Honda mba project
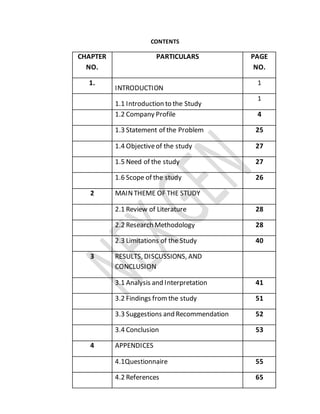
- 1. CONTENTS CHAPTER NO. PARTICULARS PAGE NO. 1. INTRODUCTION 1 1.1 Introduction to the Study 1 1.2 Company Profile 4 1.3 Statement of the Problem 25 1.4 Objectiveof the study 27 1.5 Need of the study 27 1.6 Scope of the study 26 2 MAINTHEME OF THE STUDY 2.1 Review of Literature 28 2.2 Research Methodology 28 2.3 Limitations of the Study 40 3 RESULTS, DISCUSSIONS, AND CONCLUSION 3.1 Analysis and Interpretation 41 3.2 Findings fromthe study 51 3.3 Suggestions and Recommendation 52 3.4 Conclusion 53 4 APPENDICES 4.1Questionnaire 55 4.2 References 65
- 2. 2 CHAPTER-1 INTRODUTION 1.1 Introduction An issue which usually generates a great deal of attention from most managers, administrators and those involved in Human Resources Management is the issue of how to successfully motivate employee. While it is true that aspects like staff recruitment, controlling, managing, leading, and many more are of great importance to the success of an organization, Employee Motivation is generally considered a core element in running a successful business. In the organizational setting the word “Motivation” is used to describe the drive that impels an individual to work. A truly motivated person is one who “wants” to work .Both employees and employers are interested in understanding motivation if employees know what strengthens and what weakens their motivation, they can often perform more effectively to find more satisfaction in their job. Employers want to know what motivates their employees so that they can get them to work harder. The concept of motivation implies that people choose the path of action they follow. When behavioral scientists use the word motivation, they think of its something steaming from within the person technically, the term motivation has its origin in the Latin word “mover” which means “to move”. Thus the word motivation stands for movement. If a manager truly understands his subordinate’s motivation, he can channel their “inner state” towards command goals, i.e., goals, shared by both the individual and the organization. It is a well known fact that human beings have great potential but they do not use it fully, when motivation is absent. Motivation factor are those which make people give more than a fair day’s work and that is usually only about sixty-five percent of a person’s capacity .Obviously , every manager should be releasing hundred
- 3. 3 percent of an individual’s to maximize performance for achieving organizational goals and at the same to enable the individual to develop his potential and gain satisfaction. Thus every manager should have both interest and concern about how to enable people to perform task willingly and to the best of their ability. At one time, employees were considered just another input into the production of goods and services. What perhaps changed this way of thinking about employees was research, referred to as the Hawthorne Studies, conducted by Elton Mayo from1924 to 1932 This study found employees are not motivated solely by money and employee behavior is linked to their attitudes. The Hawthorne Studies began the human relations approach to management, whereby the needs and motivation of employees become the primary focus of managers. 1.1.2 Definition of Motivation Motivation is a process that starts with a physiological or psychological deficiency or need that activates behavior or a drive that aimed at a goal or an incentive. "The only way to get people to like working hard is to motivate them. Today, people must understand why they're working hard. Every individual in an organization is motivated by something different." - Rick Pitino “Employee motivation is a reflection of the level of energy, commitment, and creativity that a company's workers bring to their jobs.” "Psychological forces that determine the direction of a person's behavior in an organization, a person's level of effort and a person's level of persistence."- G. Jones and J. George from the book "Contemporary Management." Basics about Motivation 1. Motivating employees starts with motivating yourself it’s amazing how, if you hate your job, it seems like everyone else does, too. If you
- 4. 4 are very stressed out, it seems like everyone else is, too. Enthusiasm is contagious. If you're enthusiastic about your job, it's much easier for others to be, too. Also, if you’re doing a good job of taking care of yourself and your own job, you'll have much clearer perspective on how others are doing in theirs. A great place to start learning about motivation is to start understanding your own motivations. The key to helping to motivate your employees is to understand what motivates them. So what motivates you? Consider, for example, time with family, recognition, a job well done, service, learning, etc. How your job is configured to support your own motivations? What can you do to better motivate yourself? 2. Always work to align goals of the organization with goals of employees as mentioned above, employees can be all fired up about their work and be working very hard. However, if the results of their work don't contribute to the goals of the organization, then the organization is not any better off than if the employees were sitting on their hands -- maybe worse off! Therefore, it's critical that managers and supervisors know what they want from their employees. These preferences should be worded in terms of goals for the organization. Identifying the goals for the organization is usually done during strategic planning. Whatever steps you take to support the motivation of your employees (various steps are suggested below), ensure that employees have strong input to identifying their goals and that these goals are aligned with goals of the organization. (Goals should be worded to be “SMARTER". 3. Key to supporting the motivation of your employees understands what motivates each of them each person is motivated by different things. Whatever steps you take to support the motivation of your employees, they should first include finding out what it is that really motivates each of your employees. You can find this out by asking them, listening to them and observing them. 4. Recognize that supporting employee motivation is a process, not at ask Organizations change all the time, as do people. Indeed, it is an ongoing process to sustain an environment where each employee can strongly motivate themselves. If you look at sustaining employee motivation as an ongoing process, then you'll be much more fulfilled and motivated yourself. 5. Support employee motivation by using organizational systems (for example, policies and procedures)--don't just count on good intentions don’t just count on cultivating strong interpersonal relationships with
- 5. 5 employees to help motivate them. The nature of these relationships can change greatly, for example, during times of stress. Instead, use reliable and comprehensive systems in the workplace to help motivate employees. For example, establish compensation systems, employee performance systems, organizational policies and procedures, etc., to support employee motivation. Also, establishing various systems and structures helps ensure clear understanding and equitable treatment of employees. 1.1.3 Importance of Motivation Motivation is a very important for an organization because of the following benefits it provides:- Puts human resources into action Every concern requires physical, financial and human resources to accomplish the goals. It is through motivation that the human resources can be utilized by making full use of it. This can be done by building willingness in employees to work. This will help the enterprise in securing best possible utilization of resources. Improves level of efficiency of employees The level of a subordinate or a employee does not only depend upon his qualifications and abilities. For getting best of his work performance, the gap between ability and willingness has to be filled which helps in improving the level of performance of subordinates. This will result into- Increase in productivity, Reducing cost of operations, and Improving overall efficiency. Leads to achievement of organizational goals The goals of an enterprise can be achieved only when the following factors take place :- There is best possible utilization of resources, There is a co-operative work environment, The employees are goal-directed and they act in a purposive manner, Goals can be achieved if co-ordination and co-operation takes place simultaneously which can be effectively done through motivation.
- 6. 6 Builds friendly relationship Motivation is an important factor which brings employees satisfaction. This can be done by keeping into mind and framing an incentive plan for the benefit of the employees. This could initiate the following things: Monetary and non-monetary incentives, Promotion opportunities for employees, Disincentives for inefficient employees. In order to build a cordial, friendly atmosphere in a concern, the above steps should be taken by a manager. This would help in: Effective co-operation which brings stability, Industrial dispute and unrest in employees will reduce, The employees will be adaptable to the changes and there will be no resistance to the change, This will help in providing a smooth and sound concern in which individual interests will coincide with the organizational interests, This will result in profit maximization through increased productivity. Leads to stability of work force Stability of workforce is very important from the point of view of reputation and goodwill of a concern. The employees can remain loyal to the enterprise only when they have a feeling of participation in the management. The skills and efficiency of employees will always be of advantage to employees as well as employees. This will lead to a good public image in the market which will attract competent and qualified people into a concern. As it is said, “Old is gold” which suffices with the role of motivation here, the older the people, more the experience and their adjustment into a concern which can be of benefit to the enterprise. 1.1.4 What motivates employees? Every person has a different reason for going to work. These reasons are as individual as whichever person you may ask. But all of the reasons for working share a common thread. We all obtain something from work we need. There is much discussion about the value of extrinsic motivation (monetary and other material rewards) versus intrinsic motivation where people re driven by what’s inside them. not by the trappings of success.
