Seeds, Seed Plants, Parts of a Seed, George Washington Carver, Young Plants Lesson PowerPoint
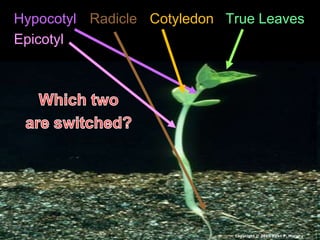
- 1. Hypocotyl Radicle Cotyledon True Leaves Epicotyl Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 3. • Next Area of Focus: ________ ? Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 4. • Activity! Imagine nuclear war broke out, or a meteor impacted on the planet, super volcanic event, or a virus killed every plant and seed, on the planet. – What next? Create a 5 step plan for you to survive. – Title your entry as your Doomsday survival plan. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 5. • Activity! Imagine nuclear war broke out, or a meteor impacted on the planet, super volcanic event, or a virus killed every plant and seed, on the planet. – What next? Create a 5 step plan for you to survive. – Title your entry as your Doomsday survival plan. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 6. • Activity! Imagine nuclear war broke out, or a meteor impacted on the planet, super volcanic event, or a virus killed every plant and seed, on the planet. – What next? Create a 5 step plan for you to survive. – Title your entry as your Doomsday survival plan. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 7. • Activity! Imagine nuclear war broke out, or a meteor impacted on the planet, super volcanic event, or a virus killed every plant and seed, on the planet. – What next? Create a 5 step plan for you to survive. – Title your entry as your Doomsday survival plan. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 8. • Activity! Imagine nuclear war broke out, or a meteor impacted on the planet, super volcanic event, or a virus killed every plant and seed, on the planet. – What next? Create a 5 step plan for you to survive. – Title your entry as your Doomsday survival plan. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 9. • Activity! Imagine nuclear war broke out, or a meteor impacted on the planet, super volcanic event, or a virus killed every plant and seed, on the planet. – What next? Create a 5 step plan for you to survive. – Title your entry as your Doomsday survival plan. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 10. • Activity! Imagine nuclear war broke out, or a meteor impacted on the planet, super volcanic event, or a virus killed every plant and seed, on the planet. – What next? Create a 5 step plan for you to survive. – Title your entry as your Doomsday survival plan. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 11. • Activity! Imagine nuclear war broke out, or a meteor impacted on the planet, super volcanic event, or a virus killed every plant and seed, on the planet. – What next? Create a 5 step plan for you to survive. – Title your entry as your Doomsday survival plan. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 12. • Activity! Imagine nuclear war broke out, or a meteor impacted on the planet, super volcanic event, or a virus killed every plant and seed, on the planet. – What next? Create a 5 step plan for you to survive. – Title your entry as your Doomsday survival plan. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 13. • Activity! Imagine nuclear war broke out, or a meteor impacted on the planet, super volcanic event, or a virus killed every plant and seed, on the planet. – What next? Create a 5 step plan for you to survive. – Title your entry as your Doomsday survival plan. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 14. • Activity! Imagine nuclear war broke out, or a meteor impacted on the planet, super volcanic event, or a virus killed every plant and seed, on the planet. – What next? Create a 5 step plan for you to survive. – Title your entry as your Doomsday survival plan. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 15. • Plants Available Sheet, Parts III, IV
- 16. • Plants Available Sheet, Parts III, IV
- 17. • Activity! Imagine nuclear war broke out, or a meteor impacted on the planet, super volcanic event, or a virus killed every plant and seed, on the planet. – What next? Create a 5 step plan for you to survive. – Title your entry as your Doomsday survival plan. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 18. • You should pack what remaining food you have and head to the Svalbard Islands to save the world. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 19. • You should pack what remaining food you have and head to the Svalbard Islands to save the world. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 20. • When you arrive in Svalbard, look for the Doomsday vault. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 21. • Head deep down the tunnel into the cold earth of the Arctic Circle….and look for? Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 22. • Video! The Doomsday Vault. – Is it worth the money? You decide. – http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QbOl72aUthM Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Learn more about the Svalbard Global Seed Vault at… http://www.regjeringen.no/en/dep/lmd/campain/svalbard-global-seed- vault.html?id=462220
- 23. • This is not a seed vault that's supposed to supply directly to farmers to plant their fields. – Insurance for crop diversity and to a way to avoid plant extinction. – Mostly for plant breeders and researchers. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 24. New Area of Focus: Seeds.
