Case of Goitre
- 1. - 1 -
- 2. A Case of Goitre History : I- Type of Patient. II- Symptoms. III- Past history. I) Type of Patient : • Physiological goiter → at puberty or pregnancy. • Colloid & primary toxicosis → 20 – 30 y. • Nodulary & 2ry toxicosis → 30 – 50 y. • Malign. Goiter → after 50 y. • Except for carcinoma all diseases of thyroid are common in male than female. II) Symptoms : 1) Neck symptoms. 2) Eye symptoms. 3) Symptoms of thyrotoxicosis. 4) Features of malignancy. 5) Symptoms of myxoedema. Neck Symptoms : 1) A lump in the neck. 2) discomfort during swallowing 3) Dyspnoea. 4) Pain. 5) Hoarseness. III) Past History • Trauma • Operation • Medication - 2 -
- 3. Diffuse enlargement of thyroid gland Colloid goiter Physiological goiter - 3 -
- 4. Asymmetrical multinodular goiter Primary toxic goiter - 4 -
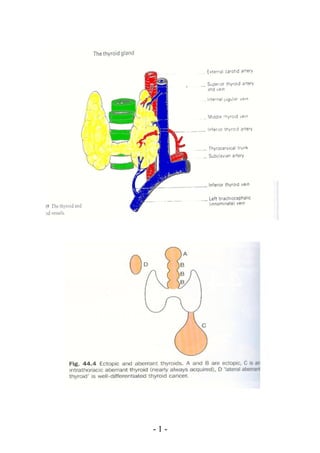
- 5. Retrosternal goiter Barium Swallow shows Dilated superior veins on the Trachea and Trunk and arm due to oesophageal deviation obstruction of superior vena Cava - 5 -
- 6. II) Symptoms : 1) Neck symptoms. 2) Eye symptoms. 3) Symptoms of thyrotoxicosis. 4) Features of malignancy. 5) Symptoms of myxoedema. 1) Neck Symptoms : 1) A lump in the neck. 2) discomfort during swallowing 3) Dyspnoea. 4) Pain. 5) Hoarseness. 1) A lump in the neck : • Onset, duration, size Usually slowly growing and painless swelling, but painful rapid enlargement suggests thyroiditis , malignancy or hemorrhage within cyst sudden enlargement of a lump caused by hemorrhage is usually painful but , a fast – growing anaplastic carcinoma is not usually painful until it invades nearly structures. 2) discomfort during swallowing • large swellings → tugging sensation during swallowing and this is not true dysphagia. • The thyroid swellings rarely obstruct the oesophagus because the oesophagus is a muscular tube which is easily stretched and pushed aside however , because the thyroid has to be pulled upwards with the trachea in first stage of deglutition , an enlarged makes swallowing uncomfortable and even difficult. - 6 -
- 7. 3) Dyspnoea : • due to deviation or compression of trachea by a mass in the thyroid. This symptom is often worse when the neck is flexed laterally or forwards. • The whistling sound of air rushing through a narrowed trachea is called "stridor". 4) Pain : • It is not a common feature of thyroid swellings acute and sub acute thyroiditis present with a painful gland and Hashimoto's disease. • Anaplastic carcinoma can cause local pain and pain related to the ear if it infiltrates surrounding structures. 5) Hoarsness : • It is significant symptom as it is probably caused by a paralysis of one recurrent laryngeal n. with means that the lump is likely to be an anaplastic carcinoma infiltrating the nerve. - 7 -
- 8. 2) Eye Symptoms : The patient may complain of staring or protruding eyes and difficulty in closing her eyelids "exophthalmos". - 8 -
- 9. 3) Symptoms of Thyrotoxicasis : • C.N.S → Nervousness , irritability , insomnia , tremor. • C.V.S → Palpitation , dyspnea on exertion , chest pain • Metabolic → ↑in appetite but loss of wt • Alimentary → Change of bowel habit usually diarrhea. • Tolerance to cold weather and excessive sweating with intolerance to hot • Change in menstruation even amenorrhea. 4) Features of Malignancy : • Features Suspicious of malignancy. a solitary nodule in the thyroid gland. • Features Suggestive of malignancy. 1- Rapid growth in size. 2- Hard consistency. 3- Fixity. 4- Pressure manifestations : • On recurrent → hoarsness of vioce. • On trachea → dyspnea. • On oesophygous → dysphagia • On carotid → absence of carotid pulsation 5- Pain indicate infiltration of nerves , expecially which referred to the ear which passes along auricular br. Of the vagus (Arnold’s nerve). 6- Increased vascularity. 7- Cold adenoma. - 9 -
- 10. • Features Sure of malignancy. Presnce of 2ry metastases and positive biopsy Metastasis in the left parietal bone from a carcinoma - 10 -
- 11. of the Thyroid. 5) Symptoms of Myxoedema : • An increase of wt with deposition of fat across the back of the neck and shoulders. • Slow thought , speech and action. • Intolerance to cold. • Loss of hair (specially outer 43 of eye brows). • Muscle fatigue. • Dry skin. • Constipation. - 11 -
- 12. III) Past History : - In thyroglossal fistula → past history of infected swelling . - In every case → past history of toxicosis . - 12 -
