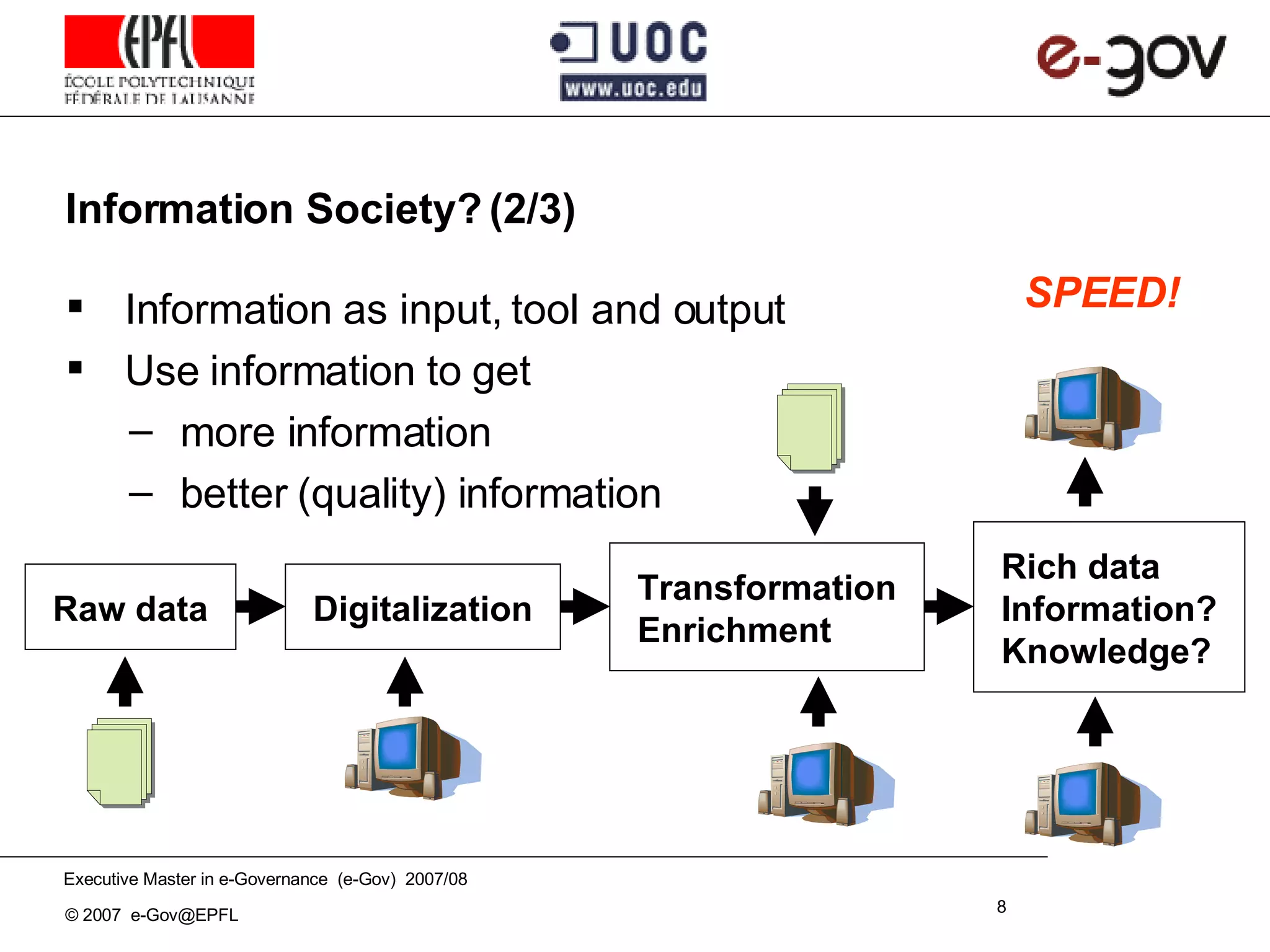
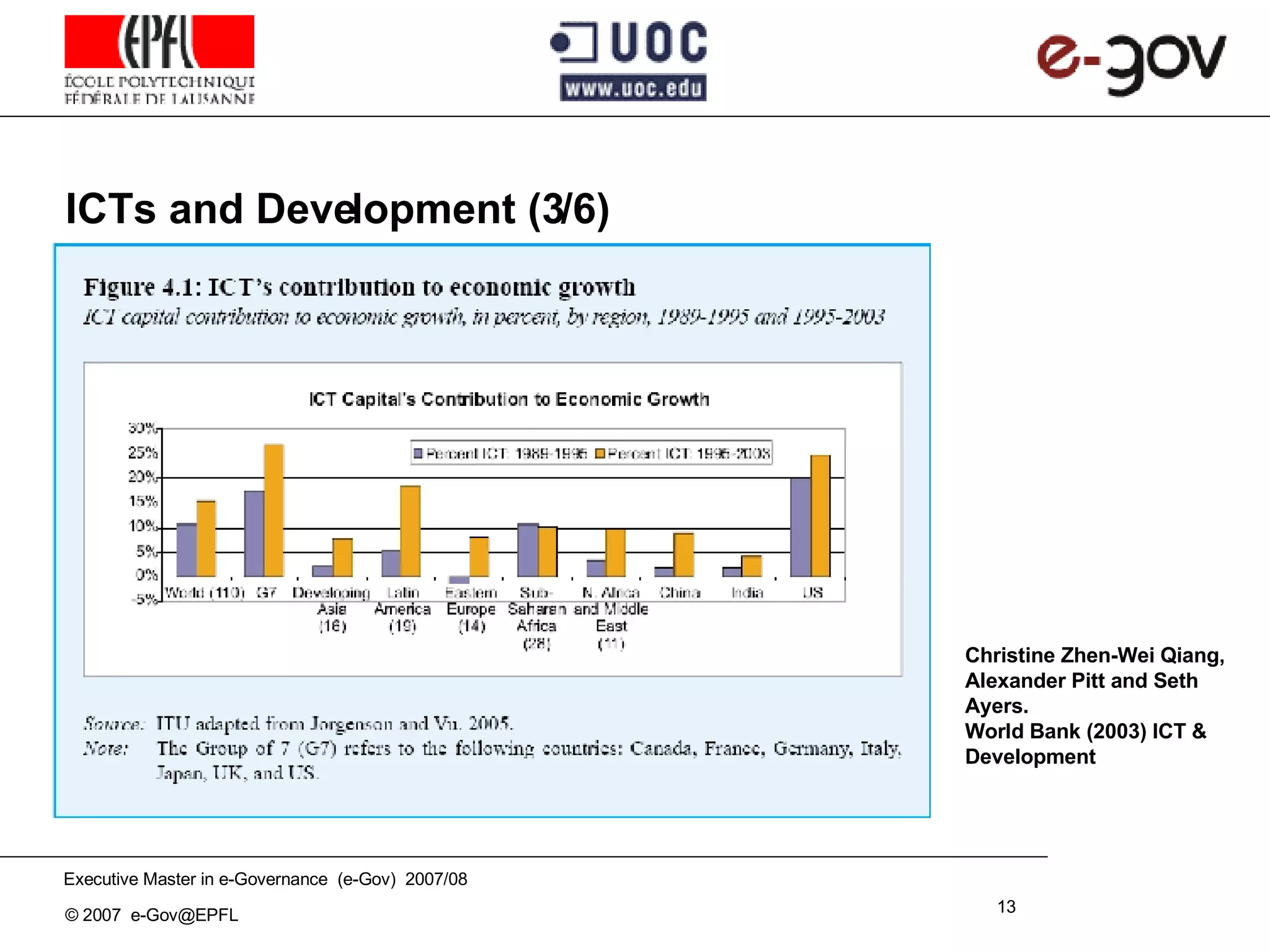
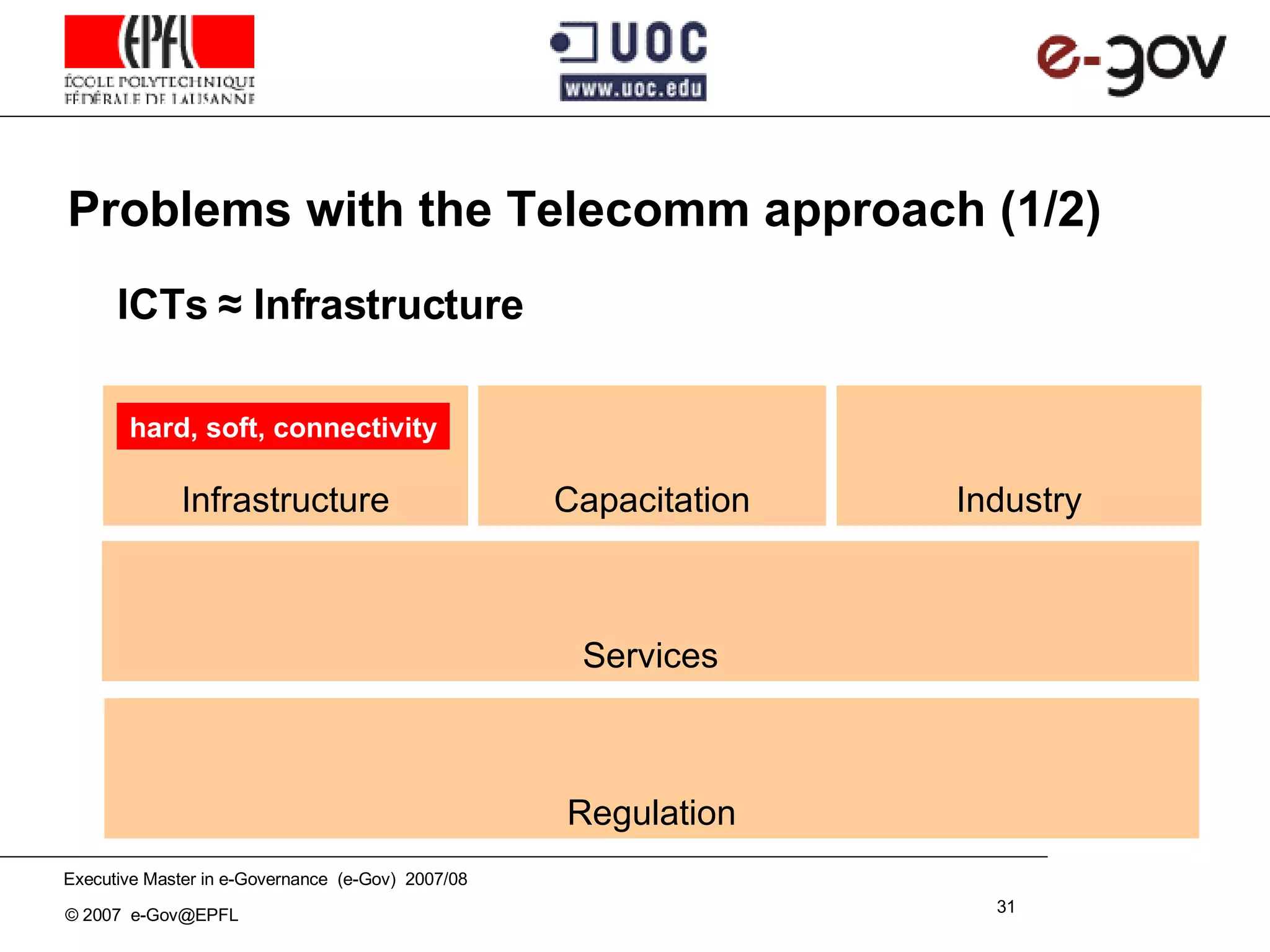
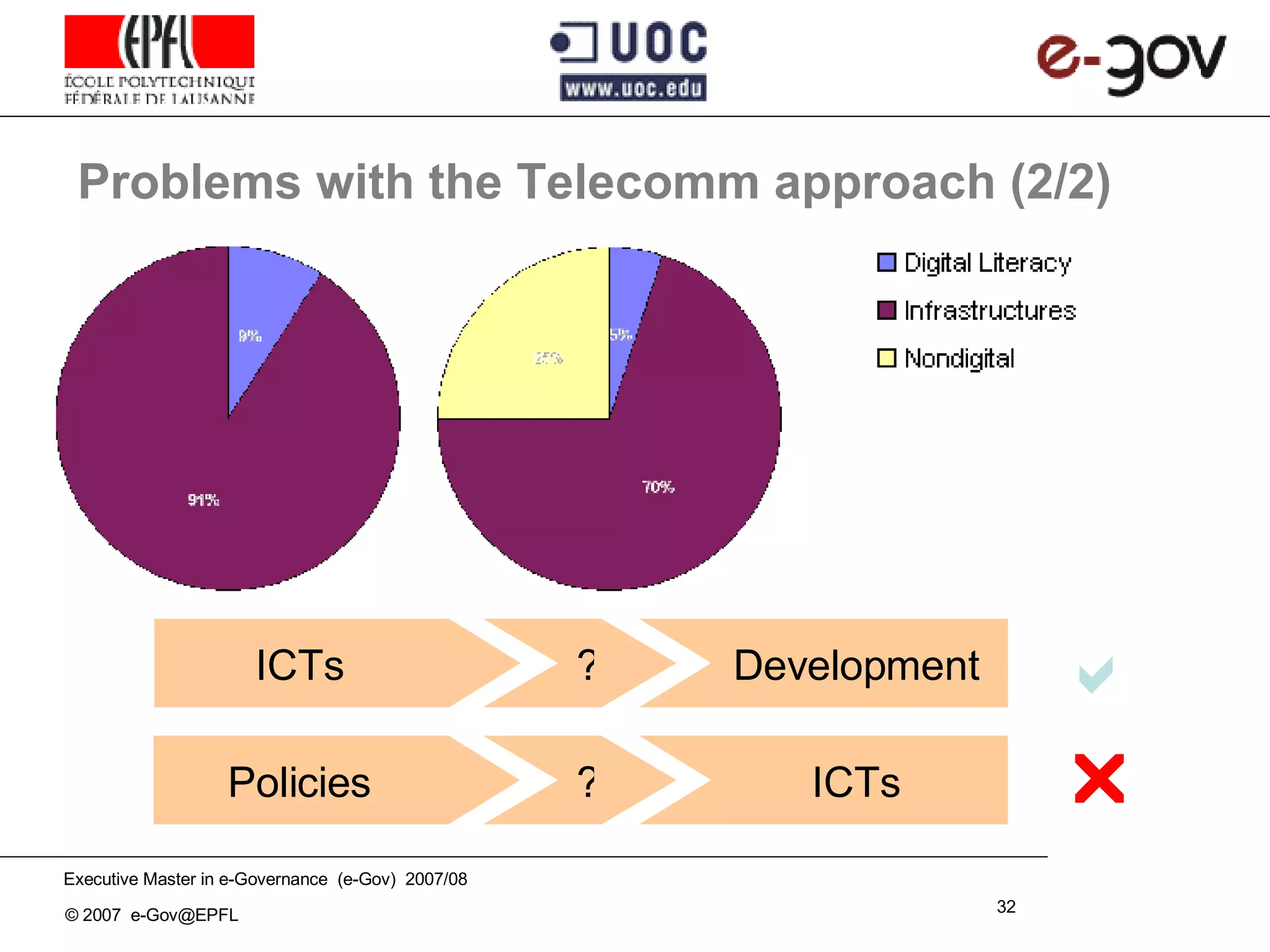
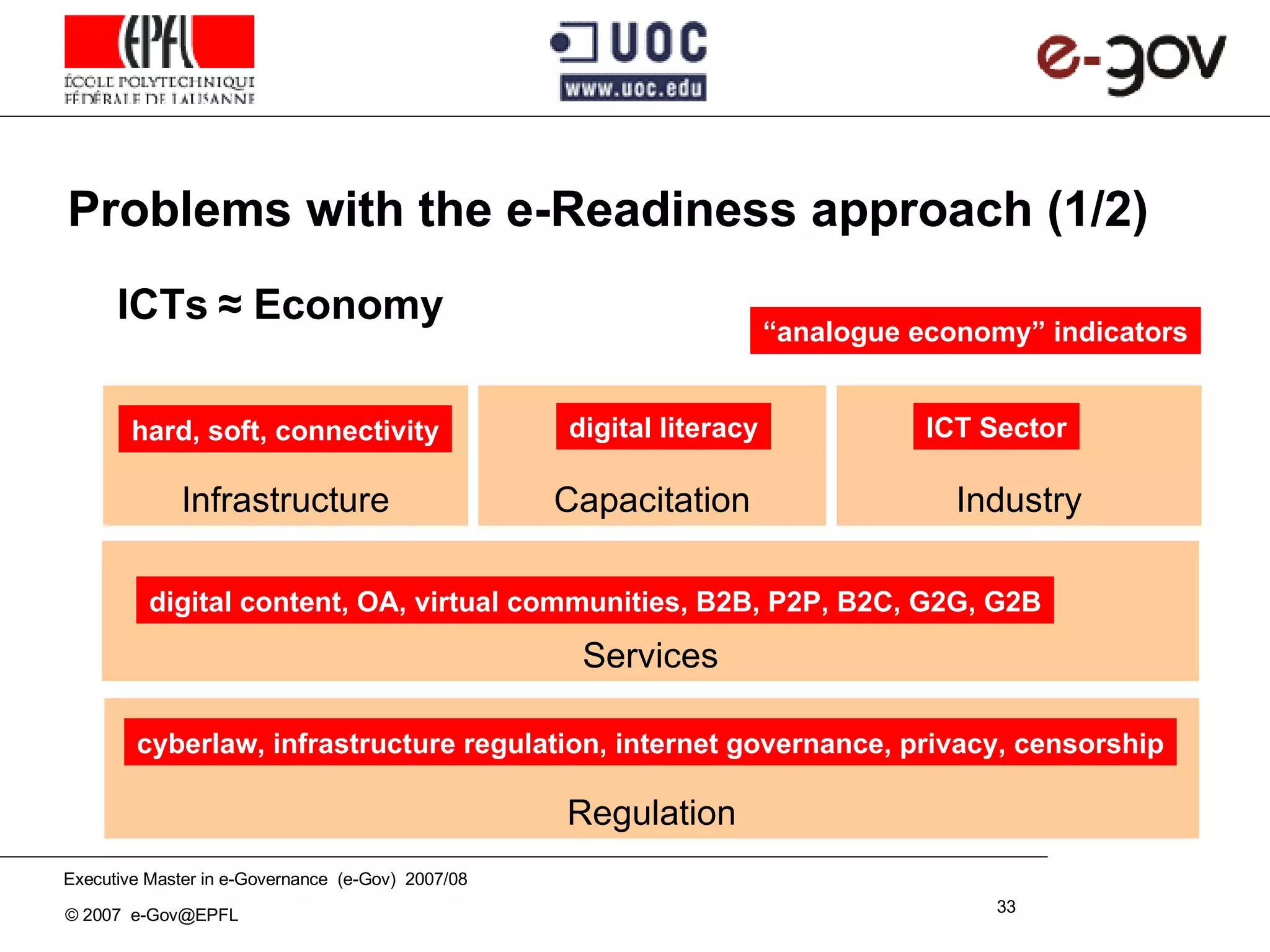
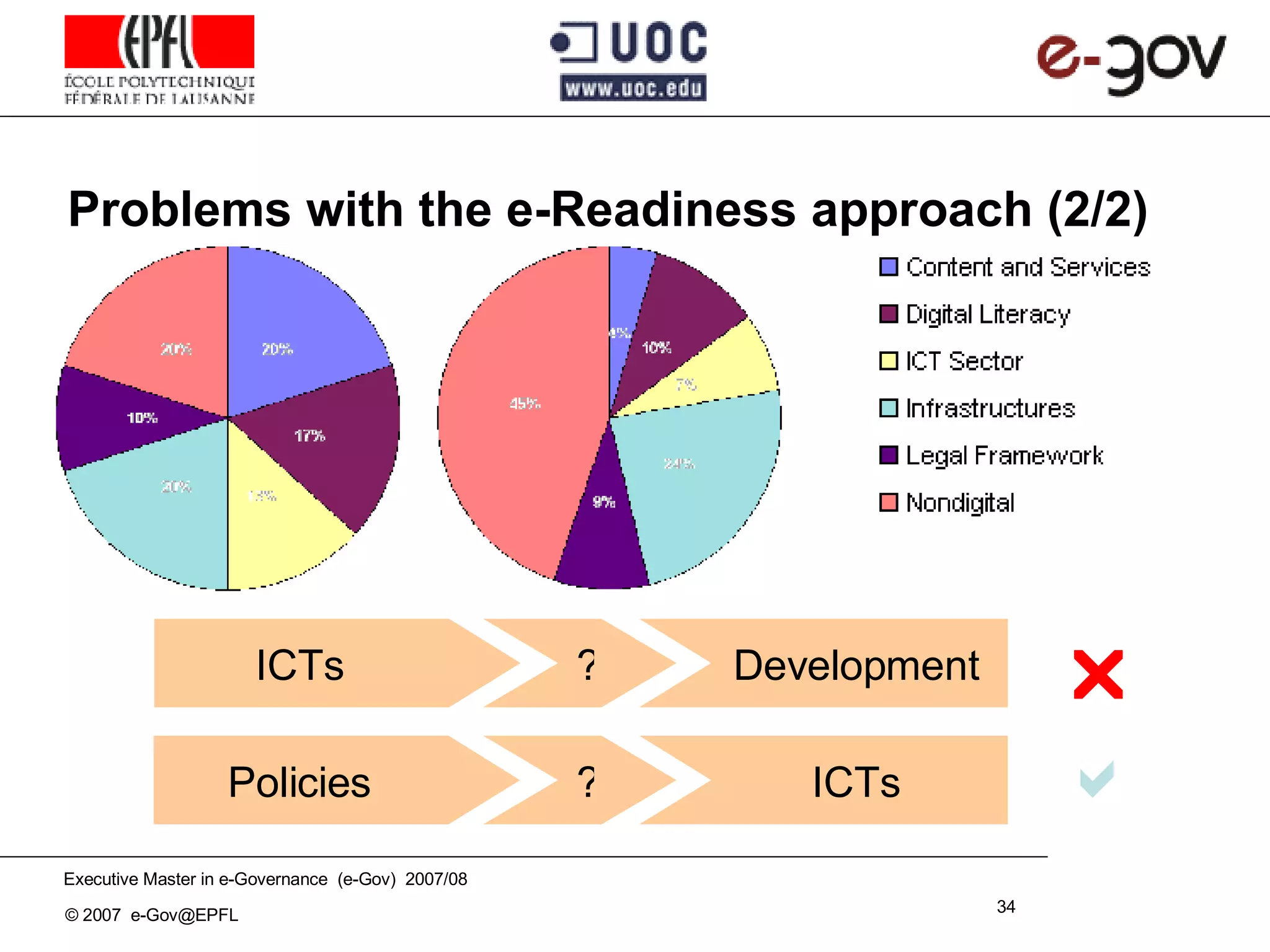
The document discusses the role of Information and Communication Technologies (ICTs) in development, emphasizing concepts like e-readiness and e-awareness in the context of the digital divide. It explores the impact of ICTs on various sectors such as health, education, and governance, and highlights the importance of infrastructure, policy, and digital literacy. Additionally, it examines the challenges and frameworks required to bridge the digital divide and promote an inclusive information society.




















![Barcelona, November 20th, 2007. Universitat Oberta de Catalunya To cite this work : Peña - López, Ismael. (200 7 ) ICT for Development: from e-Readiness to e-Awareness <http://ictlogy.net/presentations/ 20071120_ ismael_pena_ ict4d_from_e-readiness_to_e-awareness .pdf> [ downloaded dd/mm/aaaa] To contact the author : http:// ismael .ictlogy.net More information please visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/2.5/ All the information in this document under a Creative Commons license: Attribution – Non Commercial – No Derivs](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/icts-for-development-from-ereadiness-to-eawareness-1195579077710128-4/75/ICTs-for-development-from-e-Readiness-to-e-Awareness-38-2048.jpg)