- 25. Seed: (Easy) A baby Plant. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 26. • Activity! Germination Observation – Planning ahead. Fill clear cup with water soaked cotton balls or paper towels. Place a large bean seed in cup so it’s pressed on to the side of the cup (visible). Record date and now wait. Clear cd Case will work as well.
- 28. Seed: (Hard) A mature fertilized plant ovule consisting of an embryo and its food source and having a protective coat. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 29. • Activity! External Seed Observation before dissection. – Please make detailed observations of the seeds on your table. Please include… – Seed coat – Where the seed attaches to the plant – Color – How is the seed spread? (Air, Animal, etc.) Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 30. • Activity! Seed Dissection. Please include… • Visual on next slide. – Cotyledon: Leaf of the developing plant with stored food – Seed Coat – Radicle – Hypocotyl – Embryo (Hypocotyl / Radicle) Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 31. • Plants Available Sheet, Parts III, IV
- 38. Seed Coat: Protects seed from drying out, aids in seed dispersal, open’s when conditions are right. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 39. Seed Dormancy: A period when the seed doesn’t grow. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 40. Seed Dormancy: A period when the seed doesn’t grow. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Learn more about seeds and seed dormancy at… http://www.ext.colostate.edu/mg/gardennotes/137.html
- 41. • Some seeds may remain dormant for many years. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 42. • Thick hard seed coat allows seed to be dormant. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 43. Dormant seeds can survive Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 44. Dormant seeds can survive • Freezing temperatures. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 45. Dormant seeds can survive • Freezing temperatures. • Droughts. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 46. Dormant seeds can survive • Freezing temperatures. • Droughts. • Some can survive through fire. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 47. Dormant seeds can survive • Freezing temperatures. • Droughts. • Some can survive through fire. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 48. Dormant seeds can survive • Freezing temperatures. • Droughts. • Some can survive through fire. • Conditions that would kill a growing plants. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 49. • Activity! (Optional) Trying to find dormant seeds within a soil and leaf liter sample. – Locate seed from sample. – Draw and describe it? – Dissect it if possible? – If you have more time, find another. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 50. • Plants use wind – - – - – - – - Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 51. • To pollinate. – Pollination: The transferring of pollen (plants sex cells) from one plant to another. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 52. • To pollinate. – Pollination: The transferring of pollen (plants sex cells) from one plant to another. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 53. • Which flower uses wind to pollinate, and which uses insects? Why? Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 54. • Which flower uses wind to pollinate, and which uses insects? Why? Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 55. • Which flower uses wind to pollinate, and which uses insects? Why? Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 56. • Which flower uses wind to pollinate, and which uses insects? Why? Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 57. • Which flower uses wind to pollinate, and which uses insects? Why? Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 59. • Pollen grains under electron microscope. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 60. • Which cone is the male cone, and cone is the female cone? Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 61. • Which cone is the male cone, and cone is the female cone? Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 62. • Which cone is the male cone, and cone is the female cone? Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 63. • Which cone is the male cone, and cone is the female cone? Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 64. • Which cone is the male cone, and cone is the female cone? Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 65. • Which is the male cone (pollen producer), and which is female (egg)? Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 66. • Which is the male cone (pollen producer), and which is female (egg)? Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 67. • Which is the male cone (pollen producer), and which is female (egg)? Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 68. • Which is the male cone (pollen producer), and which is female (egg)? Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 69. • Which is the male cone (pollen producer), and which is female (egg)? Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 70. • Try again, Which is male, and which is female. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 71. • Try again, Which is male, and which is female. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 72. • Try again, Which is male, and which is female. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 73. • Try again, Which is male, and which is female. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 74. • Try again, Which is male, and which is female. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 75. • By having the female cones at the top Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 76. • By having the female cones at the top, and the male cones near the bottom, Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 77. • By having the female cones at the top, and the male cones near the bottom, it increases the chances that the tree won’t self pollinate. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 78. • By having the female cones at the top, and the male cones near the bottom, it increases the chances that the tree won’t self pollinate. – You want to get new genetic information. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 79. • Female cone is generally near the top of the tree. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 80. • Female cone is generally near the top of the tree. While the smaller male (pollen producer) is scattered around. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 81. • Female cone is generally near the top of the tree. While the smaller male (pollen producer) is scattered around. – Why the top for the seed producer? Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 82. • Answer! The small paper-like seeds can easily be dispersed by the wind at the top of the tree. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Wind
- 83. • Answer! The small paper-like seeds can easily be dispersed by the wind at the top of the tree. – Being at the top ensures that it won’t self pollinate. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy D O W N
- 84. • To disperse seeds. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 85. • Plants can disperse seeds by… – Wind. – Water. – Animal. – Tension. – Fire. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 86. • Plants can disperse seeds by… – Wind. – Water. – Animal. – Tension. – Fire. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 87. • Plants can disperse seeds by… – Wind. – Water. – Animal. – Tension. – Fire. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 88. • Plants can disperse seeds by… – Wind. – Water. – Animal. – Tension. – Fire. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 89. • Plants can disperse seeds by… – Wind. – Water. – Animal. – Tension. – Fire. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 90. • Plants can disperse seeds by… – Wind. – Water. – Animal. – Tension. – Fire. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 91. • Plants can disperse seeds by… – Wind. – Water. – Animal. – Tension. – Fire. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 92. • Plants can disperse seeds by… – Wind. – Water. – Animal. – Tension. – Fire. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 93. • Plants can disperse seeds by… – Wind. – Water. – Animal. – Tension. – Fire. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 94. • Plants can disperse seeds by… – Wind. – Water. – Animal. – Tension. – Fire. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 95. • Plants can disperse seeds by… – Wind. – Water. – Animal. – Tension. – Fire. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Note: Fire doesn’t disperse the seed but triggers germination. It is covered here as it pertains to abiotic factors. Note: Fire doesn’t disperse the seed but is a necessary part of some plants life cycle.
- 96. Factors that break seed dormancy. - - - - Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 97. Mechanical Abrasion. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 98. Digestion processes of animals. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 100. Temperatures – Warm and Cold + Fire. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 101. Water Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 102. • Activity! Germination Observation – Planning ahead. Fill clear cup with water soaked cotton balls or paper towels. Place a large bean seed in cup so it’s pressed on to the side of the cup (visible). Record date and now wait.
- 103. • Activity! Germination Observation – Planning ahead. Fill clear cup with water soaked cotton balls or paper towels. Place a large bean seed in cup so it’s pressed on to the side of the cup (visible). Record date and now wait.