- 13. Past history of medication. Past history of previous operation. Examination I) General Examination : 1) Face. 2) Examination for signs of toxicosis : A) Eye signs. B) Tremor. C) C.V.S. D) Hands. E) Legs. 3) Search for metastases. In suspected Hashimoto's → liver and spleen should be examined. 1) Face : • Anxious stare é protruding eyes and fullness of thyroid region → primary thyrotoxicosis. • Pale puffy face é protruding tongue and thick lips → cretinism. 2) Examination for signs of toxicosis : A) Eye Signs : 11 Mild exophthalmos : "widening of palpebral fissure due to retraction of the upper eye lids without any bulging of the eyes". • Stellwag's sign +ve. • Von Graefe's sign +ve. 11 Moderate exophthalmos : "actual bulging of eyeballs from increased deposition of retrobulbar fat". • Dalymple's sign +ve. • Joffroy's sign +ve. 11 Severe exophthalmos : "due to intra orbital aedema and congestion" → marked protrusion of eyes. • Mobius sign +ve. - 13 -
- 14. 11 Malignant exophthalmos : " it is progressive form , particularly after thyroidectomy é impairment of corneal sensitivity and paralysis of eye muscles. B) Tremor : Thyrotoxicosis causes a fine , fast tremor and demonstrated by : 1. Stretching out the hands. 2. Putting out the tongue for minute at least. 3. Closing the eye lids lightly for a while. 4. In severe cases , the whole body becomes shaky and trembling. C) C.V.S : • Pulse → rate , rhythm , character In thyrotoxicosis → ↑rate , irregular auricular fibrillation. • Signs of congestive Ht failure. • B.P → ↑systolic ↓diastolic So pulse p. ↑ ↑. • Sleeping pulse : Less than 90 Min → Mild Less than 90 – 110 Min → Moderate Over 110 Min → Severe D) Hands : • Fell the pulsation. • In primary toxic goitre → warm / sweaty • In neurosis → cold / clammy • Detection of tremors E) Legs : Pretibial myxedema → rare sign but usually after thyroidectomy starts bilateral pitting with arranged coloured pigmentation by time → solid oedema with red colour. - 14 -
- 15. Pretibial myxedema 3) Search for metastases : In suspected cases : • Cervical lymph nodes. • Bones → skull & long bones • Chest , liver & Abdomen. II. Local Examination Inspection Palpation Percussion Auscultation A) Lump. B) Skin. C) Neck. A) For thyroid by two methods. B) Relations. C) Lymph nodes. Inspection A) Lump : • Site , size , shape , pulsations , particular features → moves é deglutition. B) Skin : • Look for thyroglossal fistula. • For scar of previous operation. • For dilated veins over the neck and upper part of the chest. - 15 -
- 16. C) Neck : • For other swelling outside the thyroid region. • For neck veins. Palpation A) For swelling and thyroid region 1) Palpate the neck from the front : • The most important part of palpation is done from behind , but , it is preferred to place your hand on any visible swelling while standing in front of the patient , to confirm your visual impression of its size , shape and surface and to find out if it is tender. 2) Palpate the neck from behind : • Stand behind the patient , placing your thumbs on the nap and tilt the head slightly forwards to relax the out neck M. let the palmar surface of your fingers rest on either side of the neck. They will be resting on the lat lobes of the thyroid gland. A small lobe can be made prominent and easier to feel by pressing firmly on the opposite side of the neck. • If you are still doubtful → ask the patient to swallow while you examining. • By this maneuver you confirm the facts about , tenderness , shape , size , surface consistency. - 16 -
- 17. B) Relations 1) To the skin : Pinch up a fold of skin and move it over the swelling. 2) To sterno mastoid : • To test one side , place your hand on the side of the patient's chin opposite to the side of the lesion and tell him to push against the resistance of your hand. To test both sides simultaneously , put your hand under the point of the chin and ask him to press down against resistance when both stern mastoids are put into action. If the swelling lies deep to the M. , which is a common occurrence , it disappears under the M. either completely or partially depending upon the size of the gland. It the swelling is situated sup. to M. it will be more apparent and movable over the contracted M. 3) To the trachea & larynx : • Whether displaced by swelling or not. Thyroid swelling may compress the trachea from both sides → giving rise "scabbard Trachea" the presence of which can be - 17 -
