GERIATRIC ASSESSMENT TP.docx
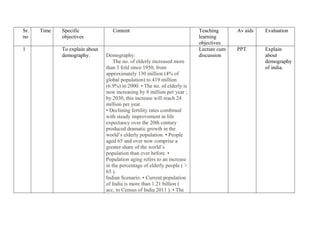
- 1. Sr. no Time Specific objectives Content Teaching learning objectives Av aids Evaluation 1 To explain about demography. Demography: The no. of elderly increased more than 3 fold since 1950, from approximately 130 million (4% of global population) to 419 million (6.9%) in 2000. • The no. of elderly is now increasing by 8 million per year ; by 2030, this increase will reach 24 million per year. • Declining fertility rates combined with steady improvement in life expectancy over the 20th century produced dramatic growth in the world’s elderly population. • People aged 65 and over now comprise a greater share of the world’s population than ever before. • Population aging refers to an increase in the percentage of elderly people ( > 65 ). Indian Scenario: • Current population of India is more than 1.21 billion ( acc. to Census of India 2011 ). • The Lecture cum discussion PPT Explain about demography of india.
- 2. total population of nation is growing at the rate of 1.41%. • In India , elderly population is over 82 million and it is expected to reach the mark of 177 million almost double by the year 2025. 2 To define geriatric. GERIATRICS DEFINITON: • It is a sub-speciality of internal medicine that focuses on health care of elderly people. • It aims to promote health by preventing and treating disease and disabilities in older adults. Lecture cum discussion leaflet Define geriatric? 3 To explain the meaning of geriatric. Meaning: • The term Geriatrics Came from the Greek word “geron” meaning “old man” and “iatros” meaning “healer”. • However , geriatrics is sometimes called medical gerontolgy. Lecture cum discussion leaflet Explain the meaning of geriatric? 4 Enumerate the theories of aging. THEORIES OF AGING A) Biological Theories of aging: 1) Programmed / Non- Stochastic Theories. - Programmed Senescence Theory Endocrine Theory. Immunology Theory. 2) Error Theories. – Wear & Tear Theory . Lecture cum discussion OHP Enumerate the theories of aging?
- 3. Cross Linking Theory. Free-radical Theory. Error Catastroph Theory. Somatic Mutation Theory. (B) Psychological Theories: 1) Personality Theory. 2) Developmental Task Theory. 3) Disengagement Theory. 4) Activity Theory. 5) Continuity Theory. 5 To explain the Programmed Senescence Theory / Hayflick Limit Theory. Programmed Senescence Theory / Hayflick Limit Theory: – In 1950’s Hayflick Suggested that the human cell is limited in no. of times it can divide, he theorized that it can divide 50 times, after which they simply stop dividing ( and hence die). He showed that nutrition has an effect on cells, with overfed cells dividing much faster than underfed cells, as cells divide to help repair and regenerate themselves. – The Hayflick Limit indicates that there is a need to slow Lecture cum dscussion PPT Explain the Programmed Senescence Theory / Hayflick Limit Theory?
- 4. down the rate of cell division if we want to live long lives. Cell division can be slowed down by diet and lifestyles etc..1) Programmed Theories: 6 To explain the Endocrine / Neuro-endocrine Theory. Endocrine / Neuro-endocrine Theory: – First proposed by Prof. Vladimir Dilman & Ward Dean MD. – The Endocrine theory states that , as we age , the endocrine system becomes less efficient and eventually leads to the effects of aging. – Hormones level are affected by factors such as stress and infection. Lecture cum discussion PPT Explain the Endocrine / Neuro- endocrine Theory? 7 To explain the Immunologic Theory. Immunologic Theory: – According to this theory , the rate of aging is controlled by the immune system . – This theory states that , as we age the no. of cells start to decrease becoming less functional. Lecture cum discussion PPT Explain the Immunologic Theory? 8 To explain the Error Theories: & Tear Theory: Error Theories: & Tear Theory: – Early Theory on aging proposed that there is a fixed storage of energy Lecture cum discussion PPT Explain the Error Theories: & Tear Theory?
