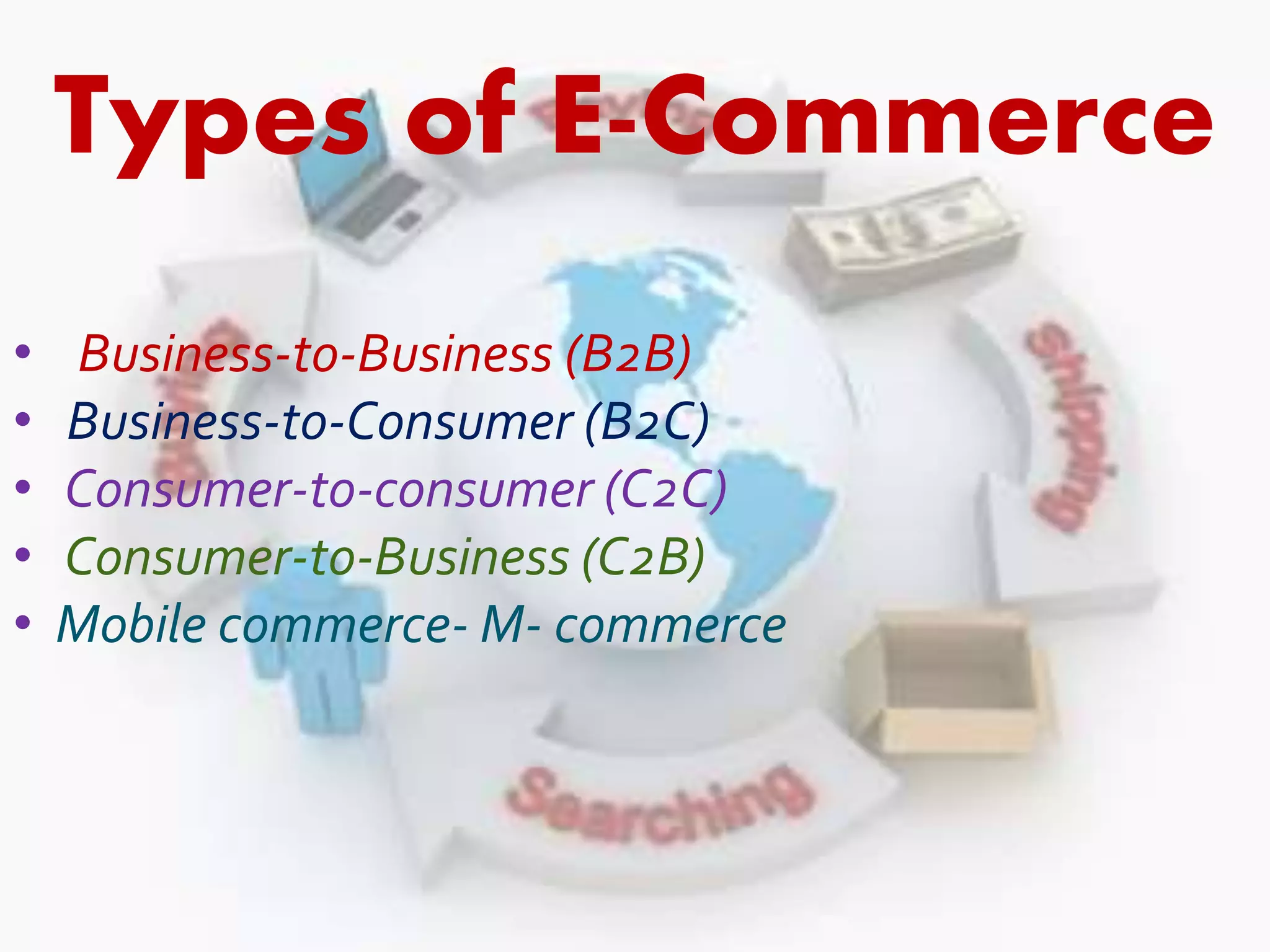
