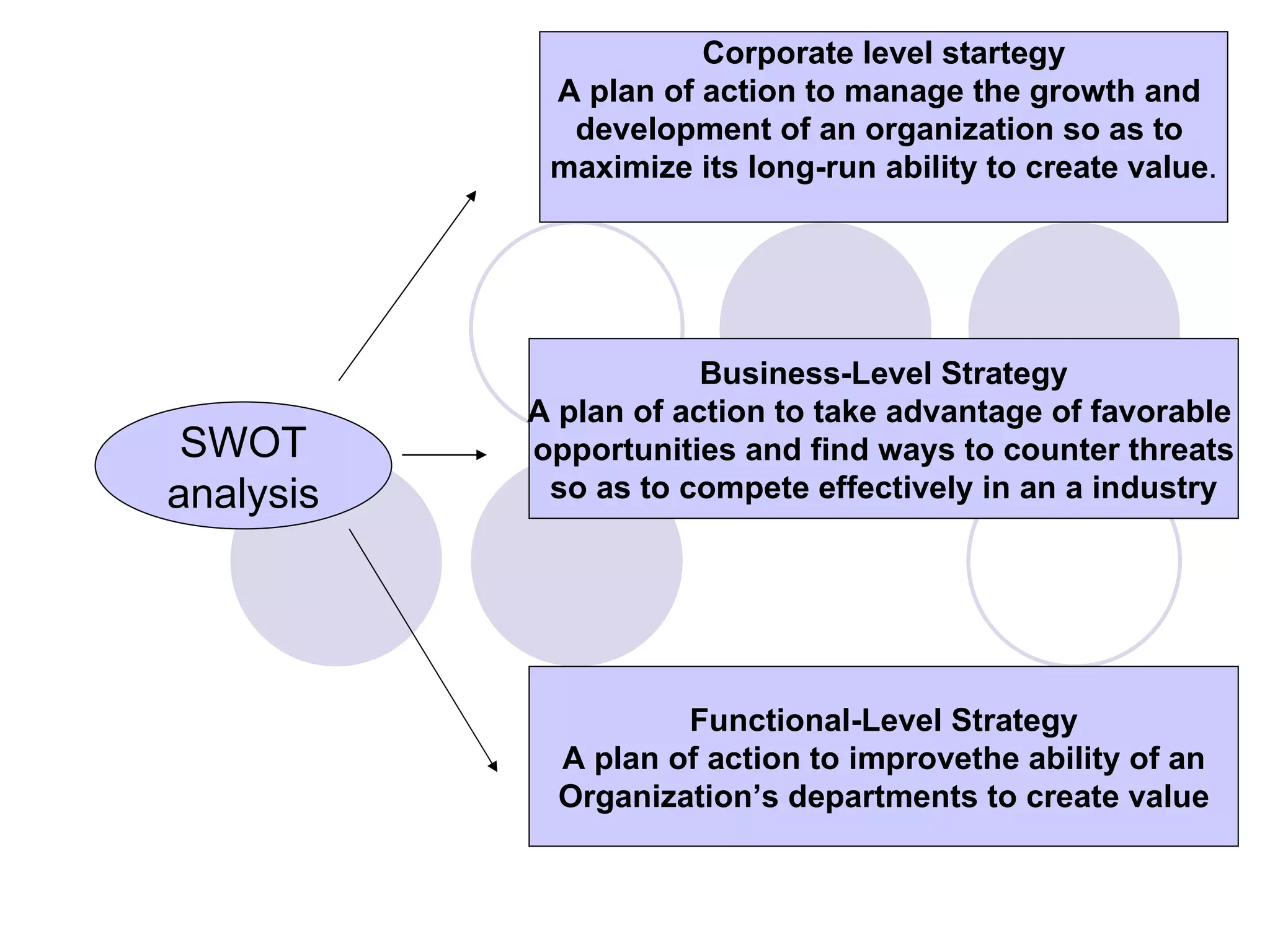
1. Planning involves identifying goals and strategies for an organization. It includes corporate, business unit, and functional level plans with time horizons from 1 to more than 5 years.
2. Key aspects of planning include determining the organization's mission and major goals, analyzing the situation to formulate strategies, and implementing strategies by allocating resources and responsibilities.
3. Effective planning provides direction, coordination, and control for an organization. It involves managers at all levels and helps the organization work toward common objectives.