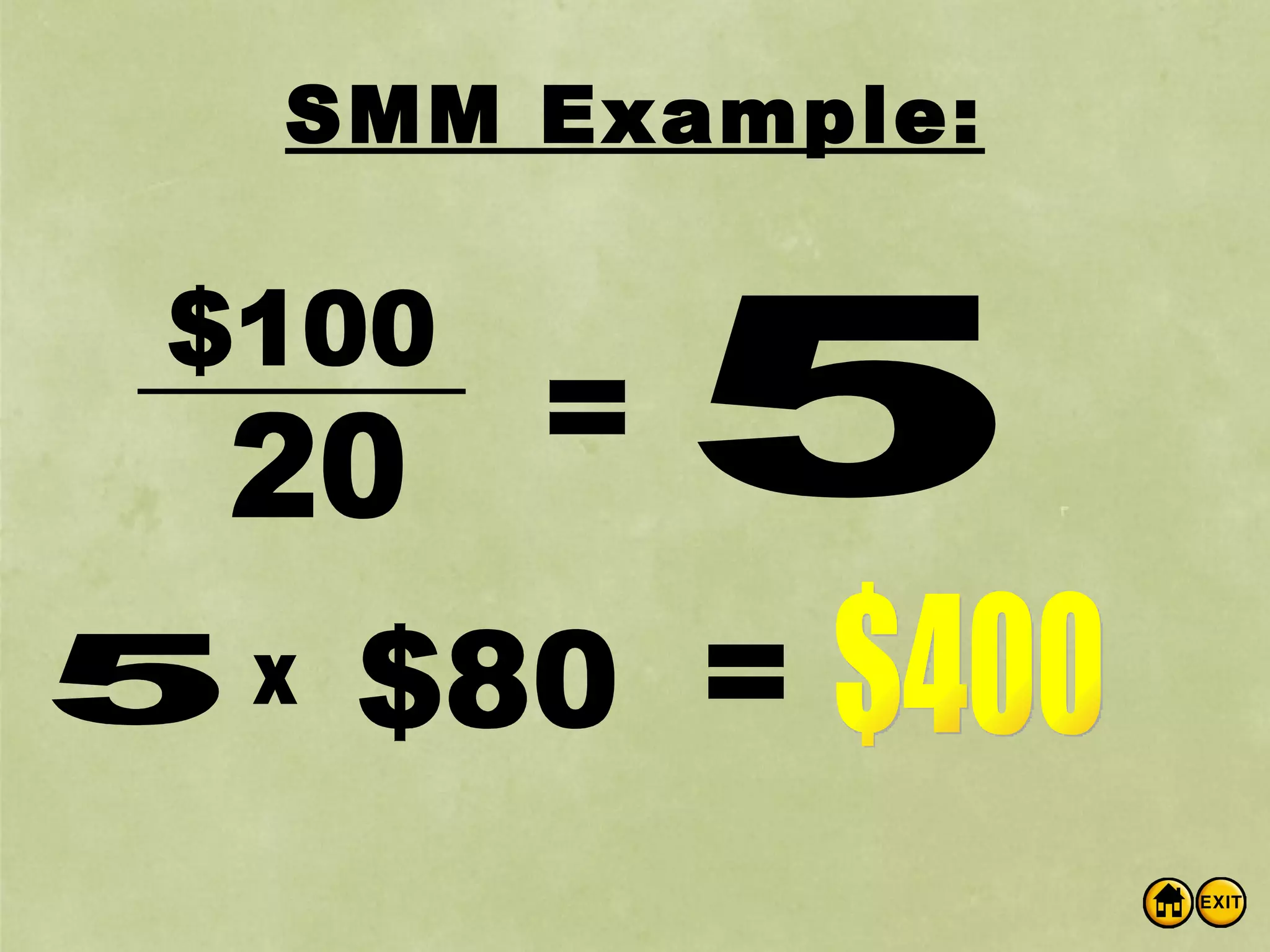Embed presentation
Downloaded 69 times



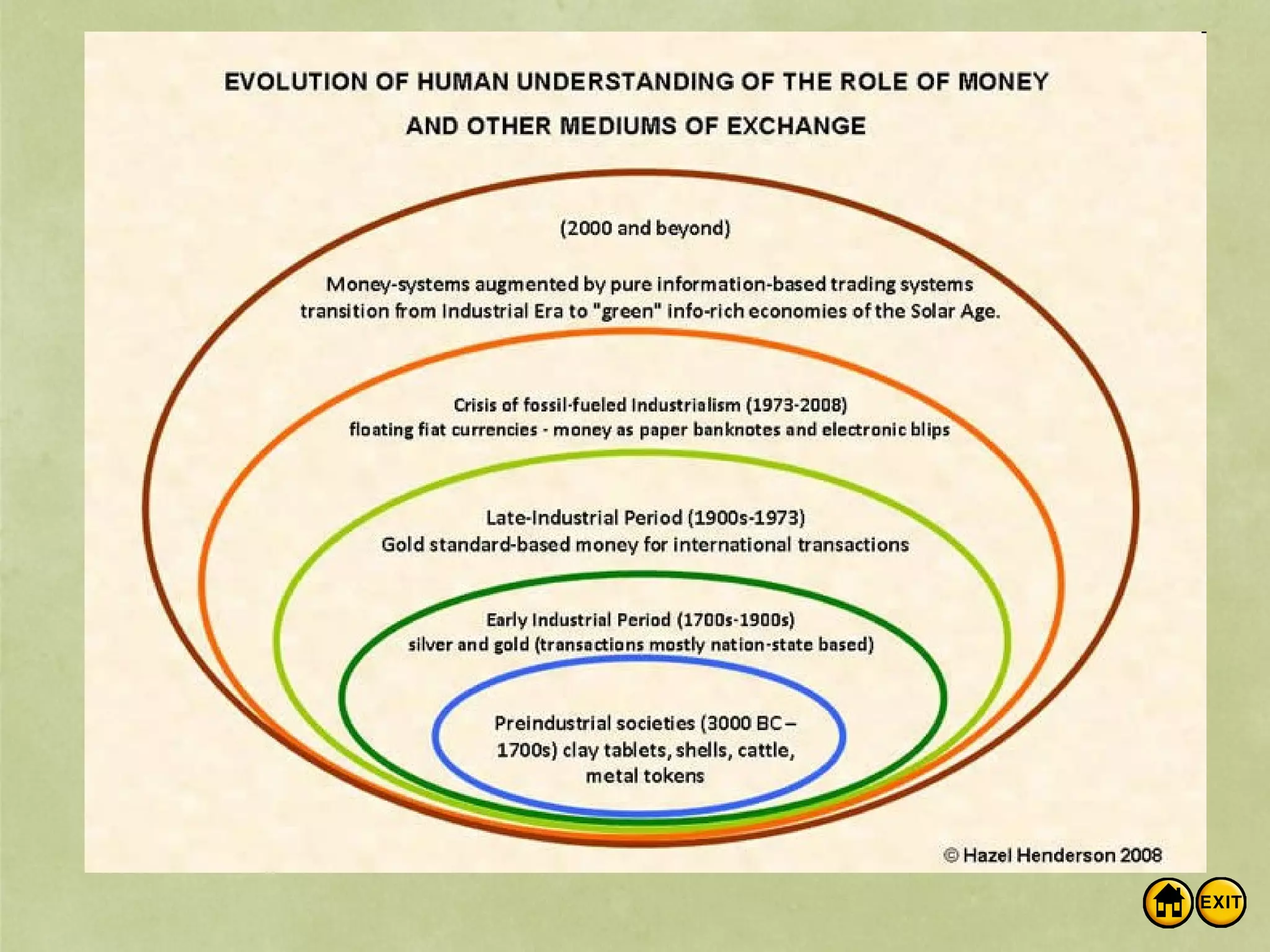