- 104. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 105. Germination: The process whereby growth emerges from a period of dormancy. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 106. Nice article about seeds and evironmental factors that control seed germination at… http://www.kew.org/science-research-data/kew-in-depth/msbp/seed-banking- technology/environmental-conditions-seed-germination/index.htm
- 107. • Activity! (Optional) You will be given plastic bags and seeds. Create a project that examines factors that control germination. – Set up experiment at school. • Don’t forget a control. – Conduct experiment at home over one week. – Record set-up and findings in your journal. – Plan on presenting. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 108. • Seed Coat is shed as cotyledons emerge after germination. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 110. • Has anyone ever seen a peanut tree before? Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 111. • Peanuts don’t grow on a tree, they grow underground beneath a small plant. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 112. • There is a tree in Australia called the peanut tree. – The seeds taste similar but are much different. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 113. • Caution! Many people are allergic to tree nuts and peanuts (peanuts are legumes / beans). Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 114. • Caution! Many people are allergic to tree nuts and peanuts (peanuts are legumes / beans). These allergies are real and dangerous. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 115. • Caution! Many people are allergic to tree nuts and peanuts (peanuts are legumes / beans). These allergies are real and dangerous. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 116. • These allergies are caused by the immune system thinking the harmless nut is dangerous. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 117. • These allergies are caused by the immune system thinking the harmless nut is dangerous. The body releases histamines in response which create many problems. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 118. • These allergies are caused by the immune system thinking the harmless nut is dangerous. The body releases histamines in response which create many problems. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 119. • These allergies are caused by the immune system thinking the harmless nut is dangerous. The body releases histamines in response which create many problems. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Learn more about peanut and other nut allergies at… http://www.foodallergy.org/allergens/peanut-allergy
- 120. • Has anyone ever seen a pineapple tree? Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 121. • Pineapples don’t grow high up on a tree, they grow closer to the ground at the top of a small plant. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 122. • Picture of pineapple plantation in Hawaii. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 123. • There is a tree commonly called the pineapple tree. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 124. • There is a tree commonly called the pineapple tree. It doesn’t have pineapples that you can eat, but looks like a giant pineapple. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 125. • Does anyone know who this person is? Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 126. • Answer: George Washington, born Feb. 22, 1732. – Commander of the Continental Army 1775- 1783, and the first President of the United States of America from 1789-1797. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 127. • Does anyone now who this person is? Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 128. • Answer! George Washington Carver. He is as important to the world of botany and agriculture as George Washington was the formation of this country. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 129. • Answer! George Washington Carver. He is as important to the world of botany and agriculture as George Washington was the formation of this country. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Learn more about the amazing George Washington Carver at… http://www.biography.com/people/george-washington-carver- 9240299
- 130. Activity! Reading about George Washington Carver. He is incredible. – Please answer 3 of the 6 questions below. • Describe George Washington Carver as a young boy about your age. • Describe some of the hardships that George Washington Carver had to overcome. • How did George Washington Carver overcome many of the hardships that he faced? • Name a few of George Washington Carvers many accomplishments? • What kind of person was George Washington Carver? How is he different than many other scientists? • George Washington Carver overcame extreme obstacles to achieve his hopes and dreams. How are you doing on your journey? Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 131. • George Washington Carver overcame… Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 132. • George Washington Carver overcame… – Born into slavery during Civil War. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 133. • George Washington Carver overcame… – Born into slavery during Civil War. – Doesn’t know his birthday. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 134. • George Washington Carver overcame… – Born into slavery during Civil War. – Doesn’t know his birthday. – Orphaned as an infant. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 135. • George Washington Carver overcame… – Born into slavery during Civil War. – Doesn’t know his birthday. – Orphaned as an infant. – Survived a life threatening childhood sickness. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 136. • George Washington Carver overcame… – Born into slavery during Civil War. – Doesn’t know his birthday. – Orphaned as an infant. – Survived a life threatening childhood sickness. – Survived bloody guerilla warfare in Missouri. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 137. • George Washington Carver overcame… – Born into slavery during Civil War. – Doesn’t know his birthday. – Orphaned as an infant. – Survived a life threatening childhood sickness. – Survived bloody guerilla warfare in Missouri. – Survived extreme poverty. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 138. • George Washington Carver overcame… – Born into slavery during Civil War. – Doesn’t know his birthday. – Orphaned as an infant. – Survived a life threatening childhood sickness. – Survived bloody guerilla warfare in Missouri. – Survived extreme poverty. – Endured racism for his entire life. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 139. • George Washington Carver became… – The greatest agricultural chemist the world has ever seen. – Earned B.S., M.S., D.Sc., Ph.D., Fellow of the Royal Society of Arts, London, and Director of Research and Experiment at Tuskegee Institute, Alabama. – Inducted into the Inventor Hall of Fame. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 140. • George Washington Carver became… – The greatest agricultural chemist the world has ever seen. – Earned B.S., M.S., D.Sc., Ph.D., Fellow of the Royal Society of Arts, London, and Director of Research and Experiment at Tuskegee Institute, Alabama. – Inducted into the Inventor Hall of Fame. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 141. • George Washington Carver became… – The greatest agricultural chemist the world has ever seen. – Earned B.S., M.S., D.Sc., Ph.D., Fellow of the Royal Society of Arts, London, and Director of Research and Experiment at Tuskegee Institute, Alabama. – Inducted into the Inventor Hall of Fame. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 142. • George Washington Carver became… – The greatest agricultural chemist the world has ever seen. – Earned B.S., M.S., D.Sc., Ph.D., Fellow of the Royal Society of Arts, London, and Director of Research and Experiment at Tuskegee Institute, Alabama. – Inducted into the Inventor Hall of Fame. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 143. • George Washington Carver… – He is responsible for vegetable-oils, soy bean technology, sustainable agricultural practices, hundreds of ideas and products. – His contributions have equaled billions of dollars to agriculture. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 144. • George Washington Carver… – He is responsible for vegetable-oils, soy bean technology, sustainable agricultural practices, hundreds of ideas and products. – His contributions have equaled billions of dollars to agriculture. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 145. • George Washington Carver… – He is responsible for vegetable-oils, soy bean technology, sustainable agricultural practices, hundreds of ideas and products. – His contributions have equaled billions of dollars to agriculture. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 146. • George Washington Carver overcame incredible obstacles to make his hopes and dreams come true. – Anything is possible. Have a dream, have a plan. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 147. • Activity! Video and Reading • George Washington Carver. – http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=sdz8XTNttd c Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 148. • You should be close to the top of page 4 in your bundled homework package.
- 162. New Area of Focus: Parts of a young plant / seed. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 183. Cotyledon: First leaves (Full of energy). Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 184. Which Boxes are the Cotyledons? A B C D E F G H I J
- 185. Which Boxes are the Cotyledons? A B C D E F G H I J
- 186. Which Boxes are the Cotyledons? A B C E F G H I J
- 187. Which Boxes are the Cotyledons? A B C E F G H I J
- 188. Which Boxes are the Cotyledons? A B C E F H I J
- 189. Which Boxes are the Cotyledons? A B C E F H I J
- 190. Which Boxes are the Cotyledons? A B C E F H I J
- 193. • Which picture is a dicotyledon and which is a monocotyledon?
- 194. • Which picture is a dicotyledon and which is a monocotyledon?
- 195. • Which picture is a dicotyledon and which is a monocotyledon?
- 196. • Which picture is a dicotyledon and which is a monocotyledon?
- 197. • Which picture is a dicotyledon and which is a monocotyledon?
- 199. Radicle: Lower embryo and root. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 200. • Do plants have a brain?
- 201. • Plants do not have a brain, but they do have the ability to respond to their environment.
- 202. • What direction does the radicle go when it emerges from the seed coat?
- 203. • What direction does the radicle go when it emerges from the seed coat? – Does a plant know up from down? Can a plant sense gravity?
- 205. • What would happen to plants if their radicle / roots grew upward, and their shoots grew downward? Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 208. “Gravitropism is a good thing.” “The world would be messed up without it.”