- 18. determined by Kocher's test i.e. slight pressure on lat lobes produce stridor. 4) To carotid sheath : • Along the post edge of swelling benign swelling → may displace the carotid sheath backwards and outwards , while malignant T. tends to surround the sheath completely and obscure the carotid pulsation. "Berry's sign". 5) To suprasternal notch : • Trying to insinuate the fingers between the supra sternal notch and the lower border of the swelling. In retrosternal type the lower border can not be left. 6) To the oesophagus : • Displacement on compression of oesophagus by enlarged gland may give to → dysphagia. 7) To recurrent laryngeal N. : • In malignant cases → hoarseness of voice. 8) To the syphthic trunk : • It may give to Horner's Syndrome - 18 -
- 19. Ptosis → slight drooping of eye lid. Enopthalmosis → slight sinking of eye ball into orbit. Anhydrosis → absence of sweating of affect side. Myosis → contraction of pupil. C) Lymph nodes : • Upper deep cervical → as sup. thyroid vein drained into it. • Lower deep cervical → as middle thyroid vein drained into it. • Mediastinal L.N. → as inf. thyroid vein drained into it. • The deeper and more medial lymphatics proceed to pretracheal , prelaryngeal and recurrent laryngeal lymph nodes before ending in the mediastinal gland. Percussion Over sternum to detect the presence of retrosternol goitre. It is not practically helpful. Auscultation In primary Toxic → systolic or continuous murmur over the gland. Measurement of circumference of the neck at the most prominent part of the lump to determine whether the swelling is increasing or decreasing in size. - 19 -
- 20. Oral and clinical Questions 1. What are other swellings moves é deglutition ? • Pharyngeal diverticulum. • Pretraceal L.N. • Laryngeocele. • Thyroglossal cyst. • Subhyoid bursitis. 2. Sometimes thyroid swelling does not move during swallowing. What are such cases ? • Huge. • Retrosternal. • Malignant, due to infiltration . • Riedel`s thyroditis, due to fibrosis. 3. What are the causes of painful goiter ? • Malignancy • Acute thyroiditis • Hemorrhage in cyst. 4. What are the causes of dullness on manubrium sterni ? • Retrosternal goiter. • Ectopic Thyroid tissue. • Pre-tracheal lymph nodes. 5. Why vital sign stable in case of toxicity during examination ? - 20 -
- 21. • Because the pat. is controlled “under treatment” by anti toxic drugs 6. What is the cause of unequal pulses in case of goitre ? • If there is retrosternal extension. 7. What are the causes of water hummer pulse ? • Thyrotoxicosis. • Anemia. • A.V. fistula. • Hepatic failure. • Hypoxic cor-pulmonale. 8. What are the causes of unilateral exophthalmos ? • Orbital cellulitis . • Orbital neoplasm. • Orbital Aneurysm of ophthalmic artery. • Cavernous sinus thrombosis. 9. What are the causes of pulsating exophthalmos ? • Arterial - Exophthalmos - Orbital aneurysm - A.V. fistula between ICA & Cavernous sinus 10. What is the difference between fine & flapping tremors ? • Fine Tremors : due to increase in metabolites leading to irritation of nerve ending resulting in tremors of a small joints of hands • Flapping Tremors : due to increase of toxins leading to irritation of Extra - pyramidal resulting in tremors of wrist joint of hand. 11. What are the causes of liver enlargement in case of goitre ? • Thyrotoxic H.F. • Auto immune “ Primary toxic & Hashimoto`s disease ”. • Thyroid lymphoma . - 21 -
- 22. • Liver metastasis . 12. What are the causes of spleen enlargement case of goitre ? • Thyrotoxic H.F. • Auto immune “ Primary toxic & Hashimoto`s disease ”. • Thyroid lymphoma . 13. What are the causes of dyspnea in case of goitre ? • Malignancy • Retrosternal goitre • Thyrotoxic H.F. 14. What are the causes of enlargement lymph node in case of goitre ? • Cancer thyroid “ papillary type ” • Lymphoma • Hashimoto`s disease • Acute thyroditis 15. What are the neck swelling which moves with deglutition and tongue protrusion ? • Thyroglossal cyst • Subhyoid bursitis 16. How can you differentiate between toxic goitre & psychoneurosis ? • In toxic goitre : there is polyphagia, warm sweaty hands, tachycardia & abnormal thyroid function tests. • In Psychoneurosis : There is anorexia , cold sweaty hands, normal sleeping pulse & normal thyroid function tests. 17. What are the best laboratory tests ? • Free thyroxine levels or total T4 & T3 resin uptake. 18. Does a “cold” nodule on thyroid scan indicate malignancy ? • All cysts & many benign adenomas show up as “cold” nodules, conversely a few thyroid cancers appear as - 22 -
