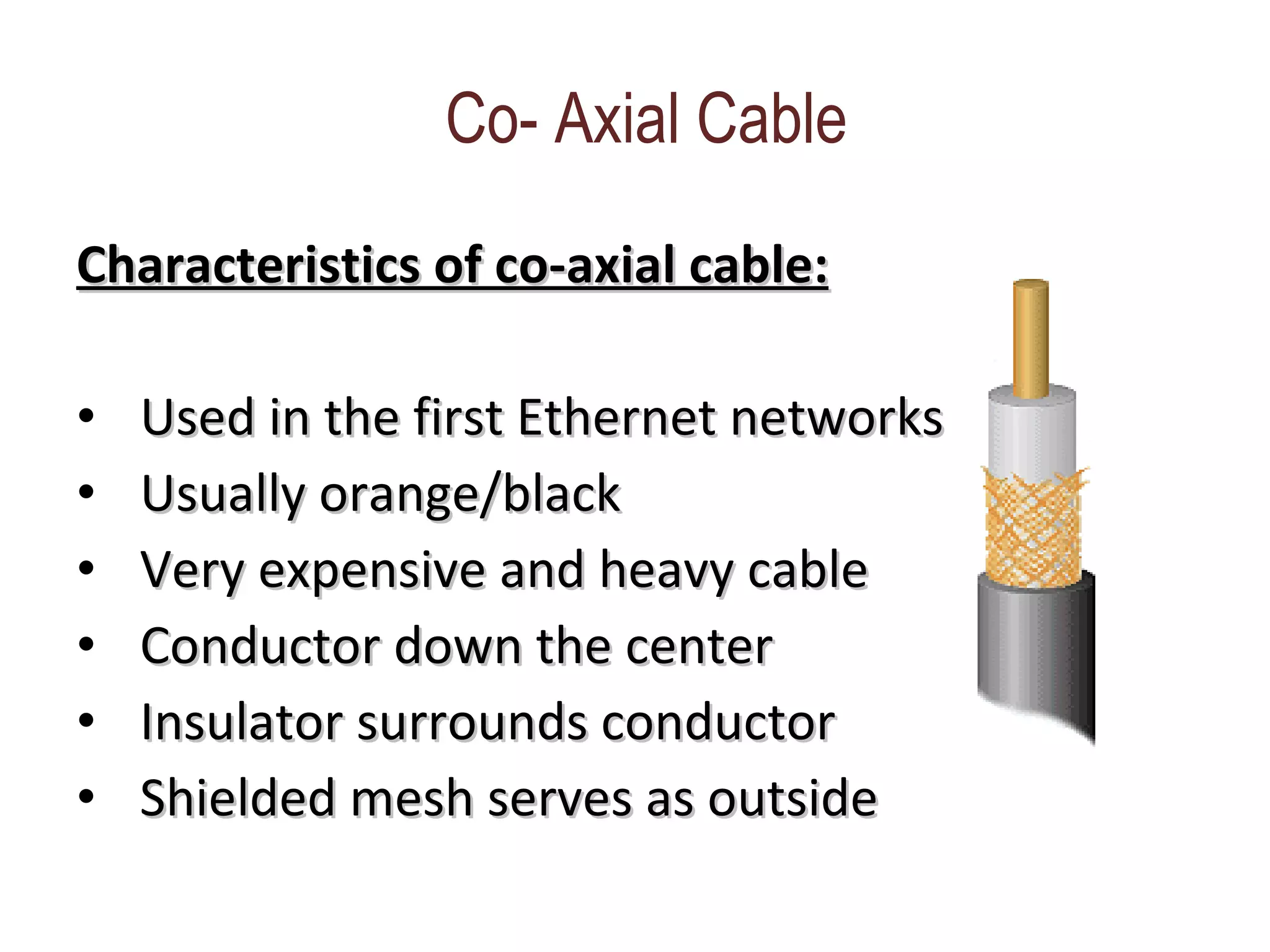
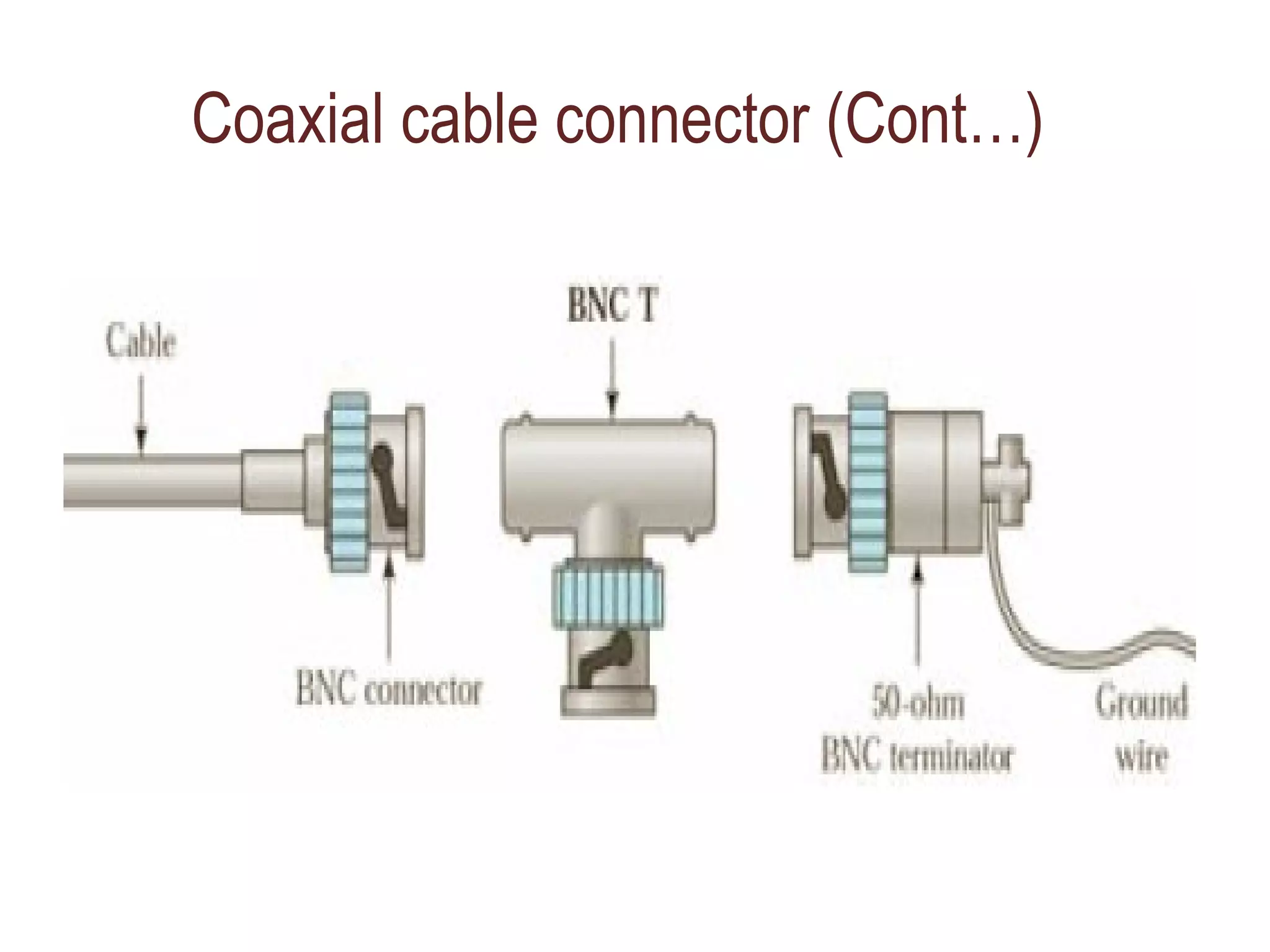
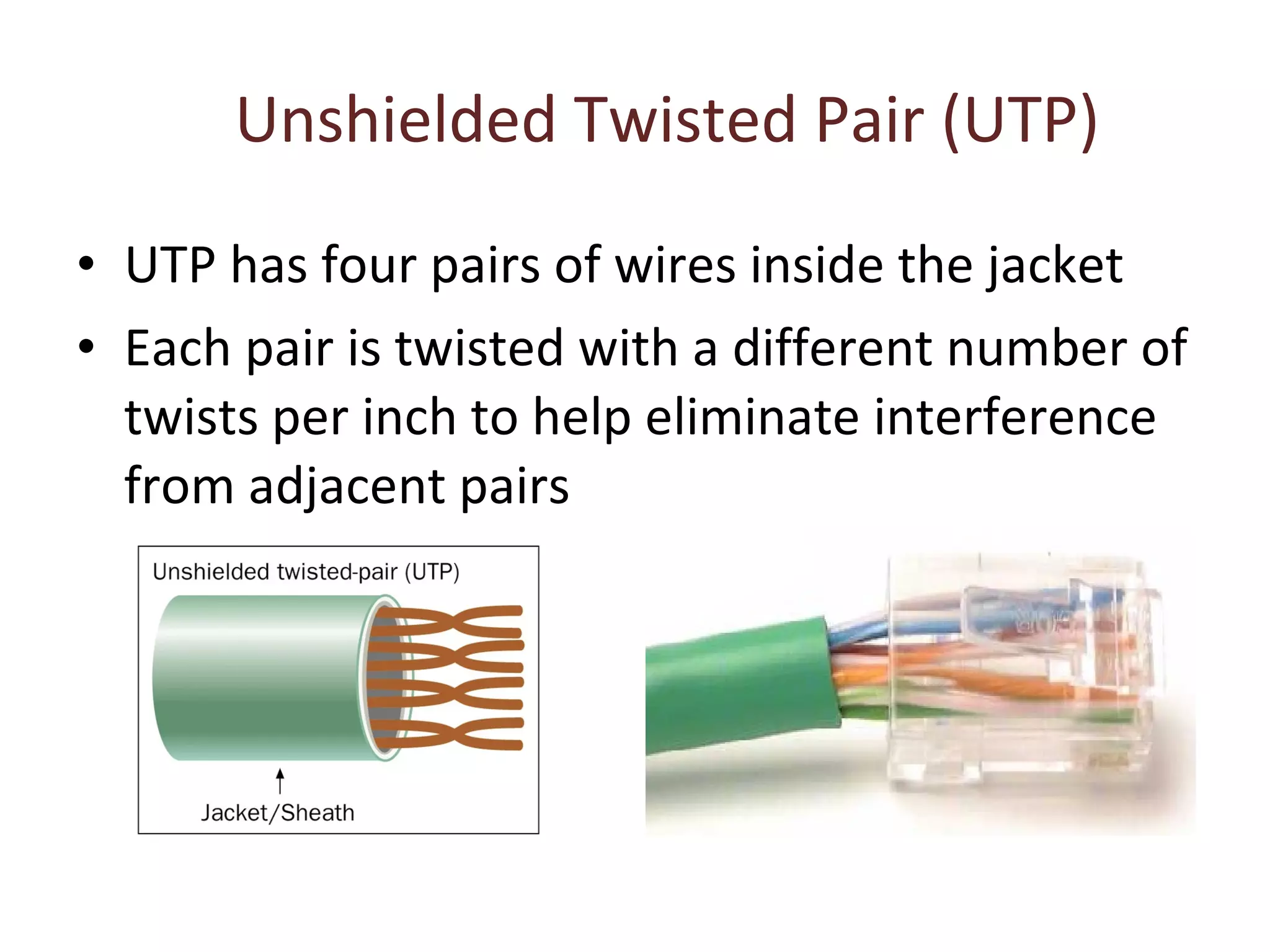
