Gout presentation
- 1. DR CHIA KOK KING Medical & Health Officer PKD Langkawi, Kedah
- 3. Gout A metabolic disease characterized by recurrent attack of acute inflammatory arthritis caused by elevated levels of uric acid in the blood (hyperuricemia). Most common rheumatic disease of adulthood The uric acid crystallizes and deposits in joints, tendons, and surrounding tissues. Hyperuricemia : overproduction/underexcretion/both Hyperuricemia ≠ Gout
- 4. (NHS Fife, Gout ManagementGuidelines, 2010)
- 5. Asymptomatic hyperuricemia Serum [urate] abnormally high without SSx Male >420μmol/L (7mg/dL) Female >360μmol/L (6mg/dL) Not life threatening and readily treatable Routine prophylactic treatment is NOT required A/W : gout, urolithiasis, nephropathy, metabolic syndrome (HPT, DM/IFG/IGT, hyperTGemia, obesity, CKD) Serum [urate] >540μmol/L (9mg/dL) were a/w greater incidence for gout Increased daily urinary urate excretion is a/w higher risk of urate and Ca oxalate stone formation (when >0.65mmol/L or 11mg/dL) Renal involvement when serum urate level is more than 2x the normal limit (0.77mmol/L or 13mg/dL in male; 0.60mmol/L or 10mg/dL) in female)
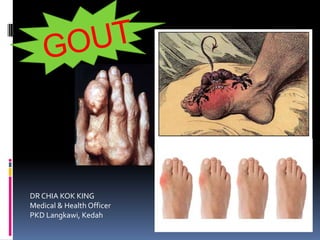
- 6. Gouty arthritis 1. Acute gout Acute, self limiting, monoarticular Painful, red, hot, swollen Usually resolves within 2 weeks if untreated May occur even if serum urate is normal LL > UL Commonly affected joints I. 1st metatarsophalangeal joint (podagra) II. Forefoot/instep III. Ankle joint IV. Knee joint V. Wrist joint VI. Elbow joint VII. Finger joints Extra-articular : olecranon bursa,Achilles tendon O/E : erythematous, warm, swelling over involved joint with extreme tenderness +/- fever skin desquamation Duration : 2 – 3 weeks, with gradual complete resolution of inflammatory signs
- 7. 2. Intercritical gout Asymptomatic period between attacks 3. Chronic gout Polyarticular arthritis + tophi formation Articular tophaceous gout may results in destructive arthropathy and secondary OA Tophaceous disease more like to occur in patients with: Polyarticular presentation Serum urate level >540 μmol/L (>9mg/dL) Disease onset at younger age (≤40 years) Sites of tophi Digits of hands and feet (most common) Pinna of ear (classic, less common) Bursa around elbows and knees Achilles tendon
- 9. Urate/gouty nephropathy Acute urate nephropathy Urate crystals renal tubules obstructive ARF DeH2O, low urine pH are precipitating factors Chronic urate nephropathy Urate crystals interstitium and renal medulla inflammation + surrounding fibrosis irreversible CRF Renal impairment can occur in ~40% in chronic gout Urate nephrolithiasis Stones flank pain/ureteric colic/hematuria Urate (radiolucent) / mixt. Calcium oxalate and/or calcium phosphate (radio-opaque) Contributing factors : hyperuricosuria, low urine output, acidic urine Urinary alkalinization (pot. Citrate or NaHCO3) dissolution of existing stones and prevention of recurrence
- 10. Diagnostic criteria Two of the following criteria are required for clinical diagnosis : 1. Clear h/o at least 2 attacks of painful joint swelling with complete resolution within 2 weeks 2. Clear history or observation of podagra 3. Presence of tophus 4. Rapid response to colchicine within 48 hours of treatment initiation Definitive diagnosis : presence of monosodium urate crystals seen in synovial fluid/tissues
- 11. Investigations Specific investigations for confirmation Serum uric acid Joint aspiration and crystal identification Not widely available To detect medical conditions a/w gout or hyperuricemia FBC Serum creatinine/urea Serum blood glucose Fasting lipid profile UFEME 24h urinary urate excretion : Useful if renal calculus proven to be urate stone Indicated if on uricosuric agent Assess risk of stone Help to indicate whether overproduction or underexcretion of urate Range : 2-4 mmol/24h or 0.34-0.67g/24h To detect complications Renal imaging Skeletal x-rays
- 13. Skeletal x-rays Acute gouty arthritis : normal; soft tissue swelling Chronic tophaceous gout : tophi, erosive bone lesions (punched out lesions), joint space is preserved until late stage, pathognomonic in foot and big toe
- 15. Renal imaging Plain abd XR detects only 10% of all urate stones IVU = investigation of choice for urate stones US KUB : investigations of choise for nephrocalcinosis, significant renal stones (>3mm) whether radio-opaque or radiolucent, obstructive nephropathy Plain CTU : most sensitive to detect any stone
- 16. Management Lifestyle modification and dietary advice Management of comorbidities Nonessential prescriptions that induce hyperuricaemia Main aim : -To achive ideal BW - Prevent acute gouty attacks - Reduce serum urate level Strict purine-free diet reduced only 15 – 20% of serum urate, thus is considered an adjunct therapy to medication.
