This document defines and provides information about the Poisson distribution:
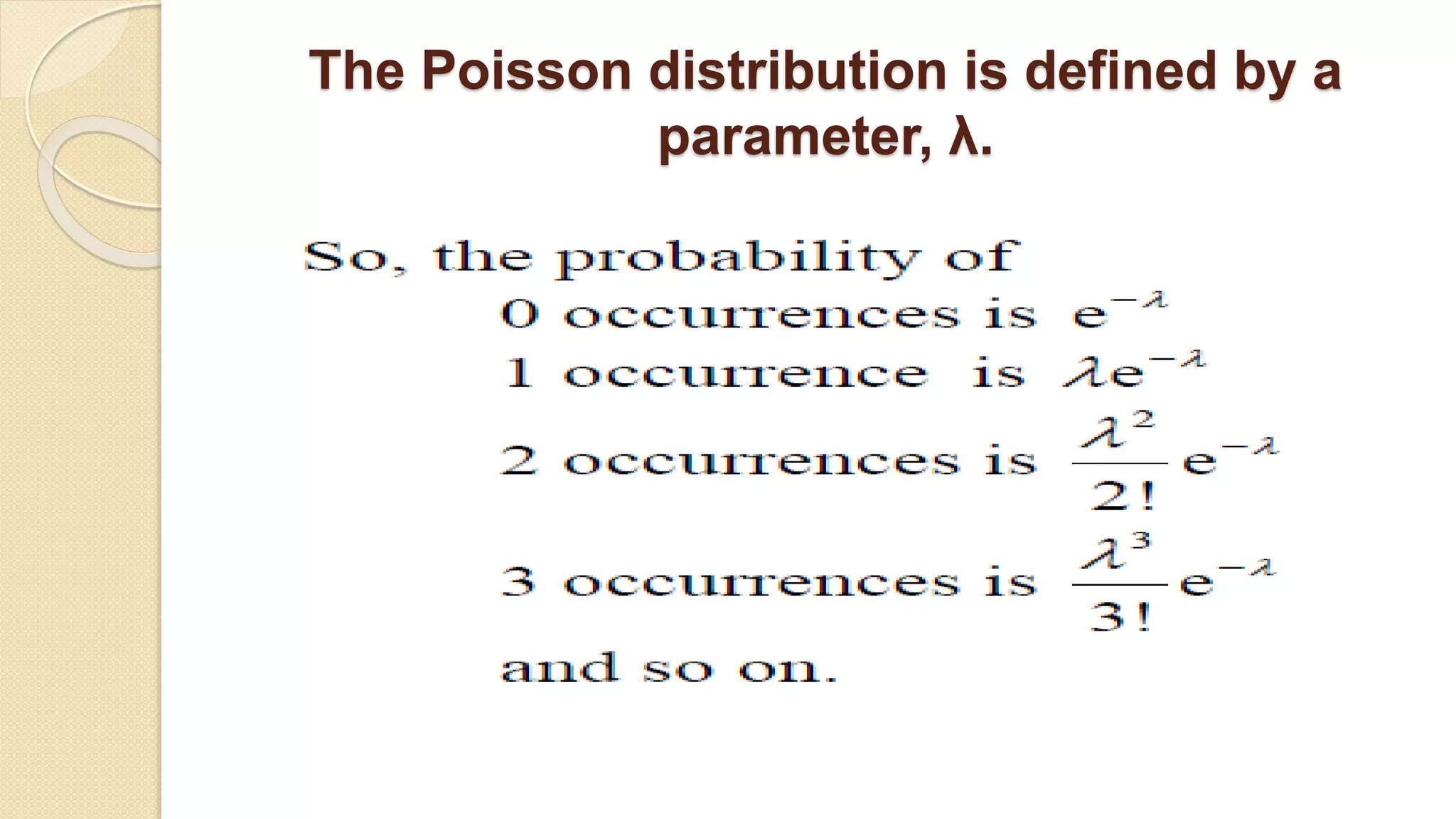
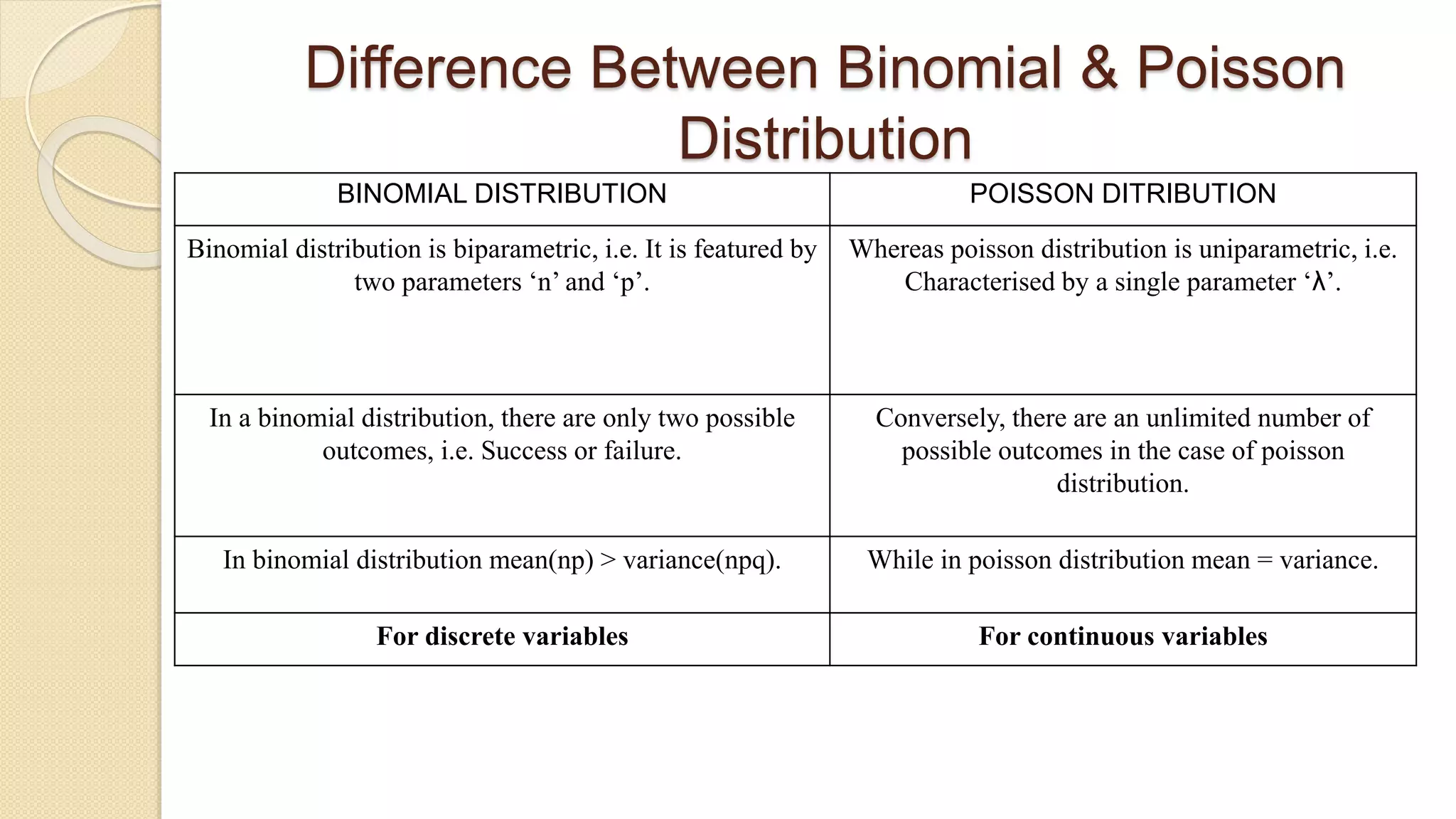
- The Poisson distribution results from Poisson experiments and is characterized by a single parameter λ, the expected number of events occurring in a fixed interval of time or space.
- The Poisson distribution formula uses λ and e to calculate the probability of a given number of events (x) occurring.
