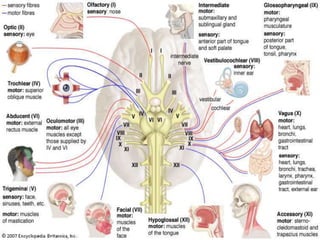
Cranial Nerves: Anatomy and Functions in 40 Characters
- 3. CONTENTS Introduction Functional component Cranial nerves Course Surgical anatomy Conclusion Reference
- 4. INTRODUCTION
- 5. Nervous System Central Nervous System Brain Spinal Cord Peripheral Nervous System 12 pairs of Cranial Nerves 31 pairs of Spinal nerves
- 6. CRANIAL NERVES I. Olfactory II. Optic III. Occulomotor IV. Trochlear V. Trigeminal VI. Abducens
- 7. VII. Facial VIII. Vestibulocochlear IX. Glossopharyngeal X. Vagus XI. Accessory XII. Hypoglossal
- 8. FUNCTIONAL COMPONENTS In addition to having similar somatic and visceral components as spinal nerves, some cranial nerves also contain special sensory and motor components
- 9. Innervations of the musculature derived from the five pharyngeal arches are First arch : Trigeminal Nerve Second arch: Facial Nerve Third arch: Glossopharyngeal Nerve Fourth arch: Superior laryngeal branch of Vagus Sixth arch : Recurrent laryngeal branch of Vagus
- 10. Functional Component Abbrev iation General Function Cranial Nerves General Somatic Afferent GSA Perception of touch, pain, temperature Trigeminal, Facial, Vagus General Visceral Afferent GVA Sensory input from viscera Glossopharyngeal, Vagus Special Afferent SA Smell, Taste, Vision, Hearing and Balance Olfactory, Optic, Facial, Vestibulocochlear, Glossopharyngeal, Vagus General Somatic Efferent GSE Motor innervations to skeletal muscles Oculomotor, trochlear, Abducent, Accessory, Hypoglossal General Visceral Efferent GVE Motor innervations to smooth muscles, heart muscles and glands Oculomotor, facial, glossopharyngeal, vagus Special Visceral Efferent/ Branchial Motor BE Motor innervations to skeletal muscles derived from pharyngeal arch mesoderm Trigeminal, Facial, Glossopharyngeal, Vagus
- 11. MOTOR
- 12. SENSORY
- 14. I - OLFACTORY NERVE Special Afferent Smell 15-20 pairs of olfactory nerves
- 16. Olfactory cells Nerves pass through the cribriform plate of the ethmoid bone Olfactory bulb(are prolongation of telencephalon) having mitral cells in the anterior cranial fossa Olfactory tract Olfactory cortex
- 17. lateral Olfactory stria Infro medial surface of the temporal lobe (piriform plate)
- 19. II- OPTIC NERVE Special Afferent Vision It is not a true cranial nerve but rather an extension of the brain carrying afferent fibres from the eyeball to the visual centres of the brain
- 20. Axons of the ganglion cells make up the optic nerve Optic disk is the central collecting point for these axons
- 22. The optic nerve leaves the orbit through optic foramen and then unite with each other to form the optic chiasma Fibres from the nasal half cross to the opposite side but the temporal fibres remain uncrossed Laterally the termination of ICA is related to the chiasma
- 23. Posterior to the chiasma, optic nerves continue as the optical tract Most of the fibres synapse with the lateral geniculate body in the thalamus From here some of the fibres go via the optic radiation to the occipital cortex Those concerned with the pupillary reflex go to the midbrain
- 24. Bipolar cells Optic nerve Optic Canal Optic Chiasma Optic Tract Lateral Geniculate nucleus Primary Visual cortex of Occipital Lobe VISUAL PATHWAY
- 25. III- OCULOMOTOR NERVE General Somatic Efferent General Visceral Efferent General somatic afferent Innervates sphincter pupillae for pupillary constriction and cilliary muscles for
- 26. Nucleus of this nerve lies in the midbrain(ventromedial part of central gray matter) Nerve passes between the posterior cerebral and superior cerebral arteries, then passes on the lateral side of the posterior communicating artery Nerve enters cavernous sinus by piercing the posterior part of its roof on the lateral side of the posterior clinoid process Passes through the sup. orbital fissure into the orbit as upper and lower divisions
- 28. This nerve is the motor nerve to Smaller upper division supplies Levator palpebrae superioris Superior rectus Larger lower division supplies Inferior rectus Medial rectus Inferior oblique
- 29. IV – TROCHLEAR NERVE General somatic efferent Supplies the superior oblique muscle Only nerve to exit from the posterior surface of the brainstem
- 30. The nucleus is in the mid brain and the nerve fibres cross midline It passes forward in the sub-arachnoid space Pierces the dura mater to lie in the lateral wall of the cavernous sinus Nerve enters the orbit through the superior orbital fissure
- 31. In the orbit it passes above the origin of the levator palpebrae superiors and ends by supplying the superior rectus on it’s orbital surface
- 33. TRIGEMINAL NERVE Largest cranial nerve Nerve of the first brachial arch. Small motor root and large sensory root It has three divisions: 1. Opthalmic 2. Maxillary 3. Mandibular
- 35. TRIGEMINAL NERVE – NUCLEAR ORIGIN There are 4 trigeminal nuclei . One motor and three sensory nuclei.
