IB Chemistry Equilibrium constant, Kc and Reaction quotient, Qc.
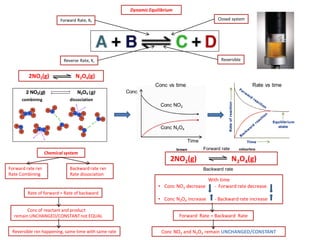
- 1. Dynamic Equilibrium Closed system Reversible Forward Rate, Kf Reverse Rate, Kr 2NO2(g) N2O4(g) Chemical system Forward rate rxn Rate Combining Backward rate rxn Rate dissociation Reversible rxn happening, same time with same rate Rate of forward = Rate of backward Conc of reactant and product remain UNCHANGED/CONSTANT not EQUAL combining dissociation Conc vs time Rate vs time Conc Time Conc NO2 Conc N2O4 With time •Conc NO2 decrease - Forward rate decrease •Conc N2O4 increase - Backward rate increase 2NO2(g) N2O4(g) Forward rate Backward rate Forward Rate = Backward Rate Conc NO2 and N2O4 remain UNCHANGED/CONSTANT brown colourless
- 2. How dynamic equilibrium is achieved in closed system? Conc of NO2 decrease ↓over time Forward rate, Kf decrease ↓ over time Forward Rate = Reverse Rate NO2 2NO2(g) N2O4(g) Conc of N2O4 increase ↑ over time N2O4 Reverse rate, Kr increase ↑ over time NO2 N2O4 1 2 Conc of reactant/product remain constant Rate 3 Time Conc NO2 N2O4 At dynamic equilibrium As reaction proceeds Concentration As reaction proceeds Rate Time Click here to view simulation
- 3. Conc vs Time How dynamic equilibrium is achieved in a closed system? 40 0 Rate forward = ½ breakdown = ½ x 40 = 20 Rate reverse = ¼ form = ¼ x 0 = 0 20 20 Rate forward = ½ breakdown = ½ x 20 = 10 Rate reverse = ¼ form = ¼ x 20 = 5 15 25 Rate forward = ½ breakdown = ½ x 15 = 8 Rate reverse = ¼ form = ¼ x 25 = 6 13 27 Rate forward = ½ breakdown = ½ x 13 = 7 Rate reverse = ¼ form = ¼ x 27 = 7 13 27 At dynamic Equilibrium Rate forward = Rate reverse Breakdown (7) = Formation (7) At dynamic Equilibrium Conc reactant 13 /Product 27 constant Rate vs Time 1/ 4 1/ 2 .. tan .. .. tan .. 1 1 rate cons t reverse rate cons t forward K K 2 13 27 tan reac t product Kc 2 1/ 4 1/ 2 1 1 K K Kc or
- 4. Dynamic Equilibrium Reversible (closed system) Forward Rate, K1 Reverse Rate, K-1 Kc = ratio of molar conc of product (raised to power of their respective stoichiometry coefficient) to molar conc of reactant (raised to power of their respective stoichiometry coefficient) Conc of product and reactant at equilibrium At Equilibrium Forward rate = Backward rate Conc reactants and products remain CONSTANT/UNCHANGE Equilibrium Constant Kc aA(aq) + bB(aq) cC(aq) + dD(aq) coefficient Solid/liq not included in Kc Conc represented by [ ] K1 K-1 a b c d c A B C D K 1 1 K K Kc Equilibrium Constant Kc express in Conc vs time Rate vs time A + B C + D Conc Time Click here notes on dynamic equilibrium Excellent Notes rate cons t reverse rate cons t forward K K .. tan .. .. tan .. 1 1