- 17. Treatment Contributing factors eg. thiazide/loop diuretics; low dose aspirin may be discontinued or substituted, if appropriate Pharmacotherapy of asymptomatic hyperuricemia is NOT necessary, except :- Persistent severe hyperuricemia - > 770μmol/L (13mg/dL) in male - > 600μmol/L (10mg/dL) in female Persistent elevated urinary excretion of urate - > 0.65mmol/L/day (11mg/day), a/w 50% increased risk of urate calculi Tumor lysis syndrome - chemotherapy/radiotherapy extensive tumor cytolysis => require pre-hydration and allopurinol to prevent acute urate nephropathy
- 18. Treatment : Acute gouty arthritis Initiation within 24 hours of onset If on Allopurinol, continue without interruption NSAIDs eg. Diclofenac, indomethacin, mefenemic acid etc Caution in h/o PUD, HPT, renal impairment, IHD, liver impairment COX-2 inhibitors (celecoxib, etoricoxib, parecoxib) = alternative for above risk factors Studies have shown that etoxicoxib (Arcoxia) has equal efficacy to indomethacin Colchicine Inhibiting mitosis and neutrophils motility and activity, leading to a net anti-inflammatory effect. Alternative drug if CI to NSAIDs, but is poorly tolerated by elderly Therapeutic index is narrow Slower onset of action Evidence base for prophylaxis is stronger than for NSAIDs (NHS Fife, Gout Management Guidelines, 2010) SE (eg. N&V, abd. pain, profuse diarrhea) limit its usefulness Dosage : 0.5mg – 0.6mg BD-QID
- 19. Steroids Can be considered in elderly people and patients with renal/liver impairment, IHD, PUD, hypersensitivity to NSAIDs IM steroids eg.Triamcinolone (40-80mg.day) or methylprednisolone (80mg/day) can be given stat Short course of oral prednisolone up to 0.5mg/kg/day can be given and tapered off over 4 -10 days SE of steroids are rare (NHS Fife, Gout ManagementGuidelines, 2010)
- 20. Treatment : chronic gouty arthritis Management of Gout, CPG 2008, MOH Malaysia
- 21. Urate lowering therapy (hypouricaemic therapy) Allopurinol should not be started until acute attack has resolved May prolong attack or lead to rebound flares if started during attack Should be started 2 weeks after attack is well- controlled Indications for ULT : 1. Frequent and disabling attacks of gouty arthritis (3 or more attacks/year) 2. Clinical or radiographic signs of erosive gouty arthritis 3. The presence of tophaceous deposits 4. Urate nephropathy 5. Urate nephrolithiasis 6. Impending cytotoxic chemo-/radiotherapy for lymphoma or leukemia
- 22. D/W with patients regarding important points at initiation of ULT 1. NSAIDs/colchicine do not lower serum urate 2. Hypouricemic drugs have no analgesic or anti- inflammatory effect 3. ULT agent should not be stopped during an attack after initiation 4. Possibility of more frequent attacks of acute gouty arthritis at the initiation of therapy, especially in the first 3 months. Prophylactic NSAIDs/colchicine can be used to reduce frequency of attack 5. Is a life-long treatment 6. Lifestyle modification is an important adjunct therapy
- 23. Management of Gout, CPG 2008, MOH Malaysia
- 24. Xanthine oxidase inhibitor ALLOPURINOL More superior than probenecid Primarily excreted by kidneys, thus need renal adjustment Aim : reduce to <360μmol/L and maintain with minimal dose of allopurinol During initiation of allopurinol therapy, colchicine (0.5mg BD) can be used as prophylaxis to reduce frequency of attacks. Can be continued until patient is attack free for 6 months or target serum urate level is achieved for 1 month. For patient who can’t tolerate colchicine, low dose NSAIDs can be used