- 36. Exists from the anterolateral surface of the pons as a large sensory root and small motor root Continues to posterior cranial fossa Middle cranial fossa by passing over the medial tip of petrous temporal bone
- 37. In middle cranial fossa the sensory root expands into trigeminal ganglion which lies in trigeminal depression The motor root is below and completely separate from the sensory root at this point Three terminal divisions of trigeminal nerve arise from the ganglion Ophthalmic, maxillary, mandibular
- 38. OPTHALMIC DIVISION Smallest of the three branches Purely sensory Passes forward in the dura matter of the lateral wall of cavernous sinus. Leaves the cranial cavity and enters through superior orbital fissure Supplies Eyeballs , Lacrimal glands Mucous membrane of nose and paranasal sinuses Skin of the forehead , eyelids, nose.
- 40. LACRIMAL BRANCH Course Passes into orbit at lateral angle of superior orbital fissure Then in anterolateral direction to reach lacrimal gland Zygomatic nerve communicates with lacrimal nerve Supplies Lacrimal gland Conjunctiva Contents of the eyes Frontal sinus Ethmoidal cells Upper eyelid Dorsum of nose Anterior part of scalp
- 41. FRONTAL The largest branch of the Ophthalmic division. It begins in the lateral wall of the anterior part of the cavernous sinus. It enters the orbit through the superior orbital fissure, midway between the apex and base of the orbit. Divides into two branches 1. Supratrochlear 2. Supraorbital
- 42. Supraorbital Passes forward & leaves orbit through supraorbital foramen Supplies: Skin of upper eyelid , Forehead , Anterior scalp region to the vertex of skull. Supratrochlear Passes toward upper medial angle of orbit Supplies: Skin of upper eyelid ,Lower medial portion of forehead.
- 43. NASOCILLIARY BRANCH OF OPTHALMIC NERVE Enters orbit through superior orbital fissure. Travels along the medial border of the orbital roof Branches in Orbit Nasal cavity Face
- 44. BRANCHES OF NASOCILLIARY NERVE Long root of the cilliary ganglion Sensory fibers Pass through ganglion without synapsing Continue on to eyeball Long cilliary nerves Usually two or three Post ganglionic fibers from superior cervical ganglion Distributed to iris & cornea
- 45. Posterior ethmoid nerve Distributed to mucous membrane lining Posterior ethmoidal cells Sphenoid sinus Anterior ethmoid nerve Supplies Anterior and middle ethmoidal cells Frontal sinus In upper part of nasal cavity divides into Internal nasal branch External nasal branch
- 46. MAXILLARY NERVE Passes forward in the dura matter of the lateral wall of cavernous sinus inferior to the opthalmic nerve Leaves the cranial cavity through foramen rotundum Passes through the ptyergopalatine fossa and the inferior orbital fissure
- 47. Br. in middle Cranial fossa Single branch- Middle meningeal nerve Br. in pterygopalatine fossa Zygomatic nerve Pterygopalatine nerve Posterior superior alveolar nerve Br. In infraorbital Groove & canal Middle superior alveolar nerve Anterior superior alveolar nerve Br. On face Inferior Palpebral Lateral nasal Superior labial
- 48. THE PTERYGOPALATINE BRANCHES Branches of Distribution.— Orbital : Periosteum of the orbit Nasal: Superior and middle concha Lining of posterior of ethmoidal sinus Posterior portion of nasal septum
- 49. ZYGOMATIC BRANCH Arises in the pterygopalatine fossa Enters the orbit by the inferior orbital fissure Divides into two branches, zygomaticotemporal Sensory innervation to skin on the side of forehead zygomaticofacial. Prominence of the cheek
- 50. Palate Greater palatine: • Sensory innervations to palatine soft tissues till the first premolar. Lesser palatine: • supplies mucous membrane of the soft palate tonsillar region. Pharynx • Mucous membrane of the nasal part of pharynx, posterior to auditory tube.