- 209. • Radicle emerges from seed coat and goes downward into the soil for support, the plant then goes upward. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 210. • Radicle emerges from seed coat and goes downward into the soil for support, the plant then goes upward. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 211. • Radicle emerges from seed coat and goes downward into the soil for support, the plant then goes upward. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 212. • Radicle emerges from seed coat and goes downward into the soil for support, the plant then goes upward. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 213. • Radicle emerges from seed coat and goes downward into the soil for support, the plant then goes upward. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 214. • Radicle emerges from seed coat and goes downward into the soil for support, the plant then goes upward. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 215. • The seed only has a small supply of energy to get the cotyledons to the surface, and the roots into the soil. – A wrong turn would be death to the young plant. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 216. Gravitrophism: Response of a plant in relation to gravity. Roots go down, shoots go up. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 217. • A plant hormone in the root tip grows more on one side in response to gravity. This sends the root downward. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 218. • A plant hormone in the root tip grows more on one side in response to gravity. This sends the root downward. – Cut the tip off of the root and… Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 219. • A plant hormone in the root tip grows more on one side in response to gravity. This sends the root downward. – Cut the tip off of the root and… Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 221. • Charles Darwin was the first European to record that plants show both a positive (up) and negative (downward) growth in response to gravity.
- 222. • Charles Darwin was the first European to record that plants show both a positive (up) and negative (downward) growth in response to gravity.
- 223. • Video! Plant Gravitropism Soundtrack and time lapse photography. Defy Gravity • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gvUj9r6M AVU Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Learn more about gravitropism at… http://herbarium.desu.edu/pfk/page8/page9/page9.html
- 224. Hypocotyl: Part of the plant between the radicle and cotyledons. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 225. • Where is the hypocotyl on this plant? Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 226. • Hypocotyl Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 227. • Hypocotyl Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 228. • Hypocotyl Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 229. • Hypocotyl Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 230. • Hypocotyl Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 231. • Where is the hypocotyl on this plant?
- 232. • Where is the hypocotyl on this plant? • Answer:
- 233. • Where is the hypocotyl on this plant? – How about the radicle,
- 234. • Where is the hypocotyl on this plant? – How about the radicle,
- 235. • Where is the hypocotyl on this plant? – How about the radicle, cotyledons,
- 236. • Where is the hypocotyl on this plant? – How about the radicle, cotyledons,
- 237. • Where is the hypocotyl on this plant? – How about the radicle, cotyledon, and first true leaves?
- 238. • Where is the hypocotyl on this plant? – How about the radicle, cotyledon, and first true leaves?
- 239. • Where is the hypocotyl on this plant? – How about the radicle, cotyledon, and first true leaves?
- 240. Which Boxes are the Hypocotyledon? A B C D E F G H I J
- 241. Which Boxes are the Hypocotyledon? A B C D E F G H I J
- 242. Which Boxes are the Hypocotyledon?B C D E F G H I J
- 243. Which Boxes are the Hypocotyledon?B C D E F G H I J
- 244. Which Boxes are the Hypocotyledon?B C D E F G H I
- 245. Which Boxes are the Hypocotyledon?B C D E F G H I
- 246. Which Boxes are the Hypocotyledon?B C D F G H I
- 248. Epicotyl: The stem of a seedling or embryo located between the cotyledons and the first true leaves. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 249. Epicotyl: The stem of a seedling or embryo located between the cotyledons and the first true leaves. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 250. • Place the arrow to the correct part of this plant so that it points to the epicotyl. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 251. • The epicotyl is the stem above the cotyledons but below the true leaves Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 252. • Is the question mark the epicotyl or hypocotyl? Why? Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 253. • It is the hypocotyl because it is below the cotyledons. Epicotyl Hypocotyl Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 254. • What is the term for where the arrow is pointing now? Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 255. • These would be called the first set of true leaves. True Leaves Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 256. Hypocotyl Radicle Cotyledon True Leaves Epicotyl Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 257. Hypocotyl Radicle Cotyledon True Leaves Epicotyl Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 258. Hypocotyl Radicle Cotyledon True Leaves Epicotyl Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 260. Hypocotyl Radicle Cotyledon True Leaves Epicotyl Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 261. Hypocotyl Radicle Cotyledon True Leaves Epicotyl Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 262. Hypocotyl Radicle Cotyledon True Leaves Epicotyl Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 264. Hypocotyl Radicle Cotyledon True Leaves Epicotyl Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 265. Hypocotyl Radicle Cotyledon True Leaves Epicotyl Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 266. Hypocotyl Radicle Cotyledon True Leaves Epicotyl Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 268. Which Box is the Epicotyl? A B C D E F G H I J
- 269. Which Box is the Epicotyl? A B C D E F G H I J
- 270. Which Box is the Epicotyl? A B C D E F G I J
- 272. • You should be close to the top of page 5 in your bundled homework package.
