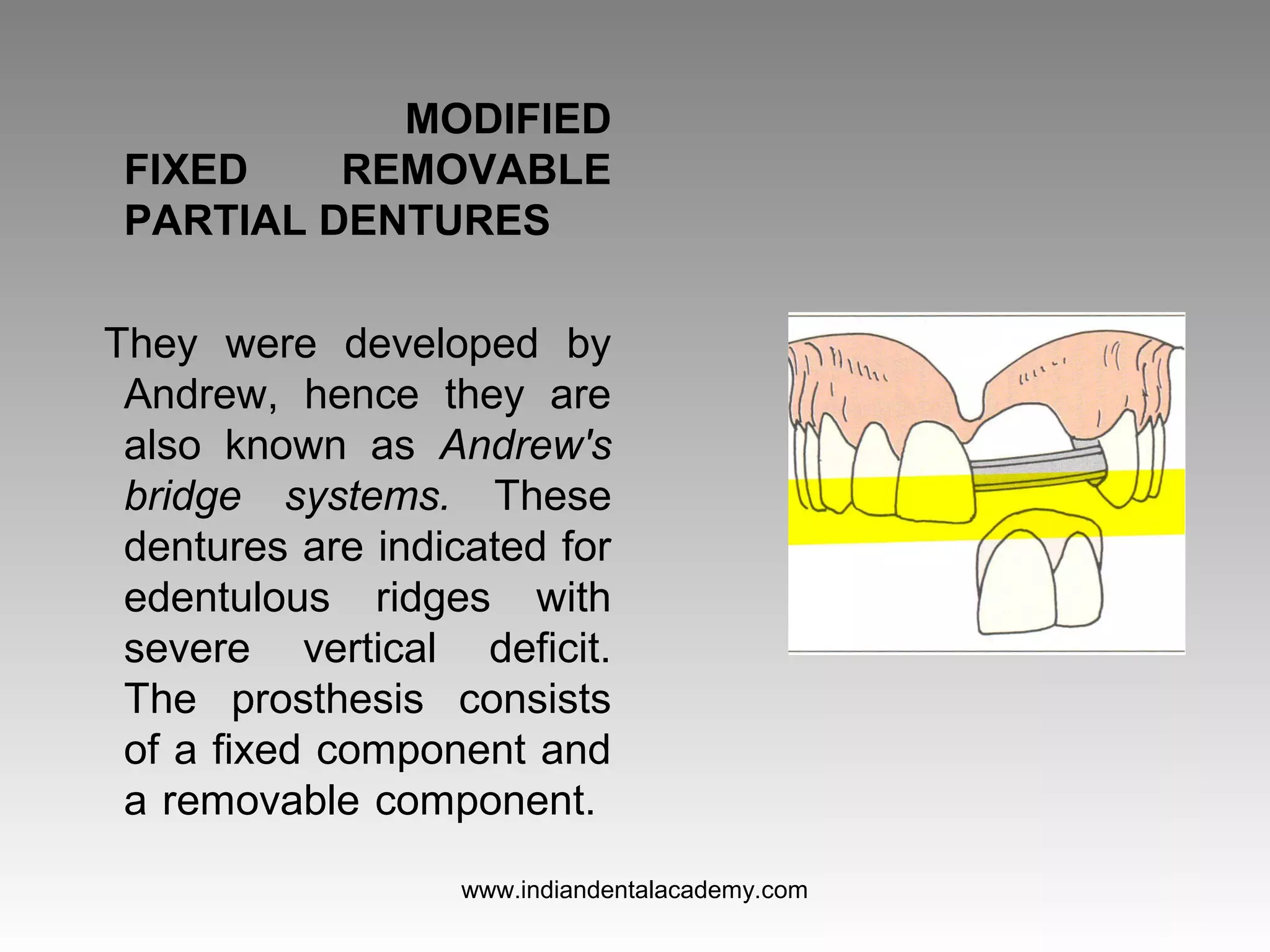
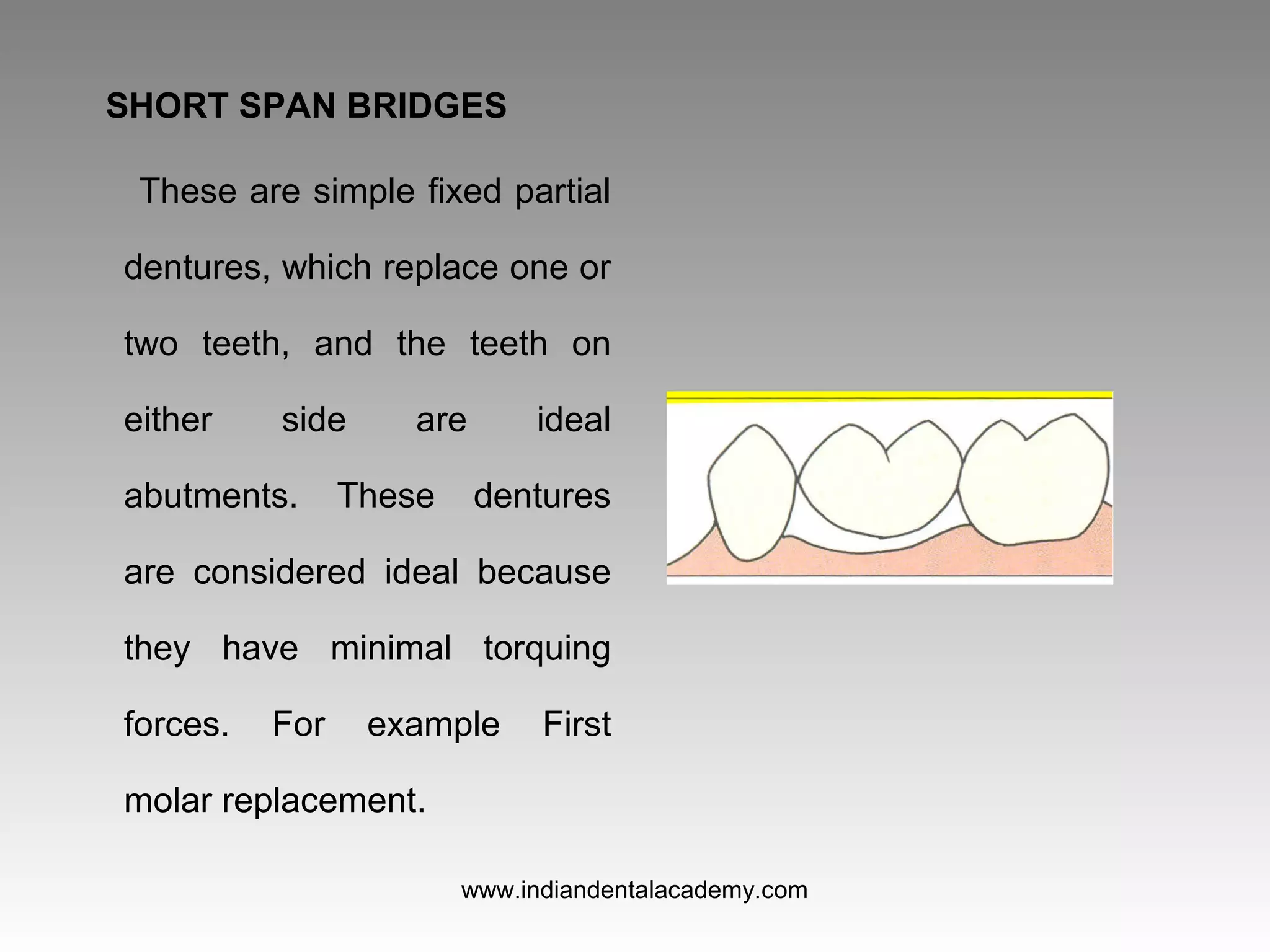
The document discusses various types of fixed partial dentures, commonly known as bridges, including their designs, advantages, and disadvantages. It details conventional, cantilever, fixed movable, removable, metal-ceramic, all-ceramic, and resin-bonded dentures, among others. Each type is evaluated based on its application, structural support, fabrication complexity, and aesthetic considerations.