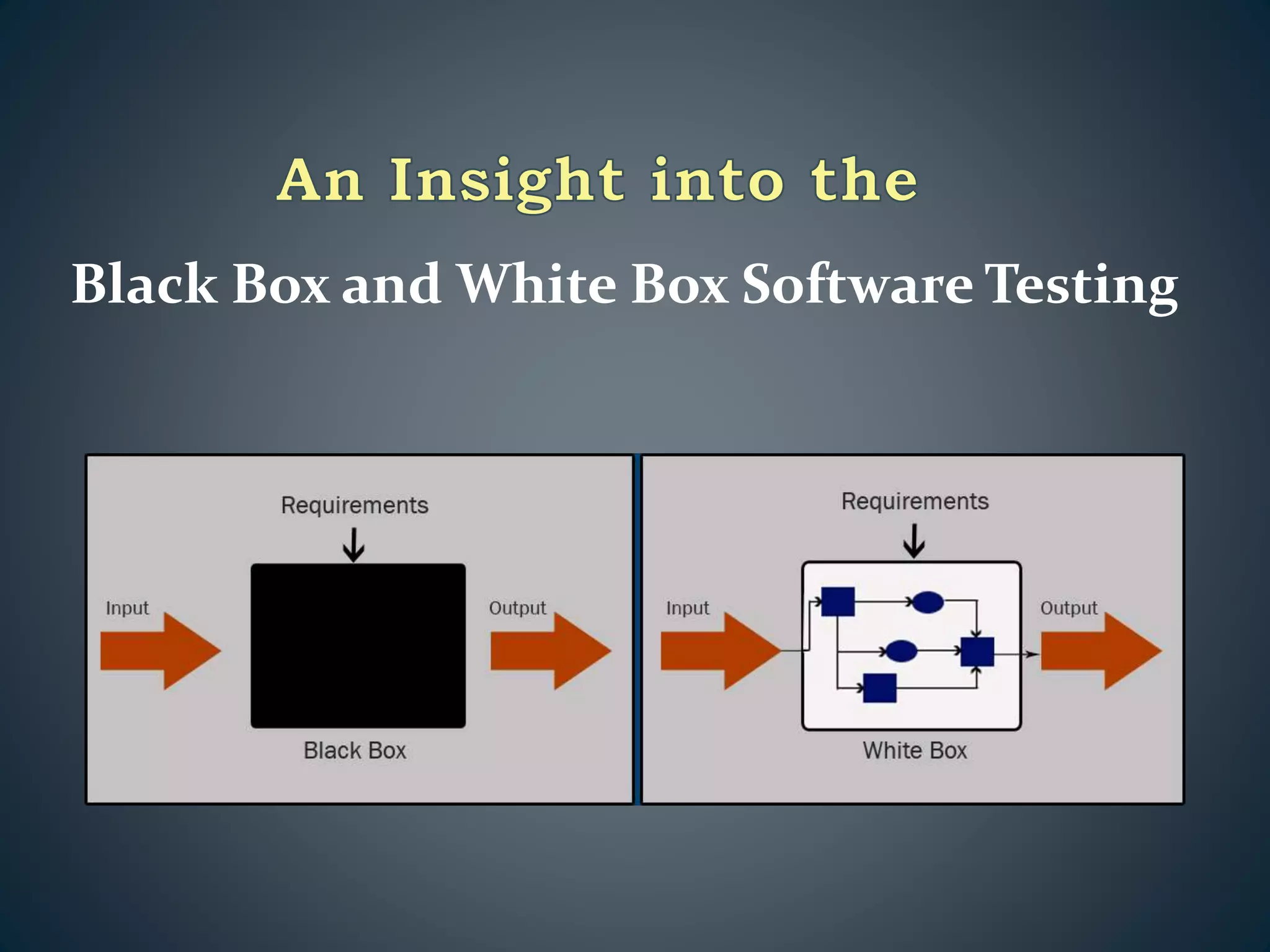
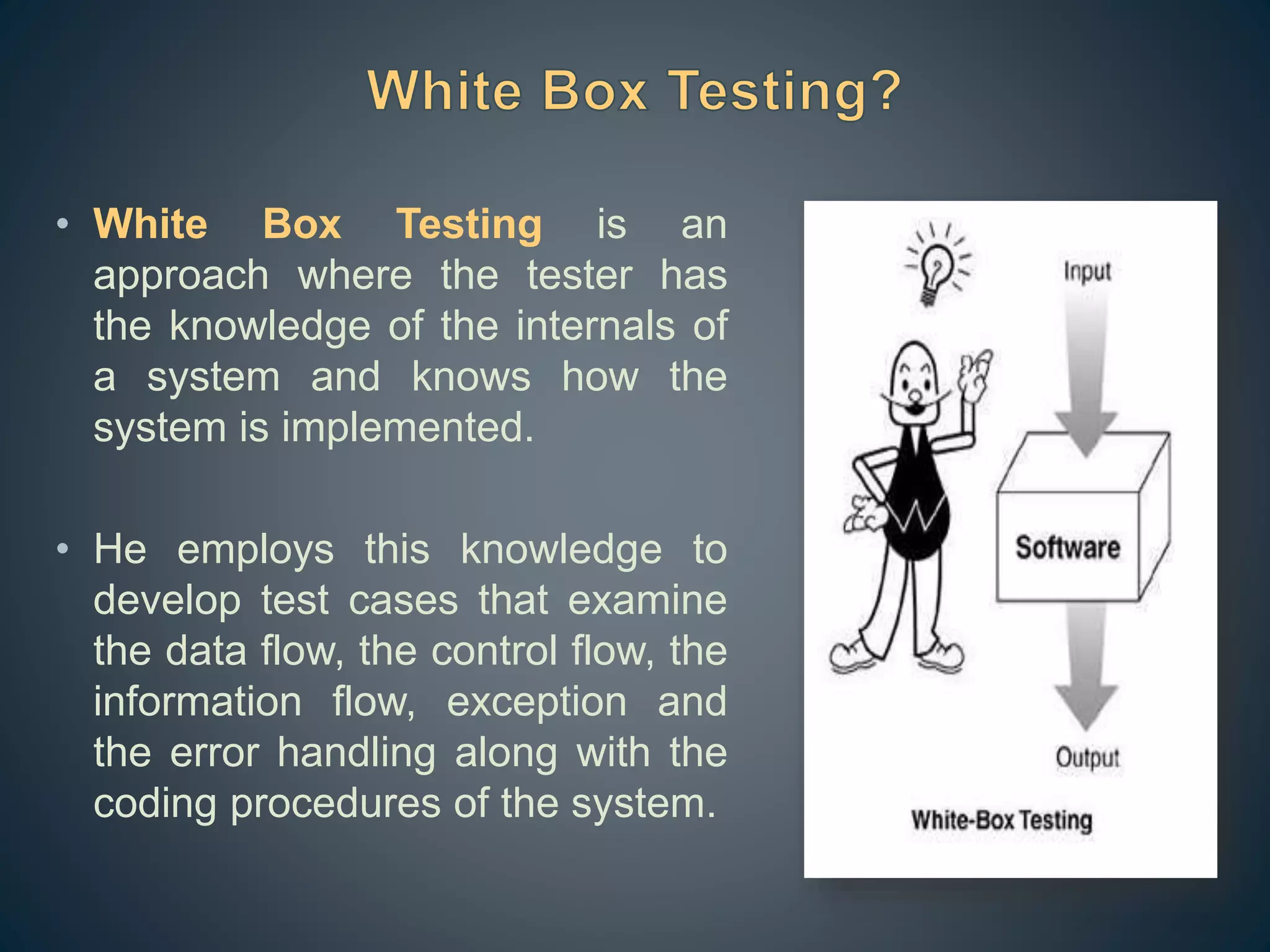
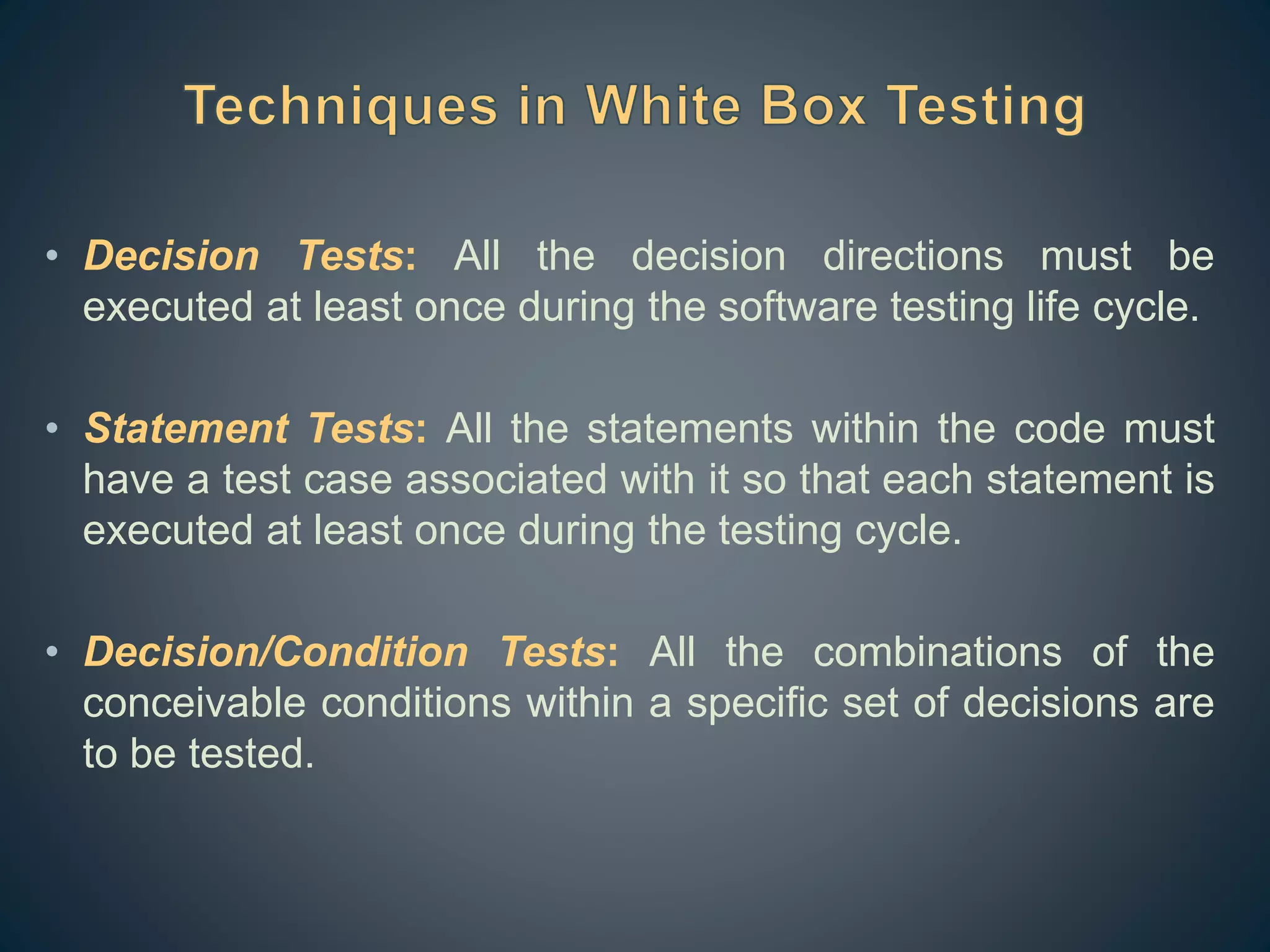
The document outlines two primary software testing approaches: black box and white box testing. White box testing involves knowledge of a system's internals to create test cases focused on data and control flows, while black box testing treats the system as an unknown entity, emphasizing functional requirements based on specifications. Various testing techniques such as boundary value analysis and equivalence class partitioning are discussed to enhance test case efficiency and coverage.