- 273. • Plants Available Sheet, Parts III, IV
- 274. Please draw the following. Half of a page of a small journal. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 275. Stem: Main trunk of a plant. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 276. Stem: Main trunk of a plant. Nodes: Place on stem where buds form. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 277. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 278. Stem: Main trunk of a plant. Nodes: Place on stem where buds form. Internode: Portion of a plant stem between nodes. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 279. Stem: Main trunk of a plant. Nodes: Place on stem where buds form. Internode: Portion of a plant stem between nodes. Petiole: The small stalk attaching the leaf blade to the stem. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 280. Stem: Main trunk of a plant. Nodes: Place on stem where buds form. Internode: Portion of a plant stem between nodes. Petiole: The small stalk attaching the leaf blade to the stem. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 298. • Activity! Trying our sketch on a real plant.
- 300. Stem: Main trunk of a plant.
- 301. Stem: Main trunk of a plant.
- 302. Stem: Main trunk of a plant. Nodes: Place on stem where buds form.
- 303. Stem: Main trunk of a plant. Nodes: Place on stem where buds form. Internode: Portion of a plant stem between nodes.
- 304. Stem: Main trunk of a plant. Nodes: Place on stem where buds form. Internode: Portion of a plant stem between nodes.
- 305. Stem: Main trunk of a plant. Nodes: Place on stem where buds form. Internode: Portion of a plant stem between nodes. Petiole: The small stalk attaching the leaf blade to the stem.
- 306. • Activity! Visiting our plants and identifying the various features of a young plant. – Please draw your plant and correctly label the following. A.) Radicle B.) Seed Coat C.) Cotyledons D.) Epicotyl E.) Hypocotyl F.) Main Stem G.) Nodes H.) Internodes I.) Petiole J.) True Leaves Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 307. • Plants Available Sheet, Parts III, IV
- 308. • Activity! Quiz Wiz 1-10. Name the part of the seed / plant or other information. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 319. • Bonus: Name this movie planet.
- 320. • Answers- Quiz Wiz 1-10. Name the part of the seed / plant or other information. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 341. • Bonus: Name the movie planet.
- 342. • Bonus: Name the movie planet.
- 343. • Bonus: Name the movie planet.
- 344. • Bonus: Name the movie planet.
- 345. • You should be close to the top of page 5 in your bundled homework package.
- 346. • Try and figure out what picture is beneath the boxes. – Raise your hand when you know. You only get one guess. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 356. • Try and figure out what picture is beneath the boxes. – Raise your hand when you know. You only get one guess. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 367. • Try and figure out what picture is beneath the boxes. – Raise your hand when you know. You only get one guess. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 391. • You should be close to the top of page 5 in your bundled homework package.
