DNA for Middle School Science
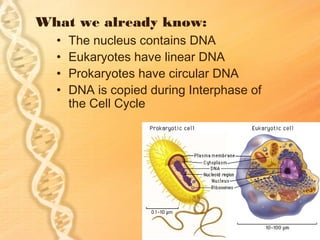
- 1. What we already know: • The nucleus contains DNA • Eukaryotes have linear DNA • Prokaryotes have circular DNA • DNA is copied during Interphase of the Cell Cycle
- 2. What we already know: • Traits are distinguishing features or characteristics • Traits are passed from parent to offspring • Traits are passed on through genes • Genes are specific sections of DNA • In sexual reproduction, offspring get half of their genes from each parent
- 3. DNA is INFORMATION • DNA= deoxyribose nucleic acid • A molecule that stores information • Contains the instructions for making proteins • Like a cookbook contains the instructions for making a cake
- 4. Proteins and Amino Acids • Proteins are large molecules made up of chains of amino acids • There are 20 different amino acids that combine into thousands of different proteins • Folding of the string of amino acids is critical for protein function
- 5. Proteins and Amino Acids • Proteins can vary in size from just 20 amino acids, like this one found in Gila Monster saliva… To this protein nicknamed “Titan” with 34,350 amino acids, found in human muscle tissue
- 6. Check for Understanding: • What is the relationship between proteins and amino acids? • What is a trait? • When is DNA copied? • What is a gene?
- 7. Check for Understanding: • What is the relationship between proteins and amino acids? • 20 amino acids come together in various combinations to make proteins • What is a trait? • Distinguishing features or characteristics • When is DNA copied? • During Interphase of the Cell Cycle • What is a gene? • A specific section of DNA that contains the code for a protein
- 8. DNA & The Genetic Code • DNA molecule is shaped like a twisted ladder • The molecule is formed from nucleotide subunits that consist of: • Phosphate • Sugar (Deoxyribose) • Nitrogen Base
- 9. DNA & The Genetic Code • The side rails of the ladder are formed by the sugar-phophates • The rungs of the ladder are formed by two bases coming together • There are four different bases in DNA • Adenine • Thymine • Cytosine • Guanine All Tigers Can Growl
- 12. DNA & The Genetic Code • The sequence (order) of bases in a strand of DNA makes the code for building proteins • The genetic code is a “triplet” code meaning that every three bases codes for one amino acid • A gene is the entire sequence of bases that codes for a specific protein • Like a recipe for a specific dish
- 13. Replication of the DNA • Replication is the copying of DNA 1. Two strands separate 2. Free-floating nucleotides match up with the nucleotides on each strand 3. Two identical molecules of DNA are made
- 14. Watch Replication in Action • This movie shows a computer animation of how DNA is replicated Another video on YouTube
- 15. Check for Understanding • What three components make up the nucleotide subunit? • What are the four bases and what is the rule about how they pair together? • Describe what is meant by a “triplet code.” • What are the steps of DNA replication?
- 16. Check for Understanding • What three components make up the nucleotide subunit? • Phosphate, Sugar, Nitrogen Base • What are the four bases and what is the rule about how they pair together? • Adenine pairs with Thymine • Cytosine pairs with Guanine • Describe what is meant by a “triplet code.” • Three bases code for one amino acid • What are the steps of DNA replication? 1. Strands separate 2. Nucleotides pair up 3. Two identical strands are made
- 17. RNA is needed to make proteins: • RNA is ribonucleic acid and is very similar to DNA except: 1. RNA has ribose sugar instead of deoxyribose sugar 2. RNA has Uracil instead of Thymine 3. RNA is a single strand
- 18. RNA is needed to make proteins: • EUKARYOTES: RNA copies the information from the DNA inside the nucleus then travels outside to the cytoplasm • PROKARYOTES: RNA and proteins are made in the cytoplasm
- 19. RNA is needed to make proteins: • Three different types of RNA are involved in making protein: • messanger RNA (mRNA) • ribosomal RNA (rRNA) • transfer RNA (tRNA) • mRNA carries the message or code outside the nucleus • rRNA makes up part of the ribosome • tRNA brings the correct amino acids to the ribosome for protein construction
- 20. Check for Understanding • How is RNA different from DNA? • What are the three types of RNA involved in making proteins?