- 7. 7 Whereas I recognize how critical extrinsic motivation is–we all need to be rewarded fairly for the job that we do-in my experience the most effective factors relating to employee motivation are related to intrinsic motivation: 1. Empowerment: Feeling trusted and empowered is a tremendous motivator. 2. Growth: Feeling that they are growing and developing personally 3. Inclusion: ‘To belong’ is a fundamental need, whether as a member of a family, peer group, network, team or company. It’s human nature to want to be on the inside, not the outside. 4. Purpose: Today people care more about what happens tomorrow, and want to contribute to ensuring the future of our children, and the health of our communities and planet. 5. Trust: the fabric that holds it all together and makes it real. Framework of motivation The framework comprises six steps:- 1) Motivation process begins with the individual’s needs. Needs are telt deprivations which the individual experiences at a given time and act as energizers. These needs may be psychological (e.g., the needs for recognition), physiological (e.g., the needs for water, air or foods) or social (e.g., the needs for friendship). 2) Motivation is goal directed. 3) A goal is a specific result that the individual wants to achieve. An employee’s goal are often driving forces and accomplishing those goals can significantly reduce needs. 4) Promotions and raises are two of the ways that organizations seek to maintain desirable behavior. They are signals to employees that their needs for advancement and recognition and their behaviors are appropriate. 5) Once the employee have received either rewards or punishments. 6) They reassess their needs. The Role of Motivation: Why do we need motivated employees? The answer is survival. Motivated employees are needed in our rapidly changing workplaces. Motivated employees help organizations survive. Motivated employees are more productive. To be effective, managers need to understand what motivates employees within the context of the roles they
- 8. 8 perform. Of all the functions a manager performs, motivating employees is arguably the most complex. This is due, in part, to the fact that what motivates employee’s changes constantly. For example, research suggests that as employees' income increases, money becomes less of a motivator (Kovach, 1987). Also, as employees get older, interesting work becomes more of a motivator. Mechanism of motivation Motivation is the process that starts with physiological or psychological deficiency or need that activate behavior or a drive that is aimed at a goal or incentive. The following diagram depicts the motivation process. Mechanism of Motivation Needs Drives Goal Deprivation Deprivation Reduction With of Drives Direction Thus, the key to understanding motivation lies in the meaning of, and relationship between needs, drives and goals Needs: Needs are created whenever there is a physiological or psychological imbalance For example: A need exists when cells in the body are deprived of food and water or when the personality is deprived of other people who serve friends or companions. Although psychological may be based on a deficiency, sometimes they are not. For instant, and individuals with a strong need to get ahead may have a history of consistent success· Drives: “Drives (Or motives) are set up to alleviate needs. Psychological needs can be simply defined as a deficiency with direction. Physiological or psychological drives are action – oriented and provide energizing thrust towards reaching an incentive or goals. They are at the very heart of the motivational process. The needs for food and water are translated into hunger and thrust drives, and the need for friend becomes a drives affiliation. Thus, drive is a psychological state which moves an individual satisfying need· Goals: At the end of the motivational cycle is the goal or incentive. It is anything that wills that will alleviate a need and reduce a drive. Thus, attaining a goal will tend to restore physiological or psychological balance and will reduce or cut off the drive. Eating food, drinking water and obtaining friends will tend to restore the balance and
- 9. 9 reduce the corresponding drives food, water and friends are the incentive are the goals in this example. 1.1.5 Types of Motivation There are many types of motivation. Motivational techniques have been experienced by every person from birth. We learn behavior through motivation. We live our whole lives because of motivation. The question that remains however is this: What motivation should a person have? This is important because our motivation decides our behavior. Some types of motivation are more effective than others. However, the perfect motivation for you can only be decided by one person: YOU . Why do people do what they do? Why do we go on every day, living our lives and trying to find justification for our existence? Some people think that they can find purpose in the things that motivate them. Others just see the motivation and react automatically. There is no one thing that motivates people to perform certain actions. People are different, so it follows that their motivations have to be different. Here are some types of motivation : Achievement – This is the motivation of a person to attain goals. The longing for achievement is inherent in every man, but not all persons look to achievement as their motivation. They are motivated by a goal. In order to attain that goal, they are willing to go as far as possible. The complexity of the goal is determined by a person's perception. To us, the terms "simple" and "complex" are purely relative. What one person thinks is an easy goal to accomplish may seem to be impossible to another person. However, if your motivation is achievement, you will find that your goals will grow increasingly complex as time goes by .
- 10. 10 Socialization – Some people consider socialization to be their main motivation for actions. This is especially evident in the situation of peer pressure. Some people are willing to do anything to be treated as an equal within a group structure. The idea of being accepted among a group of people is their motivation for doing certain things. Incentive motivation – This motivation involves rewards. People who believe that they will receive rewards for doing something are motivated to do everything they can to reach a certain goal. While achievement motivation is focused on the goal itself, incentive motivation is driven by the fact that the goal will give people benefits. Incentive motivation is used in companies through bonuses and other types of compensation for additional work. By offering incentives, companies hope to raise productivity and motivate their employees to work harder . Fear motivation – When incentives do not work, people often turn to fear and punishment as the next tools. Fear motivation involves pointing out various consequences if someone does not follow a set of prescribed behavior. This is often seen in companies as working hand-in-hand with incentive motivation. Workers are often faced with a reward and punishment system, wherein they are given incentives if they accomplish a certain goal, but they are given punishments when they disobey certain policies. Change motivation- Sometimes people do things just to bring about changes within their immediate environment. Change motivation is often the cause of true
- 11. 11 progress. People just become tired of how things are and thus, think of ways to improve it. Natural Motivations- Motivation is the most common type of motivation and happens the most often. It is the motivation people get when naturally motivated. Fear motivations- Fear Motivation happens often within the workforce when under pressure to complete a task. Booster motivations- Booster Motivations is normally self driven to overcome a task you have set yourself. 1.1.6 Methods of Motivation There are as many different methods of motivating employees today as there are companies operating in the global business environment. Still, some strategies are prevalent across all organizations striving to improve employee motivation. The best employee motivation efforts will focus on what the employees deem to be important. It may be that employees within the same department of the same organization will have different motivators. Many organizations today find that flexibility in job design and reward systems has resulted in employees' increased longevity with the company, improved productivity, and better morale. Empowerment - Giving employees more responsibility and decision- making authority increases their realm of control over the tasks for which they are held responsible and better equips them to carry out those tasks. As a result, feelings of frustration arising from being held accountable for something one does not have the resources to carry out are diminished. Energy is diverted from self-preservation to improved task accomplishment.
- 12. 12 Creativity And Innovation - At many companies, employees with creative ideas do not express them to management for fear that their input will be ignored or ridiculed. Company approval and toeing the company line have become so ingrained in some working environments that both the employee and the organization suffer. When the power to create in the organization is pushed down from the top to line personnel, employees who know a job, product, or service best are given the opportunity to use their ideas to improve it. The power to create motivates employees and benefits the organization in having a more flexible work force, using more wisely the experience of its employees, and increasing the exchange of ideas and information among employees and departments. These improvements also create an openness to change that can give a company the ability to respond quickly to market changes and sustain a first mover advantage in the marketplace. Learning - If employees are given the tools and the opportunities to accomplish more, most will take on the challenge. Companies can motivate employees to achieve more by committing to perpetual enhancement of employee skills. Accreditation and licensing programs for employees are an increasingly popular and effective way to bring about growth in employee knowledge and motivation. Often, these programs improve employees' attitudes toward the client and the company, while bolstering self-confidence. Supporting this assertion, an analysis of factors which influence motivation-to-learn found that it is directly related to the extent to which training participants believe that such participation will affect their job or career utility. In other words, if the body of knowledge gained can be applied to the work to be accomplished, then the acquisition of that knowledge will be a worthwhile event for the employee and employer. Quality Of Life - The number of hours worked each week by American workers is on the rise, and many families have two adults working those increased hours. Under these circumstances, many workers are left wondering how to meet the demands of their lives beyond the workplace. Often, this concern occurs while at work and may reduce an employee's productivity and morale. Companies that have instituted flexible employee arrangements have gained motivated employees whose productivity has increased. Programs incorporating flextime, condensed workweeks, or job sharing, for example, have been successful in focusing overwhelmed employees toward the work to be done and away from the demands of their private lives. All motivation ultimately comes from within a person.
- 13. 13 Monetary Incentive - For all the championing of alternative motivators, money still occupies a major place in the mix of motivators. The sharing of a company's profits gives incentive to employees to produce a quality product, perform a quality service, or improve the quality of a process within the company. What benefits the company directly benefits the employee. Monetary and other rewards are being given to employees for generating cost-savings or process-improving ideas, to boost productivity and reduce absenteeism. Money is effective when it is directly tied to an employee's ideas or accomplishments. Nevertheless, if not coupled with other, nonmonetary motivators, its motivating effects are short- lived. Further, monetary incentives can prove counterproductive if not made available to all members of the organization. Other Incentives - Study after study has found that the most effective motivators of workers are nonmonetary. Monetary systems are insufficient motivators, in part because expectations often exceed results and because disparity between salaried individuals may divide rather than unite employees. Proven nonmonetary positive motivators foster team spirit and include recognition, responsibility, and advancement. Managers, who recognize the "small wins" of employees, promote participatory environments, and treat employees with fairness and respect will find their employees to be more highly motivated. One company's managers brainstormed to come up with 30 powerful rewards that cost little or nothing to implement. The most effective rewards, such as letters of commendation and time off from work, enhanced personal fulfillment and self-respect. Over the longer term, sincere praise and personal gestures are far more effective and more economical than awards of money alone. In the end, a program that combines monetary reward systems and satisfies intrinsic, self- actualizing needs may be the most potent employee motivator. 1.1.7 Factors for Lack ofMotivationin the Workplace A drop in staff motivation can become contagious if the cause is not identified and addressed. Management needs to be conscious of employee motivation, and that means being able to identify the factors that cause a lack of motivation in the workplace. Become familiar with the factors that can degrade staff motivation and design plans to combat these productivity killers.
- 14. 14 Rumors The important thing to remember about rumors is that they are not always wrong. Some rumors have basis in fact, but that does not make them good for employee morale. An employee that hears a rumor that she may be laid off experiences an instant drop in motivation. To deal with the problem of rumors in the workplace, it is important for management to share important information with the staff in a timely manner. This helps employees to feel confident that management will address rumors and encourages staff members to wait on information from the company before acting on a rumor. Inadequate Job Skills Employees are motivated to succeed at jobs for which they feel prepared and properly trained. Before moving an employee into a position of greater responsibility or before allowing any changes to an employee's job duties, be certain that employee has had the training needed to get started. Putting an employee in a position where she feels she has inadequate job skills will erode the employee's confidence and stifle any motivation to succeed. Goal Flaws Employees are not motivated by the notion that their hard work will make company owners and executives rich, the more internalized a company's goals sound, the less motivated employees are to fulfill those goals. The company needs to focus on the customer and give employees a chance to feel as though it has done something substantial to help the customer. For example, develop a referral program that encourages customers that have recently purchased products to recommend other people that your sales professionals can call on. The company and sales staff benefit from the increase in business, but the sales staff also gets to see the appreciation of past clients in the form of potential new business. Overwork Employees that are overworked are likely to lose motivation regardless of how much overtime pay they are receiving. If you know a period is coming where extra hours will need to be worked, develop a schedule in advance and give your employees ample warning so they can make preparations in their personal life. Make sure the staff schedule still allows employees to spend time with their families and get away from the stress of working too much. 1.1.8 Techniques of Employee Motivation
- 15. 15 Here are some motivations techniques that will help to get staff re-energised and engaged at work. To begin with, make sure you have the right conditions in place so that your work culture supports motivation. Make sure you offer: √ Fair pay and conditions √ A comfortable, safe, working environment √ Opportunities for employees to socialize and make friends √ clearly defined work responsibilities and goals √ Education and training opportunities √ Career opportunities As a manager, you play a key role in building on a solid foundation and motivating employees. Remember that 70% of people leave their boss, not the company. So what can you do to make sure that employees are switched on at work? Here are some practical motivation techniques that you can use to improve motivation in your workplace: 1. Treat Employees as Individuals Do you make assumptions about what motivates your employees? Some are likely to be career focused, but others may see their work as a place to make friends and earn money.Find out what motivates employees outside of work. Some enjoy a challenge such as a sporting activity; others may like to be on committees so they can use their organizational skills. Use their innate talents in the workplace where possible to keep them motivated. Set goals which stretch their abilities. Make goals SMART - specific, measurable, achievable, relevant and time framed.