- 23. “warm” nodules. Therefore thyroid scans are reliable in diagnosing malignancy. 19. What is the main difference in metastatic tendencies between papillary & follicular cancers ? • Papillary cancers metastasize to neck first. Follicular cancer metastasize distantly ( Hematogenous ) 20.What are the causes of diffuse enlargement of thyroid ? • Physiological goitre little enlargement and soft. • Colloid goitre may huge , always elastic • Primary thyrotoxicosis may be minimal and soft. • Hashimoto’s disease very firm. • Riedel’s diseases woody thyroid. Written Questions 2- Retrosternal goitre. 3- Management of malignant goitre. 4- Thyrotoxicosis : • Investigation • Treatment 5- Clinical evaluation and management of solitary nodule. - 23 -
- 24. TREATMENT OF TOXIC GOITER - 24 -
- 25. The problem of clinically solitary nodule and its evaluation Clinically only one macroscopic nodule is found , but microscopic changes will be present throughout the gland. This is one form of clinically solitary nodule which is refered to as cystadenoma of the thyroid and its commonest site is at junction of the isthmus with one lobe , and although it appears solitary multiple small adenometa are scattered around it. When there is a solitary nodule of thyroid it is must be differentiated from true adenoma. Solitary nodule True adenoma - Poor encapsulation - Good encapsulation - Variable structure - Uniform structure - Similar in structure - Different from adjacent of adjacent thyroid T. thyroid T. - no compression on - Compression on adjacent gland adjacent gland - 25 -
- 26. Causes of solitary nodule in thyroidCauses of solitary nodule in thyroid 11..solitary nodular goitersolitary nodular goiter.. 22..Toxic nodular goiterToxic nodular goiter.. 33..Malignant nodule (medullary adenomaMalignant nodule (medullary adenoma(( 44..True adenoma of thyroidTrue adenoma of thyroid.. Adenoma of thyroid may beAdenoma of thyroid may be:: --Embryonal adenomaEmbryonal adenoma 11..--Fetal or micro-follicular adenomaFetal or micro-follicular adenoma --Colloid or macro-follicular adenomaColloid or macro-follicular adenoma --Hurthle-cell adenoma with acidophilic cytoplasmHurthle-cell adenoma with acidophilic cytoplasm --Papillary cystadenoma highly suspicious of being malignantPapillary cystadenoma highly suspicious of being malignant.. InvestigationInvestigation of solitary noduleof solitary nodule:: 11..Thyroid ScanningThyroid Scanning:: --Hot nodule = overactive noduleHot nodule = overactive nodule Takes up isotope , while the surrounding tissue does not ,Takes up isotope , while the surrounding tissue does not , here , the surrounding. T. is inactive because the nodule ishere , the surrounding. T. is inactive because the nodule is producing such high levels of thyroid hormones that T.S.H isproducing such high levels of thyroid hormones that T.S.H is suppressedsuppressed.. --Worm nodule = active noduleWorm nodule = active nodule Takes up isotope and so does normal surrounding tissueTakes up isotope and so does normal surrounding tissue about itabout it.. --Cold nodule = inactive nodule Takes up no isotopeCold nodule = inactive nodule Takes up no isotope D.D of cold noduleD.D of cold nodule:: degenerative cyst, calcification, haemorrhage, abscessdegenerative cyst, calcification, haemorrhage, abscess or hydatid cystor hydatid cyst.. 22..Ultrasound (echographyUltrasound (echography(( - 26 -
- 27. ••It is helpful to differentiate solitary from multiple nodulesIt is helpful to differentiate solitary from multiple nodules ••It is also used for differentiating solid from cystic lesionsIt is also used for differentiating solid from cystic lesions.. 33..BiopsyBiopsy ••FNAC or Trucut or Excisional biopsyFNAC or Trucut or Excisional biopsy.. Treatment of solitary noduleTreatment of solitary nodule:: 11..EnucleationEnucleation:: Removal of the nodule from it`s capsule. But it is notRemoval of the nodule from it`s capsule. But it is not recommended because recurrence is the rule as therecommended because recurrence is the rule as the nodule is never solitarynodule is never solitary.. 22..Resection EnucleationResection Enucleation:: Excision of the nodule with the surrounding thyroid tissueExcision of the nodule with the surrounding thyroid tissue.. It is the recommended operation asIt is the recommended operation as we remove the scatteredwe remove the scattered small nodules around the clinical solitary nodulesmall nodules around the clinical solitary nodule.. 33..HemithyroidectomyHemithyroidectomy:: Removal of the affected lobe together with the isthmus andRemoval of the affected lobe together with the isthmus and pyramidal lobe. The specimen must be sent for biopsypyramidal lobe. The specimen must be sent for biopsy.. It is the operation of choiceIt is the operation of choice.. - 27 -
- 28. - 28 -
- 29. - 29 -