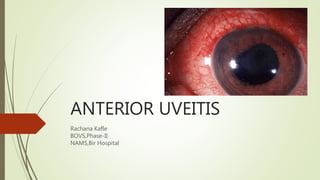
Anterior uveitis - SIGNS, SYMPTOMS AND TREATMENT
- 2. Presentation layout Anatomy of uvea Uveitis introduction Classification of uveitis Anterior uveitis introduction Etiology of AU Clinical features,complications and D/D Investigations Treatment of AU
- 3. Anatomy of uvea UVEA constitutes- middle vascular coat 3 parts- a)iris b)ciliary body c)choroid Developmentally, structurally and functionally- indivisible color varies from light blue to dark brown
- 4. Developmental milestones 9TH WEEK GESTATION- 12TH WEEK GESTATION- 5TH MONTH- all layers of choroid seen & iris fully developed 6TH MONTH- dilator muscle begins to form, sphincter muscle is fully formed POSTNATAL PERIOD- dilator muscle fully formed by 5 years, iris stromal pigment develops after birth
- 5. MACROSCOPIC APPEARANCE OF IRIS TWO SURFACES A)ANTERIOR SURFACE Collarette- zigzag line, 2mm from pupil, thickest, represents attachment of pupillary membrane Divides surface into- a) CILIARY ZONE- c/b b) PUPILLARY ZONE- Between collarette and pigmented frill B)POSTERIOR SURFACE- dark brown/black Contains- A) Schwalbe’s contraction folds B) Schwalbe’s structural furrows C) Circular furrows
- 7. FOUR LAYERS- a)Anterior limiting layer- b) Iris stroma- •Forms main bulk •Consists of collagenous tissue with mucopolysaccharide C) Anterior epithelial layer D)Posterior pigmented epithelial layer Anterior continuation of non pigmented epithelium of ciliary body
- 9. Ciliary body Forward continuation of choroid at ora serrata Triangular in cut section, ant side of its form part of angle, in middle attached to iris and outer part lies against sclera Triangle – two parts a) Anterior part- ciliary processes (pars plicata) 2-2.5mm b)Posterior part- smooth (pars plana) 5mm wide temporally & 3mm nasally
- 10. Structure of ciliary body MICROSCOPIC STRUCTURE 1.SUPRACILIARY LAMINA- outermost part 2. 2.STROMA- Consists Ciliary muscle- non striated, triangular in cut section, 3 parts a.Longitudnal/meridional fibres- origin from scleral spur, inserts into suprachoroidal lamina b.Circular fibres- in inner portion, nearest to lens c.Radial fibres- obliquely placed 3)Layer of pigmented epithelium- forward continuation of RPE 4)Layer of non pigmented epithelium- forward continuation of sensory retina 5)Internal limiting membrane-lines NPE Forward continuation of internal limiting membrane of retina
- 11. Choroid Posterior most part Extension- optic disc to ora serrata Inner surface- smooth, brown and in contact with RPE Outer surface-rough and in contact with sclera Thickness- posteriorly 0.22mm anteriorly 0.10mm
- 12. Microscopic structure of choroid 1) Suprachoroidal lamina- lamina fusca Thin layer, continues anteriorly with supraciliary lamina of ciliary body 2) Stroma – plenty of pigmented cells, macrophages,mast and plasma cells 3) choriocapillaris- rich capillary network 4)Basal lamina- Bruch’s membrane/lamina vitrae-Innermost layer
- 13. Uveitis Term uveitis- inflammation of uvea However, clinically there is some association from the nearby structures
- 14. Classification of uveitis A. Anatomical classification Acc to SUN, uveitis is classified anatomically : a. Anterior uveitis b. Intermediate uveitis c. Posterior uveitis d. Pan uveitis
- 15. B.Clinical classification a.Acute uveitis b.Chronic uveitis c.Recurrent uveitis C.Pathological uveitis a.Suppurative/purulent uveitis b.Non suppurattive uveitis i.Granulomatous ii.Non granulomatous D.Etiological classification a.Infectious uveitis b.Non infectious uveitis c.Masquerade syndrome
- 16. Anterior uveitis Inflammation of the uveal tract from the iris upto the plars plicata of ciliary body i.e ….. It may be sub divided into A. Iritis B. Iridocyclitis C. Anterior cyclitis Aetiology Uveitis (anterior) Anterior uveitis (the most common form of uveitis: 75% of all cases of uveitis). Annual incidence 12 per 100,000 population it may affect all ages, although it is most common in individuals in the third and fourth decades. (https://www.college-optometrists.org/guidance/clinical-management-guidelines/uveitis-anterior-acute-and-recurrent- .html) (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6095364/)
- 17. Etiology of uveitis/AU Depending upon the offending agent of uveitis, A. infectious i. exogenous ii.secondary iii.endogenous B.non infectious i.auto-immune a.HLA-associated b.others ii.Atopic iii.Toxic iv.Idiopathic specific nonspecific
- 18. Infectious uveitis a.Exogenous infection b.Secondary infection c. Endogenous infection Different types of infectious uveitis a.Bacterial b.Viral c.Fungal d.Parasitis e.Rickettsial
- 19. Clinical features Clinically it may be present as acute or chronic uveitis: Acute: Symptoms more severe like photophobia, redness, lacrimation and decreased vision Chronic: Signs more severe than symptoms, however eye may be presented white as that of very minimal symptoms
- 20. Symptoms Pain: complain of skull aching which typically Worsen at night Acute Severe Radiates along V1 nerve distribution dominant symptom of AAU Redness: feature of AAU, and occur due to circum corneal congestion, as a result of hyperemia of anterior ciliary vessels due to the effect of toxins, histamines and histamine like substances and axon reflexes. Photophobia and Blepharospasm: in AAU, due to reflex between sensory fibers of fifth CN {WHICH ARE IRRITATED} and motor fibres of seventh CN supplying the orbicularis oculi
