Blink reflex
- 1. Blink Reflex BY: SYED IRSHAD MURTAZA TECHNOLOGIST NEUROPHYSIOLOGY AKUH KARACHI Date: 18-07-2012
- 2. IM 18-07- 2012.
- 3. • Definition:- Reflex is an efferent response to an afferent stimulation. • Its also known as reflex arc response because there is an afferent segment, synapses with inter-neurons and then there is an efferent limb, all these making an arc of activity hence called Reflex Arc Response. IM 18-07- 2012.
- 4. INTRODUCTION : Blink reflex is essentially the electrical correlate of the clinically evoked corneal reflex. Blink reflex is capable of evaluating the cranial nerves and their proximal segments. The afferent limb of blink reflex is ophthalmic division of trigeminal (V) nerve (which can be stimulated mechanically or electrically) and the facial (VII) nerve mediates the efferent arc. IM 18-07- 2012.
- 5. Advantages • The blink reflex study is a useful electrophysiological technique for the evaluation of patients with: • ● Involvement of trigeminal or facial nerve. • ● Variety of demyelinating polyneuropathies • ● Central Lesion in the Brainstem IM 18-07- 2012.
- 6. Anatomy • The afferent limb of the blink reflex is mediated by sensory fibers of the supraorbital branch of the ophthalmic division of the trigiminal nerve (V) and the efferent limb by motor fibers of the facial nerve (VII). • Just as with the corneal reflex, ipsilateral electrical stimulation of the supraorbital branch of the trigiminal nerve elicits a facial nerve (eye blink) response bilaterally. IM 18-07- 2012.
- 7. Application Methods Position of Patient: Lying on the couch with eyes closed. Recording Electrodes : Active electrode placed laterally over the orbicularis occuli muscles Reference placed on the side of the nose, OR Chin. Ground Electrode : Placed submentally on the neck or forehead. IM 18-07- 2012.
- 8. Stimulating Site Supraorbital nerve is stimulated which is the branch of Trigeminal Nerve (Cranial Nerve V) with cathode placed over the supra-orbital foramen/notch on one side and anode placed on the forehead. IM 18-07- 2012.
- 9. PARAMETERS SWEEP TIMEVE/LOCITY: 5-10 (msec/div) • SENSITIVITY: 200 (µv/div) • FILTERS: (HFF:20Hz, LFF: 10KHz) • STIMULATION DURATION/RATE: 0.01msec/2 Hz • INTERVAL : Between successive stimuli is set at atleast 30 sec to minimize interactions between them. • (If R1 is not recorded easily, reduce the interstimulus interval to 5msec so that facilitation resulting from first stimulus permits R1 to be elicited.) IM 18-07- 2012.
- 10. BY IM/EK. 18-07-2012 10
- 11. Response to Electrical Stimulus • Stimulation of the ipsilateral supraorbital nerve results in an afferent response along the trigiminal nerve to both the main sensory nucleus of V (mid Pons) and the nucleus of the spinal tract of V (lower Pons and medulla) in the brain stem. • Through a series of interneuron’s in the Pons and lateral medulla, the nerve impulse next reaches the ipsilateral and contralateral facial nuclei, from which the efferent signal travels along the facial nerve bilaterally. IM 18-07- 2012.
- 12. IM 18-07- 12 2012.
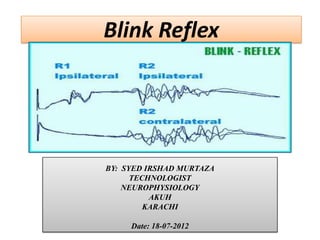
- 13. REFLEX RESPONSE • Two distinct components are there, which as following 1. EARLY R1 2. LATER R2 • 1. EARLY R1 COMPONENT: • Elicited only on the side that is stimulated. Relatively stable. Short lasting and of low amplitude. A disynaptic pathway between the main sensory nucleus of the trigeminal nerve and the ipsilateral facial nucleus. IM 18-07- 2012.
- 14. Cont, 2. LATER R2 COMPONENT Present on both sides following unilateral stimulation. More variable. Long lasting and of higher amplitude. A polysynaptic connections between the spinal nucleus of the trigeminal nerve and bilateral facial nucleus. IM 18-07- 2012.
- 15. REFLEX RESPONSE • EARLY R1 COMPONENT: • If latency > 13ms, then its abnormal • Interside difference in latency < 1.2ms. • LATER R2 COMPONENT: • If ipsilateral latency > 41ms and contralateral latency > 44ms, then its abnormal. • The latency difference between ipsilateral and contralateral response recorded simultaneously following unilateral stimulation is < 5ms. • The latency difference between R2 evoked by stimulation on each side in turn should be < 7ms. IM 18-07- 2012.