- 51. THE POSTERIOR SUPERIOR ALVEOLAR BRANCHES Leave maxillary division before entering inferior orbital fissure Posterior surface of maxilla Supplies Mucous membrane of maxillary sinus Maxillary molar & gingiva
- 52. THE MIDDLE SUPERIOR ALVEOLAR BRANCH Leaves the maxillary nerve in posterior part of infraorbital canal Downward & anteriorly toward apices of maxillary bicuspids Supplies 1. Maxillary bicuspids 2. Mesiobuccal root of maxillary 1st molar
- 53. THE ANTERIOR SUPERIOR ALVEOLAR BRANCH Descends from infraorbital nerve inside infraorbital foramen in anterior part on infraorbital canal. Supplies Central incisors Lateral incisors Cuspid teeth
- 54. BRANCHES ON THE FACE The Inferior Palpebral Branches Skin and conjunctiva of the lower eyelid The External Nasal Branches The skin of the side of the nose. The Superior Labial Branches Skin & mucous membrane of upper lip.
- 55. MANDIBULAR NERVE Leaves the inferior margin of trigeminal ganglion Leaves the skull through the foramen ovale. The motor root also passes through the foramen ovale. Unites with sensory component of mandibular nerve outside the skull
- 56. • Meningeal • Nerve to medial pterygoidTrunk • Deep temporal • Lateral pterygoid • Massetric • Buccal Anterior division • Auriculotemporal • Lingual • Inferior alveolar Posterior division
- 57. MENINGEAL BRANCH Given off just after union of sensory & motor root. Enter foramen spinosum Accompanies middle meningeal artery Supplies dura mater of middle cranial fossa
- 58. Supplies medial pterygoid Branch to a. Otic ganglion b. Tensor tympani c. Tensor veli palatini Nerve to medial pterygoid
- 59. Nerve to lateral pterygoid: Supplies lateral pterygoid muscle Masseter nerve Passes above lateral pterygoid & enter masseter muscle Deep temporal nerve Anterior, middle & posterior deep temporal nerves Pass upwards to reach deep surface of temporalis Buccal nerve Anteriorly & laterally between two heads of lateral pterygoid. At about the level of 2nd & 3rd molar. ANTERIOR DIVISION
- 60. AURICULOTEMPORAL NERVE Arises by two roots which form a ring through middle meningeal artery passes. Backward in infratemporal fossa & crosses neck of mandible laterally behind TMJ Branches 1. Auricular 2. Superficial temporal 3. Auricular or TMJ 4. Secretomotor to Parotid
- 61. Smaller of two branches of posterior division Passes medially to lateral pterygoid muscle Lies parallel to inferior alveolar nerve Passes deep, reach side of the base of tongue. Passes forward, loops downward & medially beneath submandibular duct. Lingual nerve
- 62. As lingual nerve passes medially to external pterygoid, it is joined by chorda tympani nerve. It supplies: i. Mucous membrane of the floor of the mouth. ii. Gingiva on the lingual of the mandible. Convey Secretory fibers Lingual nerve carry three type of fibers Fiber for ordinary sensation Fibers for taste Secretomotor fibers
- 63. INFERIOR ALVEOLAR NERVE Passes downward on medial side of lateral pterygoid & mandibular ramus In mandibular foramen, descends & distributed throughout mandible Branches to mandibular teeth & reach mental foramen Two terminal branches, Mental nerve& incisive nerve leave through mental foramen
- 65. VI – ABDUCENS NERVE General somatic efferent and afferent Supplies the lateral rectus muscle
- 66. Arises from the brain stem between the pons and medulla It passes upward forward and laterally through the cisterna pontis to reach the cavernous sinus Lying at first lateral then infero lateral to the Internal carotid artery Nerve enters the orbit through the medial part of superior orbital fissure Ends by supplying the lateral rectus muscle ocular surface
- 68. VII - FACIAL NERVE General somatic afferent Special visceral afferent General visceral afferent Special visceral efferent General visceral efferent
- 71. Sensory supply to parts of external acoustic meatus and deeper part of auricle Special taste sensation from anterior two third of the tongue Parasympathetic supply to lacrimal gland, sub mandibular and sublingual salivary glands, mucous membranes of the nasal cavity, hard and soft palate
