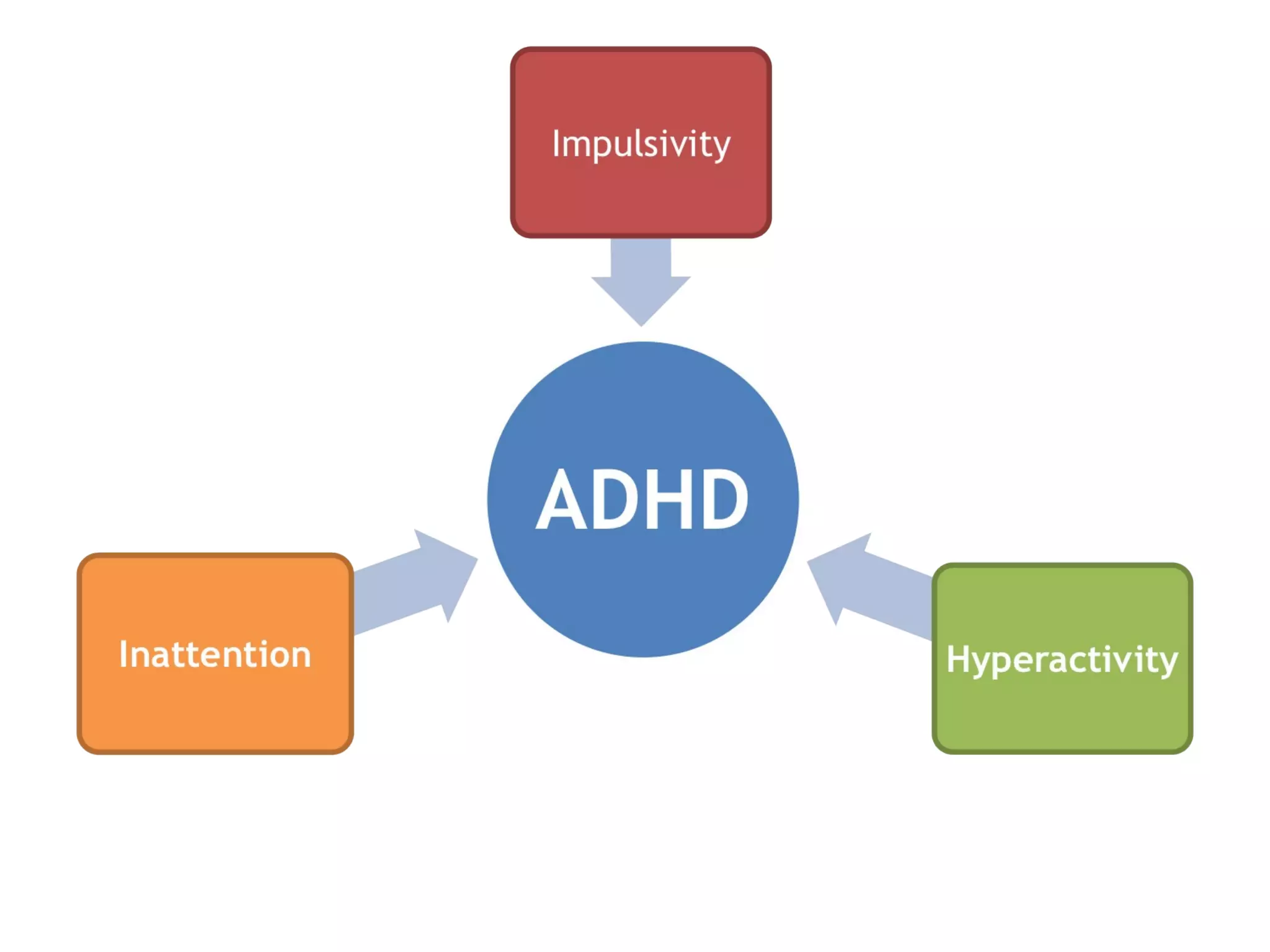
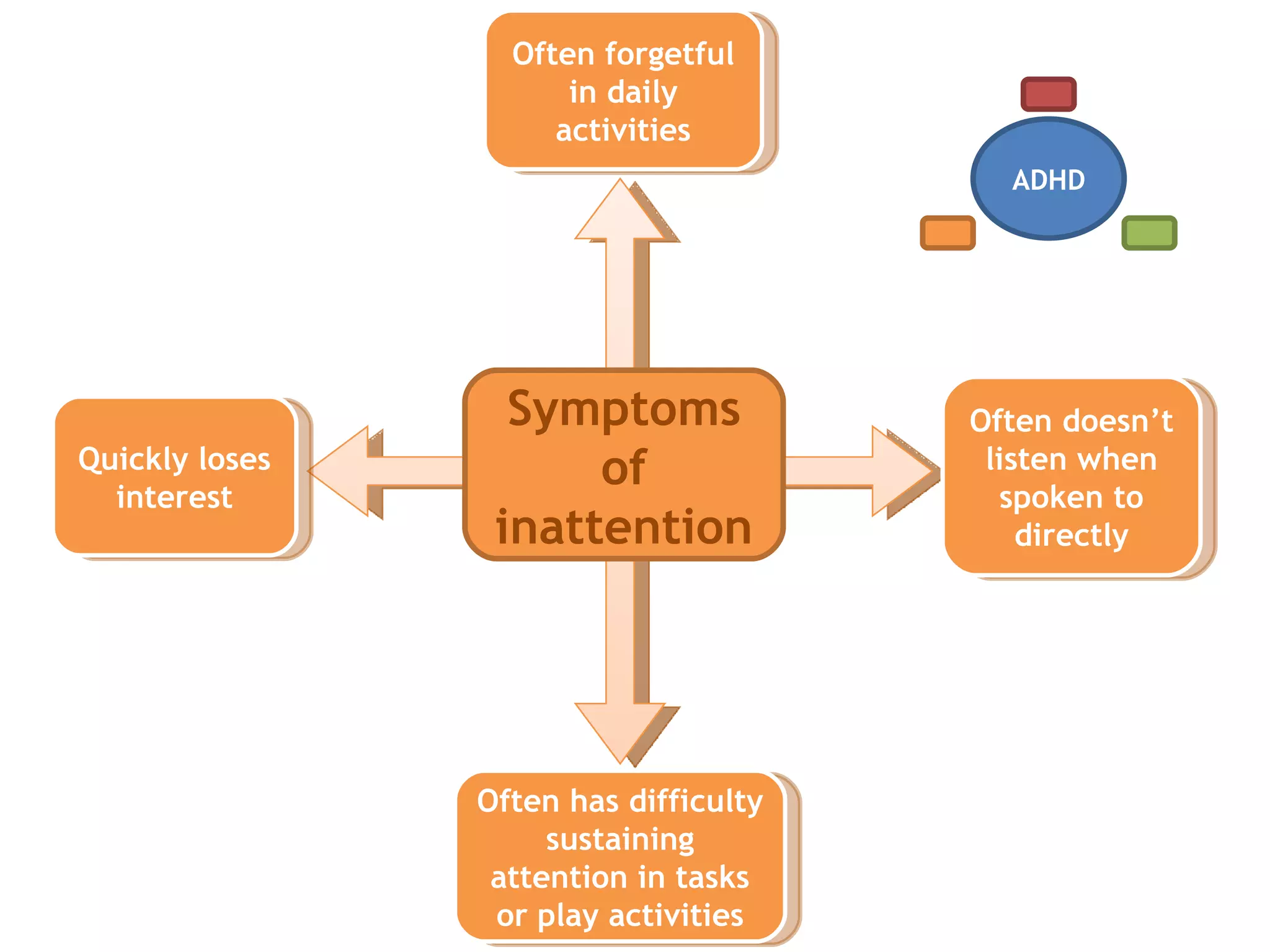
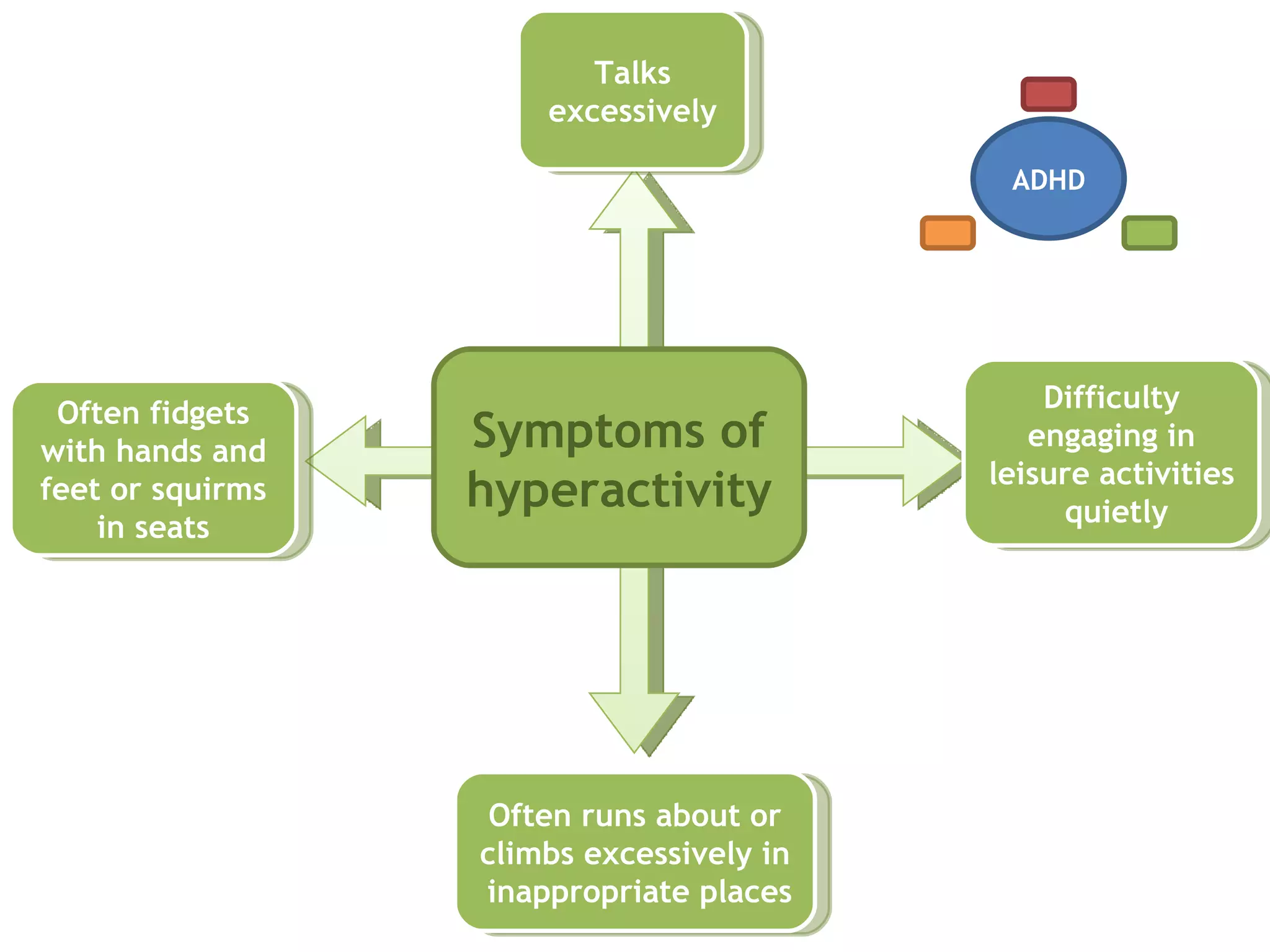
