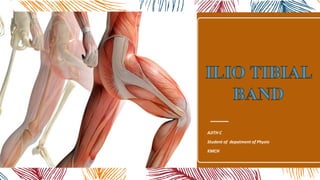
Deep layer of (Iliotibial) IT band
- 1. AJITH C Student of depatment of Physio KMCH
- 2. Another Names: IT band (Iliotibial band) Iliotibial tract Maissiat’s band
- 4. Synapses – Introduction – Anatomy – Special features – Biomechanical functions – Applied anatomy (patho anatomy) – Examination
- 5. INTRODUCTION – The thigh is enveloped in a layer of Fibrous tissue known as the Fascia latae , which thickens in the lateral side of thigh and is described as the iliotibial band (ITB). – The iliotibial band (ITB) is a thick band of fascia formed proximally at the hip by the fascia of the Tensor fasciae Latae (TFL) , Gluteus Maximus, and Gluteus Medius muscles. – The ITB is connected intimately with the TFL anteriorly and the gluteus maximus posteriorly in the region distal to the greater trochanter. – Ilio means ilium bone of pelvis, tibial means tibia leg (shine) bone. The name itself says that it is extended from the ilium to the tibia.
- 7. Fascia lata – Fascia is classified into 3 ; Superficial fascia Deep fascia Visceral fascia
- 8. – Intro : the fascia lata is a deep fascial investment of the whole thigh musculature and is analogous to a strong, extensible and elasticated stocking. It begins most proximally around the iliac crest and Inguinal ligament and ends most distally to the bony prominence of the Tibia , where it continues to becomes the deep fascia of the leg (the Crural fascia). – There are 3 modifictions of the Fascia lata, which are known as the; SAPHENOUS OPENIG ILIOTIBIAL TRACT INTERMUSCULAR SEPTA
- 9. Attachment – The fascia lata forms multiple superior attachments around the pelvis and Hip region. Posterior : sacrum and coccyx Lateral : iliac crest Anterior : inguinal ligament , Superior pubic rami. Medial : inferior ischiopubic rami , Ischial tuberosity , Sacrotuberous ligament. – The fascia lata is also continuous with regions of deep and superficial fascia at its superior aspect. The deep iliac fascia descends from the thoracic region at the diaphragm.
- 10. – It covers the entire iliacus and psoas regions and blends with the fascia lata superiorly. Superficial fascia from the inferior abdominal wall (Scarpa’s fascia) and perineal region both blend with the fascia lata just below the inguinal ligament. – The lateral thickening of fascia lata forms the Iliotibial tract and receives tendon insertions superiorly from gluteus maximus and TFL . The widened band of fibers descends the lateral thigh and attaches to the lateral tibial condyle on the anterolateral (Gerdy’s) tubercle.
- 11. – The fascia lata ends at the Knee joint where it then becomes the deep fascia of the leg (the Crural fascia). Attachments are made at bony prominence around the knee including the femoral and tibial condyles, patella, head of fibula and the tibial tuberosity. – The deep aspect of fascia lata produces 3 intermuscular septa which attach centrally to the femur. The lateral septum joins to the lateral lip of linea aspera and the medial &anterior septa attach to the medial lip. These attachments then continue along the whole length of the femur to include the supra condylar lines.
- 12. Tensor fascia latae (TFL) – Tensor – to tense , fascia – band , latae – side or lateral. – Origin : It arises from the anterior part of the iliac crest (Outer edge of the iliac crest and lateral to the Sartorius) , Anterior superior iliac spine (ASIS). – Insertion : Anterior border upper part of the ITB. – Nerve supply : Superior gluteal nerve (L4-S1). – Action: Flexion , Abduction, Medial rotation of the Hip.