- 5. Large Kc • Position equilibrium shift to right • More products > reactants Magnitude of Kc a b c d c A B C D K Extend of reaction How far rxn shift to right or left? Not how fast a b c d c A B C D K Small Kc • Position equilibrium shift to left • More reactants > products c K c K Position of equilibrium 2CO2(g) ↔ 2CO(g) + O2(g) 92 3 10 c K 2H2(g) + O2(g) ↔ 2H2O(g) 81 310 c K H2(g) + I2(g) ↔ 2HI(g) 2 8.710 c K 1 Kc • Position equilibrium lies slightly right • Reactants and products equal amount Reaction completion Reactant favoured Reactant/Product equal Product favoured c K Temp dependent Extend of rxn Not how fast
- 6. Equilibrium Constant Kc a b c d c A B C D K aA(aq) + bB(aq) cC(aq) + dD(aq) Conc of product and reactant at equilibrium Equilibrium expression HOMOGENEOUS gaseous rxn 4NH3(g) + 5O2(g) ↔ 4NO(g) + 6H2O(g) N2(g) + 3H2(g) ↔ 2NH3(g) NH4CI(s) ↔ NH3(g) + HCI(g) 2SO2(g) + O2(g) ↔ 2SO3(g) 5 2 4 3 6 2 4 NH O NO H O Kc 3 2 1 2 2 3 N H NH Kc 1 1 3 K NH HCI c 0 4 1 1 3 NH CI NH HCI Kc 1 2 2 2 2 3 SO O SO Kc Equilibrium expression HETEROGENOUS rxn CaCO3(s) ↔ CaO(g) + CO2(g) 0 3 1 2 1 CaCO CaO CO Kc 1 2 1 K CaO CO c CH3COOH(l) + C2H5OH(l) ↔ CH3COOC2H5(l) + H2O(l) 1 2 5 1 3 1 2 1 3 2 5 CH COOH C H OH CH COOC H H O Kc Equilibrium expression HOMOGENEOUS liquid rxn Cu2+ (aq) + 4NH3(aq) ↔ [Cu(NH3)4]2+ 4 3 2 1 2 3 4 ( ) Cu NH Cu NH Kc Reactant/product same phase Reactant/product diff phase
- 7. aA bB 2aA 2bB bB aA aA bB aA bB a b c A B K aA bB Equilibrium Constant Kc Equilibrium Constant Kc b a c B A K ' c c K K ' 1 inverse X2 coefficient ' 2 c c K K coefficient 2 1 a b c A B K 2 1 2 1 ' c c c K K 2 K ' 1 a b c A B K a b c A B K a b c A B K 2 2 ' 2 1 aA bB bB cC a b ci A B K b c cii B C K + 2 reactions + aA cC a c a b b c c A C A B B C K ' c cii ci K K K ' Effect on Kc Inverse Kc Square Kc Square root c K Multiply both Kc 2 1 cii K ci K
- 8. N2(g) + O2(g) ↔ 2NO(g) 2NO(g) + O2(g) ↔ 2NO2(g) 19 2.3 10 ci K 6 310 cii K 2NO2(g) ↔ N2(g) + 2O2(g) 13 19 6 7 10 2.3 10 3 10 c c c ci cii K K N2(g) + 2O2(g) ↔ 2NO2(g) K K K 13 7 10 c K ' 12 13 ' 1.42 10 7 10 1 1 c c c K K K HF(ag) ↔ H+ (aq) + F - (aq) H2C2O4(ag) ↔ 2H+ (aq) + C2O4 2 - (aq) 4 6.8 10 ci K 6 3.8 10 cii K 2HF(ag) + C2O4 2- ↔ 2F - (aq) + H2C2O4(aq) 2HF(ag) ↔ 2H+ (aq) + 2F - (aq) 2H+ (ag) + C2O4 2- ↔ H2C2O4(aq) ' 2 4 2 7 6.8 10 4.6 10 c ci K K 5 6 '' 2.6 10 3.8 10 1 1 cii c K K 4.6 10 2.6 10 0.12 7 5 ' '' c c c c K K K K Kc for diff rxn Adding 2 rxns + Inverse rxn Adding 2 rxns 2HF(ag) + C2O4 2- ↔ 2F - (aq) + H2C2O4(aq) + HF(ag) ↔ H+ (aq) + F - (aq) 4 6.8 10 ci K x2 coefficient H2C2O4(ag) ↔ 2H+ (aq) + C2O4 2 - Inverse rxn 6 3.8 10 cii K 2HF(ag) ↔ 2H+ (aq) + 2F - (aq) 2H+ (ag) + C2O4 2- ↔ H2C2O4(aq) Add 2 rxn ' 7 4.6 10 c K '' 5 2.610 c + K Effect on Kc Effect on Kc Inverse rxn Inverts expression Doubling rxn coefficient Squares expression Tripling rxn coefficient Cubes expression Halving rxn coefficient Square root expression Adding 2 reactions Multiplies 2 expression c K 1 2 c K 3 c K c K ii c i c K K Square Kc Invert Kc Multiply Kc 1 2 3 N2(g) + 2O2(g) ↔ 2NO2(g)