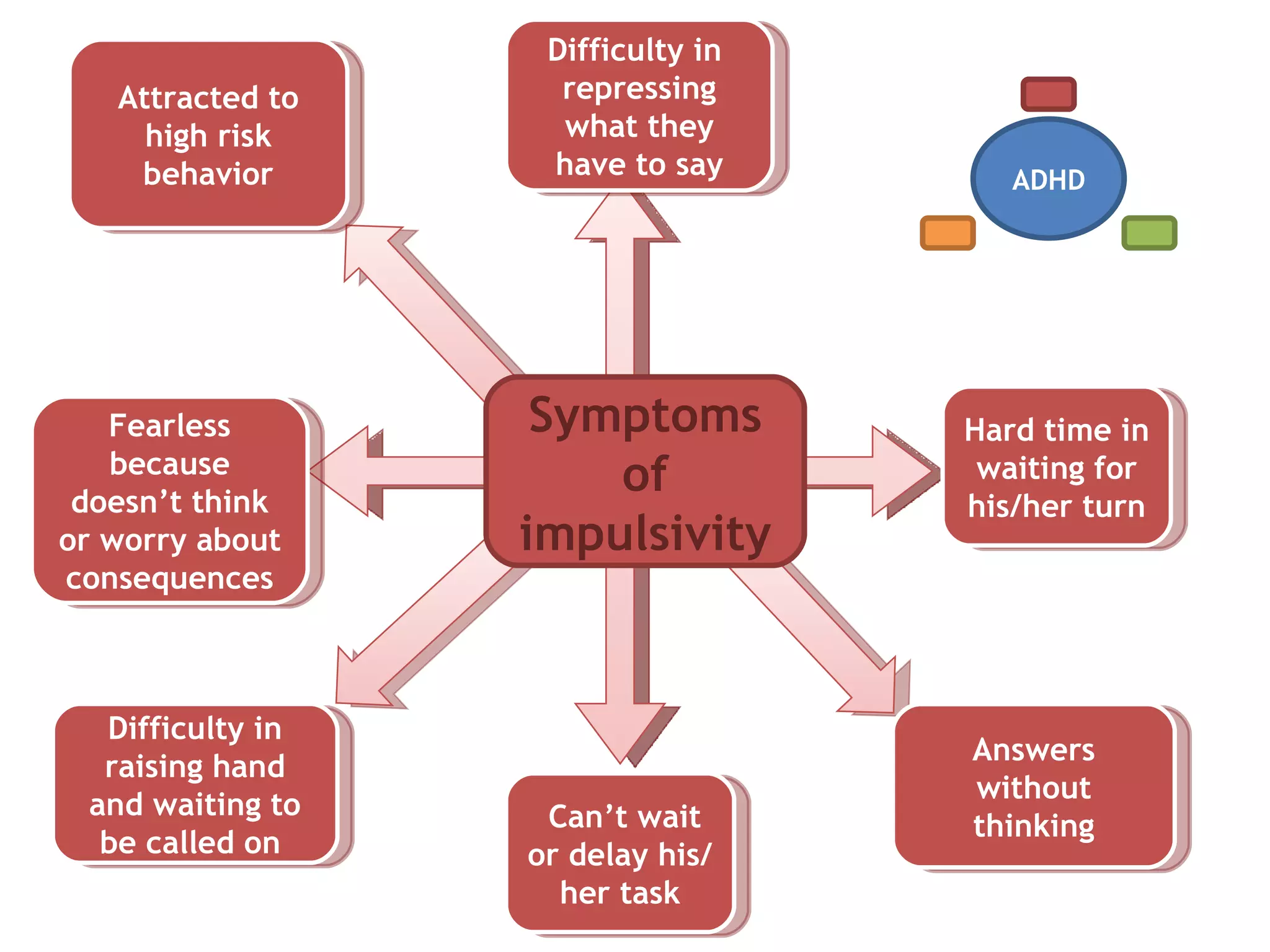
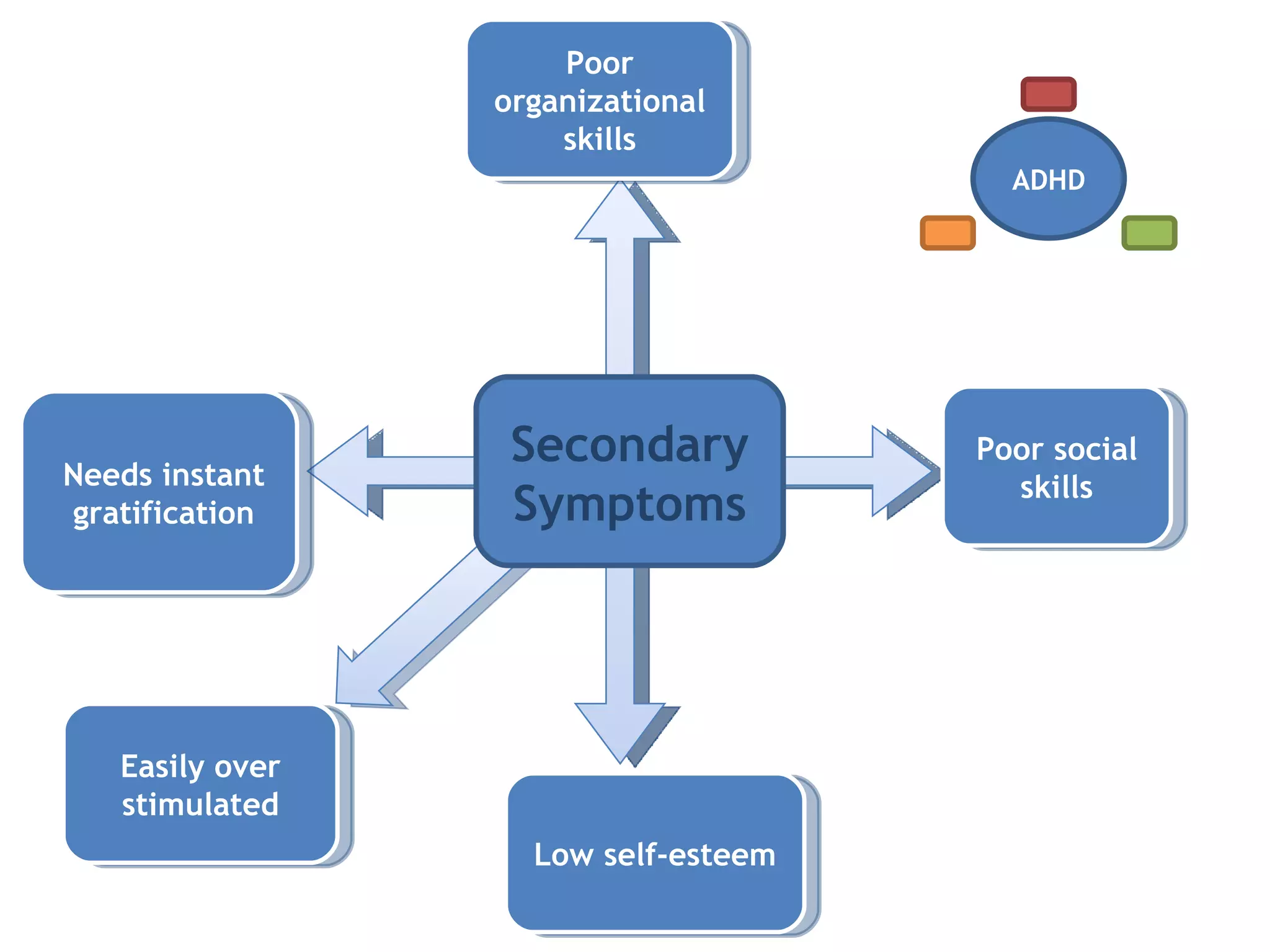
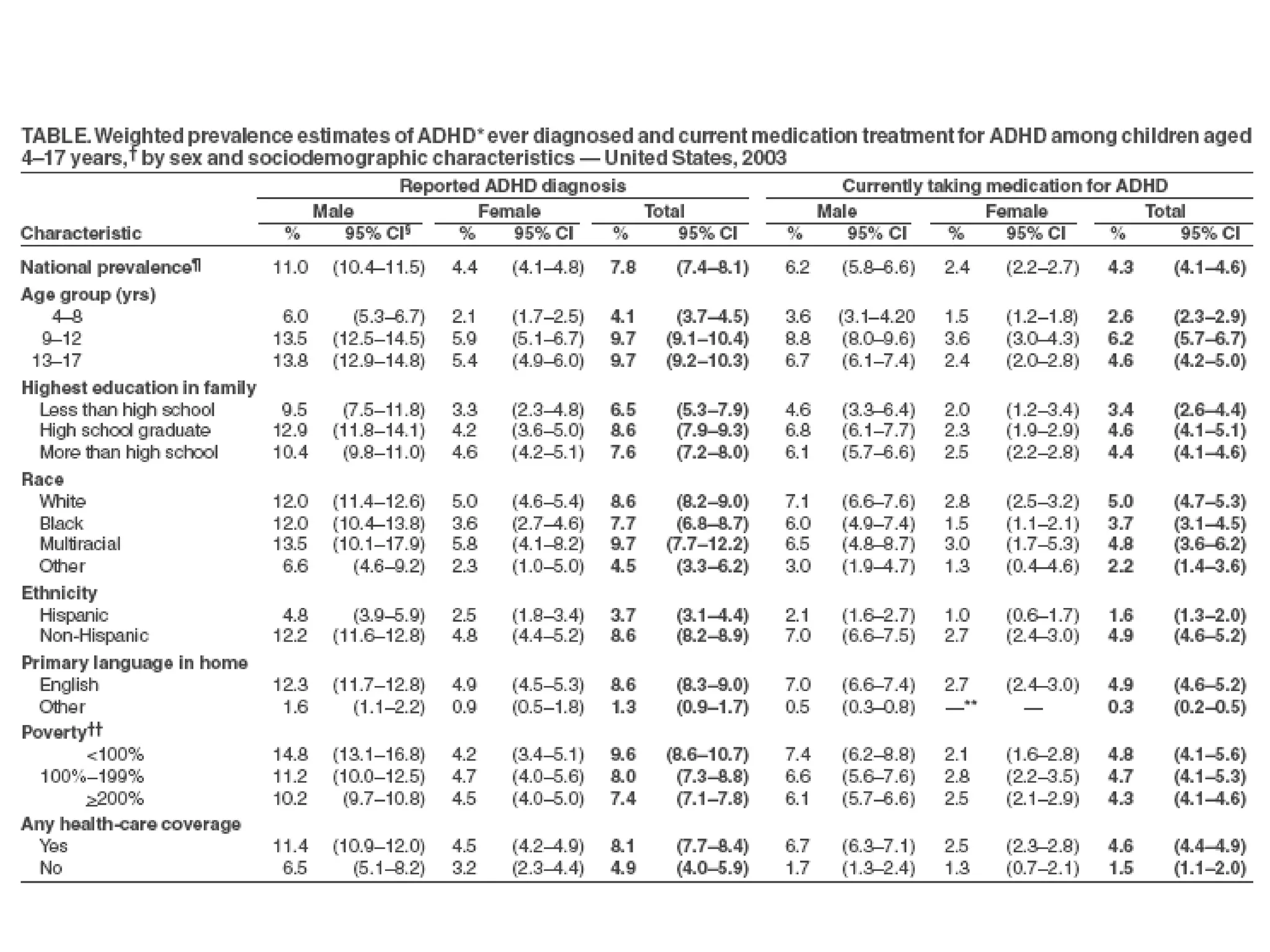