- 72. Motor innervation to muscles of facial expression, scalp ( derived from the second arch) stapedius posterior belly of digastric stylohyoid muscles
- 73. Facial nerve is attached to the lateral surface of the brain stem, between pons and medulla Consists of larger motor root and small sensory root ( intermediate nerve) They leave the cranial cavity through the internal acoustic meatus
- 75. Facial nerve is closely associated with the vestibulocochlear nerve The two roots fuse and enters the facial canal in the petrous temporal bone Near this point the nerve enlarges as the geniculate ganglion
- 77. It gives of the greater petrosal nerve at this bend Facial nerve continues along the bony canal Gives off the nerve to stapedius and chorda tympani before exiting the skull through the stylomastoid foramen
- 79. Within the facial canal Greater petrosal nerve(supply the secretomotor fibers to lacrimal gland and mucous glands of nasal cavity and palate.)
- 81. Nerve to stapedius supplies the stapedius muscle Chorda tympani Consist two types of fibers i. Preganglionic parasympathetic (GVE) fibers, provides secretomotor supply to submandibular & sublingual glands. ii.Special viseral afferant fibers carries taste sensation from ant. 2/3 of the tongue.
- 82. At it’s exit from the stylomastoid foramen Posterior auricular Auricularis posterior Occipitalis Intrinsic muscle of the back of the auricle Digastric Post. Belly of digastric Stylohyoid Stylohyoid muscles
- 83. Terminal branches within the parotid gland Temporal Zygomatic Buccal Marginal mandibular Cervical Communicating branches to adjacent cranial and spinal nerves
- 84. Temporal Branch o Auricularis anterior o Auricularis superior o Frontalis o Orbicularis oris o Corrugator supercilli
- 85. Zygomatic: Orbicularis oris Marginal mandibular Muscles of lower lip and chin Cervical branch Platysma
- 86. VIII –VESTIBULOCOCHLEAR NERVE Special Afferent Hearing and balance Vestibular component for balance Cochlear component for hearing
- 88. After emerging from the internal acoustic meatus it crosses the posterior cranial fossa within the substance of the petrous part of temporal bone The nerve attaches to the lateral surface of the brainstem, between pons and medulla It is closely associated with the facial nerve
- 90. Vestibular ganglia (consist of bipolar sensory neurons) divides in 3 distinct branches Superior, inferior & singular nerve innervates the sensory receptor for equilibrium(cristae ampullaris and maculae)in membranous labyrinth of int. ear. The cochlear nerve ganglion is called spiral ganglion & innervates the sensory receptor of hearing – the organ of Corti.
- 91. IX – GLOSSOPHARYNGEAL NERVE General somatic afferent Special visceral afferent General visceral afferent General visceral efferent Special visceral efferent
- 92. Motor supply to stylopharyngeus Secretomotor to parotid gland Gustatory to post. one third of tongue Sensory to pharynx, tonsil, soft palate, post. one third of tongue, carotid body and carotid sinus
- 93. Arises as several rootlets on the anterolateral surface of the upper medulla oblongata The rootlets cross the posterior cranial fossa Enter the jugular foramen Merge to form glossopharyngeal nerve before exiting from jugular foramen Within or immediately outside jugular foramen are superior and inferior ganglia
- 95. In the jugular foramen the nerve is lodged in the deep groove and is separated from vagus and accessory nerves. Outside the foramen it passes forward between the internal jugular vein and internal carotid artery. It turns forward winding round the lateral aspect of stylopharyngeus (passes between external and internal carotid artery)reaches the pharynx and gives away pharyngeal branches. It enters the submandibular region by passing deep to hyoglossus and divides into tonsillar and lingual branches.