- 21. Lacrimation occurs as a reflex of Vth CN (afferent) and secretomotor of seventh CN(efferent) Diminution of vision a. Ciliary spasm –induces ? b. Vitreous exudates c. Exudates in pupillary area {pupillary block} d. CME e. Sec. glaucoma f. Turbid aqueous g. Complicated Cataract
- 22. Signs A . Lid Edema Mild, may accompany a severe attack of AAU B . Ciliary congestion ccc is marked in AU, it may be differentiated from superficial congestion occurring in acute conjunctivitis
- 24. C. Corneal signs 1.KPs: KPs are pathogenic sign of AU. Are proteinaceous cellular deposits occurring at the back of the cornea mostly arranged in triangular fashion occupying the centre and inferior part of the cornea due to convetion currents in the aqueous humour. Different morphology of KPs are Mutton fat KPs in granulomatous iridocyclitis and composed of epitheloid cells and macrophages Large,thick ,fluffy and lardaceous KPs ,having greasy or waxy appearance usually a few -10-15 in no Small and medium KPs small,discrete,dirty white KPs arranged irregularly at the back of cornea they may be numerous these are pathognomic of nongranulomatous uveitis and are composed of lymphocytes
- 25. Fine KPs : also also called as ‘satellite’ KPs,typically cover entire corneal endothelium and form the so called endothelial dusting. Are seen in Fuchs heterochromic iridocyclitis,herpetic iritis and CMV retinitis. Old KPs are sign of healed uveitis either of the abive described KPs with healing process shrink,fade,become pigmented and irregular in shape(crenated margin) old mutton fat KPs usually have a ground glass appearance due to hyalinization 2.cornea edema toxic endothelitis and raised IOP when present 3.Posterior corneal opacity may be formed in long standing cases of iridocyclitis
- 28. D.ANTERIOR CHAMBER SIGNS: Aqueous cells Early sign On oblique illum.:1 mm long 1mm wide slit with max light and magnifications Grading:
- 29. Aqueous flares D/t leakage of protein into the aqueous humor from the leaky vessels On oblique illumination: a point of beam projected on the iris plane Protein particles seen floating the beam of light: Tyndall phenomenon Grading: Hypopyon: sterile pus in AC Changes in depth and shape of AC Changes in the angle of anterior chamber
- 30. Exudates in AC angle Celss and Flare in AC
- 31. Hypopyon
- 32. E.Iris signs 1. Loss of normal pattern 2. Muddy in color in active stage & hyper/ hypopigmented 3. Iris nodules: Aggregations of lymphyocytes and epitheloid cells. Koeppe’s nodules …. Busacca’s nodules…. 4. Posterior synechiae Adhesion of posterior surface of iris to anterior surface of cornea a. Segmental b. Annular c. Total
- 33. Koppe’s and Busacca’s Posterior synechiae
- 35. F.Pupillary signs 1. Narrow pupil 2. Sluggish pupillary reaction and miosis 3. Irregular pupil; festooned pupil 4. Fibrinous exudate; occlusio pupil 5. Ectropion pupillae-contraction of fibrinous exudate on ant sur of iris
- 36. Sluggish pupillary reaction and miosis Festooned pupil
- 38. G.Lens signs 1. Pigment dispersion on lens surface 2. Fibrin exudates on lens surface 3. Complicated cataract: Polychromatic lusture 4. Bread crumb appearance 5. Cyclitic membrane: retrolental, fibrovascular membrane which stretches across the back of the lens
- 41. H.Viterous ,choroidal and retinal signs 1. Exudates and inflammatory cells 2. CME 3. Choroiditis
- 42. I.Changes in IOP 1. Normal 2. Increased (sec glaucoma) 3. Decreased (in acute iridocyclitis - acute ciliary shock chronic,longlasting iridocyclitis -atrophy of ciliary process leading to phthisis bulbi)
- 45. Complications Complicated cataract Secondary glaucoma Cyclitic membrane Choroiditis Retinal signs Serous retinal detachment,CME,RD, scars Periphlebitis/papilitis Band shaped keratopathy Phthisis bulbi Early glaucoma Late glaucoma
- 48. CME Choroiditis
- 49. D/D Causes painful red eye Granulomatous & Non granulomatous Uveitis i.e Etiological D/d
- 53. Difference between granulomatous and non granulomatous
- 55. INVESTIGATIONS A.Hematological Examination It includes following tests: • TLC/DLC: Gross idea of inflammatory response of body • ESR: r/o Chronic infection • Blood sugar: r/o DM • Blood Uric Acid: r/o Gout • Seological Test: Syphilis, toxoplasmosis & histoplasmosis • Test for: Anti Antinuclear Antibodies CRP Rh factor Anti- streptolysin O LE cells
- 56. B.Urine Examination: For WBC, Pus cells, RBS Culture : r/o Urinary tract infection C.Stool Examination ; For Cysts & ova to r/o parasitic infestations. D . Radiological Investigation : CXR , Paranasal sinus, Sacroiliac joints , Lumbar spine. E. Skin Tests: Tuberculin test, Kveims test & Toxoplasmin test
- 58. Treatment of iridocyclitis I. Non specific treatment a.Local therapy b.systemic therapy c.Physical measures II. Specific treatment for the cause III. Treatment complications 1) Cycloplegics 2) Corticosteroids 3) Broad spectrum antibiotics. 1. Corticosteroids 2. Non-Steroidal Anti inflammatory Drugs(NSAIDS) 3. Immunosupressives
- 59. I.NON-SPECIFIC TREATMENT: A. LOCAL THERAPY A. LOCAL THERAPY 1. Cycloplegics 2. Corticosteroids 3. Broad spectrum antibiotics.
