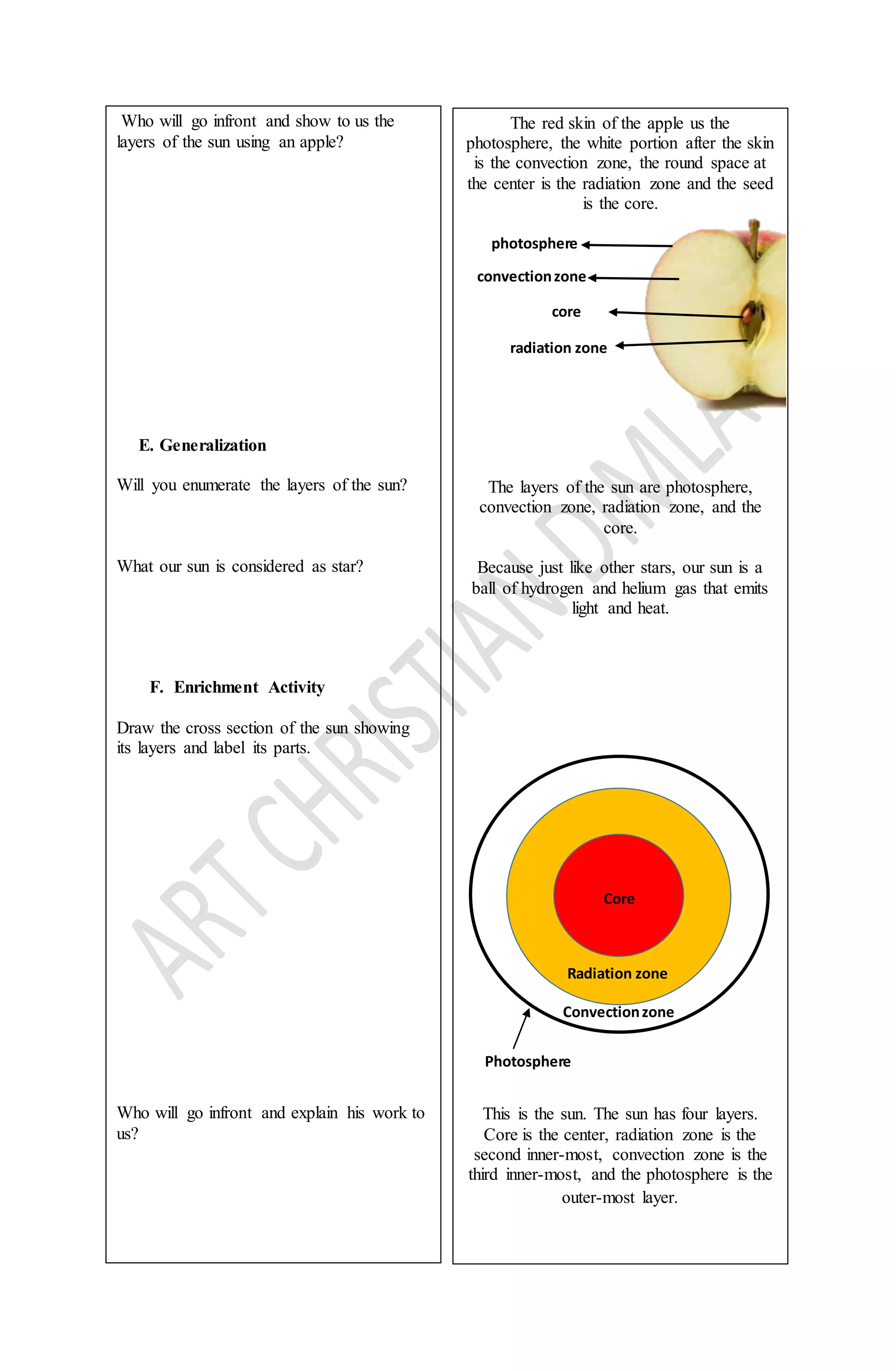
This document outlines a lesson plan about the layers of the sun. It identifies four main layers: the photosphere, convection zone, radiation zone, and core. The photosphere is the sun's surface and outermost layer with a temperature of 6,600°C. The convection zone transports energy outward through convection currents. The radiation zone emits radiation, while the core is the innermost part composed of molten rock where hydrogen is converted to helium. The lesson uses activities like labeling diagrams and models to help students understand and describe each layer of the sun.