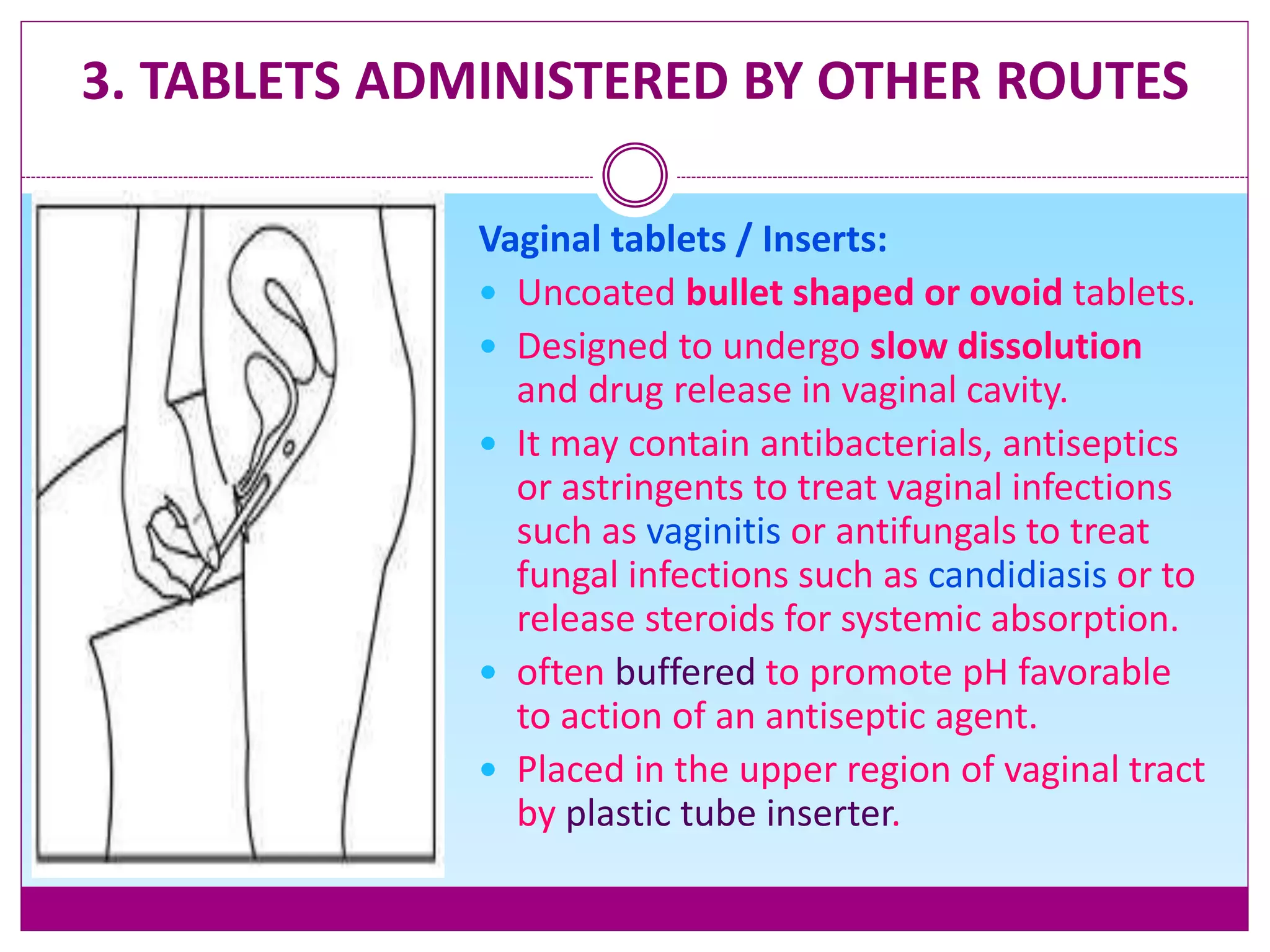
Tablet excipients serve several important functions in tablet manufacturing including improving properties like flow, stability, and bioavailability. Common excipients include diluents, binders, disintegrants, and lubricants. Tablets can be classified based on their route of administration, drug delivery system, and manufacturing method. Key types include compressed, enteric coated, chewable, sublingual, and effervescent tablets. Excipients allow tablets to be designed for rapid or delayed drug release depending on the therapeutic need.