- 9. H2 + I2 ↔ 2HI 50 c K 1 2 1 2 2 H I HI Kc 2HI ↔ H2 + I2 2 1 2 1 ' 2 HI H I Kc 0.02 50 ' 1 1 c c K K 2SO2 + O2 ↔ 2SO3 1 2 2 2 2 3 SO O SO Kc 200 c K SO2 + O2 ↔ SO3 200 14.1 ' c c K K 2 1 4SO2 + 2O2 ↔ 4SO3 40000 200 , ' 2 2 c c c K K K N2(g) + 3H2(g) ↔ 2NH3(g) 3 2 1 2 2 3 N H NH Kc Kc is 170 at 500K Determine if rxn is at equilibrium when conc are at: [N2] =1.50, [H2] = 1.00, [NH3] = 8.00 1.501.00 8.00 3 2 1 2 2 3 c c Q N H NH Q • Rxn not at equilibrium • Shift to right, favour product • Qc must increase, till equal to Kc IB Questions Determine Kc for inversing rxn inverse Determine Kc for halving rxn 2 1 1 2 2 2 2 3 SO O SO Kc halving Determine Kc for doubling rxn 2SO2 + O2 ↔ 2SO3 doubling 1 2 2 2 2 3 SO O SO Kc 200 c K 2 1 2 2 2 2 3 SO O SO Kc 1 2 4 3 170 c 42.7 K c Q c c Q K
- 10. Kc and Qc H2(g) + I2(g) ↔ 2HI(g) c K Constant at fixed Temp 1 2 1 2 2 H I HI Kc At equilibrium Independent of initial conc Initial conc of H2 , I2 and HI 4.00 c Q 1 2 1 2 2 H I HI Qc 46.4 1.14 10 0.12 10 2.52 10 2 1 2 1 2 2 c K 46.4 c K Expt Initial Conc H2 Initial Conc I2 Initial Conc HI 1 0.0500 0.0500 0.100 Initial conc of H2 , I2 and HI Expt Initial Conc H2 Initial Conc I2 Initial Conc HI 1 2.40 x 10-2 1.38 x 10-2 0 Expt Equilibrium Conc H2 Equilibrium Conc I2 Equilibrium Conc HI 1 1.14 x 10-2 0.12 x 10-2 2.52 x 10-2 At equilibrium conc Not at equilibrium H2(g) + I2(g) ↔ 2HI(g) 4.00 0.050 0.050 0.100 2 c Q Predict the direction of rxn Difference between c Q Conc of product/reactant at equilibruim conc Reaction quotient at particular time Not at equilibrium conc Varies NOT constant
- 11. Kc and Qc H2(g) + I2(g) ↔ 2HI(g) 1 2 1 2 2 H I HI Kc 46.4 1.14 10 0.12 10 2.52 10 2 1 2 1 2 2 c K 46.4 c K At equilibrium conc c c Q K c c Q K c c Q K Reaction at equilibrium More product > reactant Rxn shift left more reactant → c c Q K c Q Bring Qc down More reactant > product Rxn shift right → more product Bring Qc up c Q c c Q K c Q Expt Initial Conc H2 Initial Conc I2 Initial Conc HI 1 0.0500 0.0500 0.100 Initial conc of H2 , I2 and HI 1 2 1 2 2 H I HI Qc 4.00 0.050 0.050 0.100 2 c Q c Q Expt Initial Conc H2 Initial Conc I2 Initial Conc HI 1 0.0250 0.0350 0.300 Initial conc of H2 , I2 and HI 1 2 1 2 2 H I HI Qc 103 0.0250 0.0350 0.300 2 c Q Click here to view notes
- 12. Kc from reaction stoichiometry H2(g) + I2(g) ↔ 2HI(g) K same 46.4 c 1 2 1 2 2 H I HI Kc 4 diff initial conc of H2 , I2 and HI At equilibrium Kc = 46.4 ( 730K) 46.4 1.14 10 0.12 10 2.52 10 2 1 2 1 2 2 c Rxn 1 K same Qc = Kc - rxn at equilibrium, no side/shift occur Qc < Kc – rxn shift right, favour product Qc > Kc – rxn shift left, favour reactant Rxn 2, 3, 4 diff initial conc more products H2(g) + I2(g) ↔ 2HI(g) c Q Rxn shift to right more reactants Rxn shift to left reac t product Qc tan reac t product Qc tan c Q c c Q K c c Q K c c Q K 1 2 1 2 2 H I HI Kc