- 5. available to the body . As time passes , the energy is depleted and because it can not be restored , the person dies. – Later, other theories emerged. The wear & tear theory stated that the body is like a machine that wears out its parts with repeated use. The effects of aging are caused by progressive damage to cells and body systems over time. This was not widely accepted. 9 To explain the Crossed linked theory. Crossed linked theory: – It also referred to as the glycosylation theory of aging , was proposed by Johan Bjorksten in 1942. – Acc. To this theory , an accumulation of cross- linked proteins damages cells and tissues, slowing down bodily processes resulting in aging. Lecture cum discussion PPT Explain the Crossed linked theory? 10 To explain the Free radical Theory. Free radical Theory: – Proposed by Denham Harman in 1956. – It states that organisms age because cells accumulate free radical damage Lecture cum discussion PPT To explain the Free radical Theory
- 6. over time . – A free radical is any atom or molecule that has a single unpaired electron in an outer shell. – Free radical are unstable, short lived and highly reactive, as they attack nearby molecules in order to steal their electrons and gain stability, causing radical chain reactions to occur. 11 To explain the Error catastrophe theory. Error catastrophe theory: – Proposed by Leslie Orgel in 1963. – It states that aging is the result of the accumulation of errors in cellular molecules that are essential for cellular function and reproduction that eventually reaches a catastrophic level that is incompatible with cellular survival. – Catastrophe means a sudden event causing damage or suffering. Lecture cum discussion PPT Explain the Error catastrophe theory? 12 To explain the Somatic theory or Gene mutation Somatic theory or Gene mutation theory: – It states that an important part of aging is determined by what happens to Lecture cum discussion PPT Explain the Somatic theory or Gene mutation
- 7. theory our genes after we inherit them. From the time of conception, our body’s cells are continually reproducing. Additionally , exposures to toxins, radiation or UV light can cause mutations in the body’s genes . – The body can correct or destroy most of the mutations, but not all of them. Eventually , the mutated cells accumulate, copy themselves and cause problems in the body’s functioning related to aging. theory? 13 To explain the Personality Theory. (B) Psychological Theories: 1) Personality Theory: – These theories address aspects of psychological growth without delineating specific tasks or expectations of older adults. – Some evidence suggests that personality characteristics in old age are highly correlated with early life characteristics. Lecture cum discussion PPT Explain the Personality Theory ? 14 To explain the Development Development task Theory: – The developmental tasks are Lecture cum discussion PPT Explain the Development
- 8. task Theory. activities and challenges that one must accomplish at specific stages in life to achieve successful aging. – Erikson (1963) described the primary task of old age as being able to see one’s life as having been lived with integrity . – In the absence of achieving that sense of having lived well, the older adult is at risk for becoming preoccupied with feelings of regret or dispair. task Theory? 15 To explain the Disengagement Theory. Disengagement Theory: – It describes the process of withdrawal by older adults from societal roles and responsibilities. – Acc. to this theory , this withdrawal process is predictable , systemic , inevitable, and necessary for proper functioning of a growing society. – The benefit to society is thought to be an orderly transfer of power from old to young. Lecture cum discussion PPT Explain the Disengagement Theory? 16 To explain the Activity Theory. – Lecture cum PPT Explain the
- 9. Activity Theory. This theory occurs when individuals engage in a full day of activities and maintain a level of productivity to age successfully . – It says , the more you do , the better you will age . – People who remain active and engaged tend to be happier , healthier , and more in touch with what is going on around them. discussion Activity Theory? 17 To explain the Continuity Theory. Continuity Theory. – Also called developmental theory. – This theory is the follow up to the disengagement and activity theories . – It emphasizes the individual previously established coping abilities and personal character traits as a basis for predicting how the person will adjust to changes of aging. Lecture cum discussion PPT Explain the Continuity Theory. 18 To Discuss The Changes Associated With Aging (Normal Aging A no. of physiological changes occur as we grow older. It is important to be able to recognize the changes of normal aging versus the effects of disease. • Untreated disease can result Lecture cum discussion PPT Explain The Changes Associated With Aging?
- 10. Process) in “excess disability” and reduce the quality of life of individuals. 1. Cardiovascular Changes: – Heart rate decreases. – Respiration decreases. – Systolic BP increases (aortaa) Biological aspects of aging: & other arteries thickened/stiffened) . – Valves b/w the chambers of heart thickened /stiffened. – Baro-receptors which monitor BP become less sensitive . Quick changes in position may cause dizziness from orthostatic hypotension. 2. Changes in Pulmonary system: – Lungs become stiffer , muscle strength diminishes, and chest wall become more rigid. – Total lung capacity remains constant but vital capacity decreases and residual volume increases. – Alveolar surface area decreases by up to 20%.