- 394. •Areas of Focus in The Plant Unit: •Plant photo tour, Plant Evolution, Importance of Algae, Lichens, The Three Types of Lichens, Non-Vascular Plants, Bryophytes, Seedless Vascular Plants (Ferns), Seeds, Seed Dormancy, Factors that Break Seed Dormancy, Germination, Parts of a Young Plant, Monocots and Dicots, Roots and Water, Types of Roots, Water Uptake and Photosynthesis, Plant Hormones, Types of Plant Tissues, Xylem and Phloem, Woody Plants, Leaves, Light and Plants, Transpiration, Guard Cells, Leaf Identification, Plant Life Cycles, Seed Plant Life Cycles, Parts of a Flower, Matured Ovaries (Fruits), Types of Fruit and much more. •Full unit can be found at… •http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Plant_Botany_Unit.html
- 395. • This PowerPoint is one small part of my Botany Unit. This unit includes…. – A 5 part 2,700 slide PowerPoint roadmap full of built-in hands-on activities, quizzes, projects, and much more. – 13 page bundled homework package that chronological follows the slideshow, modified version, answer keys, and detailed lesson notes. – 2 PowerPoint Review Games with answers, videos links, rubrics, crosswords, projects, curriculum guides, materials lists, and much more. – http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Plant_Botany_Unit.html
- 399. • More Units Available at… Earth Science: The Soil Science and Glaciers Unit, The Geology Topics Unit, The Astronomy Topics Unit, The Weather and Climate Unit, and The River and Water Quality Unit, The Water Molecule Unit. Physical Science: The Laws of Motion and Machines Unit, The Atoms and Periodic Table Unit, Matter, Energy, and the Environment Unit, and The Science Skills Unit. Life Science: The Diseases and Cells Unit, The DNA and Genetics Unit, The Life Topics Unit, The Plant Unit, The Taxonomy and Classification Unit, Ecology: Feeding Levels Unit, Ecology: Interactions Unit, Ecology: Abiotic Factors, The Evolution and Natural Selection Unit and The Human Body Systems and Health Topics Unit Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 400. • Please visit the links below to learn more about each of the units in this curriculum – These units take me about four years to complete with my students in grades 5-10. Earth Science Units Extended Tour Link and Curriculum Guide Geology Topics Unit http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Geology_Unit.html Astronomy Topics Unit http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Astronomy_Unit.html Weather and Climate Unit http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Weather_Climate_Unit.html Soil Science, Weathering, More http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Soil_and_Glaciers_Unit.html Water Unit http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Water_Molecule_Unit.html Rivers Unit http://sciencepowerpoint.com/River_and_Water_Quality_Unit.html = Easier = More Difficult = Most Difficult 5th – 7th grade 6th – 8th grade 8th – 10th grade
- 401. Physical Science Units Extended Tour Link and Curriculum Guide Science Skills Unit http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Science_Introduction_Lab_Safety_Metric_Methods. html Motion and Machines Unit http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Newtons_Laws_Motion_Machines_Unit.html Matter, Energy, Envs. Unit http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Energy_Topics_Unit.html Atoms and Periodic Table Unit http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Atoms_Periodic_Table_of_Elements_Unit.html Life Science Units Extended Tour Link and Curriculum Guide Human Body / Health Topics http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Human_Body_Systems_and_Health_Topics_Unit.html DNA and Genetics Unit http://sciencepowerpoint.com/DNA_Genetics_Unit.html Cell Biology Unit http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Cellular_Biology_Unit.html Infectious Diseases Unit http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Infectious_Diseases_Unit.html Taxonomy and Classification Unit http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Taxonomy_Classification_Unit.html Evolution / Natural Selection Unit http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Evolution_Natural_Selection_Unit.html Botany Topics Unit http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Plant_Botany_Unit.html Ecology Feeding Levels Unit http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Ecology_Feeding_Levels_Unit.htm Ecology Interactions Unit http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Ecology_Interactions_Unit.html Ecology Abiotic Factors Unit http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Ecology_Abiotic_Factors_Unit.html
- 402. • Thank you for your time and interest in this curriculum tour. Please visit the welcome / guide on how a unit works and link to the many unit previews to see the PowerPoint slideshows, bundled homework, review games, unit notes, and much more. Thank you for your interest and please feel free to contact me with any questions you may have. Best wishes. • Sincerely, • Ryan Murphy M.Ed • ryemurf@gmail.com
- 403. • The entire four year curriculum can be found at... http://sciencepowerpoint.com/ Please feel free to contact me with any questions you may have. Thank you for your interest in this curriculum. Sincerely, Ryan Murphy M.Ed www.sciencepowerpoint@gmail.com