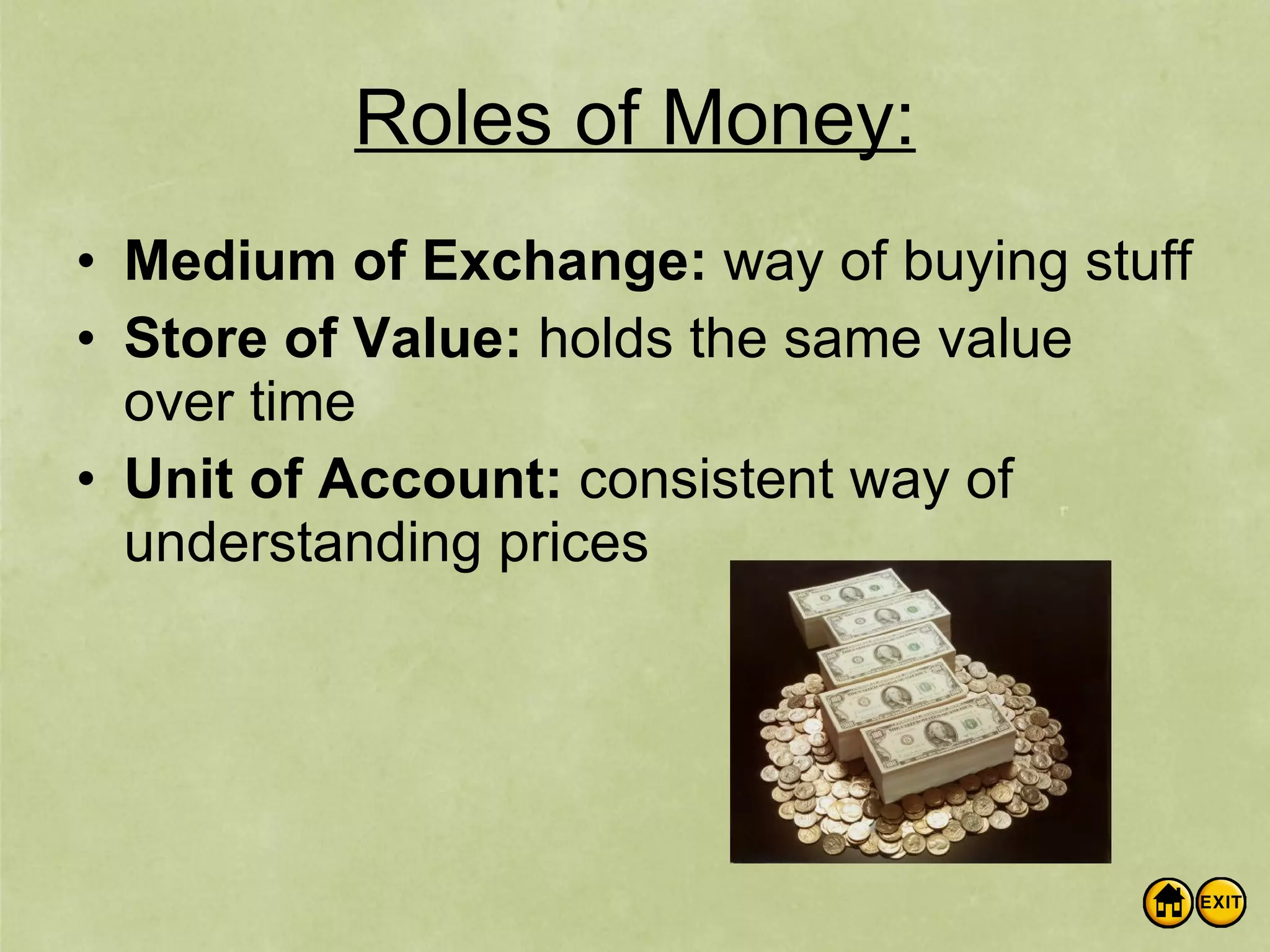

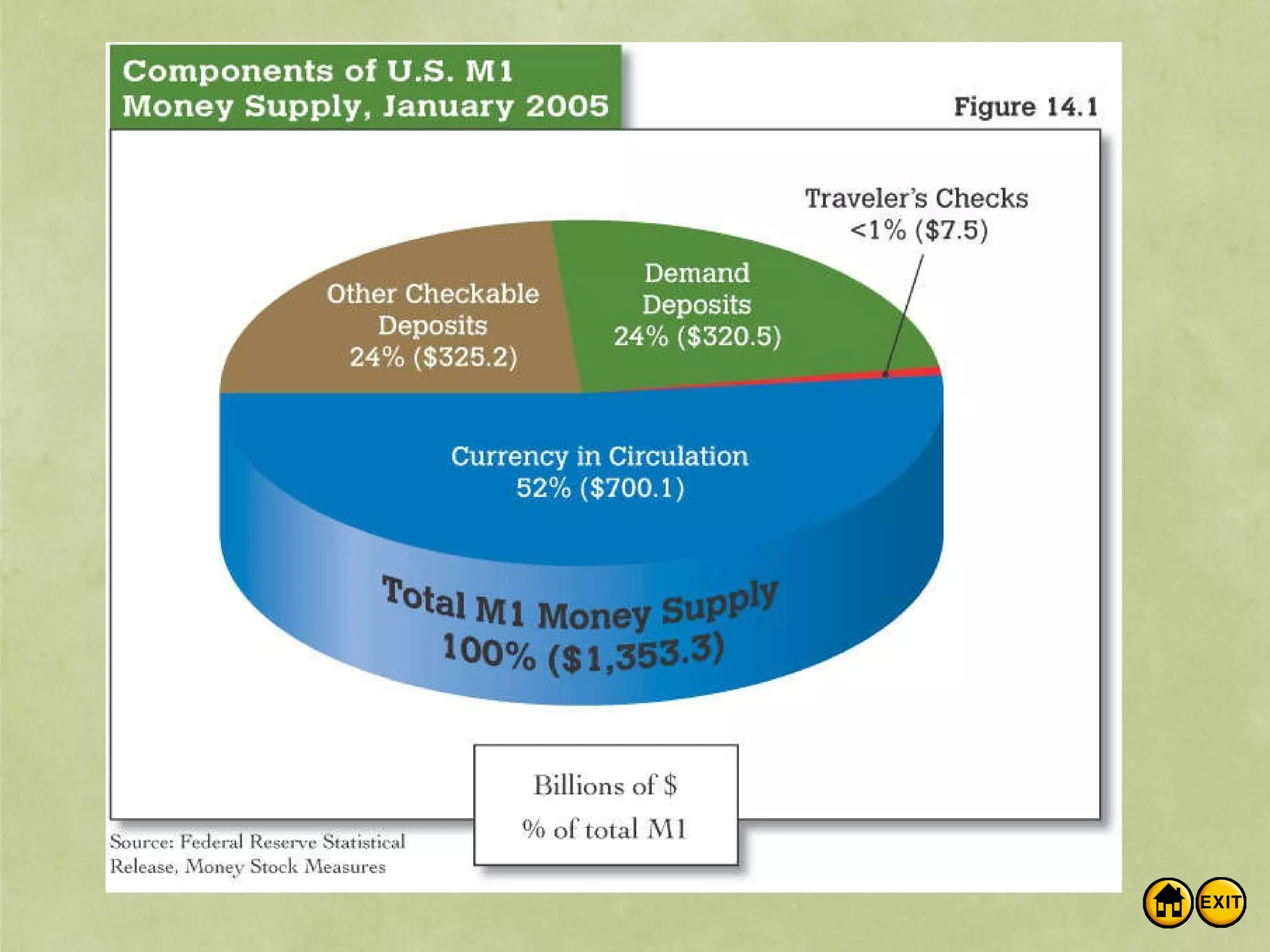
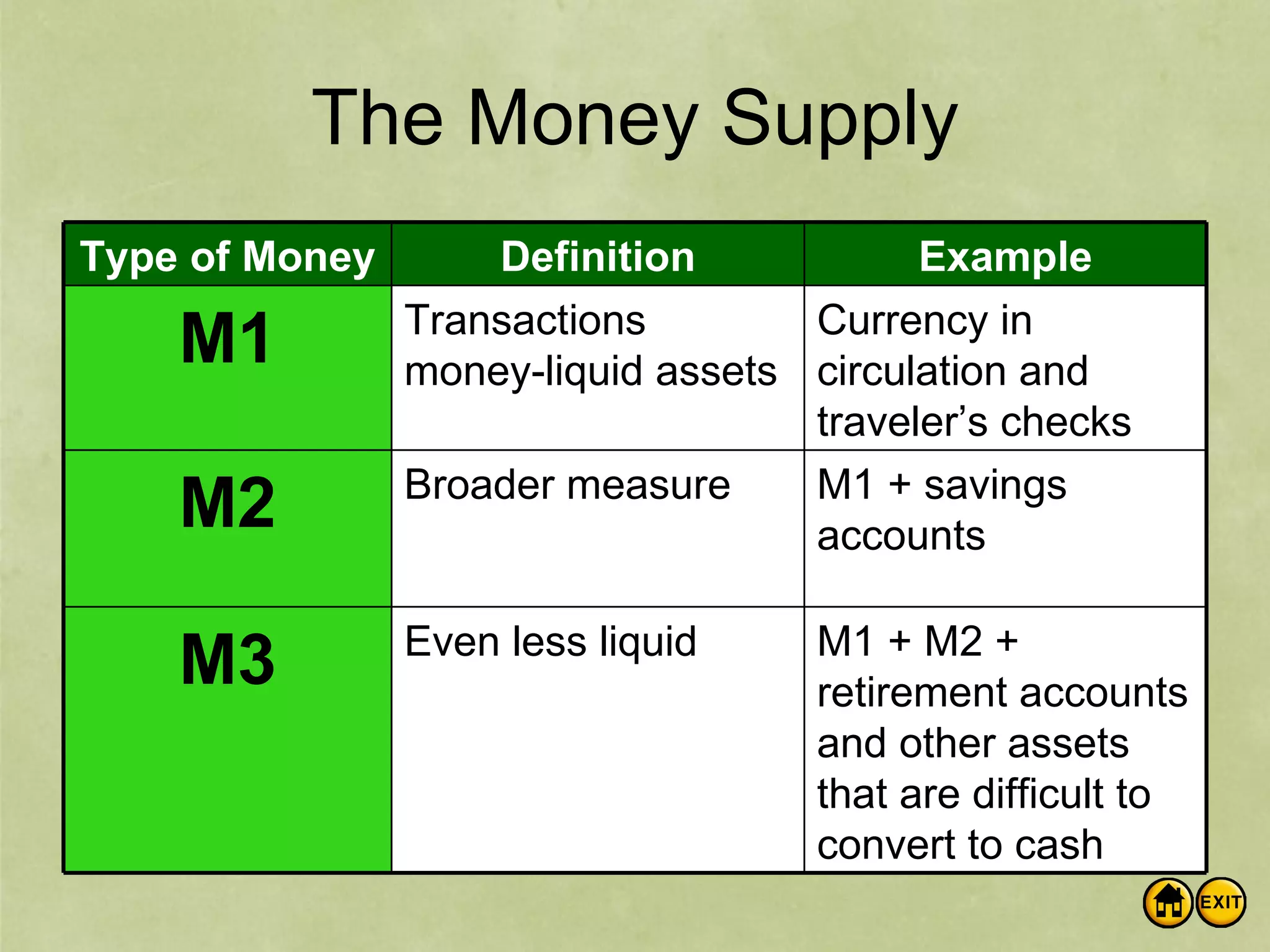
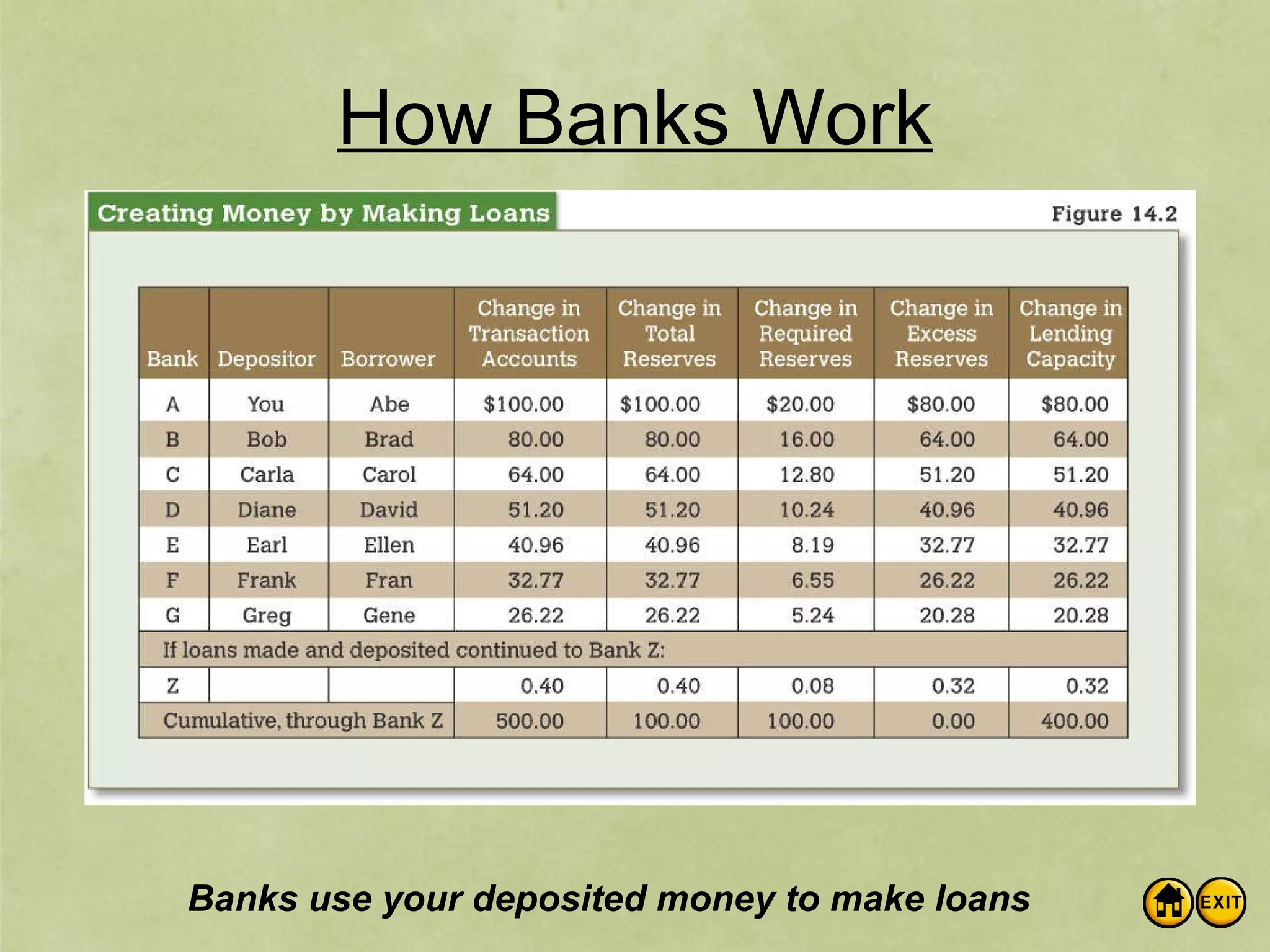