- 16. 16 Treat Employees with Respect Get to know your employees on a personal level, and offer support when needed, even if it is only to listen to their concerns. Ask your employees for their opinions where possible, for example if you are changing systems or introducing new equipment. Being involved in decision making is one of the best motivation techniques. Catch your employees doing something well and praise them - and if you do this in front of others, it makes the employee feel even better. Giving employees recognition for their efforts will motivate them to repeat the process. Provide Opportunities for Employee Learning and Development Encourage a learning climate, through structured on-the-job training programmes, job transfers, inter-disciplinary projects and support for further education. Aim to have your employees constantly learning new skills and gaining new knowledge. This will reduce the level of stagnation that can easily occur in a business. Promote from within where feasible - and invest the time and support in developing employees so they can take on new opportunities. Some managers worry that by offering a high level of training to employees, they may leave the business for better opportunities elsewhere. Remember this allows other employees to rise up and take their place! Also the word will spread that you are a good employer - which may encourage a higher caliber of external job applicants. Make the Workplace a Fun Place Having fun is one of the best motivation techniques. And small things can make all the difference.. √ bringing sweets to team meetings √ sharing non-business news through e.g. newsletters √ arranging activities such as lunchtime yoga sessions √ surprising employees with a birthday cake √ asking the employees for their opinion on what would make the workplace a fun place!
- 17. 17 Morale Boosters Measuring Morale There's only one way to know how good morale really is in your company: ask the people who work there. Street Smarts: The Tournament Morale took a real beating this fall. But there's nothing that lifts the spirits like some friendly competition. Revving Up the "P" Word (Productivity) Though productivity is often defined in numbers, it relies very heavily upon people and their attitudes. Leading in Hard Times CEOs offer 10 tips for leading your company through bleak times. Non-Cash Incentives Low-Cost Ways to Build Employee Commitment Consider the power of the five I's. It Takes More than Pay to Keep Good Workers Companies are finding a number of ways to expand responsiveness and flexibility beyond traditional compensation programs to retain top employees. Incentives for All Generations The one-size-fits-all approach no longer suits today's multigenerational workplaces. Check this list of desired perks for mature workers, baby boomers, Gen Xers, and more. Winter Holiday Rewards The hectic holiday season is the time to show off a well-thought-out reward strategy that helps your workforce stay motivated and focused.
- 18. 18 Perks You Can Afford In this classic Inc. article, take a look at some unique employee benefits that can help you create an environment your workers won't want to leave. Motivation by Compensation Trust but Verify In addition to providing valuable information on the company's 20 restaurants, the Noodles & Co. secret shopper program is used as a motivational tool. The Store that Stark Built Not only does every employee at Debra's Natural Gourmet have a management role, in a move unheard of in retail, profits are shared amongst the team. In a Former Life: Alan Schultz This CEO learned a valuable lesson during his past life as a steelworker: A company should compensate its sales force based on fair and reachable short- term goals. Hands On: Showing Up Are your workers not in the habit of showing up every day? Try instituting a bonus system to encourage perfect attendance. Turn Motivation Inside Out Inside sales teams often go unrecognized and unrewarded. To motivate them and build a winning sales team all around, reward sales support staffers with commissions, too. Goals, Roles, Pay, and Performance If you've promised goal-based compensation, you need to clearly communicate roles, goals, and paths; otherwise, you may end up with disgruntled employees. Turbo charger Your Bonus Plan Take a regular bonus plan and add a kicker—an increase in the payout if certain targets are met.
- 19. 19 1.1.9 Theories of Motivation At a simple level, it seems obvious that people do things, such as go to work, in order to get stuff they want and to avoid stuff they don't want. Why exactly they want what they do and don't want what they don't is still something a mystery. It's a black box and it hasn't been fully penetrated. Overall, the basic perspective on motivation looks something like this: In other words, you have certain needs or wants (these terms will be used interchangeably), and this causes you to do certain things (behavior), which satisfy those needs (satisfaction), and this can then change which needs/wants are primary (either intensifying certain ones, or allowing you to move on to other ones). A variation on this model, particularly appropriate from an experimenter's or manager's point of view, would be to add a box labeled "reward" between "behavior" and "satisfaction". So that subjects (or employees), who have certain needs do certain things (behavior), which then get them rewards set up by the experimenter or manager (such as raises or bonuses), which satisfy the needs, and so on..
- 21. 21 1.3 PROBLEM STATEMENT “Problem statement is a statement in which focusing on some variable. It provides opportunity to establish why these variables are important”. There is the more need to research on motivation, goal is that what employees is to perform at their best and achieve the objects or not in a specific time. In this the problem is that many of the employers who don’t work for everyone have struggled for different incentive programs to motivate their employee. This is the problem which is faced by the many employees of that company. In problem statement, currently problem must be exist in that organization and the manager should need to be improved in that organization. Motivating is the major component of management. Many of the mangers of that company do different things for example: production, sales prices, performance and etc. the problem statement of the research is: Why the incentives not for everyone why only for employees? Why work of the human resources department is not performing well in that organization? Why the bank not introducing the new products, bank boost the development of product and increase the range of facilities so that the rate of interest increase on various product? How motivational incentives impact to the employee at their best optimal business result?
- 22. 22 1.4 SCOPE OF STUDY The motivation of study is that data collected from the different branches of the bank of the Punjab and the study on the employees of that bank. In this bank 45 employees are worked in this bank and fill the questionnaire during the period of two weeks. We were visited in different branches of bank every day and the employees of those branches were requested that questionnaire must comprise on 15 different questions. And the different scales should be used in questionnaire like nominal scale, ordinal scale, interval scale and ratio scale. These scales which is used to find or analyzed the result. The questions which is used in questionnaire must be related to the monetary and non- monetary incentives, values of incentives and etc.
- 23. 23 1.5OBJECTIVES OF STUDY Objectives must be clear and understandable. We must clear understanding about the inspiration and motivational incentives. How to receive the high rate of interest. To understand how the requests of incentives is effective in a bank. Must be understand the relationship between motivational incentives and the performance of the employees
- 24. 24 1.6NEED FOR STUDY In importance of the study we used the two approaches for find the employee motivation first is conducting the interviews of the employee and the second is to fill the questionnaire from the employees of the different banks. We analyze the detail of different incentives systems and get the other information related to the motivation of employees. After that we give the some suggestion and recommendation
- 25. CHAPTER 2 RESEARCH METHDOLOGY 2.1 REVIEW OF LITRATURE Employee motivation is central to many aspects of industrial and organizational development the individual performance and growth in the organization influenced by varied function constant changing environment have also an influence on individual at personal level According to scientific management employee motivation is based on most pragmatic an essential pessimistic philosophy that man is maintained by money. The individual involvement, loyalty, dedication to job and organization seed to be low key affair, the loyalty, dedication and involvement leads to organization effectiveness productivity as well as individual growth and enhancement. Employee motivation is commonly measured in seven areas that is physical, salary and perks, promotion, policy, job security, work interest, relation, welfare facilities. Studying employee motivation which influence and determine human behavior in worth because ultimately all the aspects related to employee motivation ultimately leads to good industrial relationship enhances inter personal relation ultimately leads to increase productivity and growth of the organization. Thus the study is an attempt to explore various factor which can affect industrial development especially related to employee motivation which can be helpful to all those and especially industrial social workers to find out effective measures and solution to deal with the loopholes and obstacles in gaining effective work. .