- 14. Gluteus maximus – “It is the Thickest muscle in our Human body.” – Origin : Posterior gluteal surface of illium, and the adjacent part of the iliac crest. The side of coccyx and posterior aspect of Sacrum. Fibers also attaches to the upper Sacrotuberous ligament and aponeurosis of the Sacrospinalis. – Insertion : posterior border of Upper part of the Iliotibial band & deep fibers inserted into the gluteal tuberosity of femur.
- 15. – Nerve supply : Inferior gluteal nerve (L5-S2). – Action : Extension & lateral rotaion of the Hip joint, Upper fibers – abduction of the hip joint, Lower fibers – adduction of the hip joint.
- 16. Gluteus medius – Origin : Anterior and posterior gluteal surface of the illium. – Insertion : Antero lateral surface of greater trochanter of femur. – Nerve supply : Superior gluteal nerve (L4-S1). – Action : Abduction and Medial rotation of the Hip joint.
- 18. Origin – The band consist of 3 layers. They are, Superficial, Intermediate and Deep layer. – Superficial- it arises from the iliac crest, superficial to the TFL. – Intermediate- it arises from the ilium slightly distal to the proximal attachment of the TFL and lies deep to the muscles. – Deep- it arises from the Supra- Acetabular fossa between the hip capsule and the tendon of the reflected head of the rectus femoris.
- 19. Insertion – The ilio tibial band continues distally to attach to the lateral inter muscular septum(which is firmly anchored to the linea aspera of the femur) and inserts into the anterolateral surface of Tibial condyle onto an attachment site known as Gerdy’s tubercle. – The IT band also attaches to the patella via the lateral patellofemoral ligament (Ilio patellar band) of the lateral retinaculum and biceps femoris tendon. – The superficial and intermediate layers of the ITB merge at the distal end of the TFL and serve as the tendon of the TFL. – The deep layer merges into the ITB just distal to where the superficial and intermediate layers of the ITB fuse.
- 21. – The 3 layers of the ITB fuse in the region of the greater trochanter and forms the proximal ITB. The ITB is not fixed at the greater trochanter, but uses it as a diversion point. – The ilio tibial band can be viewed as (1)tendinous portion and (2)ligamentum portion. – (1) a tendinous portion consisting of the proximal band to the lateral femoral epicondyle attachment , and – (2) a ligamentum portion between the lateral femoral epicondyle and Gerdy’s tubercle on the tibia.
- 23. Nerve supply NERVE SUPPLY : – TFL inserted into the ITB and is innervated by the Superior gluteal nerve (L4,L5,S1) – The Gluteus maximus muscle also inserts into the ITB and is innervated by the Inferior gluteal nerve (L5,S2). – Sensation to the overlying skin is provided by 2 sources; Predominate supply is from the lateral femoral cutaneous nerve Superior portion of the skin cephalad to the greater trochanter is innervated by the lateral cutaneous branch of T12.
- 25. Comments by Robert Schleip – This third layer (deep layer) of the ITB is mostly (in 83% of the cases) not connected with the TFL muscle, and of course also not connected with any Gluteal muscle . – Is there any other muscular forces to tension this fascial layer for adapting its Morphology? That is expansional tension of the Vastus lateralis muscle. – Vastus lateralis muscle contraction will increase its diameter and therby stretch the overlying fibers of the deep layer of ITB. While this also effects the other 2 layers of the ITB. – the described independence of this third layer from the usual proximal muscular extension puts an additional emphasis on the importance of the Vastus lateralis for the functioning of the ITB.
- 27. AUSTRIAN STUDY; Superficial / Intermediate Length- 50cm (50.1 ± 3.8cm) layer Length - 10cm (10.4 ± 1.3cm) Deep layer - Width - 3cm (3.3 ± 0.6cm) Thickness - 584µm
- 29. – Insertion point of ITB reinforcing the anterolateral aspect of the Knee joint(stabilizes the knee laterally). – Despite the muscular attachments to the proximal end of the ITB, it remains an essentially passive structure of the knee joint. For example , a contraction of the TFL or the gluteus maximus muscles that attach to the proximal end of the ITB produce only minimal longitudinal excursion of the band distally. – Fiberous band moves or “rolls” over the lateral femoral condyle during knee flexion/extension because fibrous connections have been observed to firmly attach the ITB to the femoral condyle. Thus, the ITB remains consistently taut, regardless of the position of the Hip or Knee. Despite its lateral location, the ITB alone provides only minimal resistance to lateral joint space opening.