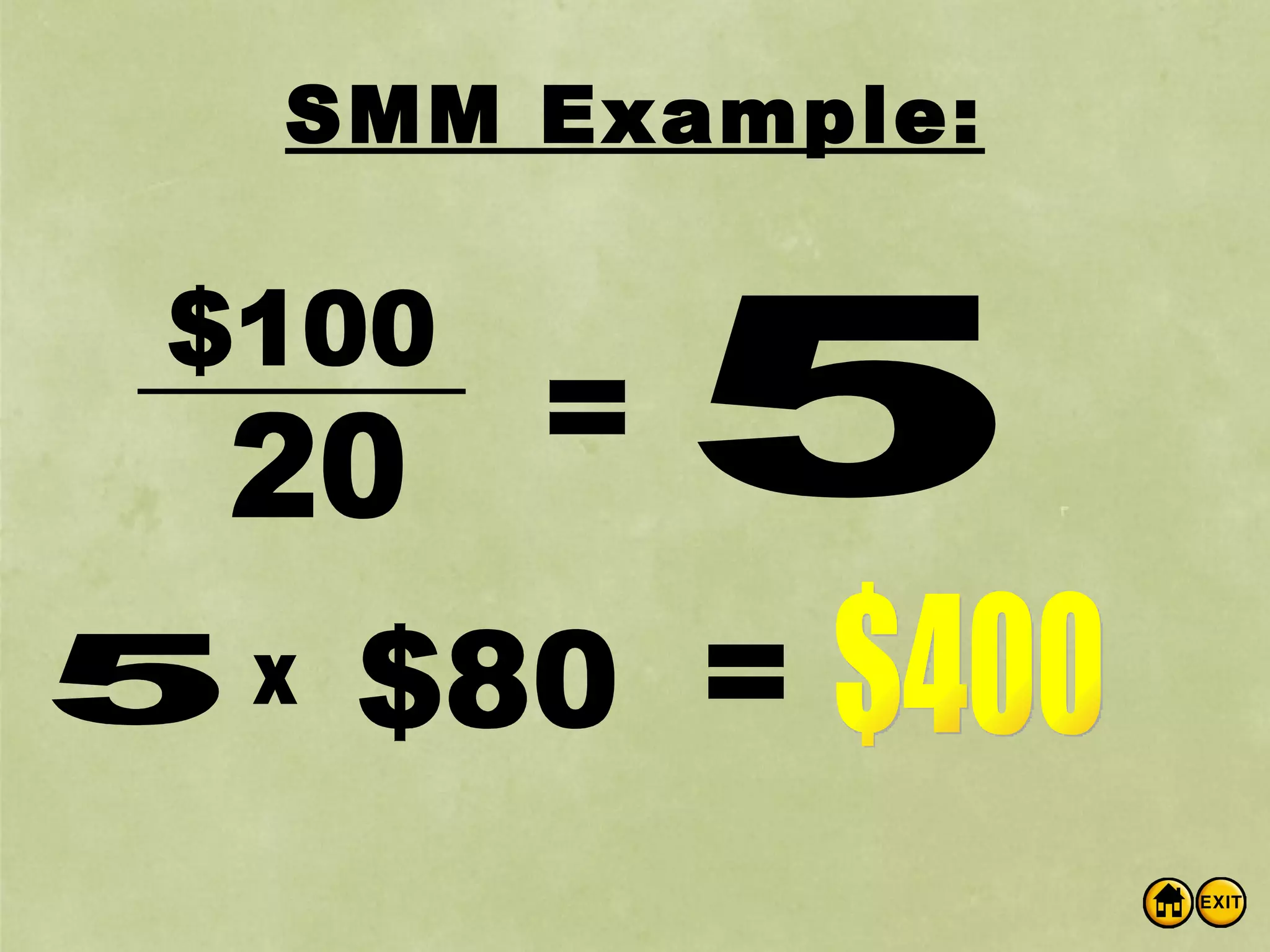

The document discusses money and banking. It defines different types of money like commodity money, representative money, and fiat money. It also lists the roles of money as a medium of exchange, store of value, and unit of account. The document then discusses what makes money valuable, such as being widely accepted and durable. It defines the different measures of money supply as M1, M2, and M3. M1 is the most liquid transactions money. Finally, it introduces how banks work by using deposits to make loans and provides an example of calculating the money supply using the simple money multiplier formula.