- 11. Alveoli tend to collapse sooner on expiration. – There is an increase in mucus production and a decrease in the activity and no. of cilia. – Body becomes less efficient In monitoring and controlling breathing. 3. Changes in genito-urinary system: – Kidney mass decreases by 25-30% and the no. of glomeruli decrease by 30-40%. These changes reduce the ability to filter and concentrate urine and to clear drugs. – With aging there is a reduced hormonal response (vasopressin) and an impaired ability to conserve salt which may increase risk for dehydration. 4. Changes in gastro- intestinal system: – Decrease in strength of muscles of mastication, taste and thirst perception.
- 12. – Decreased gatric motility with delayed emptying . – Atrophy of protective mucosa. – Malabsorption of CHO, vit B12 , vit D, folic acid and calcium. – Impaired sensation to defecate. – Reduced hepatic reserve. – Decreased metabolism of drugs. 5. Stomach : – Atrophic gastritis. – Achlorhydria (insufficient production of stomach acid). – Gastric ulcers (after the age of 60 years, and can be benign of malignant). • Liver: – Reduced blood flow. – Altered clearance of some drugs . – Diminishing the capacity to regenerate damaged liver cells. 6. • Intestine: – Prevalence of diverticulitis
- 13. increases with age. – Reduced peristalsis (intestinal muscle contractions) of large intestine. 7. Changes in Immune system: – Increased vulnerability to infections, tumors and immune disease. – Less production of antibodies. – Mortality rate from infection is much higher than in young. (example: pneumonia or sepsis, UTI.) 8. . Changes in musculo-skeletal system: – Muscles generally decrease in strength , endurance, size and weight. – Loss of about 23% of muscle mass by age 80 as both the no. and size of muscle fibers decrease. – Loss of an average of about 2 inches of height. – Compression of vertebrae, etc.
- 14. 9. Changes in Integumentary system : Skin: – Wrinkling , pigment alteration and thinning of skin. – Elastin and collagen decrease. – Reduction in size of cells. – Loss of subcutaneous layer of fatty deposits. – Inability of skin to retain moisture. 10.Hair: – by age 50 years, the hair of more than half of all is 50% gray. It is due to decrease in the production of melanin. ( can be hormonal and hereditary ). 11.Changes in sensory system: Vision: – Most common, about 95% of people aged 65 years or more report wearing glasses or need glasses to improve their vision. Lens of eye become yellowed, cloudy. Hearing: – Membrane in middle ear including the eardrum become
- 15. less flexible with age. – Vestibular begins to degenerate with age leading hearing loss. Smell: – No. of functioning smell receptors decreases. – There is an increase in the threshold for smell. Taste: – Taste also diminishes with age. – Atrophy of tongue occurs with age and this may diminishes sensitivity to taste. Touch: – Sense of touch and response to painful stimuli decreases. – Actual no. of touch receptors decreases which results in a higher threshold for touch. 12. Changes in Endocrine system: Pancreas: – Muscle cells become less sensitive to the effects of insulin produced in body. – The normal fasting glucose
- 16. level rises 6-14 mg/dl every 10 years. – Type 2 Diabetes mellitus occurs when the body develops resistance to insulin. 13.Adrenal glands: – Aldosterone levels are 30% lower in adults aged 70 to 80 years than in younger adults. Lower aldosterone levels may cause orthostatic hypotension. – Secretion of cortisol diminishes by 25% with age. Psychological aspects of aging: 1. Memory functioning: – Age related memory deficiencies have been reported in literature. – Short term memory and long term memory does not show similar changes. 2. Intellectual functioning: – These abilities of older people do not decline but do become obsolete (out of date). – The age of their formal educational experiences is
- 17. reflected in their intelligence scoring. 3. Learning abilities: – The ability to learn is not diminished by age. – Studies however, have shown that some aspects of learning do change with age. 4. Adaptation to the tasks of aging: – Loss of grief. – Attachments to others. – Maintenance of self identity. – Dealing with death. 5. Psychiatric disorders in later life: – Delirium. – Dementia. – Depression. – Schizophrenia. – Anxiety disorders. – Personality disorders & sleep disorders. c) Socio-cultural aspect of aging: Old age brings many important socially induced changes, some of which have
- 18. the potential for negative effect on both the physical & mental wellbeing of older persons. d) Sexual aspects of aging: Sexuality and the sexual needs of elderly people are frequently misunderstood, repressed and ignored. 19 To describe the Special concerns of the elderly population: 1. Retirement: – Sadock Special concerns of the elderly population: & Sadock (2007) reported that, of those people who voluntarily retire, most re-center the work force with 2 years. – The reasons they give for doing this include negative reactions to being retired , feelings of being unproductive , economic hardship , and loneliness. – Retirement has both social and economic implications for elderly individuals 2. Elder abuse : – Abuse of elderly individuals Lecture cum discussion Chart Describe the Special concerns of the elderly population?