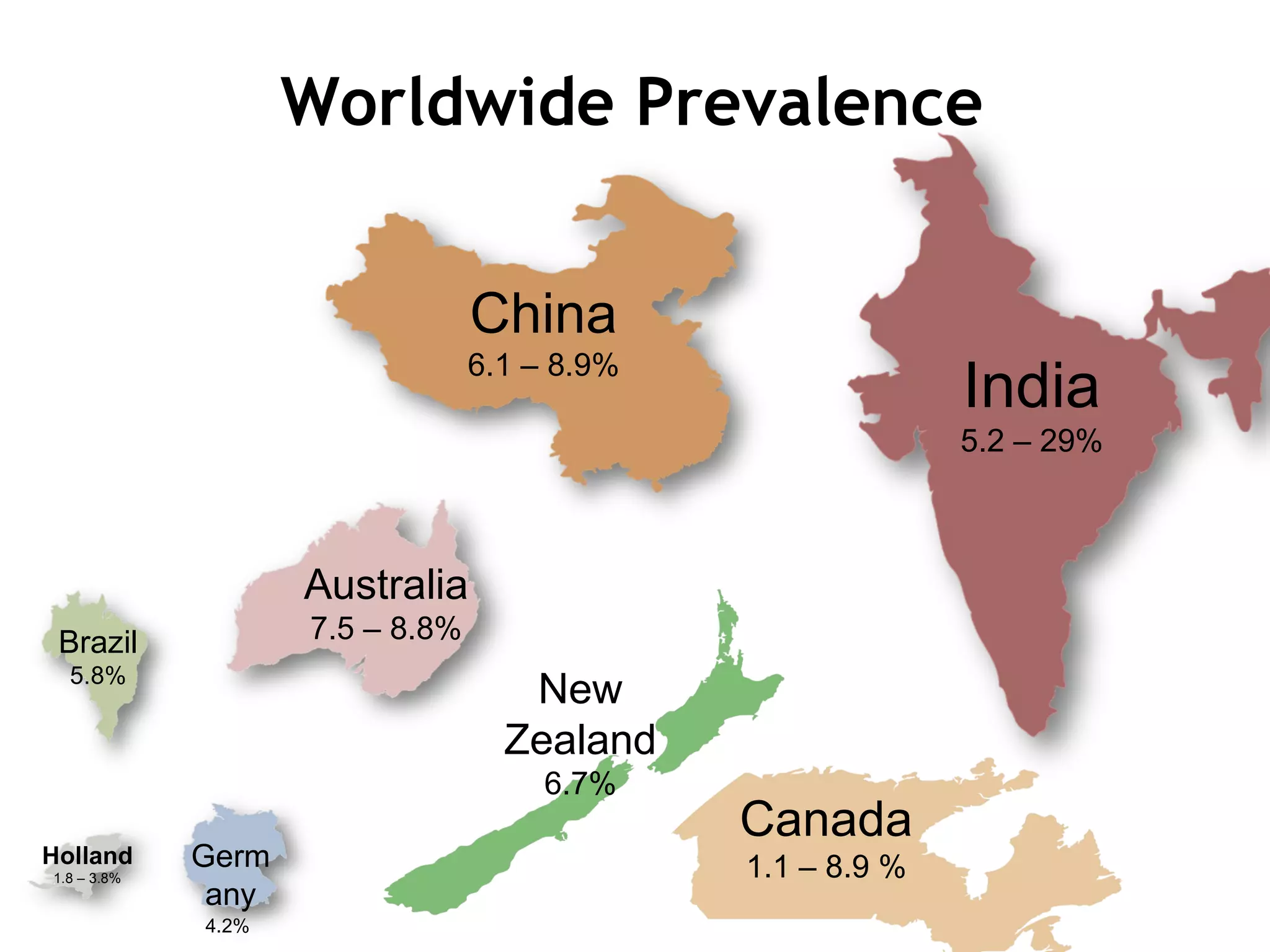
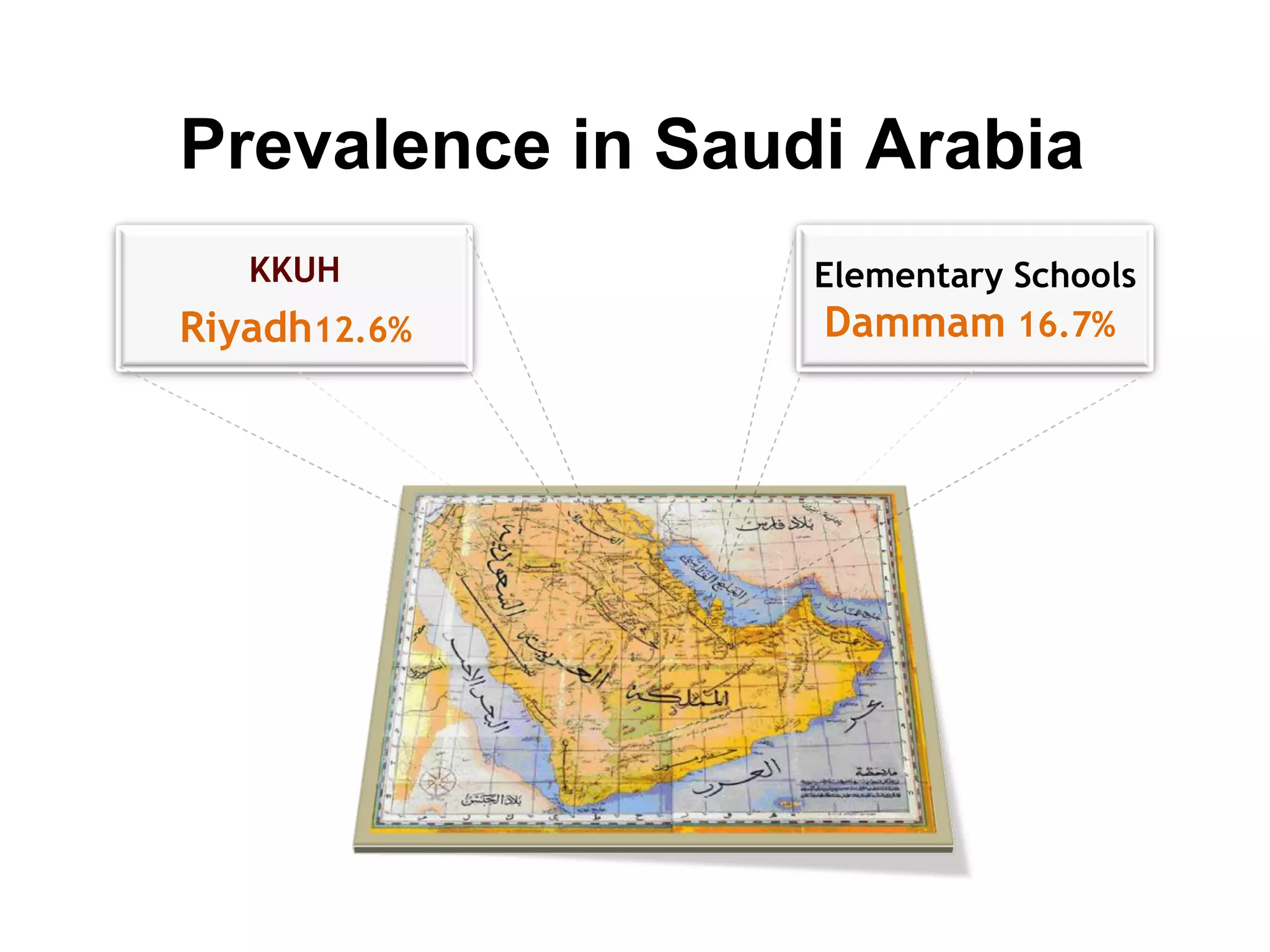
1) ADHD is a neurobiological disorder that