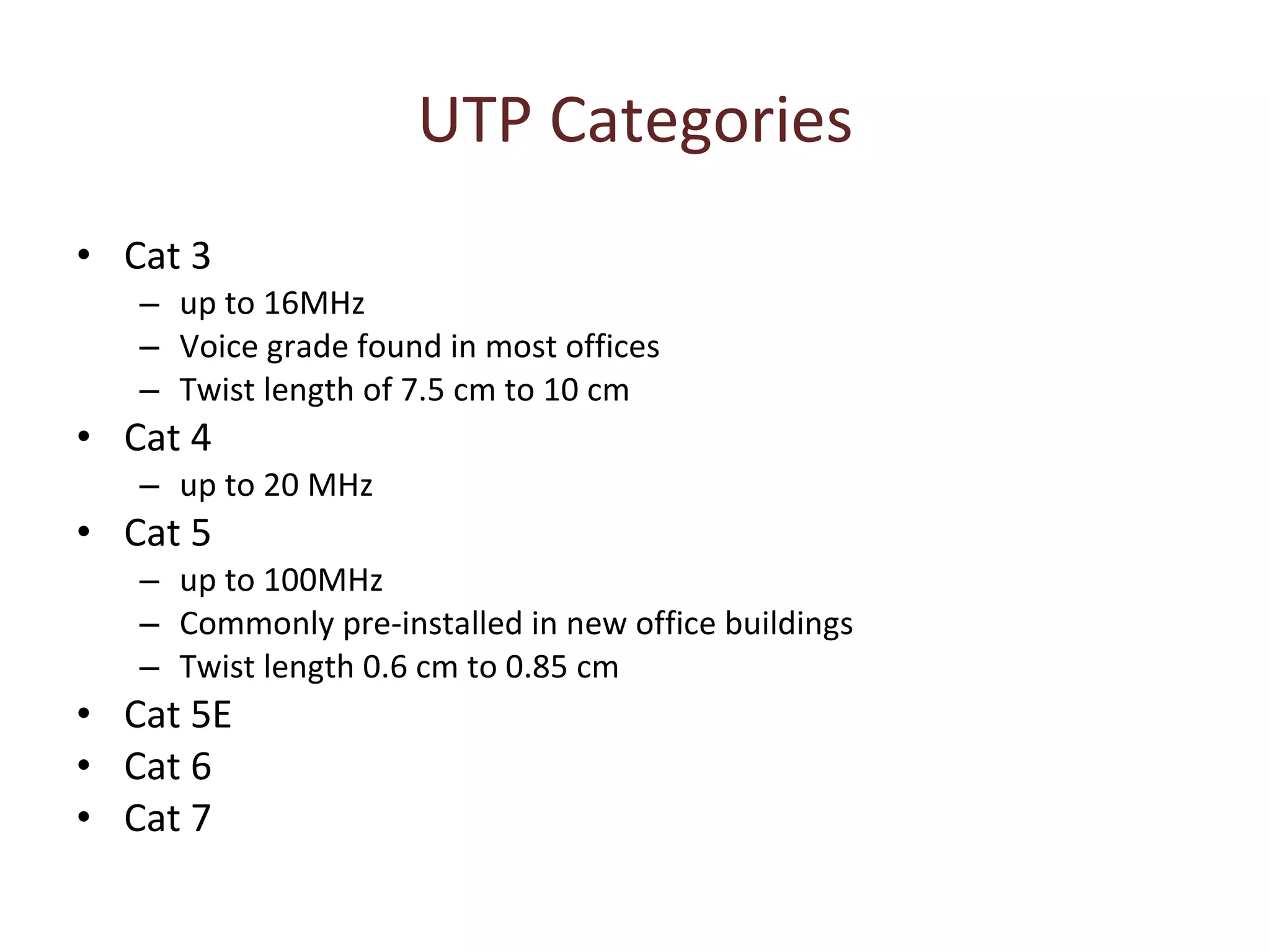
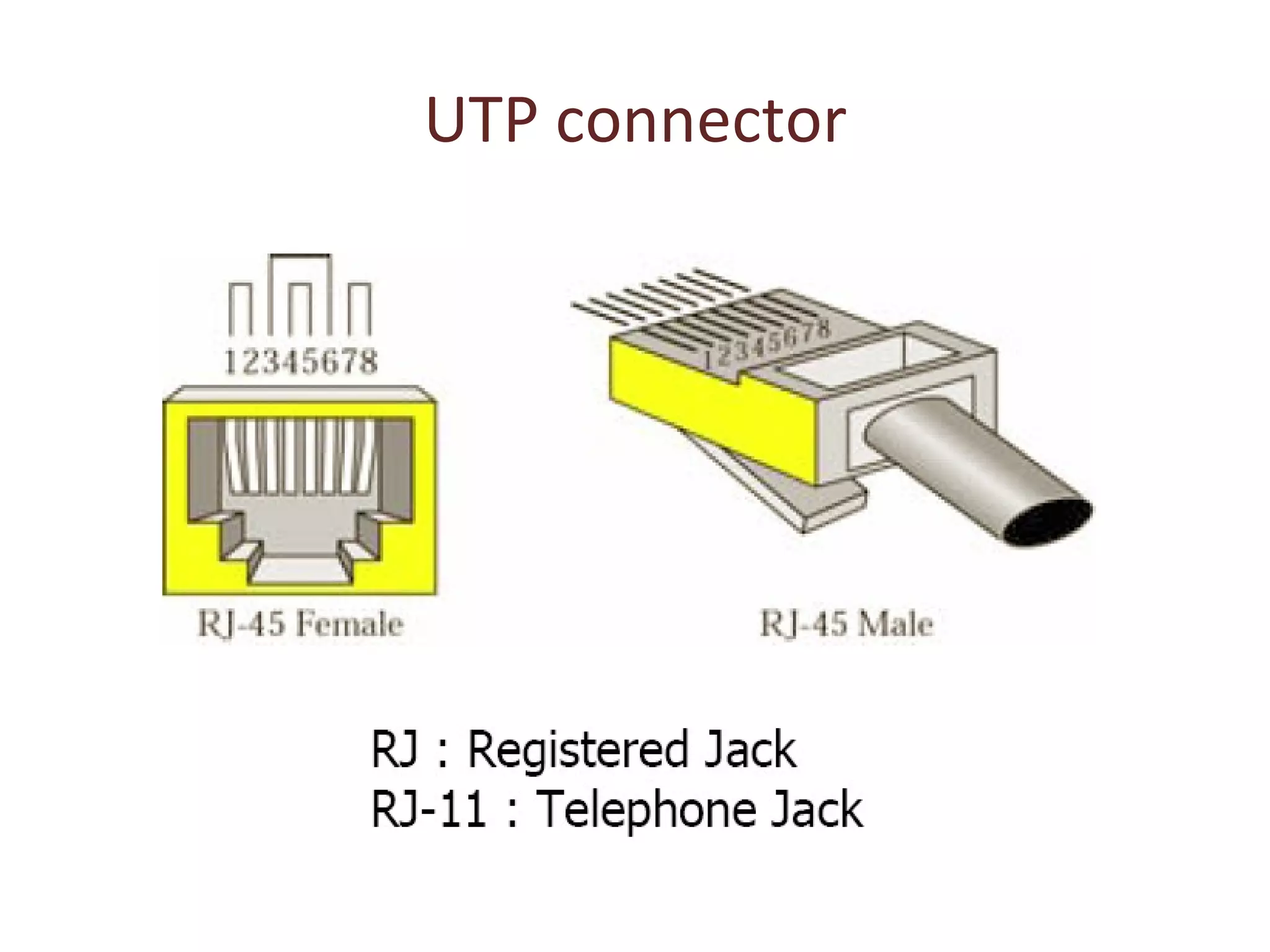
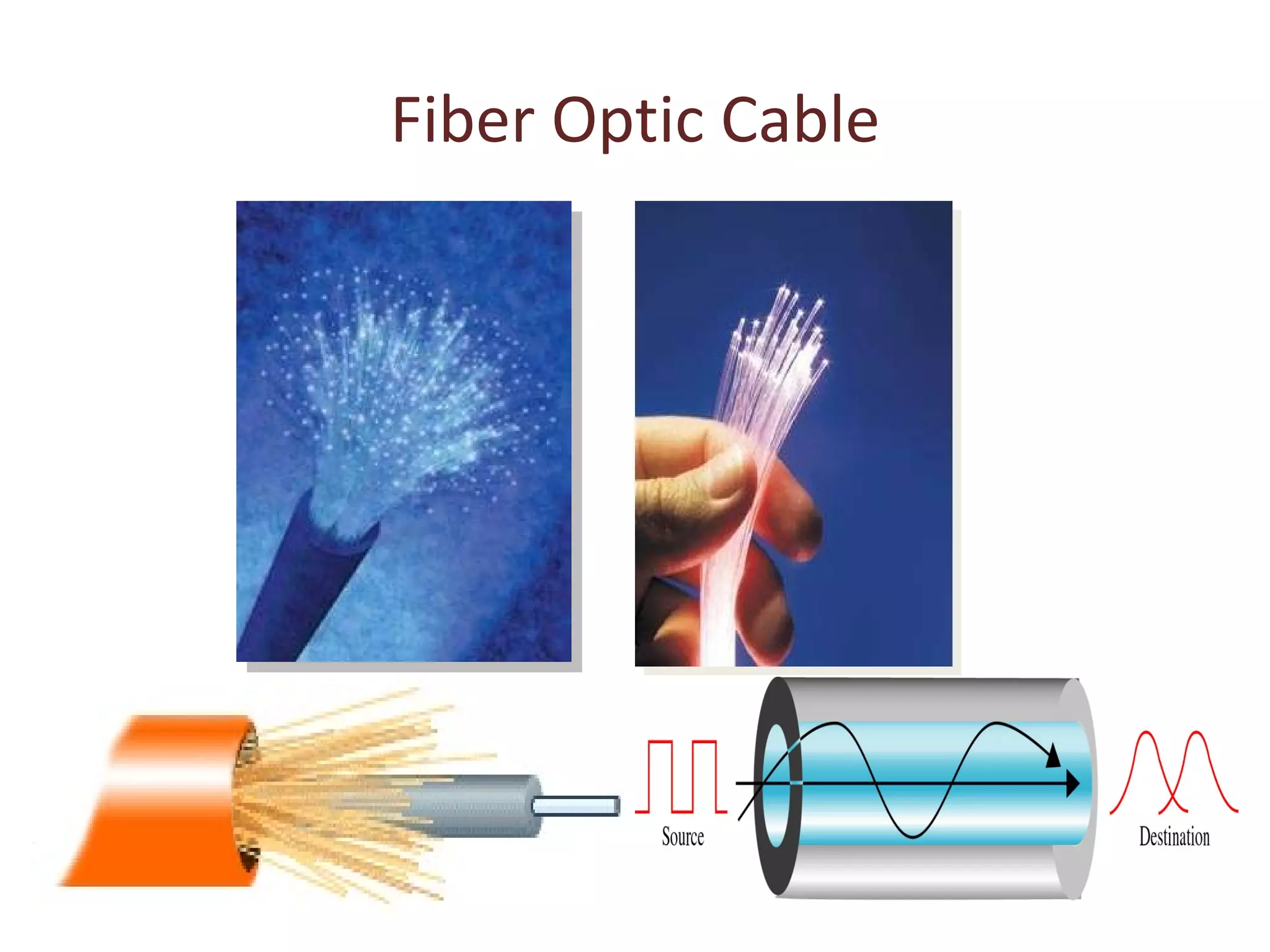
The document summarizes different types of transmission cables including coaxial cable, twisted pair cable, and fiber optic cable. Coaxial cable uses a central conductor surrounded by insulation and shielding, and was commonly used in early Ethernet networks. Twisted pair cable consists of two copper wires twisted together to reduce interference, and comes in unshielded and shielded varieties. Fiber optic cable uses glass cores to transmit light signals and is more expensive but can transmit over greater distances and speeds with less signal loss than other cables.