- 26. 26 SAMPLING METHOD Researcher has selected respondents randomly that is why simple random sampling method is used. SAMPLE SIZE Sample of present study consists 40 respondents of various departments of madhur Dairy RESEARCH DESIGN This study is exploratory and descriptive in nature. VARIABLES (1). Independent: Sex, age, income (2). Dependant: Employee motivation. TOOLS OF DATA COLLECTION Primary tool: Interview schedule Secondary tool: library, books, journals, internet, news paper, magazines OPERATIONAL DEFINITION Specter (1997) defines employee motivation simply as “the degree to which people like their jobs.” . 2.3 RESEARCH METHOLOGY In this section I will describe and explain the concepts, models and theories that are relevant in the field of motivation and necessary to facilitate a comprehensive analysis and Understanding
- 27. 27 of the research question .It may be useful to conceptualize the term financial Motivation and what its concepts are. A broader definition of motivation will be introduced. What is motivation? According to Greenberg and Baron (2000 p190) this definition could be divided into three main parts. The first part looks at arousal that deals with the drive, or energy behind Individual (s) action. People turn to be guided by their interest in making a good impression On others, doing interesting work and being successful in what they do. The second part referring to the choice people make and the direction their behavior takes. The last part deals with maintaining behavior clearly defining how long people have to persist at attempting to meet their goals. Kreitner (1995), Buford, Bodleian &Linder (1995), Higgins (1994) all cited in Linder (1998,p3) defined motivation as “the psychological process that gives behavior purpose and Direction, a predisposition to behave in a purposive manner to achieve specific unmet needs, An unsatisfied need, and the will to achieve, respectively. Young (2000, p1) suggest that motivation can be defined in a variety of ways, depending on Who you ask .Ask some one on the street, you may get a response like “its what drives us”or “its what make us do the things we do.” Therefore motivation is the force within anindividualthat account for the level, direction, and persistence of effort expended atwork.z10Halepota (2005, p16) defines motivation as “a persons active participation and commitments achieve the prescribed results.”Halepota further presents that the concept of motivation is abstract because different strategies produce different results at different times and there is nosingle strategy that can produce guaranteed favourable results all the times.” According to Antonioni (1999, p29), “the amount of effort people are willing to put in their Work depends on the degree to which they feel their motivational needs will be satisfied. On the other hand, individuals become de- motivated if they feel something in the organization Prevents them from attaining good outcomes. It can be observed from the above definitions that, motivation in general, is more or less basically concern with factors or events that moves, leads, and drives certain human action or Inaction over a given period of time given the prevailing conditions. Furthermore the definitions sugge st that there need to be an” invisible force” to push people to do something inreturn. It could also be deduced from the definition that having a motivated work force or creating an environment in which high levels of motivation are maintained remains challenge for today’s management. This challenge may emanate from the simple fact that motivation is not a fixed trait –as it could change with changes in personal, psychological ,financial orsocial factors. For this thesis, the definition of motivation by Greenberg & Baron (2003) is adopted, as it is more realistic and simple as it considers the individual and his performance. Greenberg&Baron defines motivation as:
- 28. 28 “The set of processes that arouse, direct, and maintain human behavior towards attaining some goal”. (Greenberg &Baron, 2003, p190) Bassett-Jones &Lloyd (2005, p931) presents that two views of human nature underlay early research into employee motivation. The first view focuses on Taylorism, which viewed people as basically lazy and work –shy”, and thus held that these set of employees can onlybe motivated by external stimulation. The second view was based on Hawthorn findings, which held the view that employees are motivated to work well for “its own sake” as well as for the social and monetary benefits this type of motivation according to this school was internally motivated. Motivation theories Even though much research been conducted on the field of financial motivation and many researchers and writers have proposed theories on the concept of financial motivation, and its role in enhancing employee’s performance in every organization some of these models have been widely used and accepted by today’s organizations leaders. In this thesis discussion on some of the motivational theories will include Alders (ERG theory), Maslow (Need theory), Vrooms (Expectancy theory), Adams (Social equity theory), Taylor (productivity theory), Herzberg (Two factor theory), Mac Gregory (theory X and Y), Geog pales (path goal theory) and skinner (Reward theory). To better understand this discussion a summary of the theories is presented and an indebt discussion on Maslow and ERG theories on which I base my thesis overlooked. Alder asserts in his Existence relatedness and growth theory commonly known as the ERG theory that there are three basic human needs: Existence, relatedness and growth, which must be meet by an employee to enable him, increase performance. Maslow (1943) suggests that human needs can be classified into five categories and that these categories can be arranged in a hierarchy of importance. These include physiological, security, belongings, esteem and self-actualization needs. According to him a person is motivated first and foremost to satisfy physiological needs. As long as the employees remain unsatisfied, they turn to be motivated only to fulfill them. When physiological needs are satisfied they cease to act as primary motivational factors and the individual moves “up” the hierarchy and seek to satisfy security needs. This process continues untfinallyselfactualisation needs are satisfied. According to Maslow the rationale is quite simple because employees’ who are too hungry or too ill to work will hardly be able to make much a contribution to productivity hence difficulties in meeting organizational goals. Vroom (1964) proposes that people are motivated by how much they want something and how likely they think they are to get it he suggest that motivation leads to efforts and the efforts combined with employees ability together with environment factors which interplay’s resulting to performance. This performance interns lead to various outcomes, each of which has an associated value called Valence. Adams (1965) on his part suggests that people are motivated to seek social equity in the Rewards they receive for high performance. According to him the outcome from job includes; pay, recognition, promotion, social relationship and intrinsic reward .to
- 29. 29 get these rewards various inputs needs to be employed by the employees to the job as time, experience, efforts, education and loyalty. He suggests that, people tend to view their outcomes and inputs as aratio and then compare these ratios with others and turn to become motivated if this ratio is high.Taylor (1911) observed the soldering by employees, which is a situation whereby workers work less than full capacity. He argued that soldering occurs due to the fact employee’s fear that performing high will lead to increasing productivity, which might cause them to lose their jobs. This slow paces of work where promoted by faulty systems however this situation is not what prevails with contemporary employees who organizations evaluate them through their performance. Herzberg suggested that there are factors in a job, which causes satisfaction. These he called Intrinsic factors (motivators) and other factor he refers to as dissatisfies (hygiene factors). According to him if the motivational factors are met, the employee becomes motivated and hence performs higher. Mac Gregory suggested that there exist two sets of employees (lazy and ambitious employees) with lazy employees representing theory X, hard and ambitious workers representing Y. According to him the lazy employee should be motivated to increase performance in an organization Geog opalaus path Goal theory of motivation states that, if a worker sees high productivity as a path leading to the attainment of one or more of his personal goals, he will turn to be a high Producer. But if he sees low productivity as the path leading to the attainment of his goal he will turn to be a low producer and hence needs to be motivated. This discussion on the above motivational theories explains the fact that the concept of Employee’s motivation has been a critical factor addressed by previous authors as what determines the core competence of every organization in achieving a competitive position. Skinner who propounded that any behavior that is rewarded tends to be repeated supported This view. The term motivation has been used in numerous and often contradictory ways. Presently there appears to be some agreements that the crucial thread that distinguishes employee’s Motivated behaviors’ from other behavior is that it is goal directed behavior, Bindra (2000 P223) argues that the core of motivating individuals lays in the goal-directaspectofbehaviour.Jones suggested “motivation is concern with how behavior gets started, is energized, is Sustained, is directed, is stopped and what kind of subjective re-action is present in the organization while this is going on. The Jones statement can be converted into a diagram Which shows the employee motivational process as it influences performance. The process of employee’s motivation Search The figure illustrates that the process begins because of tension within drives or needs of an employee. Next there is a search within the company or groups or within employee tofulfilhis desires. When the employee is satisfied with his financial motivation he redefines his desires and needs and the process is initiated again. These groups of researchers were over the years divided into what was later labeled the Content and process theories of motivation. According to steers, mowday &Shapiro
- 30. 30 Tension or drive To fulfill or need Fulfillment and Re-definition of needs Goal directed Behavior (2004,p382) the process generated during this period, makes this period referred to as “the golden age of work motivation theories”. “Never before and, some would argue, never since has so much progress been made in Explicating the aetiology of work motivation” (steers et al., 2004, pp380-383) Bassett-Jones & Lloyd (2005,p 932) suggests that the “content theorists led by Herzberg, assumed a more complex interaction between both internal and external factors, and explored the circumstances in which individuals respond to different internal and external stimuli. On the other hand, process theory, where victor Vroom was the first exponent considers how factors internal to the person result in different behaviours. From the focus point of these two groups, one could observe that the process theories attempt or try to understand the thinking processes an individual might go through in determining how to behave in a workplace. The primary focus was on how and why questions of motivation,how a certain behaviour starts, developed and sustained over time.It is true that human behaviour in general is dynamic and could affect the individual’spersonal altitude as well as factors surrounding that individual. These exogenous factors eminent from the environment in which the individual operates generate stimuli to employees. It is my belief that employees in general are goal seeking and look for challenges and expect Positive re-enforcement at all times. Hence it could only be of benefit if organisations could provide these rewards and factors. Though I have discussed earlier in this thesis that employees are financially motivated, motivation could be seen as a moving target, as what Motivates differs among different people. And may even change for the same person over a given period of time, developments within the modern organisation has probably made Motivating employees ever more difficult due to the nature of every individual, behaviourincreasing the complexity of what can really motivate employees. According to Bassette-jones & Lloyd (2005,p.932) “expectancy, equity, goal setting and reinforcement theory have resulted in the development of a simple model of motivational alignment. The model suggest that once needs of employees are identified, and organizational objectives and also satisfy employee needs .If poorly aligned, then low motivation will be the Outcome”.