- 21. Check for Understanding • How is RNA different from DNA? 1. RNA has ribose sugar instead of deoxyribose sugar 2. RNA has Uracil instead of Thymine 3. RNA is a single strand • What are the three types of RNA involved in making proteins? 1. messanger RNA (mRNA) 2. ribosomal RNA (rRNA) 3. transfer RNA (tRNA)
- 22. • Transcription produces a Transcription single-stranded molecule of RNA • One strand of DNA is the template or pattern • The steps of transcription are: 1. The DNA molecule opens up along a gene 2. RNA nucleotides (A,U,C,G) match up and join the open DNA strand 3. The complete RNA strand is released and moves to the cytoplasm
- 23. • Transcription is different than Transcription replication: 1. Only one strand of DNA is transcribed so only one strand of mRNA is produced 2. The mRNA is released, it does not stay attached to the DNA 3. Many copies of mRNA can be made from a single gene in a short period of time • Transcription on YouTube
- 24. Check for understanding • What are the steps of transcription? • How is transcription different than replication?
- 25. Check for understanding • What are the steps of transcription? 1. The DNA molecule opens up along a gene 2. RNA nucleotides (A,U,C,G) match up and join the open DNA strand 3. The complete RNA strand is released and moves to the cytoplasm • How is transcription different than replication? 1. Only one strand of DNA is transcribed so only one strand of mRNA is produced 2. The mRNA is released, it does not stay attached to the DNA 3. Many copies of mRNA can be made from a single gene in a short period of time
- 26. Translation • Translation is how cells TRANSLATE the language or code of nucleotide bases into the language of amino acids • Translation occurs in the cytoplasm at the ribosome • If DNA is the cookbook, and mRNA is the recipe, then the ribosome is the kitchen and tRNA is the chef!
- 27. Translation • rRNA is part of the ribosome that attaches to the mRNA • tRNA has a triplet of bases on one end and can attach to a single amino acid on the other end • tRNA does the translation of bases to amino acids when it matches up with mRNA
- 29. Brain Break! • Link to Translation Video • Another video that reviews Translation and Transcription
- 30. Translation 1. Translation begins when a ribosome attaches to the beginning of an mRNA molecule 2. A tRNA molecule carrying an amino acid matches up to a complementary triplet on mRNA on the ribosome 3. The ribosome attaches one amino acid to another as it moves along the mRNA molecule 4. The tRNA molecules are released after the amino acids they carry are attached to the growing chain of amino acids 5. The ribosome completes the translation when it reaches the end of the mRNA strand and the newly made protein molecule is released
- 31. The Central Dogma • The process of making proteins is the same in all cells • This is the foundation of molecular biology, biochemistry, and genetics Transcription Translation DNA RNA Protein Another YouTube video!
- 32. Check for understanding • Where does translation occur? • Which RNA makes up the ribosome? • Which RNA is the “recipe?” • Which RNA does the actual translation of bases into amino acids? • What is the “central dogma” of molecular biology?
- 33. Check for understanding • Where does translation occur? • In the cytoplasm • Which RNA makes up the ribosome? • rRNA • Which RNA is the “recipe?” • mRNA • Which RNA does the actual translation of bases into amino acids? • tRNA • What is the “central dogma” of molecular biology? Transcription Translation DNA RNA Protein
- 34. Replication, Transcription, Translation Challenge! • Copy this DNA sequence: • A-T-G-A-C-G • Write the base pairs of the complimentary strand of DNA (replication) • Write the complimentary mRNA strand to your new strand (transcription) • Use the chart to find the correct amino acids that the tRNA would attach to the protein (translation)
- 35. The Universal Genetic Code
- 36. The Universal Genetic Code
- 37. Check your answers: • Replication: • T-A-C-T-G-C • Transcription • A-U-G-A-C-G • Translation • Met (Methionine) and Thr (Threonine)
- 38. A HISTORY OF DNA •(1928) Frederick Griffith •Discovers that a “transforming factor” changes harmless bacteria into deadly bacteria •(1952) Rosalind Franklin •Takes x-ray photographs of DNA •(1953) James Watson and Francis Crick •Use Franklin’s images to describe the structure of DNA •(1962) Watson, Crick, and Wilkins win the Nobel Prize, Franklin has already died from cancer (1958) so she does not get recognition