- 60. 1. Cycloplegics Short acting cycloplegics: Tropicamide 1% e/d (3hrs) Cyclopentolate 1% e/d(24hrs) Long acting cycloplegics Homatropine 2% e/d(4days) Atropine sulphate 1% e/d (7- 14days)
- 61. MOA of cycloplegics Relieves pain: Relieves spasm of iris sphincter & ciliary m. Prevents posterior synechiae formation Breaks posterior synechiae Reduces hyperemia & vascular permeability which reduces exudation
- 62. 2.CORTICOSTEROIDS: TO REDUCE INFLAMMATION Commonly used steroids: Long acting: Dexamethasone Betamethasone Hydrocortisone Prednisolone Triamcinolone Short acting: Fluoromethalone Loteprednol Fluocinolone
- 63. ROUTE OF ADMINISTRATION: Topical: Eye drops or eye ointments 6times a day Anterior subtenon’s injection For severe cases
- 65. 3.BROAD SPECTRUM ANTIBIOTIC Doesn’t have much role in anterior uveitis
- 66. B.SYSTEMIC THERAPY 1. Corticosteroids 2. Non-Steroidal Anti inflammatory Drugs(NSAIDS) 3. Immunosupressives
- 67. 1.CORTICOSTEROIDS Indication: In Intractable anterior uveitis Prednisolone: 1mg/kg bdwt & taper gradually according to response Side effects: Glaucoma & Cataract
- 68. 2.NSAIDs Used when steroid are contraindicated or not tolerated. Phenylbutazone & oxyphenylbutazone
- 69. 3.IMMUNOSUPPRESSIVES In corticosteroid resistant or intolerant cases In specific inflammations: a. Bechet’s syndrome b. Sympathetic ophthalmitis c. VKH d. Pars planitis
- 70. C. Physical Measures 1. Hot fomentation more antibodies are brought and toxins are drained 2. Dark goggles helps in photophobia,lacrimation and blepharospasm
- 71. SPECIFIC TREATMENT Tuberculosis: ATT Parenteral Penicillin : Syphilis HSV: Acyclovir
- 73. TREATMENT OF COMPLICATION 1. Inflammatory Glaucoma: Timolol 0.5% BD & Tab. Acetazolamide 250mg BD Contraindicated are Latanoprost & Pilocarpine. 2. Post-inflammatory Glaucoma(d/t ring synechiae): Laser iridotomy 3. Complicated Cataract: Cataract surgery,After 3mths of quiet period. 4. Retinal Detachment: Anterior vitrectomy 5. Phthisis bulbi : Enucleation
- 74. Just as different fads that seize the imagination of the general public are often carried to excess, so diagnostic or therapeutic fads may take over in the practice of medicine. Analysis of 33 surveys of the causes of uveitis reported by ophthalmologists over the course of 120 years shows how some diagnoses such as syphilis and tuberculosis fell from favor because tests ruled out these diseases, whereas others such as toxoplasmosis became popular because of the finding of the organism in a few cases by a famous ophthalmic pathologist. Yet others (pars planitis, sarcoidosis) were not even causes of disease, but rather merely descriptive, or the ocular component of a systemic disease whose etiology and pathogenesis remain unknown. We will examine the waxing and waning of these diagnostic categories and the impressive confidence of some clinicians in their own diagnostic acumen as they made diagnoses often unsupported by objective evidence. (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9657289/)
- 76. 1. Comprehensive ophthalmology by AK Khurana 2. Kanski’s clinical ophthalmology 8th edition 3. Parson’s eye disease 4. Americal Academy of ophthalmology(AAO) 5. American Optometric Association(AOA) 6. https://www.college-optometrists.org/guidance/clinical-management- guidelines/uveitis-anterior-acute-and-recurrent-.html