- 31. 31 According to (Wiley, 1997,p264) “modern approaches to motivation may be organised into three related clusters: (1) personality-based views (2) cognitive choice or decision approaches and (3) goal or self-regulation perspective; where personality-based views emphasize the influence of enduring personal characteristics as they affect goal choice and striving. Workplace behaviour is posited to be determined by persons current need state in certain Universal need category. Cognitive choice approaches to work motivation emphasize two determinant of choice and action; expectations, and subjective valuation of the consequences associated with each alternative. These expectancy value theories are intended to predict an individual choice or decision. Goal framework to work motivation emphasis the factors that influence goal striving which focuses on the relationship between goals and work behavior. The assumption is that an employee’s conscious intentions (goals) are primary determines of Task-related motivation since goals directs their thoughts and action”. It is worth noting that an in-depth review of all the different theories mentioned above, is beyond the scope of this thesis. However, the personality-based perspective of work motivation within which Maslow need theory of motivation and Alders ERG theory falls will provide the main support and serve as a foundation for the research reported in this thesis. Specifically, as organisational scholars have paid a great deal of attention to the idea that people are motivated to use their jobs as mechanisms for satisfying their needs. This thesis intend to use Maslows hierarchy of need theory of motivation as a foundation to identify the factors that motivate today’s employees, and in the process determine a ranking order of factors that motivates these employees, the original Maslow theory will be looked at more detail hereof. History and Explanation of Maslow’s Hierarchy of Need Theory The “motivation to work” published by Maslow probably provided the field of organizational behaviour and management with a new way of looking at employees job altitudes or behaviours in understanding how humans are motivated. Probably the best- known Conceptualization of human needs in organizations has been proposed by this theory. Abraham Maslow was a clinical psychologist, who introduced his theory based on personal judgment which was generally known as the need hierarchy theory. According to him if people grew in an environment in which their needs are not met, they will be unlikely to function as healthy individuals or well-adjusted individuals. This idea was later applied to organizations deemphasize the idea that unless employees get their needs met on the job, they will not function’s effectively as possible. Specifically Maslow theorised that people have five types of needs and that these are activated in a hierarchical manner. This means that these needs are aroused in a specific order from lowest to highest, such that the lowest-order need must be fulfilled before the next order need is triggered and the process continues. If you look t this in a motivational point of vie Maslow’s theory says that a need can never be fully met, but a need that is almost fulfilled does not longer motivate. According to Maslow you need to know where a person is on the Hierarchical pyramid in order to motivate him/her. Then you need to focus on meeting that person’s needs at that level (Robbins 2001)According to Greenberg and Baron (2003,p192) the five needs identified by
- 32. 32 Maslowcorresponds with the three needs of Alderfers ERG theory. Where as Maslow theory specifiesthat the needs be activated in order from lowest to highest Alder’s theory specifies that theneeds can be activated in any order. His approach is much simpler than Maslows. Alder specifies that there exist three main needs as opposed to five postulated by Maslow. Thishuman basic needs include existence, relatedness and growth. These needs according to Alderneed not necessarily activated in any specific order and may be activated at any time. According to him Existence needs corresponds to Maslow’s physiological needs and safety needs. Relatedness needs corresponds to Maslow’s social needs and growth needs corresponds to esteem and self-actualization needs by Maslow Below is a summary of these needs that in this thesis are divided into Deficiency needs (Psychological, safety, social needs) and Growth needs (esteem, self- actualization needs). Factors Explanation � Physiological needs are the need at the bottom of the triangle and include the lowest order need and most basic. This includes the need to satisfy the fundamental biological drives such as food, air, water and shelter. According to Maslow organizations must provide employees with a salary that enable them to afford adequate living conditions. The rationale here is that any hungry employee will hardly be able to make much of any contribution to his organization. � Safety needs this occupies the second level of needs. Safety needs are activated after Physiological needs are met. They refer to the need for a secure working environment free from any threats or harms. Organizations can provide these need by providing employees with safety working equipment e.g. hardhats, health insurance plans, fire protection etc. The rationale is that employees working in an environment free of harm do their jobs Without fear of harm. � Social needs: This represents the third level of needs. They are activated after safety needs are met. Social needs refer to the need to be affiliated that is (the needed to be loved and accepted by other people). To meet these needs organisations encourage employees Participation in social events such as picnics, organisations bowling etc � Esteem needs this represents the fourth level of needs. It includes the need for self- respect and approval of others. Organisations introduce awards banquets to recognize distinguished achievements � Self-actualization: This occupies the last level at the top of the triangle. This refers to the need to become all that one is capable of being to develop ones fullest potential. The rationale here holds to the point that self-actualised employees represent valuable assets to the organization human resource. Most research on the application of need theory found that although lower-level managers are able to satisfy only their deficiency needs on the jobs, managers at the top level of Organizations are able to satisfy both their deficiency and growth needs (Greenberg &Baron 2003 p.194) this view was supported by Shipley & Kelly (1988, p.18) Shipley & Kelly (1988, p.18) argue that as “need satisfaction is an attitude, and that it isperfectly possible for a worker to be satisfied with his/her need, but not be motivated the Reverse of which holds equally true. Hence,
- 33. 33 need satisfaction and motivation are not synonymous and both need fulfillment and un- fulfillment can have negative as well as positiveinfluence on motivation Organizational /managerial Applications of Maslow’s Need theory The greatest value of Maslow’s need theory lies in the practical implications it has for every Management of organizations (Greenberg & Baron 2003 p.195). The rationale behind thetheory lies on the fact that it’s able to suggest to managers how they can make their employees or subordinates become self-actualized. This is because self- actualized employees are likely to work at their maximum creative potentials. Therefore it is important to make employees meet this stage by helping meet their need organisations can take the following Strategies to attain this stage � Recognize employee’s accomplishments: Recognizing employee’s accomplishments is an important way to make them satisfy their esteem needs. This could take the form of awards, plagues etc.. According to (Greenberg & Baron 2003, p197) research carried out in GTE Data services in Temple Terrace, Florida shows that awards are given to employees who develop ways of improving customer’s satisfaction or business performance. But it should be noted that according to Greenberg &Baron awards are effective at enhancing esteem only when they are clearly linked to desired behaviours. Awards that are too general fail to meet this specification. � Provide financial security: Financial security is an important type of safety need. So Organizations to motivate their employees need to make them financially secured by involving them in profit sharing of the organization. In a research carried out with AT&T and Wang showed that 50% of their employees received financial outplacement services to assist laid-off employees in securing new jobs. � Provide opportunities to socialize: Socializations is one of the factors that keep employees feel the spirit of working as a team. When employees work as a team they tend to increase their performance. Research conducted on IBM shows that it holds a “family day” picnic each spring near its Armonk, New York headquarters. � Promote a healthy work force: Companies can help in keeping their Employees physiological needs by providing incentives to keep them healthy both in health and mentally. In a research carried out at the Hershey Foods Corporation and Southern California Edison Company showed that Employees are provided with insurance rebates with health lifestyles while extra premiums were given to those with risk habits like smoking. Criticisms of Maslow’s Need theory of motivation
- 34. 34 Maslow proposed that if people grew up in an environment in which their needs are not meet,they would be unlikely to function healthy, well-adjusted individuals. Research testingMaslow’s theory has supported the distinction between the deficiencies and growth needs butShowed that not all people are able to satisfy their higher-order needs on the job. Accordingthe results of the research managers from higher echelons of organizations are able to satisfyboth their growth and deficiency needs lower level managers are able to satisfy only theirdeficiency needs on the job. Maslow’s theory has not received a great deal of support withrespect to specific notion it proposes (Greenberg &Baron 2003, p195). To them this model is theorized to be especially effective in describing the behavior of individuals who are high ingrowths need strength because employees who are different to the idea of increasing their growth will not realize any physiological reaction to their jobs. Centers & Bgental (1966, .193) in their carried out among a cross-section of the Working population in Los Angeles, posited survey “background factors, altitudes and aspirations affects workers needs, expectations and situation assessment”. According to Graham &Messner (1998, p.196) there are generally three major criticisms directed to the need theoryand other content theories of motivation. (A) There is scant empirical data to support their conclusions, (b) they assume employees are basically alike, and (c) they are not theories of motivation at all, but rather theories of job satisfaction. This was supported by the views of Nadler & Lawler (1979) in Graham &Messner (2000, p 188). Nadler & Lawler (1979) cited in Graham & Messner (2000, p.198) where also critical of theneed theory of motivation. They argue that the theory makes the following unrealisticassumptions about employees in general that: (a) all employees are alike (b) all situations arealike and that (c) there is only one best way to meet needs. Another critic to this view wasBasset-Jones & Lloyd (2004, p 961). Basset-Jones & Lloyd (2004, p 961) presents that in general, critics of the need theory arguethat it is as a result of the natural feeling of employees to take credit for needs met and dissatisfaction on needs not met. Nonetheless and regardless of the heavy criticism levied at the hierarchy of need theory, I Believe that this theory has a made a significant contribution in the field of organizational behavior and management especially in the area of employee motivation and remains attractive to both researchers and managers alike. The incorporation of the need theory intothe work environment today could be as a result of the contributions made so far by MaslowsHierarchy of need theory. Empirical studies on employee motivation using the original and Adapted Maslow’s model If any person has to come up with the question that is there any need for employees motivation? The answer to this type of question of-course should be simple-the basic survival of every organization be it public or private limited before, today and in the foreseeable future lies in how well its work force is motivated to meet the objectives of the organization. This explains why the human resource department in today’s organization is became a focus of its core functions. I think that motivated employees are needed in this rapidly Business world where the principal-agent conflict is the issue confronting most managers. Most organisationsnow consider their human resources as their most valuable assets (a strategic or competitive advantage). Therefore, in order to