- 30. With the knee flexed , however, the combination of the ITB , the lateral collateral ligament and the popliteal tendon can provide even greater assistance in resisting anterior displacement of the tibia on the femur as well as increase the stability of the lateral side of the joint.
- 31. – Additional fibrous connections from the ITB to the biceps femoris and vastus lateralis muscles from a sling behind the lateral femoral condyle, which assist the anterior cruciate ligament in restraining posterior femoral (or anterior tibial) translation with the knee near full extension. – Patella attachment portion of the ITB become tense as the knee moves in to a flexed position. As we shall see, this attachment of the ITB to the lateral border of the patella may affect the patellofemoral joint function. – Postural function: The ITB is of critical importance to asymmetrical standing (pelvic slouch). The upward pull on the lower attachment of the ITB thrusts the knee back into hyperextension, thereby locking the knee and converting the limb into a rigid supportive pillar.
- 32. – Adipose tissue is present between the ITB and bony interface. As the knee moves from full extension to 30˚ of flexion , compression of the highly vascularized and richly innervated adipose tissue increases between the ITB and the lateral epicondyle of femur. – The adipose tissue is less compressed in full extension, which may account for the complaints of pain at the distal insertion of the ITB during 30˚ of flexion and not at full extension in patients with iliotibial band symptoms. – Deep layer stabilizes the anterior aspect of the hip joint as well as the Rectus femoris and vastus lateralis. – It also allows the TFL and Gluteus maximus muscles to support the extension of the knee while standing , walking , running and biking. – Action; flexion , abduction , and external rotation of the Hip joint*
- 35. PATHO ANATOMY or (applied anatomy) 1) Snapping syndrome of Hip / snapping Hip syndrome (coxa saltans) 2) Greater trochanteric pain syndrome (GTPS) / Trochanteric bursitis . 3) Iliotibial band syndrome (ITBS) / Iliotibial band friction syndrome (ITBFS) / IT band insertion pain syndrome
- 36. 4) It also creates the Lateral patellar tracking syndrome / patellofemoral pain syndrome / Anterior knee pain syndrome / patellar overload syndrome (Because the ITB also attaches to the patella via patello femoral ligament or iliopatellar band).
- 37. EXAMINATION or DIAGNOSIS – Ober’s test and Modifyed ober’s test – Renne test – Noble’s test or Noble’s compression test – Self IT band syndrome test. And also, – Clark’s test or Patellar Grind test – Fabers test or Patrick’s test
- 38. REFERENCE: – B.D.Chourasia (Human anatomy) – Frank H. Netter. MD (Atlas of human anatomy) – Austrian case study (A study of Deep layer of Iliotibial band) – Evans P england . (The postural functions of ITB) – Recondo JP , Salvador E , Villanua JA (Functional anatomy of the Knee – lateral stabilization of the knee) – Grood ES , Noyes FR , Butler DL (Ligamentous and capsular restraints preventing straight medial and lateral laxity in intact human cadavers) – Fair clough J , Hayashi K , Toumi H, (Functional anatomy of the ITB during flexion and extension of the Knee) – Terry GC , hughston JC , Norwood LA (Anatomy of the iliopatellar band & ITB) – Goh LA , Chhem RK , Wang SC (ITB thickness & sonographic measurements in asymphtamatic volunteers) – Hamill J , Miller R , Noehren B (A prospective study of ITB strain in runners&clinical biomechanics) – Puniello MS, (ITB tightness & Patellofemoral dysfunctions).