affects children and leads to symptoms of inattention, impulsivity, and hyperactivity.
2) These symptoms are present in everyone but are more predominant in individuals with ADHD.
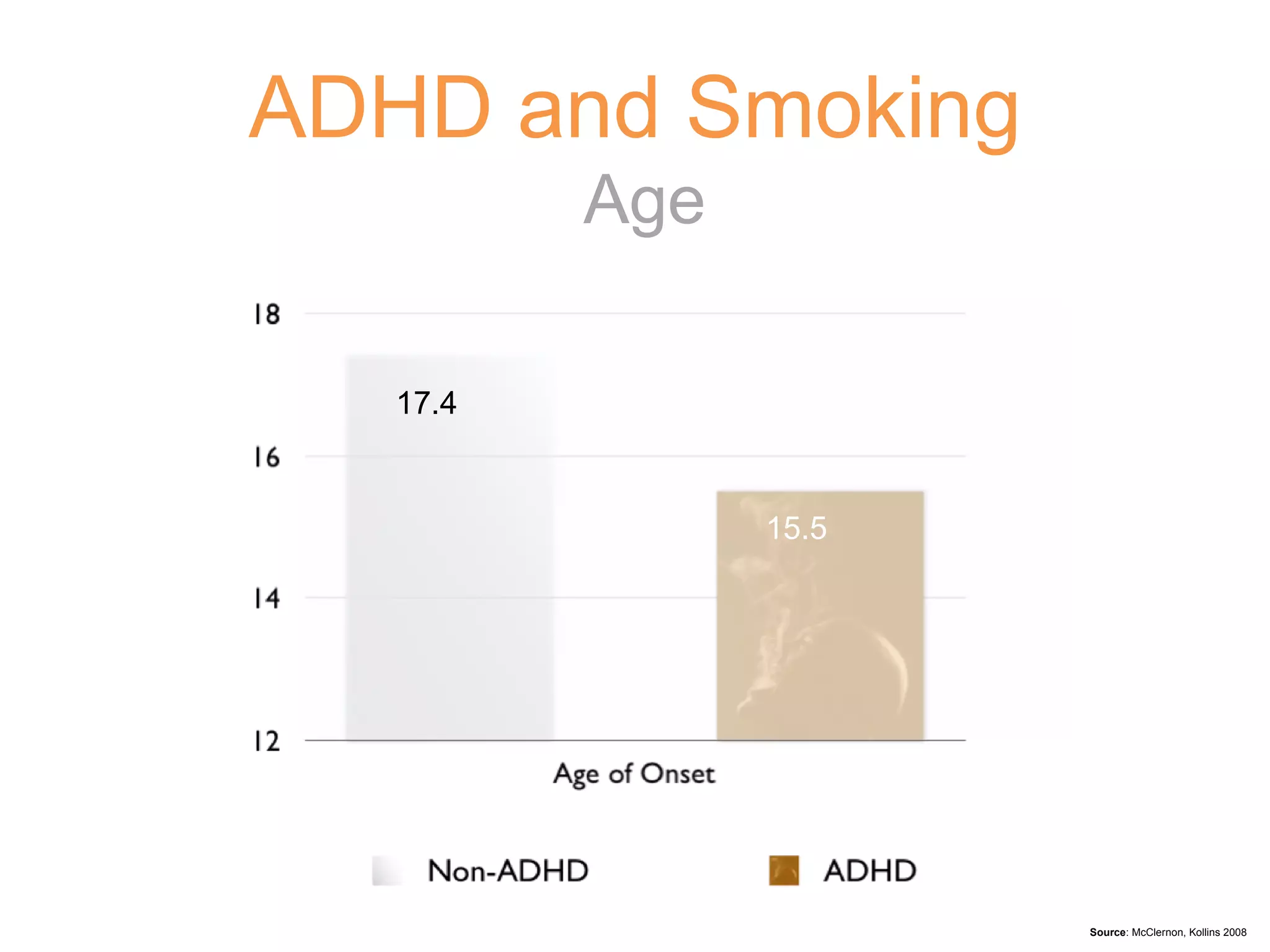
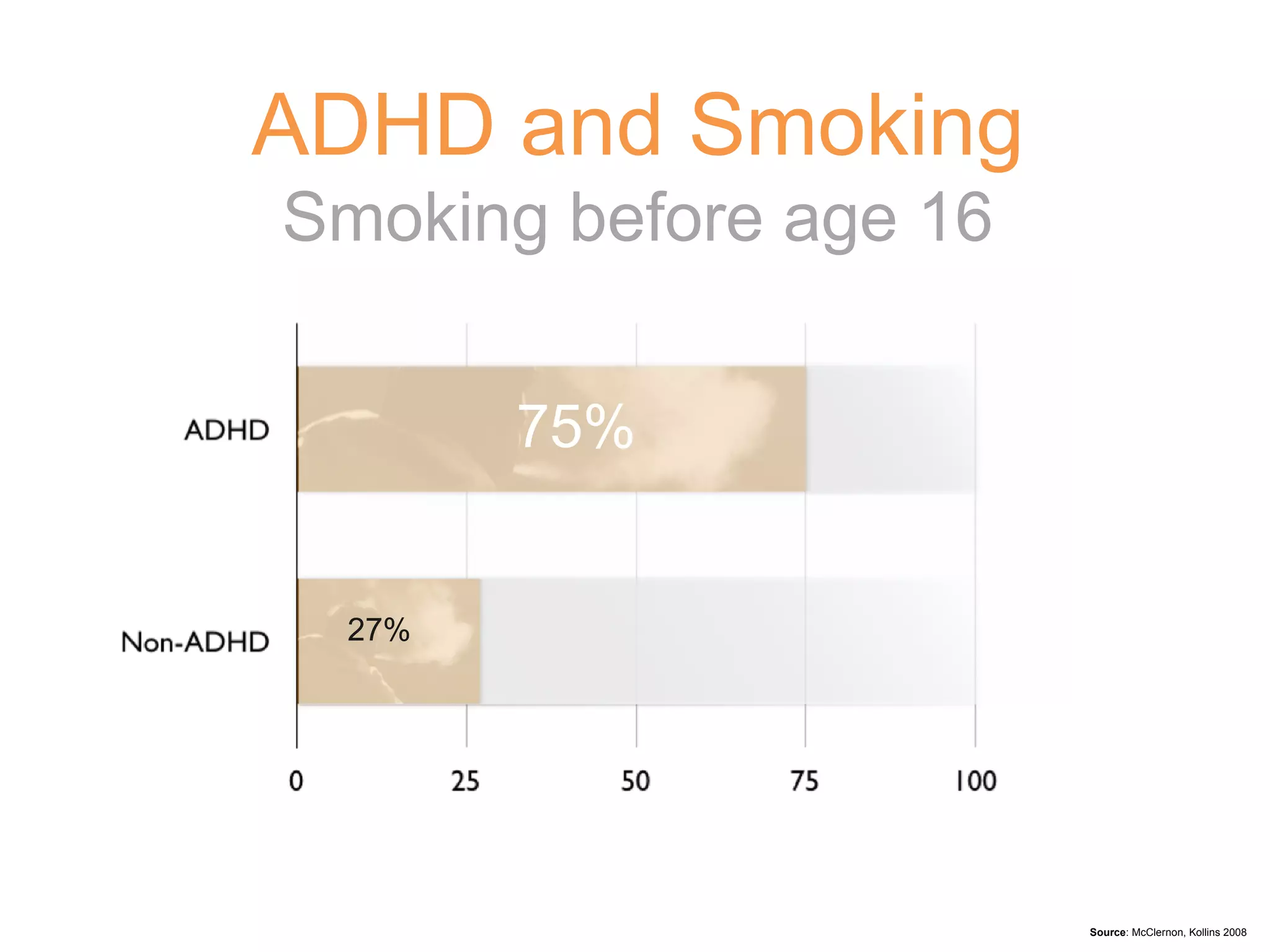