- 16. REFLEX RESPONSE • EARLY R1 COMPONENT: • Delay or absence indicates a disturbance of trigeminal or facial nerve or both on that side. • LATER R2 COMPONENT: • Involvement of R2 indicates the site of lesion when R1 is abnormal. • Trigeminal nerve lesions is characterized by bilateral delay or attenuation of R2 when the affected side of the face is stimulated. • Facial nerve lesions is characterized by delay of R2 on the affected side, whichever side is stimulated. IM 18-07- 2012.
- 17. BLINK REFLEX INDICATION • Facial /Bells palsy (facial paralysis resulting from a dysfunction of the cranial nerve VII (the facial nerve) • Polyneuropathy • Lesions of the V nerve • Synkinesis of facial muscles (involuntary movements due to miswiring of nerves after trauma) • Hemi facial spasm (frequent involuntary contractions) • Acoustic neuroma (slow-growing tumor of the nerve that connects the ear to the brain (cochlear nerve)) • Lesions in brain stem and spinal cord • Multiple Sclerosis (a chronic autoimmune disorder affecting movement, sensation, and bodily functions, caused by destruction of the myelin insulation covering nerve fibers (neurons) in the CNS ) • Wallenberg syndrome (difficulty in swallowing and hoarseness due to paralysis of the ipsilateral vocal cord.) IM 18-07- 2012.
- 18. CLINICAL APPLICATION In Bell’s Palsy, the response is initially nearly normal becoming abnormal after few days. R1 - delayed or abnormal during the first few weeks suggesting demyelination. In certain polyneuropathies - Direct response and R1 component delayed. In comatose patients and acute phase of CVA - R2 delayed. IM 18-07- 2012.
- 19. CLINICAL APPLICATION • In hemifacial spasm or facial synkinesis following aberrant reinnervation there is spread of blink reflex into muscles other than orbicularis oris. • In multiple sclerosis, the R1- delayed on one or both the sides and alterations in the R2 component is less specific. And if R2 is abnormal (with normal R1), it is suggestive of lateral medullary lesion. • In Wallenberg’s syndrome, the R1 - normal and R2 - delayed or absent bilaterally with the stimulation of the affected side of the face IM 18-07- 2012.
- 20. BLINK REFLEX PATTERNS NORMAL BLINK RESPONSE: Intact trigiminal and facial nerve IM 18-07- 2012.
- 21. Unilateral trigeminal lesion: Stimulating the affected side, there will be a delay or absence of all potentials (ipsilateral R1 and R2,contralateral R2). Stimulating the unaffected side results in normal potentials, including the ipsilateral R1 and R2 and the contralateral R2. IM 18-07- 2012.
- 22. Unilateral facial lesion: Stimulating the affected side results in delay or absence of the ipsilateral R1 and R2,but a normal contralateral R2. Stimulating the unaffected side results in a normal ipsilateral R1 and R2,but delayed or absent contralateral R2.
- 23. Unilateral midpontine lesion (main sensory nucleus V and/or lesion of the pontine interneuron’s to the ipsilateral facial nerve nucleus) or both. Stimulating the affected side results in an absent or delayed R1, but an intact ipsilateral and contralateral R2. Stimulating the unaffected side results in all normal . potentials, including R1 and ipsilateral and contralateral R2
- 24. • Unilateral medullary lesion (interneuron’s to the ipsilateral facial nerve nucleus). • Stimulating the affected side results in a normal R1 and contralateral R2, but an absent or delayed ipsilateral R2. • Stimulating the unaffected side results in normal ipsilateral R1 and R2 potential, but a delayed or absent contralateral R2. IM 18-07-2012.
- 25. Blink reflex can be affected in Demyelinating peripheral neuropathy. In demyelinating neuropathies, all potentials of the blink response may be markedly delayed or absent, reflecting slowing of either or both motor and sensory pathway IM 18-07- 2012.
- 26. Bilateral Trigeminal Nerve Nucleus lesion: Stimulating on either side will result in delayed/absent Ipsi R1 bilaterally. While bilateral Ipsi R2 and Contra R2 will remain preserved. IM/EK 18-07- 2012.
- 27. REFERENCES • EMG AND NEUROMUSCULAR DISORDER BY David C. Preston • Snell’s Human anatomy • Kimura J. Electodiagnosis in diseases of Nerve& Muscles Diligence is the mother of good fortune. IM/EK 18-07- 2012.
