Organic matter
- 1. Organic Matter by Abbas falah gharib PhD student Osmangazi University
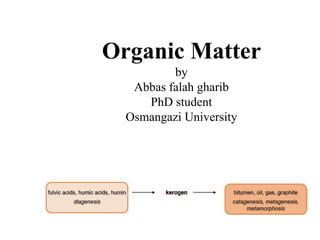
- 2. The most important types of organic matter in geosphere are the fulvic and humic acids, humin, kerogen (in coal, oil shales, source rocks or scattered in the sediments), bitumen, oil, gas and graphite. The particulate organic matter in sedimentary sequences ranges from disseminated occurrences of organic particles to concentrated organic matter in coals. The classification of the organic matter based on H/C and O/C atomic ratios (van Krevelen, 1993) distinguishes three main types of kerogens (Type I, Type II and Type III) that initially were associated to specific geological settings. Type I and Type II will be dealth with next, but before that Type III will be explained shortly. Coal, usually described as Type III kerogen, is a combustible sedimentary rock composed of lithified plant debris. This plant debris was originally deposited in a swampy depositional environment. The prolonged burial of the peat at depths of up to several kilometers, compaction, pressure and the influence of elevated temperatures for long periods of time (million years) are known as the coalification process that change peat into coal. Coal did not appear until the Devonian period due to the lack of terrestrial plants, although some organic matter derived from marine algae occurs in Precambrian sedimentary rocks.
- 3. Kerogene Kerogene is a fossilized mixture of insoluble organic material that, when heated, breaksdown into petrole- um and natural gas. Kerogene consists of carbon, hydrogen,oxygen, nitrogen, and sulfur an d forms from compacted organic material,including algae, pollen, spores and spore coats, a nd insects. It is usually found in sedimentary rocks, such as shale(Greek wax and -gen, birth). Types of kerogen The type of kerogen present determines source rock quality. The more oil prone a kerogen, the higher its quality. Four basic types of kerogen are found in sedimentary rocks. A single type or a mixture of types may be present in a source rock, it divided into four types depending on the chemical properties of kerogen . Kerogen type Predominant hydrocarbon potential Amount of hydrogen Typical depositional environment I Oil prone Abundant Marine II Oil and gas prone Moderate Mixture III Gas prone Small Terrestrial IV Neither (primarily composed of vitrinite) or inert material None Terrestrial(?)
- 5. Kerogen and hydrocarbon potential I
- 6. II
- 7. • Types of kerogen and Ro
- 8. Depending on the microscopic properties of kerogen • 2. Sapropelic Kerogen • (spores and pollens) 1. Humic Kerogen 2. Sapropelic Kerogen 3. Kerogen constituted by (woody fragments, and then (spores and pollens) Amorphous Organic Matter Vitrinite and others coal macerals) (unstructured, unrecognizable OM)
- 9. Photomicrograph showing Type I kerogen assemblage Photomicrograph showing Type II kerogen assemblage
- 10. Kerogen maturity The hydrocarbon potential of organic carbon depends on the thermal history of the rocks containing the kerogen. Both temperature and the time at that temperature determine the outcome. Medium temperatures (< 175 C) produce mostly oil and a little gas. Warmer temperatures produce mostly gas. Vitrinite reflectance (Ro) is used as an indicator of the level of organic maturity
- 11. Macerals are the microscopic organic components typically identified in coals. They derive from terrestrial, lacustrine and marine plant remains, and their appearance is a function of the parent material, of initial decomposition before and during the peat stages and also of the degree of evolution undergone. Macerals are distinguished from one to another on the basis of their physico-optical properties and universal acceptance is given to the ICCP classification of macerals in three groups: liptinite, inertinite and huminite/vitrinite. Maceral groups
- 12. Main components of maceral groups
- 14. Photomicrographs: 1,2,3,5: reflected white light; 4,6: fluorescence. 1,2) Bituminous coal with vitrinite, inertinite and liptinite. Carboniferous age 3,4 ) Telohuminite and resinite (liptinite) in a carbonaceous shale. Cretaceous. 5,6) Oil shale (Tasmanite algae, Liptinite, right image). Jurassic.
- 16. • I APPRECIATE YOUR ATTENTION