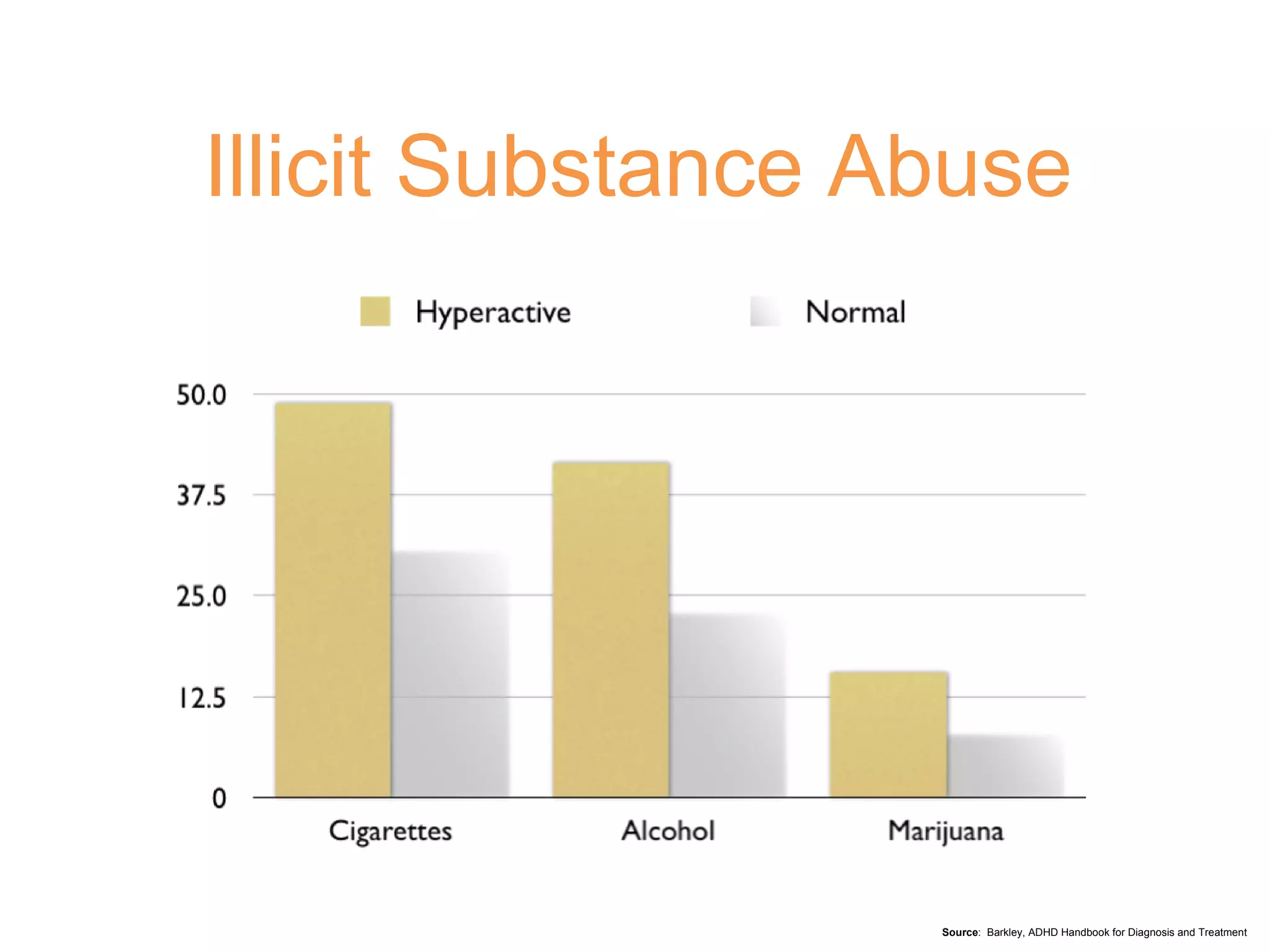
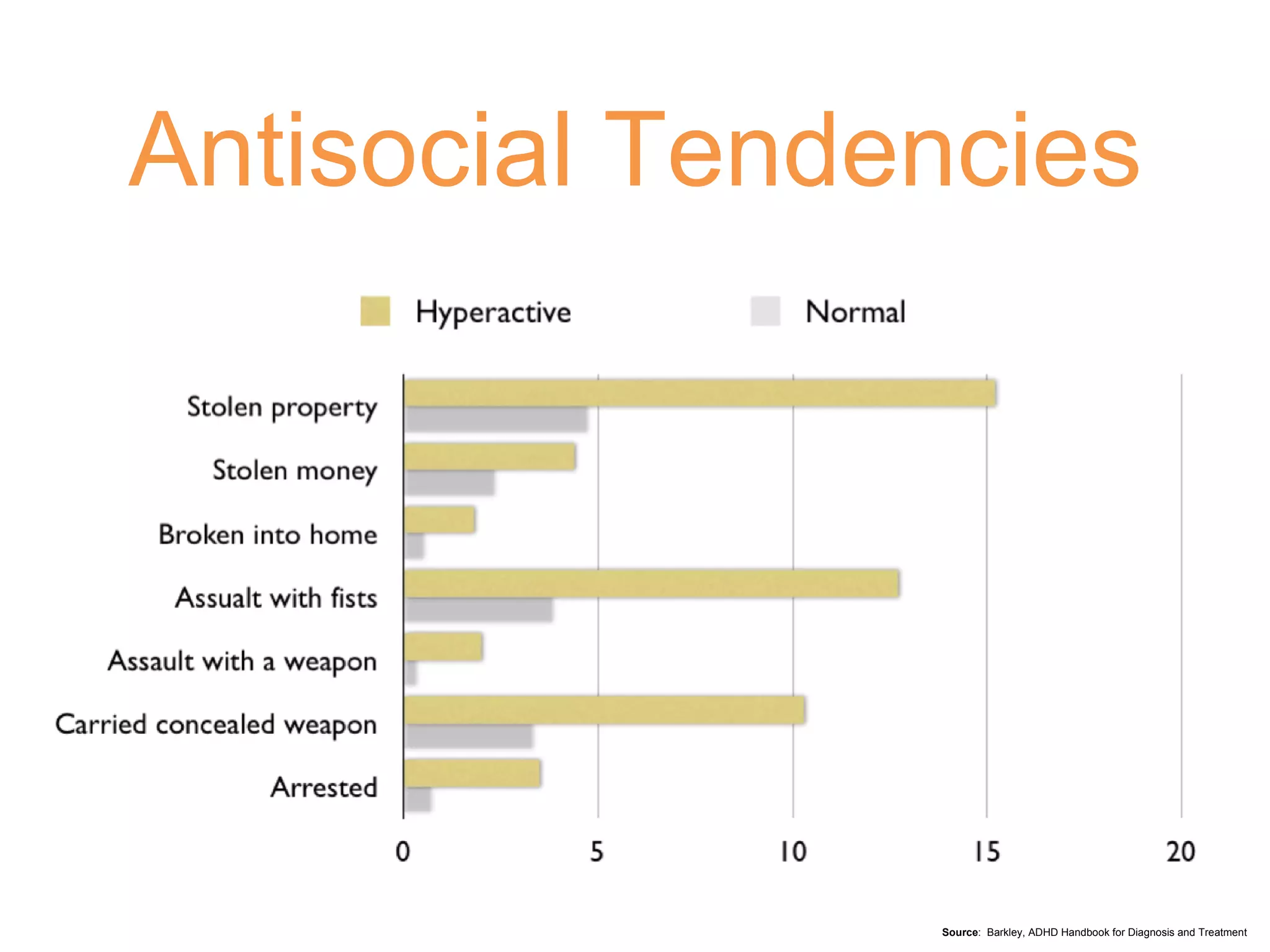
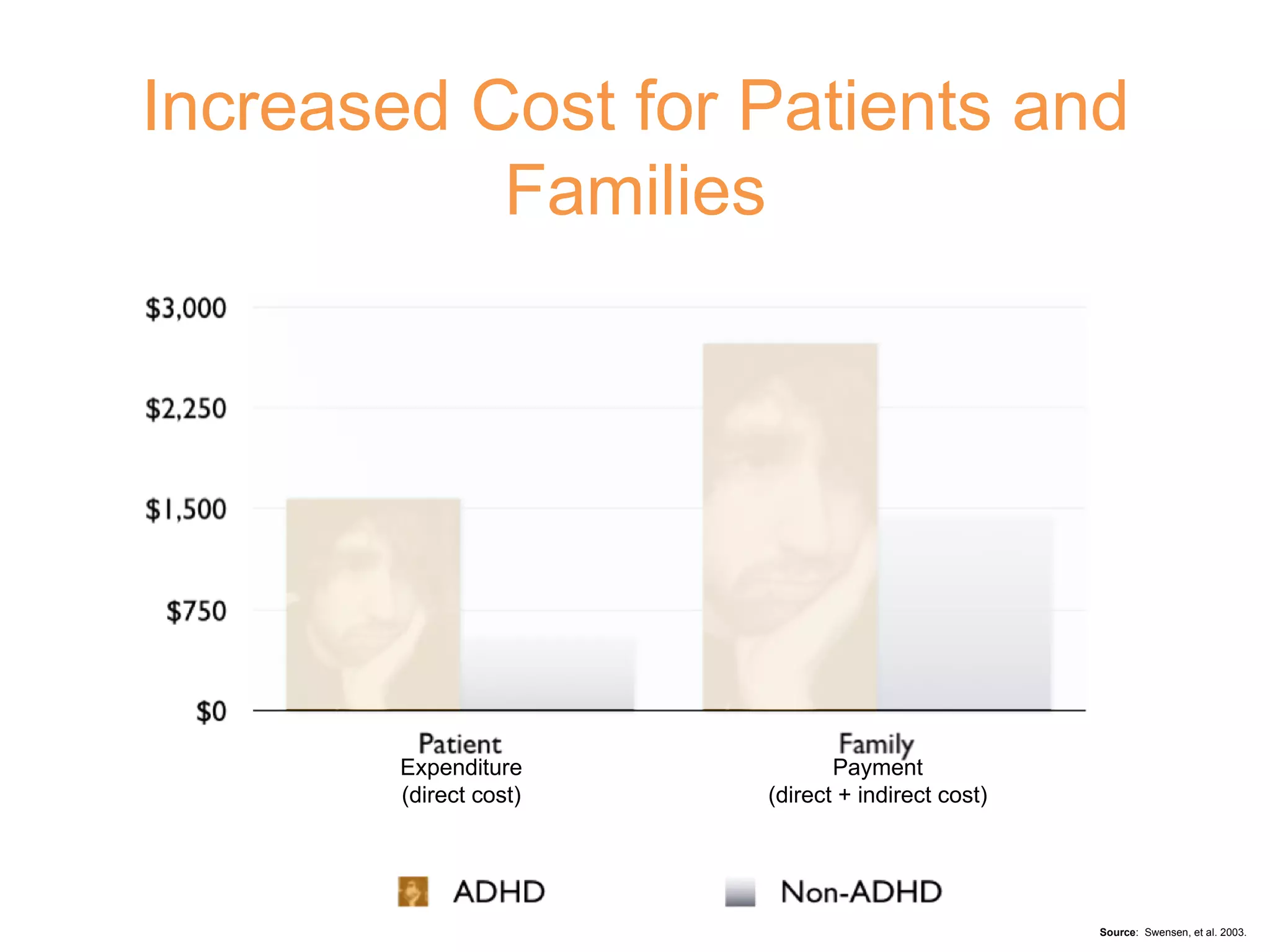