- Examples are provided to demonstrate calculating probabilities using the Poisson distribution for situations like births at a hospital and product failures.
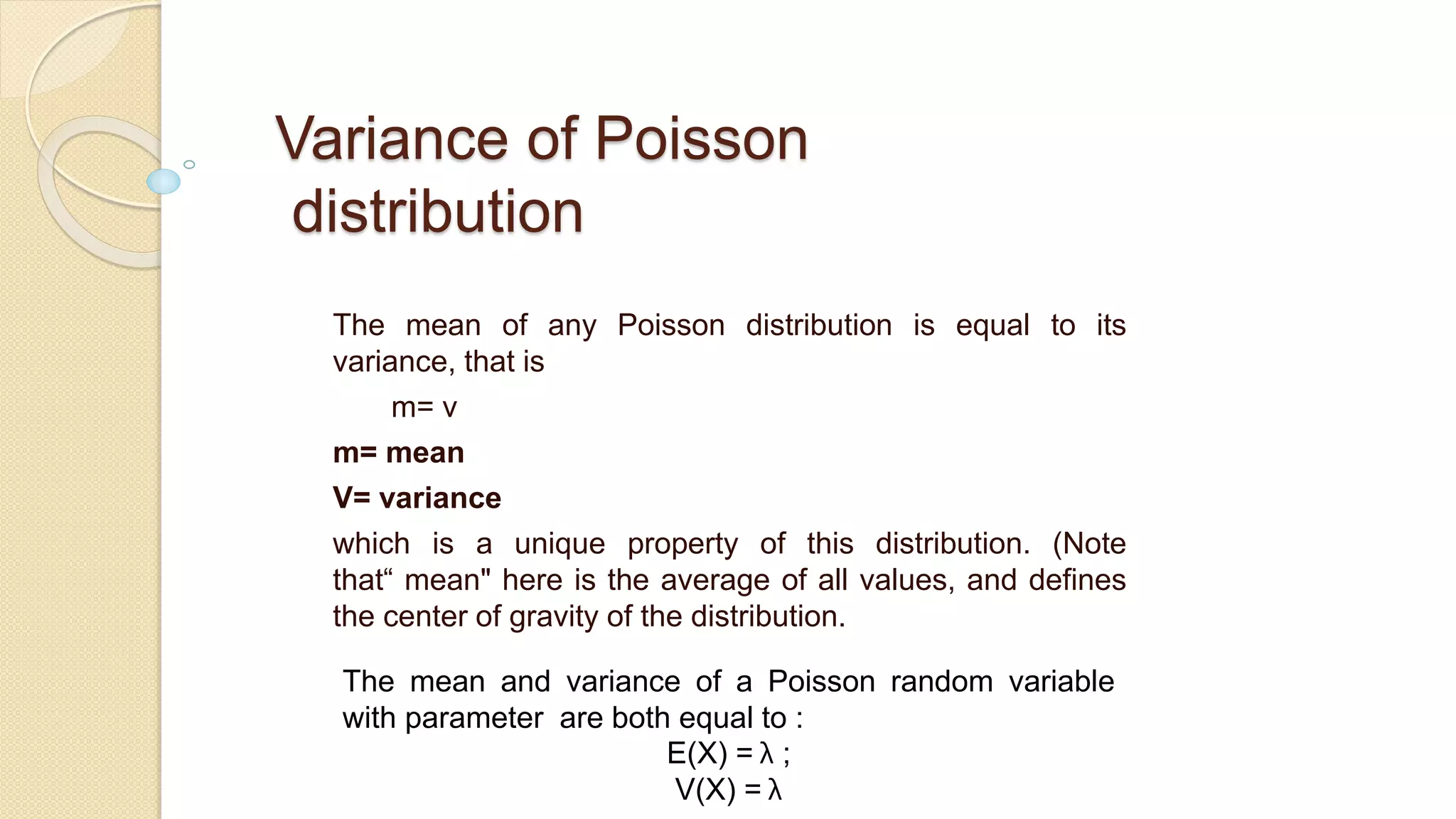
- Key properties of the Poisson distribution are that the mean and variance are both equal to λ.