- 25. Normal renal function : Start at 100 – 150mg OD, increasing by 100 – 150mg steps every 2 - 5 weeks till 300mg OD, max 900mg/day (severe disease) With prophylactic colchicine 0.5mg BD for up to 12 months (NHS Fife, Gout ManagementGuidelines, 2010) Starting dose should be not >100mg/day and less in moderate to severe CKD, with gradual upward titration (ACR,Guidelines for Management of Gout, 2012) Indications for starting allopurinol must be clear, as life threatening complications can occur Rash Bone marrow suppression Aplastic anemia Agranulocytosis Granulomatous hepatitis and jaundice Hypersensitivity syndrome (fever, rashes, hepatitis, eosinophilia, renal impairment)
- 26. Uricosuric agent PROBENECID An alternative to allopurinol in patients with NORMAL RENAL FUNCTION RP before commencement of probenecid Dosage : 0.5 – 1g in divided doses, may be increased to 1.5 – 2g SE : GI disturbance Hypersensitive rash CI : - uric acid overproduction and overexcretion (24 hrs urinary urate excretion morethan 800mg/day) - urate nephropathy - urate nephrolithiasis Losartan has modest uricosuric effect Fenofibrate too Risk of crystal precipitation
- 27. (NHS Fife, Gout ManagementGuidelines, 2010)
- 28. Treatment of urate nephropathy Increase urine output 3L of H2O/day with urine output >2.5L if not ESRF Increase urine pH Prevent urate stone formation and promote dissolution of stone Target urine pH : 6.5 – 7 Potassium citrate 40 – 50mmol/day (max 100mmol/day) Sodium salt : Ural sachet (with analgesic properties) Dosage : 1 – 2 sachets QID CI in renal impairment/hypernatraemia Decrease urate excretion Dietary purine intake restriction Treat with allopurinol
- 29. Treatment of urate nephrolithiasis Intrarenal stones <5mm can be observed unless causing pain Intrarenal stone 5 – 15mm or complex staghorn calculi refer to urologist for ESWL or PCNL Ureteric stones : conservative management If uncomplicated (min obstruction/no sepsis), and size <5mm, at lower ureter may pass spontaneously If fail to pass after 2 weeks refer for removal Pure urate stones can be chemolysed by pot. Cit. or Ural (oral/direct irrigation) Long term chemoprophylaxis using pot. Cit. has shown to be highly effective
- 30. Surgical intervention Last resort for gouty arthritis Removal of tophi Joint fusion Joint replacement Ulceration of tophi : debridement, dressing with sodium bicarbonate solution Indications for chronic tophaceous gout : Advanced tophi deposition resulting in major joint destruction Loss of involved joint movements a/w severe pain Tophi collection causing pressure symptoms, eg carpal tunnel syndrome of wrist Tophaceous ulcer Cosmetic eg ear lobe tophi
- 31. When to reduce ULT????? If serum urate <360μmol/L , and have been no gouty attacks for 1 year can reduceT. allopurinol by 100mg. Check serum urate 6 monthly, if still <360μmol/L can further reduce Patients that have tophi are most likely to require lifelong ULT
- 32. Referral to specialist Unclear etiology Refractory SSx (fails to respond within 14 days with treatment) Difficulty in achieving target serum urate level/recurrent attacks despite onT. allopurinol 900mg OD Uncontrolled acute gout attacks when serum urate <360μmol/L Renal impairment Adverse effects of ULT/Intolerance
- 33. (NHS Fife, Gout ManagementGuidelines, 2010)
- 34. References Management of Gout, CPG 2008, MOH Malaysia 2012 American College of Rheumatology, Guidelines for Management of Gout), part 1, part 2 NHS Fife, Gout Management Guidelines, 2010