- 97. Tympanic branch (jacobson’s nerve) Secretomotor supply of parotid gland and other small glands in the vestibule of the mouth Motor branch: stylopharyngeus: Carotid sinus nerve: carotid sinus & body
- 98. Pharyngeal branches: Mucous membrane and serous glands of oropharynx Taste fibres Tonsillar branch: Mucous membrane of the palatine tonsil & palate Lingual Posterior one third of the tongue taste & general sensation
- 99. X – VAGUS NERVE General somatic afferent Special visceral afferent General visceral afferent General visceral efferent Special visceral efferent
- 101. Sensory supply to larynx, laryngopharynx, deeper part of auricle, part of external acoustic meatus and dura in the posterior cranial fossa Sensory from aortic body chemoreceptors and aortic arch baroreceptors, esophagus, bronchi, lungs, heart, and abdominal viscera of foregut and midgut
- 102. Taste from epiglottis and pharynx Innervates the smooth muscles and glands in the pharynx, larynx, thoracic viscera and abdominal viscera of the foregut and midgut Innervates palatoglossus, muscles of soft palate ( except tensor veli palatini), pharynx ( except stylopharyngeus) and larynx
- 103. Vagus nerve arises as a group of rootlets on the anterolateral surface of the medulla oblongata just inferior to the rootlets arising to form the glossopharyngeal nerve Rootlets enter the jugular foramen
- 104. In the foramen they merge to form one fibre Leaves the cranial cavity by passing through the middle of the jugular foramen The nerve descends within the carotid sheath in between and posterior to the internal jugular vein and common and internal carotid artery
- 105. Right vagus enters the thorax by crossing the first part of sub clavian artery and inclining medially behind the brachiocephalic vessels Left vagus enters by passing between the left common carotid and left sub clavian arteries behind internal jugular and brachiocephalic veins
- 106. Vagus bears two ganglia Superior Lies in the jugular foramen Inferior Lies below the base of the skull Formed where accessory portion of the spinal accessory joins the vagus
- 107. Branches Superior ganglion, in the jugular foramen Meningeal : Supplies dura of the posterior cranial fossa Auricular : Supplies concha, root of the auricle, posterior half of external auditory meatus and the tympanic membrane Communicating branches to the glossopharyngeal and cranial roots of accessory nerve
- 108. Inferior ganglion in the neck Pharyngeal : forms the pharyngeal plexus and supplies the muscles of the pharynx and soft palate Carotid : supplies the carotid body and sinus Sup. Laryngeal External : supplies cricothyroid, branches to inferior constrictor and to the pharyngeal plexus Internal : Supplies the mucous membrane of the larynx upto the vocal folds
- 109. Recurrent laryngeal Intrinsic muscles of larynx except cricothyroid Sensory nerves to larynx below the level of vocal chords Cardiac branches to deep cardiac plexus To trachea and oesophagus To inferior constrictor
- 110. Cardiac branches They go to the superficial cardiac plexus and the deep cardiac plexus
- 111. XI – ACCESSORY NERVE General somatic efferent It has two roots : cranial and spinal Cranial root is accessory to vagus Motor root arise from the motor neurons of the upper segments of cervical spinal cord
- 112. Spinal root supplies the sternocleidomastoid muscle and trapezius muscle
- 113. Cranial root is distributed through the branches of vagus to the muscles of palate( except tensor palati & tympani) All intrinsic muscle of larynx All pharynx muscle except stylopharangeus
- 114. The cranial roots emerge from posterolateral sulcus of the medulla In the jugular foramen the cranial root briefly unites with the cervical root and again separates as it passes out of the foramen Cranial nerve fuses with the vagus and the inferior ganglion and is distributed through the branches of the vagus
- 115. The cervical roots unite to form a single trunk in the vertebral canal and enter the cranium through foramen magnum Along with glossoparyngeal and vagus it reaches the jugular foramen It leaves the skull through the middle part of the jugular foramen
- 116. Extracranially the nerve descends vertically between internal jugular vein and internal carotid artery deep to the parotid and to the styloid process Then it runs downwards and backwards superficial to the internal jugular vein and deep to the SCM