- 19. may be psychological , physical or financial . And the Neglect may be intentional or unintentional. – Psychological abuse includes yelling, insulting, harsh commands, threats, silence and social isolation. – Physical abuse is described as striking. Shoving, beating or restraints. – Financial abuse refers to misuse or theft of finances, property to fulfill the physical needs of an individual who can not do so independently. – In addition, elderly individuals may be the victims of sexual abuse . 20 To Describe the common problems in oldage. COMMON PROBLEMS IN OLD AGE 1. • Alzheimer’s Disease: – It is a slow and gradual disease that begins in part of brain that controls memory. – It affects a greater no. of Lecture cum discussion Describe the common problems in oldage?
- 20. intellectual and emotional and behavioral abilities , it has no known cause for this disease. – As person grows older, he is at greater risk of developing Alzheimer’s . After 60, the risk is one in 20, but after 80 it is one in 5. 2. Strokes: – About 15 million people have stroke , each year it is a 2nd leading cause of death for older than 60yrs of age . • Heart disease: – Hypertension (silent killer). • Osteoarthritis : – It is most common form of arthritis . • Rheumatoid Arthritis: – Inflammation of joint lining in the synovial (free moving ) joints. 3. Diabetes: – Due to lack of movement or work in old aged people. • Urinary incontinence: – About 1/3rd of women and 10% of all men above age of 60
- 21. have incontinence. – In this people loose control over their bladder and bowel movements. 4. Social isolation. 1. STEPS TAKEN BY GOVT. o National Policy for Older Persons: It was announced in 1999 by the. Ministry of Social Justice & Empowerment Objectives are: – To enable and support voluntary organizations and NGO ’s to supplement the care provided by family. – To provide care and protection to vulnerable groups. – To provide health care facility to elderly and to promote research & training facilities to care givers. – To create awareness among elderly persons to develop themselves in to fully independent citizen. Revision of national policy on older persons: It was created in March 14,
- 22. 2010. Age of senior citizen is different for different benefits , such as: – 60 years for concession in railways. – 60 years by banks for extra 0.5% interest to senior citizen. – 63 years for concession in air journey by Indian airlines. – 65 years for benefit to senior citizens under income tax. 20 Summary We have seen the following points in the seminar: To explain about demography. To define geriatric. To explain the meaning of geriatric Enumerate the theories of aging. To explain the Programmed Senescence Theory / Hayflick Limit Theory. To explain the Immunologic Theory. To explain the Error Theories: & Tear Theory To explain the Crossed linked theory To explain the Free radical Theory. To explain the Error catastrophe theory. To explain the Somatic theory or
- 23. Gene mutation theory To explain the Personality Theory. To explain the Development task Theory To explain the Disengagement Theory. To explain the Activity Theory To explain the Continuity Theory. To Discuss The Changes Associated With Aging (Normal Aging Process) To describe the Special concerns of the elderly population: Bibliography 21 Bibliography Bibliography: Basheer. P, shabeerkhan . Yasmeen S. A concise textbook of advanced nursing practice first edition; EM-ESS medical publisher; page no . 455-460 • Kaplan, shaddok “ Concise Text Book of Psychiatry”, page no: 300-4315.
- 24. • Barbara Kozier “Fundamentals of Nursing” Pearson Education. 7th edition.Page no.987-961 • Taylor, Lillis, Lemone “Fundamentals of Nursing-art and science of Nursing Care” lippincott, 4th edition.Page no.1222-1226 • Ruth F Craven,J Hirne “Fundamentals of Nursing” lippincott, 3rd edition.Page no.1173-1187