- 35. 35 effectively and efficiently utilize this strategic asset, I believe managers and the organization as a whole, must be able and willing to understand and hopefully provide the factors that motivate its employees within the context of the roles and duties they perform. This is because highly motivated employees are the cause of high productivity levels and hence higher profits for the organization. Having noted this rationale the next question one may ask are what factors motivated today’s employees”? According to Wiley (1997, p265) at some point during our lives, virtually every person may have to work. He claims that working is such a common phenomenon that the question “what Motivates people to work is seldom asked. Wiley went on to say that “we are much moreLikely to wonder why people climb mountains or commit suicide than to question themotivational basis of their work”,. Therefore, exploring the altitudes that employees holdconcerning factors that motivate them to work is important to creating an environment thatencourages employee motivation. From the much amount of literature available on employee motivation, it is clearly evidentthat a lot of surveys regarding employees and what motivates them have been undertaking. These employee motivation surveys have been conducted in many different job situations,among different categories of employees using different research methods and applications. One of the very first survey to be conducted was on industrial workers by (Hershey & Blanchard, 1969) over the years, similar or different survey employees have been carried outsee (Kovach, 1987, 1993) (Wiley, 1995), (Lindner, 1998, 1999) According to a research carried out by Kovach on industrial employees who were asked torank ten “job rewards” factors based on personal preferences where the value 1 represented most preferred and 10 being the least preferred. The results were as follows (1) full Appreciation of work done (2) feeling of being (3) sympathetic help with personal problems(4) Job security (5) Good wages and salaries (6) interesting work (7) promotion & Growth (8)employee’s loyalty (9) Good working conditions (10) tactful discipline During the periods of (1946, 1981 & 1986) when employee surveys were carried out, Supervisors were at the time asked to rank job rewards, as they taught employees would rankthem. The rankings by the supervisors were relatively consistent for each of the years. Theserankings were as follows: (1) Good wages (2) Job security (3) promotion and Growth (4)working conditions (5) interesting work (6) personal loyalty to employees (7) tactfuldiscipline (8) full appreciation (9) sympathetic help with personal problems (10) recognition (Kovach 1987 p.49-54) The results from the supervisor survey indicated that their ranking had not changed over theStudy period with regards their collective perception of factors that motivate employees. Thisshows that they had a very inaccurate perception of what motivates employees but also thatthey did not realise the importance of the need theory In a survey by Wiley (1997, p.278) in which approximately 550 questionnaires were Administered to person employed at different industries and divided into 5 subgroups, or Categories namely: (occupation, gender, income levels, employment status and age) they were asked to rank 10 factors according to the level of importance each is in motivating them toperform best with the most important factor ranked 1 and the least important ranked 10th. The survey concluded with the following collective rank order by respondents: (1) Good wages (2) full appreciation of work done (3) job security (4) promotion (5) interesting work (6) company loyalty to employees
- 36. 36 (7) Good working conditions (8) tactful discipline (9)recognition (10) sympathetic help with personal problems The results from a representative sample of the labour force in seven different countries byHarpaz (1991 p.75) showed that the two most dominant work goals were “interesting work “and Good wages”; He further concluded that these two factors were consistent across different Organizational levels, between genders and age groups.Quinn (1997) also cited in Harpaz (1991 p.311) concluded, “When the ratings of twenty three job related factors (including the need factors) were carried out, the conclusion reached was that no single factor was pre-eminently important”. He further pointed out that, “The most aspect of the worker job was that of sufficient resources to perform a task. From the above studies presented so far, the rankings by different subgroups have shown semantic differences in the importance placed on different motivational factors. For example (Kovach, 1987, Wiley, 1997 and Harpaz, 1990) .The discrepancies in these research findings supports Nelsons (2001, p.2) positional view that “what motivates employees differs and may change for the same employee over time”. It is appropriate at this level to give a brief summary of the previous researches in this thesis. Even though the original need hierarchy theory was presented some 50 years ago, some of its if not all factors remain of significant importance to employees today. The large number of earlier and recent studies investigating employee motivation using sometimes the original or modified version of Maslow’s theory, may continue the appreciation of this theory and the issue of employee motivation. The literature also shows that where the original theory was lacking (short comings or criticised for), has been greatly taken into consideration. Researchers have taken issues such as differences in gender, age, income, culture & countries etc and how these may affect or influence employee work motivation extensively. The commonality between these previous researches is the agreement that certain factors are more important as motivational factors than others and that these factors may change from one employee to another. These previous studies have also been taken using different methods, from surveys, questionnaires, face-face interviews, but their outcomes have not differed significantly. A possible explanation could be due to the fact that even. 2.3LIMITATION OF THE SUTDY Time constraint was one of the limitations during the data collection. Responses received were not free from respondent biases because of their apprehension that it might affect their career
- 37. 37 CHAPTER 3 RESULTS, DISCUSSIONS, AND CONCLUSION 3.1 Analysis and Interpretation Gender Frequency Percentage (%) Male 31 77.5 Female 9 22.5
- 38. 38 Above table shows that 77% percent (n=31) respondent belongs to a male-group of percent 23% (n=9) Table no-5.2 Table show age wise distribution of respondent. Age Frequency Percentage (%) 18 to 25 years 8 20 26 to 35 years 15 37.5 36 to 45 years 11 27.5 77% 23% Gender male female
- 39. 39 Above 45 years 6 15 Total 40 100 Above table shows that 20% percent (n=08) respondent belongs to age-group of 18 -25, 37.5% percent (n=15) belongs to age-group of 26-35, 27.5% percent (n=11) belongs to age-group of 36-45 while 15% percent (n=6) belongs to age- group of above 45 years. Table no-5.3 Table shows the educational qualification of the respondent. Education Frequency Percentage (%) S.S.S 18 45% 20% 37.5% 27.5% 15% percentage of age 18 to 25 years 26 to 35 years 36 to 45 years Above 45 years
- 40. 40 H.S.C 6 15% Graduate 10 25% Post Graduate 1 2.5% Other 5 12.5% Total 40 100% Above table shows that 45% percent (n=18) respondent had their educational qualification up to primary level, 15% percent (n=6) respondent had their educational qualification up to secondary level, 22.5% percent (n=10) respondent had their educational qualification up to higher secondary level, 12.5%percent (n=5) respondent had their educational qualification up to graduation level while 05% percent (n=2) respondent had their educational qualification up to post graduate level. Table no- 5.4 Table shows the work of span of the respondent. 45% 15% 22.5% 2.5% 13% Education S.S.S H.S.C Graduate Post Graduate Other
- 41. 41 experience Frequency Percentage (%) 1 – 5 years 14 35% 6 – 10 years 12 30% 11 – 15 years 9 22.5% Above 15 years 5 12.5% Total 40 100% Above table shows that 35% percent (n=14) respondent belongs to age-group of 1 – 5years, 30% percent (n=12) belongs to age-group of 6 – 10 years, 22.5% percent (n=9) belongs to age-group of 11 – 15 years, while 12.5% percent (n=5) belongs to age-group of above 15 years. Table no- 5.5 Table shows present salary and incriment of the respondent. 35% 30% 23% 14% Percentage work of span 1 – 5 years 6 – 10 years 11 – 15 years Above 15 years
- 42. 42 Employee response Frequency Percentage (%) Strongly agree 4 10% Agree 27 67.5% Uncertain 3 7.5% Disagree 4 10% Strongly disagree 2 5% Total 40 100% Above table shows that 10% percent (n=4) respondent with strongly agree, 67.5% percent (n=27) respondent with agree, 7.5% percent (n=3) respondent with uncertain,10% percent (n=4) respondent with disagree,5% percent (n=2) respondent with strongly agree. 10% 67% 8% 10% 5% percentage ofpresent salary and incriment Strongly agree Agree Uncertain Disagree Strongly disagree
- 43. 43 Table no-5.6 Table shows financial or financially related reward systemin my organization. Employee response Frequency Percentage (%) Strongly agree 2 5% Agree 22 55% Uncertain 5 12.5% Disagree 8 20% Strongly disagree 3 7.5% Total 40 100% Above table shows that 5% percent (n=2) respondent with strongly agree, 55%percent (n=22) respondent with agree, 12.5%percent (n=5) respondent with uncertain,20% 5% 55%12% 20% 8% percentage of financial or financially related reward system Strongly agree Agree Uncertain Disagree Strongly disagree
- 44. 44 percent (n=8) respondent with disagree,7.5% percent (n=3) respondent with strongly disagree. Table no- 5.7 Table shows working conditions are clean,pleasant & safe of respondent. 67% 28% 0% 5% 0% working conditions are clean,pleasant & safe of respondent. Strongly agree Agree Uncertain Disagree Strongly disagree Employee response Frequency Percentage% Strongly agree 67.5 65.5% Agree 27.5 27.5% Uncertain 0 0% Disagree 5 5% Strongly disagree 0 0% Total 40 100%
- 45. 45 Above table shows that 67.5% percent (n=27) respondent with strongly agree, 27.5%percent (n=11) respondent with agree, 0%percent (n=0) respondent with uncertain,5% percent (n=2) respondent with disagree,0% percent (n=0) respondent with strongly disagree. Table no-5.8 Table shows welfare facilities provided by the company. Employee response Frequency Percentage (%) Strongly agree 11 27.5% Agree 25 62.5% Uncertain 1 2.5% Disagree 3 7.5% Strongly disagree 0 0% Total 40 100%
- 46. 46 Above table shows that 27.5% percent (n=11) respondent with strongly agree, 62.5%percent (n=25) respondent with agree, 2.5%percent (n=1) respondent with uncertain,7.5% percent (n=3) respondent with disagree,0% percent (n=0) respondent with strongly disagree. Table no-5.9 Table shows policies and procedures of respondent. Employee response Frequency Percentage (%) Strongly agree 10 25% Agree 22 55% Uncertain 3 7.5% Disagree 5 12.5% Strongly disagree 0 0% total 40 100% 27% 62% 3% 8% 0% percentage of walfere facilities Strongly agree Agree Uncertain Disagree Strongly agree
- 47. 47 Above table shows that 25% percent (n=10) respondent with strongly agree, 55%percent (n=22) respondent with agree, 7.5%percent (n=3) respondent with uncertain,12.5% percent (n=5) respondent with disagree,0% percent) respondents with strongly disagree. Table no 5.10 Table shows relation with my superior peer and subordinates of Respondent. Employee response Frequency Percentage(%) Strongly agree 34 85% Agree 6 15% Uncertain 0 0% Disagree 0 0% Strongly disagree 0 0% total 40 100% 25% 55% 7% 13% 0% percentage ofpolicies and procedures Strongly agree Agree Uncertain Disagree Strongly disagree