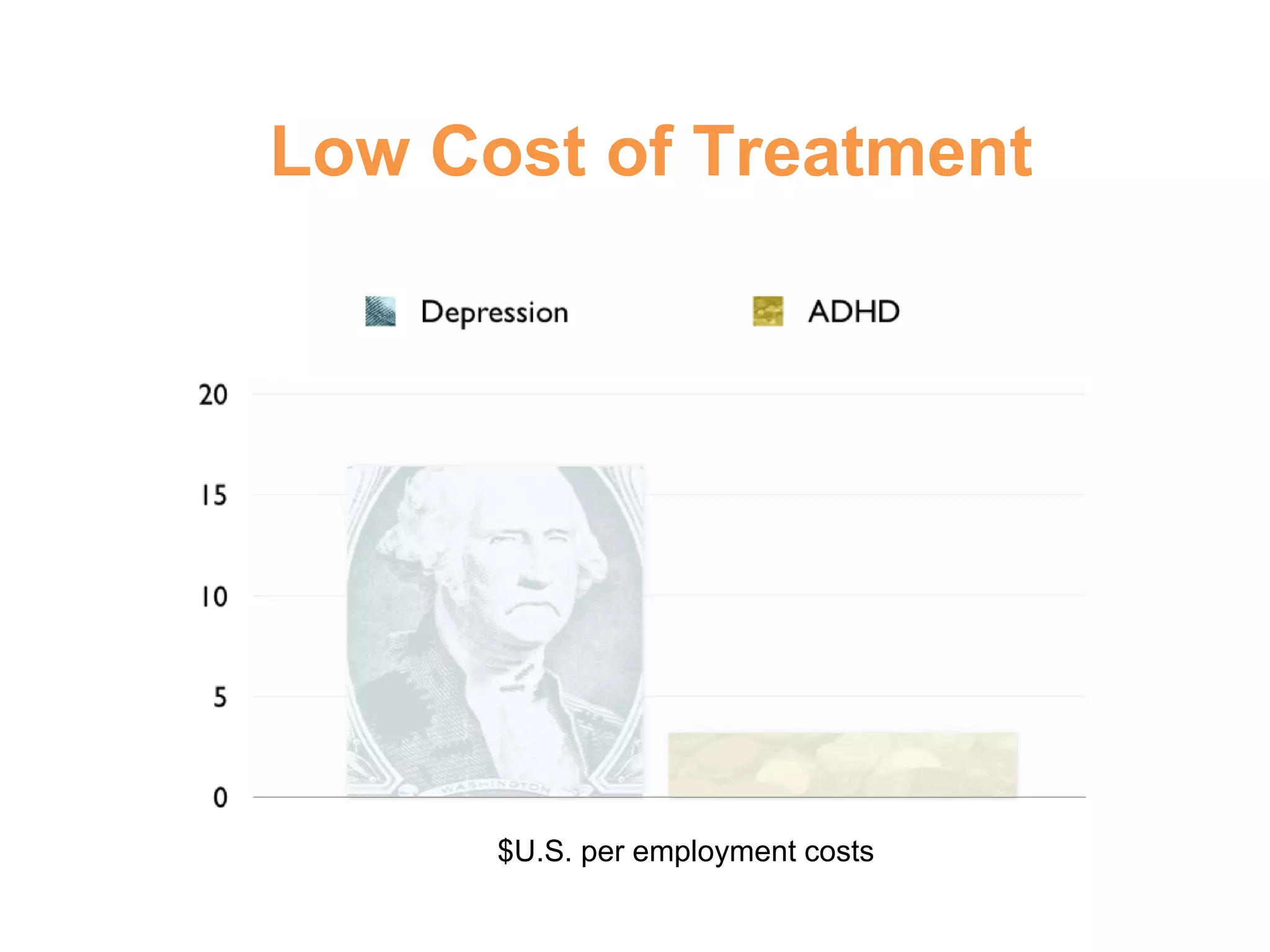
3) Left untreated, ADHD can have negative impacts such as higher rates of smoking, substance abuse, antisocial tendencies, and an economic burden of over $30 billion in the United States each year.