- 118. XII – HYPOGLOSSAL NERVE General somatic efferent Supplies the all intrinsic and extrinsic ( except palatoglossus) of the tongue
- 120. It arises from the anterior surface of the medulla, Passes laterally across the posterior cranial fossa and exists through the hypoglossal canal It first lies deep to the internal jugular vein then crosses the vagus laterally and reaches in front
- 121. It curves forward, hooks around the lower sternocleidomastoid branch of occipital artery, crosses the ICA and ECA and the loop of lingual artery and passes deep to post belly of digastric to enter the submandibular region Nerve then continues forward on the hyoglossus and genioglossus, enters the substance of the tongue to supply the muscles
- 123. BRANCHES Meningeal branch Styloglossus Hypoglossus Genioglossus Geniohyoid Thyrohyoid
- 124. It supplies the extrinsic muscles Styloglossus Genioglossus Hyoglossus Intrinsic muscles Superior longitudinal Inferior longitudinal Transverse Vertical
- 125. Conclusion
- 126. Reference Lee McGregor’s Surgical Anatomy Grey’s Anatomy Sicher and DuBrul’s Oral anatomy B D Chaurasia’s Human Anatomy(5TH edition) Vishram singh 2nd edition Internet
Editor's Notes
- Nerves Origin from 1,2 frm forebrain 3,4 mid brain 5,6,7,8, pons 9,10,11,12 frm medula A cranial nerve palsy may be the first sign of a space occupying intra cranial lesion. K
- The 12 pairs of cranial nerves are numbered according to how they emerge from the brain stem
- Edinger west phal goes or gives innervation to ciliary ganglion 11 nerve only cranial part emerges
- Olfactory cells are bipolar which acts as receptors and conductors Sensory nerve
- Olfactory cells reside in the mucosa of the superior nasal concha and the upper part of the nasal septum
- Olfactory cells reside in the mucosa of the superior nasal concha and the upper part of the nasal septum
- Optic n is covered by pia matter and sub archanoid matter and has a outer covering as dura matter Dura mater makes a sleave around the optic nerve means csf is also around the optic nerve
- Optic system is prolongation of dianchephalon They r central tracts Peripheral nerve axon r lined by schwan cells Where as fiber in optic r myelinated by oligodendroglia. And affect by diseases which effect purely cns
- Termination of ICA is
- motor
- Parasympathetic fibres synapse in the ciliary ganglion from where the post – ganglionic fibres supply the ciliary muscle (accommodation) and constrictor muscles of the pupil
- motor
- It is the smallest and most slender of all the cranial nerve
- Gsa:scalp,mucous membranes of oral,nasal cavities and para nasal sinus,nasopharynx,external acoustic meatus,part of tympanic membrane,orbital contents,dura matter in ant and middle cranial fossa
- Sensory ganglion is located within the cranial cavity whereas all the other sensory ganglia is located outside the crnial cavity
- Major sensory nerve of the head
- Tgn-in a deprssion (the trigeminal depression)lies in petrous part of temporal bone in a dural cave
- Smallest branch of opthalmic nerve
- Internal nasal branch (lateral and medial) External nasal branch (skin of the ala of vestibule and tip of nose)
- Zygomaticotemporal - supplies skin over anterior temporal fossa region Zygomaticofacial - skin over zygomatic bone
- In ifra orbitall groove nd canal
- Thus mandibular nerve is the only division of trigeminal nerve with motor component.
- Almost entire mucosa of cheek Buccal gingiva of mandibular molars
- lower teeth mylohyoid anterior belly of digastric
- This is the most susceptible to damage of all cranial nerve during increased intracranial pressure As the sharp bone edges may damage the nerve ( temporal part of bone)
- mixed
- Arises 6 mm above the stylomastoid foramen and enters middle ear through the posterior canaliculus
- sensory
- Vestibular ganglia also called scarpa”s ganglion
- mixed
- Longest cranial nerve mixed
- motor
- tensor palati & tympani which is supplied by mand nerve. Nerve to medial prtygoid Stylopharangeus supplied by glossophrangeal nerve
- motor
- THIRTEENTH CRANIAL NERVE: THE CLOACAL NERVE also known as the “zero nerve” or “nerve N”. The intermediary nerve has always been considered a ramification of the facial nerve,
- As a surgeon we should know the coarse of the nerves thoroly so that we can avoid its damage while the surgery. And diGNOSIS AND NEUROLIGIA