- 48. 48 Above table shows that 85% percent (n=34) respondent with strongly agree, 15%percent (n=6) respondent with agree, 0%percent uncertain, disagree, strongly disagree. Table no 5.11 Table shows supervisor take interest in our problem, well being future Employee response Frequency Percentage(%) Strongly agree 7 17.5% Agree 30 75.5% Uncertain 3 7% Disagree 0 0% Strongly disagree 0 0% 85% 15% 0% 0% 0% policies and procedures of respondent Strongly agree Agree Uncertain Disagree Strongly disagree
- 49. 49 total 40 100% Above table shows that17% percent (n=7) respondent with strongly agree, 75%percent (n=35) respondent with agree, 8%percent (n=3) respondent with uncertain, 0%percent , disagree, strongly disagree. Table no 5.12 Table shows setting and achieving challenging goal Employee response Frequency Percentage(%) Strongly agree 5 12.5% Agree 29 72.5% Uncertain 04 10% Disagree 02 05% 17% 75% 8% 0% 0% superviser take intrest in our problem, well being future Strongly agree Agree Uncertain Disagree Strongly disagree
- 50. 50 Strongly disagree 0 0 Total 40 100% Above table shows that 12% percent (n=5) respondent with strongly agree, 73%percent (n=29) respondent with agree, 10%percent (n=4) respondent with uncertain5% percent (n=2) respondent with disagree,0% percent) respondents with strongly disagree. Table no 5.13 Table shows recognized and praised for my good performance Employee response Frequency Percentage(%) Strongly agree 5 12.5% Agree 25 62.5% Uncertain 03 7.5% 12% 73% 10% 5% 0% setting and achieving challenging goal Strongly agree Agree Uncertain Disagree Strongly disagree
- 51. 51 Disagree 07 17.5% Strongly disagree 0 0 total 40 100% Above table shows that 12% percent (n=5) respondent with strongly agree, 62%percent (n=25) respondent with agree, 8%percent (n=3) respondent with uncertain18% percent (n=7) respondent with disagree,0% percent) respondents with strongly disagree. Table no 5.17 Table show organization helps me in all possible way to know my 12% 63% 8% 17% 0% recognized and praised for mygood performance Strongly agree Agree Uncertain Disagree Strongly disagree Employee response Frequency Percentage (%) Strongly agree 8 20% Agree 28 70%
- 52. 52 Above table shows that 20% percent (n=8) respondent with strongly agree, 70%percent (n=28) respondent with agree, 2.5%percent (n=1) respondent with uncertain7.5% percent (n=3) respondent with disagree,0% percent(n=0) respondents with strongly disagree. 20% 70% 4% 8% 0% organizationhelps me in all possible way to know my Strongly agree Agree Uncertain Disagree Strongly disagree Uncertain 1 2.5% Disagree 03 7.5% Strongly disagree 0 0% Total 40 100%
- 53. 53 Table no 5.18 Table show organization we are a given a chance to our present our ideas & the same is give due weight age in decision making Above table shows that 0% percent (n=0) respondent with strongly agree, 55%percent (n=22) respondent with agree, 0%percent (n=0) respondent with uncertain25% percent (n=10) respondent with disagree, 20% percent (n=8) respondents with strongly disagree. 0% 55% 0% 25% 20% organizationwe are a given a chance to our present our ideas & the same is give due weight age in decision making Strongly agree Agree Uncertain Disagree Strongly disagree Employee response Frequency Percentage (%) Strongly agree 0 0% Agree 22 55% Uncertain 0 0% Disagree 10 25% Strongly disagree 8 20% Total 40 100%
- 54. 54 Table no 5.19 Table show management of our calls for active participation of the employee in the dat to day function of the organization 25% 63% 12% 0% 0% management of our calls for active participation of the employee in the dat to day function of the organization Strongly agree Agree Uncertain Disagree Strongly disagree Employee response Frequency Percentage (%) Strongly agree 10 25% Agree 25 62.5% Uncertain 5 12.5% Disagree 0 0% Strongly disagree 0 0% Total 40 100%
- 55. 55 Above table shows that 25% percent (n=10) respondent with strongly agree, 62%percent (n=25) respondent with agree, 13%percent (n=5) respondent with uncertain0% percent (n=0) respondent with disagree, 0% percent (n=0) respondents with strongly disagree. Table no 5.20 Table show prestige of my organization outside company is good 10% 90% 0% 0% 0% prestige of my organizationoutside company is good Strongly agree Agree Uncertain Disagree Strongly disagree Employee response Frequency Percentage (%) Strongly agree 4 10% Agree 36 90% Uncertain 0 0% Disagree 0 0% Strongly disagree 0 0% Total 40 100%
- 56. 56 Above table shows that10 % percent (n=4) respondent with strongly agree, 90%percent (n=36) respondent with agree, 0%percent (n=0) respondent with uncertain0% percent (n=0) respondent with disagree, 0% percent (n=0) respondents with strongly disagree. Table no 5.21 Table shows I am getting maximum pleasure from my work Employee response Frequency Percentage (%) Strongly agree 28 70% Agree 7 17.5% Uncertain 0 0% Disagree 5 12.5% Strongly disagree 0 0% Total 40 100%
- 57. 57 Above table shows that70 % percent (n=28) respondent with strongly agree, 17%percent (n=7) respondent with agree, 0%percent (n=0) respondent with uncertain12.5% percent (n=5) respondent with disagree, 0% percent (n=0) respondents with strongly disagree. Table no 5.22 Table shows added authority and responsibility to present job will be more interesting and rewarding 70% 19% 0% 13% 0% I am getting maximumpleasure from my work Strongly agree Agree Uncertain Disagree Strongly disagree Employee response Frequency Percentage (%) Strongly agree 10 25% Agree 22 55% Uncertain 05 12.5% Disagree 03 7.5% Strongly disagree 0 0%
- 58. 58 Above table shows that25 % percent (n=10) respondent with strongly agree, 55%percent (n=22) respondent with agree, 12.5%percent (n=5) respondent with uncertain7.5% percent (n=5) respondent with disagree, 0% percent (n=0) respondents with strongly disagree Table no 5.23 Table shows authority toencourage juniors is quite common in my organization 25% 55% 12% 8% 0% added authority and responsibility to present job will be more interestingand rewarding Strongly agree Agree Uncertain Disagree Strongly disagree Total 40 100%
- 59. 59 Above table shows that17 % percent (n=7) respondent with strongly agree, 62%percent (n=25) respondent with agree, 0%percent (n=0) respondent with uncertain13% percent (n=5) respondent with disagree, 8% percent (n=3) respondents with strongly disagree Table no 5.24 Table shows job contet and responsibilities are appropriate 17% 63% 0% 12% 8% authority to encourage juniors is quite common in my organization Strongly agree Agree Uncertain Disagree Strongly disagree Employee response Frequency Percentage (%) Strongly agree 7 17.5% Agree 25 62.5% Uncertain 0 0% Disagree 05 12.5% Strongly disagree 03 7.5% Total 40 100%
- 60. 60 Above table shows that17 % percent (n=7) respondent with strongly agree, 62%percent (n=25) respondent with agree, 5%percent (n=2) respondent with uncertain10% percent (n=4) respondent with disagree, 5% percent (n=2) respondents with strongly disagree 17% 63% 5% 10% 5% job contet and responsibilitiesare appropriate Strongly agree Agree Uncertain Disagree Strongly disagree Employee response Frequency Percentage (%) Strongly agree 7 17.5% Agree 25 62.5% Uncertain 2 5% Disagree 04 10% Strongly disagree 02 5% Total 40 100%
- 61. 61 Table no 5.25 Table shows organization tries to make the job more challenging which prevents us from getting bored on the job Above table shows that20 % percent (n=8) respondent with strongly agree, 57%percent (n=23) respondent with agree, 8%percent (n=3) respondent with uncertain10% percent (n=4) respondent with disagree, 5% percent (n=2) respondents with strongly disagree 20% 58% 8% 10% 5% organizationtries to make the job more challenging which prevents us fromgetting bored on the job Strongly agree Agree Uncertain Disagree Strongly disagree Employee response Frequency Percentage (%) Strongly agree 8 20% Agree 23 57.5% Uncertain 3 7.5% Disagree 04 10% Strongly disagree 02 5% Total 40 100%
- 62. 62 Table no 5.26 Table shows appropriate workis given to me according to my skill and potential 10% 50% 5% 20% 15% Appropriatework is given to me according to my skill and potential Strongly agree Agree Uncertain Disagree Strongly disagree Employee response Frequency Percentage (%) Strongly agree 4 10% Agree 20 50% Uncertain 2 5% Disagree 8 20% Strongly disagree 6 15% Total 40 100%
- 63. 63 Above table shows that10 % percent (n=4) respondent with strongly agree, 50%percent (n=20) respondent with agree, 5%percent (n=2) respondent with uncertain20% percent (n=8) respondent with disagree, 15% percent (n=6) respondents with strongly disagree Table no 5.27 Table shows leadership also influences the level of motivation Employee response Frequency Percentage (%) Strongly agree 3 7.5% Agree 17 42.5% Uncertain 3 7.5% Disagree 15 37.5% Strongly disagree 2 5% Total 40 100%
- 64. 64 Above table shows that7 % percent (n=3) respondent with strongly agree, 42%percent (n=17) respondent with agree, 8%percent (n=2) respondent with uncertain38% percent (n=8) respondent with disagree, 5% percent (n=2) respondents with strongly disagree 3.2 FINDING FROM THE STUDY Most of respondent 37.5 % (n=15) were belongs to age-group of 26 -35 Years, Most of respondent 45 % (n=18) had their educational qualification up to s.s.c, Majority of the respondent 35 % (n=14) works in span of (1-5) years. 1. Employee motivation information Majority of respondent 67.5% (n=27) agree whit present salary and increment. Majority of respondent 55% (n=222) agree whit financially related reward system Majority of respondent 67.5 % (n=27) were strongly agree with working condition. Majority of respondent 62.5 % (n=25) were agree with welfare facilities and. 27.5 % (n=11) were strongly agree with welfare facilities Majority of respondent 85 % (n=34) were relation with superior peers and subordinates are good. 8% 42% 7% 38% 5% leadership also influences the level of motivation Strongly agree Agree Uncertain Disagree Strongly disagree
- 65. 65 Majority of respondent 75.5% (n=30) were supervisors take interest in our problem. Majority of respondent 72.5 % (n=29) were enjoy setting and achieving challenging goal. Majority of respondent 62.5% (n=25) were recognized and praised for my good performance. Most of respondent 57.5 % (n=23) clear and effective system of performance appraisal & career development. Majority of respondent 77.5% (n=31) agree whit right opportunities in this organization for my personal growth and promotion. Majority of respondent 70% (n=28) were organization helps me in all possible 20%(n=8) organization helps me in all possible . Majority of respondent 62.5% (n=25) agree and 25% (n=10) strongly agree for management of our calls for active participation of the employee in the day to day functions of the organization Most of respondent 90 % (n=36) agree and 10% (n=4) strongly agree were organization outside company is good. Majority of respondent 70 % (n=28)I am getting maximum pleasure from my work Majority of respondent 55% (n=22) were added authority and responsibility to present job will be more interesting and rewarding. Most of respondent 62.5% (n=25) delegation of authority to encourage juniors is quits common in my organization. Most of respondent 62.5% (n=25) were my job content and responsibilities are appropriate for me. Majority of respondent 75% (n=30) were appropriate work is given to me according to my skill and potential Most of respondent 42.5% (n=17) were agree and 37.5% (n=15) for disagree leadership also influences the level of motivation.
- 66. 66 3.2 SUGESSTION AND RECOMMENDATION In the Madhur dray employees feel that the salary structure is very good but give amount is not satisfactory. 55%of the employees are satisfied by their salary and increment, financial reward. as it is very low rate The higher number of employees (85%) has given strongly agree. It means in madhur dray the belongingness o employees are very good. They have a good relationship with everyone. 65% of employees are satisfied with recognition programs and performance appraisal system. But 35%of the employee is still feeling that the performance appraisal system and recognition programmer are not proper. Hence HR department should know why the employees are not satisfied whit the performance appraisal system and which type of recognition program me they want in future. The higher numbers of employees have given positive response but still there is scope for improvement. The HR department should make the job more challenging. Exciting and meaningful by the factor like goal setting. Creative work. Job rotation. Skill diversity.