- 13. Kc and Qc H2(g) + I2(g) ↔ 2HI(g) 1 2 1 2 2 H I HI Kc 4.00 c Q 1 2 1 2 2 H I HI Qc 46.4 1.14 10 0.12 10 2.52 10 2 1 2 1 2 2 c K 46.4 c K Expt Initial Conc H2 Initial Conc I2 Initial Conc HI 1 0.0500 0.0500 0.100 Initial conc of H2 , I2 and HI At equilibrium conc Not at equilibrium H2(g) + I2(g) ↔ 2HI(g) 4.00 0.050 0.050 0.100 2 c Q c c Q K c c Q K Reaction at equilibrium More reactant > product Rxn shift right → more product Bring Qc up c Q c Q c c Q K 4.00 c Q 46.4 c < K
- 14. Kc and Qc H2(g) + I2(g) ↔ 2HI(g) 1 2 1 2 2 H I HI Kc 103 c Q 1 2 1 2 2 H I HI Qc 46.4 1.14 10 0.12 10 2.52 10 2 1 2 1 2 2 c K 46.4 c K Initial conc of H2 , I2 and HI At equilibrium conc Not at equilibrium H2(g) + I2(g) ↔ 2HI(g) c c Q K c c Q K Reaction at equilibrium More product > reactant Rxn shift left more reactant → c c Q K c Q Bring Qc down c Q Expt Initial Conc H2 Initial Conc I2 Initial Conc HI 1 0.0250 0.0350 0.300 103 0.0250 0.0350 0.300 2 c Q 103 c Q 46.4 c > K
- 15. How dynamic equilibrium is shifted when H2 is added ? • Add H2 , Qc decrease • Position equilibrium shift to right • Rate forward and reverse increase • New equilibrium conc achieved when Rate forward Kf = Rate reverse Kr • More product NH3 ,but Kc unchanged N2(g) + 3H2(g) ↔ 2NH3(g) 4.07 c K Equilibrium disturbed H2 added. More reactant At equilibrium Conc reactant/product no change At new equilibrium Conc reactant/product no change 2.24 c Q Equilibrium Conc H2 = 0.82M Equilibrium Conc N2 = 0.20M Equilibrium Conc NH3 = 0.67M 3 2 1 2 2 3 N H NH Kc 1 3 2 0.20 0.82 0.67 c K New Conc H2 = 1.00M Conc N2 = 0.20M Conc NH3 = 0.67M 3 2 1 2 2 3 N H NH Qc 1 3 2 0.20 1.00 0.67 c Q 4.07 c K New Equilibrium Conc H2 = 0.90M New Equilibrium Conc N2 = 0.19M New Equilibrium Conc NH3 = 0.75M 1 3 2 0.19 0.90 0.75 c K 3 2 1 2 2 3 N H NH Kc 4.07 c K Shift to the right - Increase product - New Conc achieve - Qc = Kc again c c Q K
- 16. How dynamic equilibrium is shifted when H2 is added ? • Add H2 , Qc decrease • Position equilibrium shift to right • Rate forward and reverse increase • New equilibrium conc achieved when Rate forward Kf = Rate reverse Kr • More product NH3 ,but Kc unchanged Rate forward Kf = Rate reverse Kr N2(g) + 3H2(g) ↔ 2NH3(g) 4.07 c K 4.07 c c Q K Equilibrium disturbed H2 added. More reactant c c Q K Equilibrium shift to right Rate forward Kf > Rate reverse Kr c Q At equilibrium Conc reactant/product no change At new equilibrium Conc reactant/product no change Qc increase until Qc = Kc c Q Rate forward Kf = Rate reverse Kr c c Q K c c Q K c c Q K
- 17. Click here to view simulation Click here simulation using paper clips Click here simulation on reversible rxn Click here on reversible rxn Simulation on Dynamic equilibrium Click here on equilibrium constant
