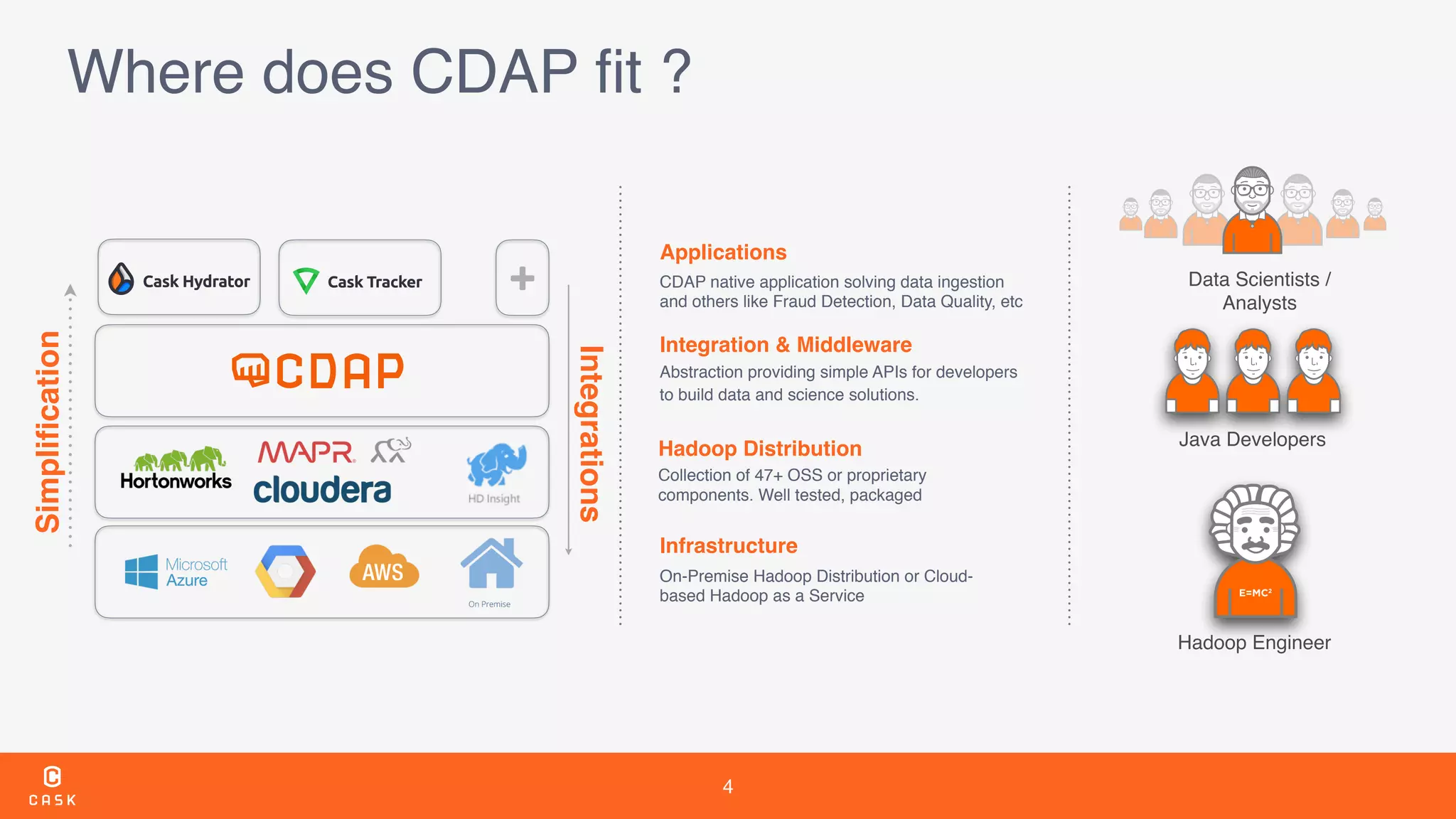
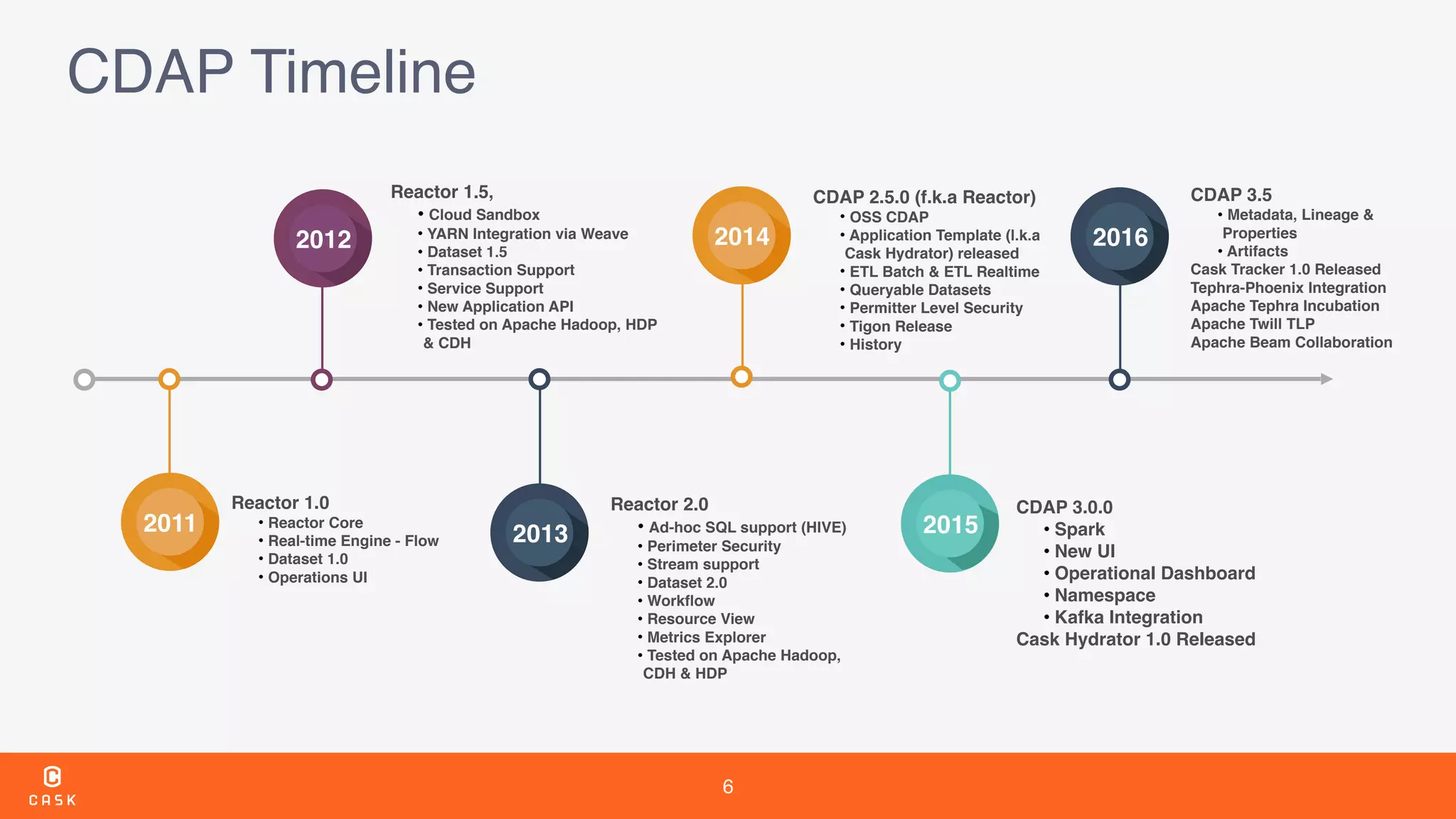
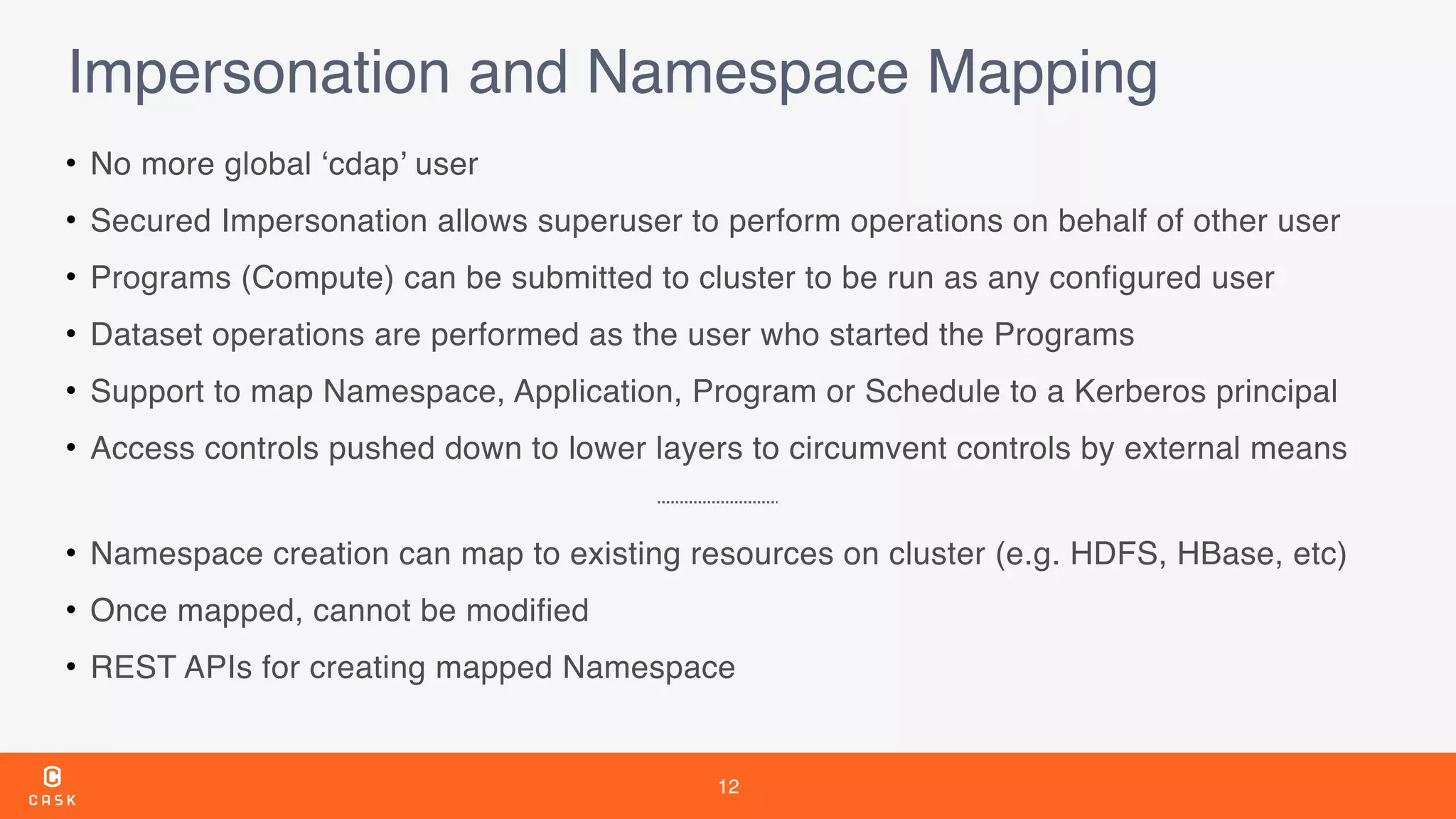
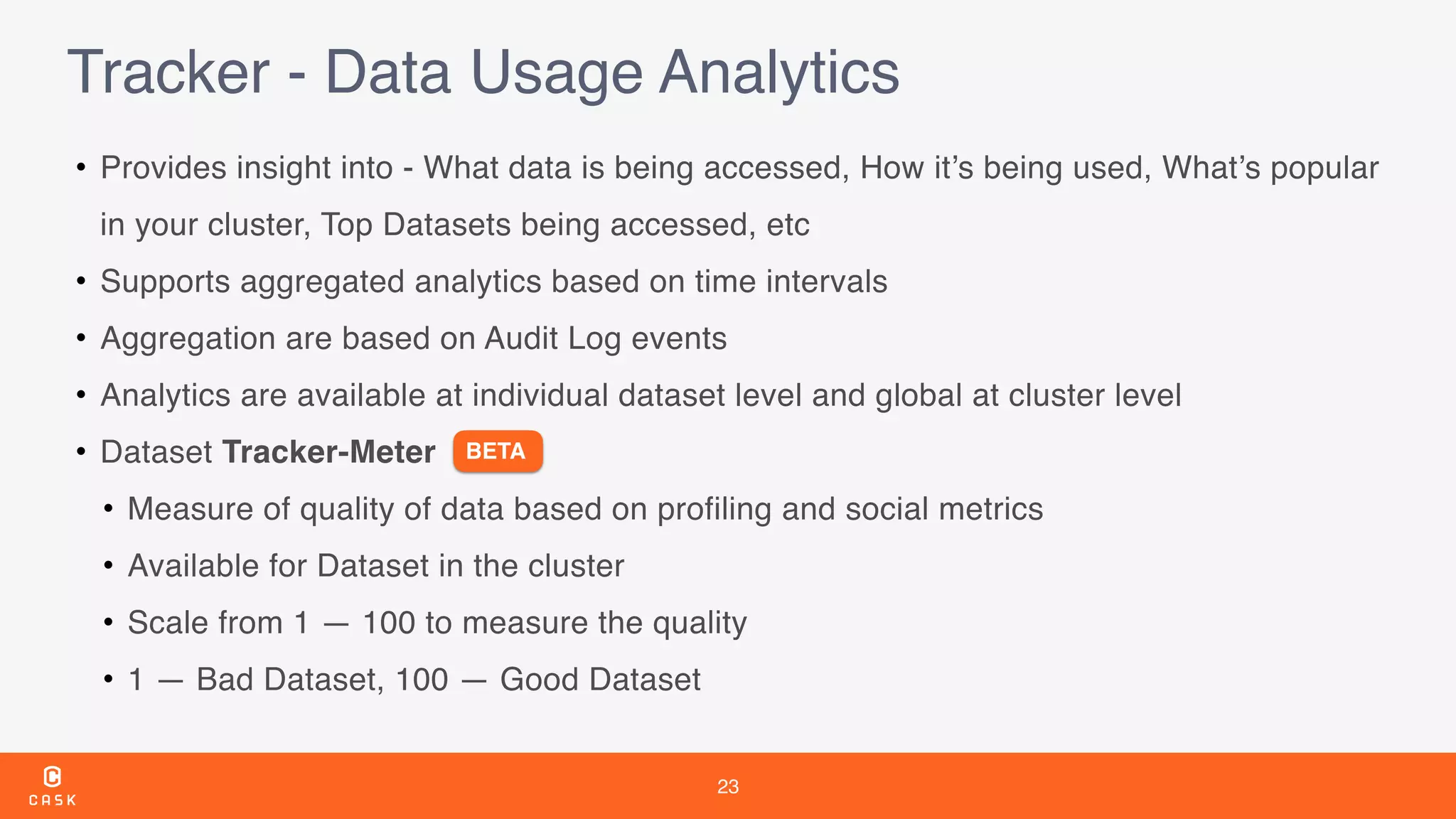
The document outlines the features and improvements introduced in CDAP 3.5, a framework for building and managing data pipelines. It highlights self-service capabilities, integration with Hadoop technologies, enhanced security measures, and new functionalities for real-time data processing and analytics. Additionally, it details the timeline of CDAP releases and the introduction of tools for metadata management and data quality tracking.