- 67. 67 3.3 CONCLUSION Motivation is an aspect which covers almost all the employee from the managing directors to his peon. The motivation is a live issue for all. Motivation is psychological concept. Motivation is not a cause but rather the effect or result of many going awry. Motivation drifters from person to person, industry to industry, level of education age, nature of work etc. Motivation may be range from very high to very low. By this study it is clear that various faction which influences motivation and productivity of the employees each as Social Security measures, welfare facilities, salary status, Bonus, heath condition, shift system and recognition of work are getting much importance. Several approaches to motivation are available. Early theories are too simplistic in their approach towards motivation. The content theories. Maslow’s need hierarchy. Herzberg’s two-factor model and alder’s erg approach are very popular To conclude employee motivation plays very important role in every organization. Good employee motivation helps to success of the organization. Unless an employee has poor motivation if always a possibility of employee disharmony and also affect some thrumming of the organization. From the financial and nonfinancial reward system make motivation in complete picture. Form this we learn that how we applied the concept of motivation for the progressive result of company
- 68. 68 CHAPTER 4 APPENDICES 4.1Questionnaire As a part of my dissertation, I am conducting a research on motivation. This questionnaire is part of the research project & I solicit your co-operation for the same. I assure that the information will be used for academic purpose only and shall be kept confidential. (1) Name: (2) Sex: male [ ] female [ ] (3) Age: (4) Designation: (5) Education: a. Ssc [ ] b. Hsc [ ] c. Graduate [ ] d. Post graduate [ ] e. Other: [ ] (6) Work on span: 1 to 5 years [ ] 6 to 10 years [ ] 11 to 15 years [ ] More than 15 years [ ] (7) I am satisfied with the present salary and increment given to me. 1) Strongly agree [ ] 2) Agree [ ] 3) Uncertain [ ] 4) Disagree [ ] 5) Strongly disagree [ ] (8) I think that financial or financially related reward system in my organization is fair and satisfactory. 1) Strongly agree [ ] 2) Agree [ ] 3) Uncertain [ ]
- 69. 69 4) Disagree [ ] 5) Strongly disagree [ ] (9) I feel that working conditions are clean, pleasant & safe in my organization. 1) Strongly agree [ ] 2) Agree [ ] 3) Uncertain [ ] 4) Disagree [ ] 5) Strongly disagree [ ] (10) I feel that my welfare facilities provided by the company are adequate and provide satisfaction to me. 1) Strongly agree [ ] 2) Agree [ ] 3) Uncertain [ ] 4) Disagree [ ] 5) Strongly disagree [ ] (11) I am aware with policies and procedures to the company and I find that satisfactory. 1) Strongly agree [ ] 2) Agree [ ] 3) Uncertain [ ] 4) Disagree [ ] 5) Strongly disagree [ ] (12) My relation with my superior peers and subordinates are good. 1) Strongly agree [ ] 2) Agree [ ] 3) Uncertain [ ] 4) Disagree [ ] 5) Strongly disagree [ ] (13) Supervisors take interest in our problem, well being and feature. 1) Strongly agree [ ] 2) Agree [ ] 3) Uncertain [ ]
- 70. 70 4) Disagree [ ] 5) Strongly disagree [ ] (14) I enjoy setting and achieving challenging goal. 1) Strongly agree [ ] 2) Agree [ ] 3) Uncertain [ ] 4) Disagree [ ] 5) Strongly disagree [ ] (15) I am recognized and praised for my good performance. 1) Strongly agree [ ] 2) Agree [ ] 3) Uncertain [ ] 4) Disagree [ ] 5) Strongly disagree [ ] (16) There is a clear and effective system of performance appraisal & career development. 1) Strongly agree [ ] 2) Agree [ ] 3) Uncertain [ ] 4) Disagree [ ] 5) Strongly disagree [ ] (17) I feel that my job has enough learning opportunities which will help me in career advancement. 1) Strongly agree [ ] 2) Agree [ ] 3) Uncertain [ ] 4) Disagree [ ] 5) Strongly disagree [ ] (18) I think there are right opportunities in this organization for my personal growth and promotion. 1) Strongly agree [ ]
- 71. 71 2) Agree [ ] 3) Uncertain [ ] 4) Disagree [ ] 5) Strongly disagree [ ] (19) My organization helps me in all possible way to know my abilities, capabilities, present performance and prospect for improvement. 1) Strongly agree [ ] 2) Agree [ ] 3) Uncertain [ ] 4) Disagree [ ] 5) Strongly disagree [ ] (20) In our organization we are a given a chance to our present our ideas & the same is given due weight age in decision making. 1) Strongly agree [ ] 2) Agree [ ] 3) Uncertain [ ] 4) Disagree [ ] 5) Strongly disagree [ ] (21) The management of our calls for active participation of the employees in the day to day functions of the organization. 1) Strongly agree [ ] 2) Agree [ ] 3) Uncertain [ ] 4) Disagree [ ] 5) Strongly disagree [ ] (22)The prestige of my organization outside company is good. 1) Strongly agree [ ] 2) Agree [ ] 3) Uncertain [ ] 4) Disagree [ ] 5) Strongly disagree [ ] (23) I feel that I am getting maximum pleasure from my work.
- 72. 72 1) Strongly agree [ ] 2) Agree [ ] 3) Uncertain [ ] 4) Disagree [ ] 5) Strongly disagree [ ] (24) I feel that the added authority and responsibility to present job will be more interesting and rewarding. 1) Strongly agree [ ] 2) Agree [ ] 3) Uncertain [ ] 4) Disagree [ ] 5) Strongly disagree [ ] (25) Delegation of authority to encourage juniors is quite common in my organization. 1) Strongly agree [ ] 2) Agree [ ] 3) Uncertain [ ] 4) Disagree [ ] 5) Strongly disagree [ ] (26) My job content and responsibilities are appropriate ( not over loaded or not under loaded) for me. 1) Strongly agree [ ] 2) Agree [ ] 3) Uncertain [ ] 4) Disagree [ ] 5) Strongly disagree [ ] (27)My organization tries to make the job more challenging which prevents us from gel ting bored on the job. 1) Strongly agree [ ] 2) Agree [ ] 3) Uncertain [ ] 4) Disagree [ ] 5) Strongly disagree [ ]
- 73. 73 (28) I think that appropriate work is given to me according to my skill and potential. 1) Strongly agree [ ] 2) Agree [ ] 3) Uncertain [ ] 4) Disagree [ ] 5) Strongly disagree [ ] (29)I believe that leadership also influences the level of motivation. 1) Strongly agree [ ] 2) Agree [ ] 3) Uncertain [ ] 4) Disagree [ ] 5) Strongly disagree [ ] 4.2 REFERENCES 1. "Financial Results: Honda Motor Company" (PDF). April 2014. Retrieved20 December 2014. 2. "Financial Results: Honda Motor Company" (PDF). April 2013. Retrieved 26 April2013. 3. ^ "FY2012 FY12 Financial Results: Honda Motor Company". May 2011. Retrieved15 June 2011. 4. Grant, Robert M.; Neupert, Kent E. (2003). Cases in contemporary strategy analysis(3rd ed.). Wiley-Blackwell. ISBN 1-4051-1180-1. Retrieved 12 November 2010 5. Johnson, Richard Alan (2005). Six men who built the modern auto industry.MotorBooks International. ISBN 0-7603-1958-8. Retrieved 12 November 2010 6. Miller, Edward (18 April 2008). "FIRST MOTORCYCLE AIRBAG EARNS TAKATA AND HONDA 2008 AUTOMOTIVE NEWS PACE INNOVATION PARTNERSHIP AWARD". Honda.com. Retrieved 28 July 2009.
- 74. 74 7. "Harga Honda Mobilio". Mobilio. Retrieved 22 November 2009. 8. "The History of Honda". Cars-directory.net. Retrieved 22 November 2009. 9. "World motor vehicle production OICA correspondents survey without double counts world ranking of manufacturers year 2011" (PDF). 10. Le top 20 des entreprises les plus innovates du monde, Challenges, 22 October 2013 Ross, Jeffrey N. (29 January 2014). "Honda is first Japanese carmaker to be a net-exporter from US". Autoblog. Retrieved 25 July 2014. 11 Alexander, Jeffrey W. (2008), Japan's Motorcycle Wars: An Industry History, UBC Press, pp. 112–116, 197–211, ISBN 978-0-8248-3328-2 12 Frank, Aaron (2003). Honda Motorcycles. Motor Books International.ISBN 978-0-7603-1077-9. Retrieved 28 January 2012. 13 Falloon, Ian (2005), The Honda Story, Haynes, pp. 9–13, ISBN 1-85960-966-X 14 Sakiya, Tetsuo (1982), Porter, Timothy, ed., Honda Motor: the men, the management, the machines, Kodansha, ISBN 978-0-87011-522-6 15 Classic Bikes from the AMA Motorcycle Hall of Fame Museum. American Motorcyclist Association. Retrieved 8 October 2013. According to legend, the machines name, since associated with a variety of Honda products, was inspired by a comment made by one of Hondas employees during a company party. The workers had pushed aside the desks to toast their efforts with home-brewed sake. 'It's like a dream,' uttered one of the attendees. The name stuck. 16 "Honda Worldwide, History". World.honda.com. Retrieved 1 January 2011. 17Paul Niedermeyer (30 March 2010). "Honda's Wild 9000 RPM Mid-Engine T360 Pickup Of 1963". The Truth about Cars. 18"Sporting Hondas – Classic Buyer's Guide". New Zealand Classic Car magazine. 21 September 2010. 19"Let's Build a Sport scar!". Honda. Retrieved 1 July 2012.
- 75. 75 20"The trouble with excellence". The Economist. 4 July 1998. Retrieved 5 April 2013. 21Sorge, Marjorie (1998). "1998 executive of the year – Honda Motor Co. president Nobuhiko Kawamoto". Automotive Industries. 22 "The History of Honda Motor Company". GearHeads. 18 May 2012. Retrieved 1 July2012. 23 "Honda Names Takahiro Hachigo New President; Replaces Takanobu Ito, who took over as chief executive in 2009". Wall Street Journal. 23 February 2015. 24 Ohnsman, Alan (20 August 2010). "Honda's Dream of U.S. Production Protects Profits as Yen Surges". Bloomberg. Retrieved 1 January 2011. 25Breakdown of net sales and other operating revenue by geographical markets from company 20Fs 26 Mangion, Patrick (08-27). "Markham saves Honda deal". Yorkregion.com. p. It was originally planned to be located in Richmond Hill, Ontario, but delays led them to look elsewhere. 27Share Manthan : http://www.sharemanthan.in/index.php/indian-companies/49-auto/2150- hero-honda 28Barr, Jonathan, ed. (July–September 2003). "1965 Honda T500F Flat Bed Utility". The Japanese Restorer in Australia (Bald Hills, Queensland, Australia) 1. "Toyota Corolla History" (PDF). Toyota Motor Corp.
- 76. 76