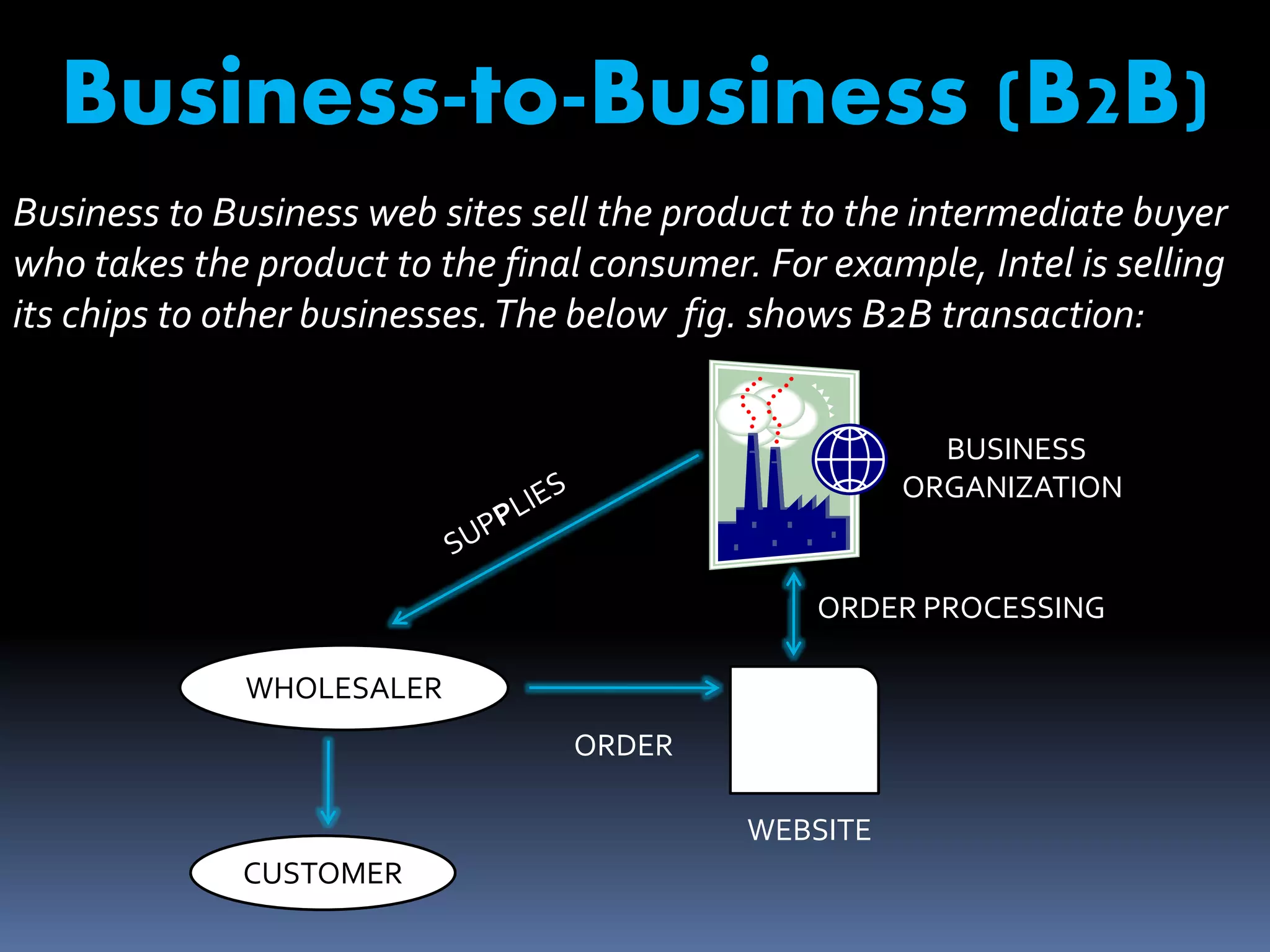
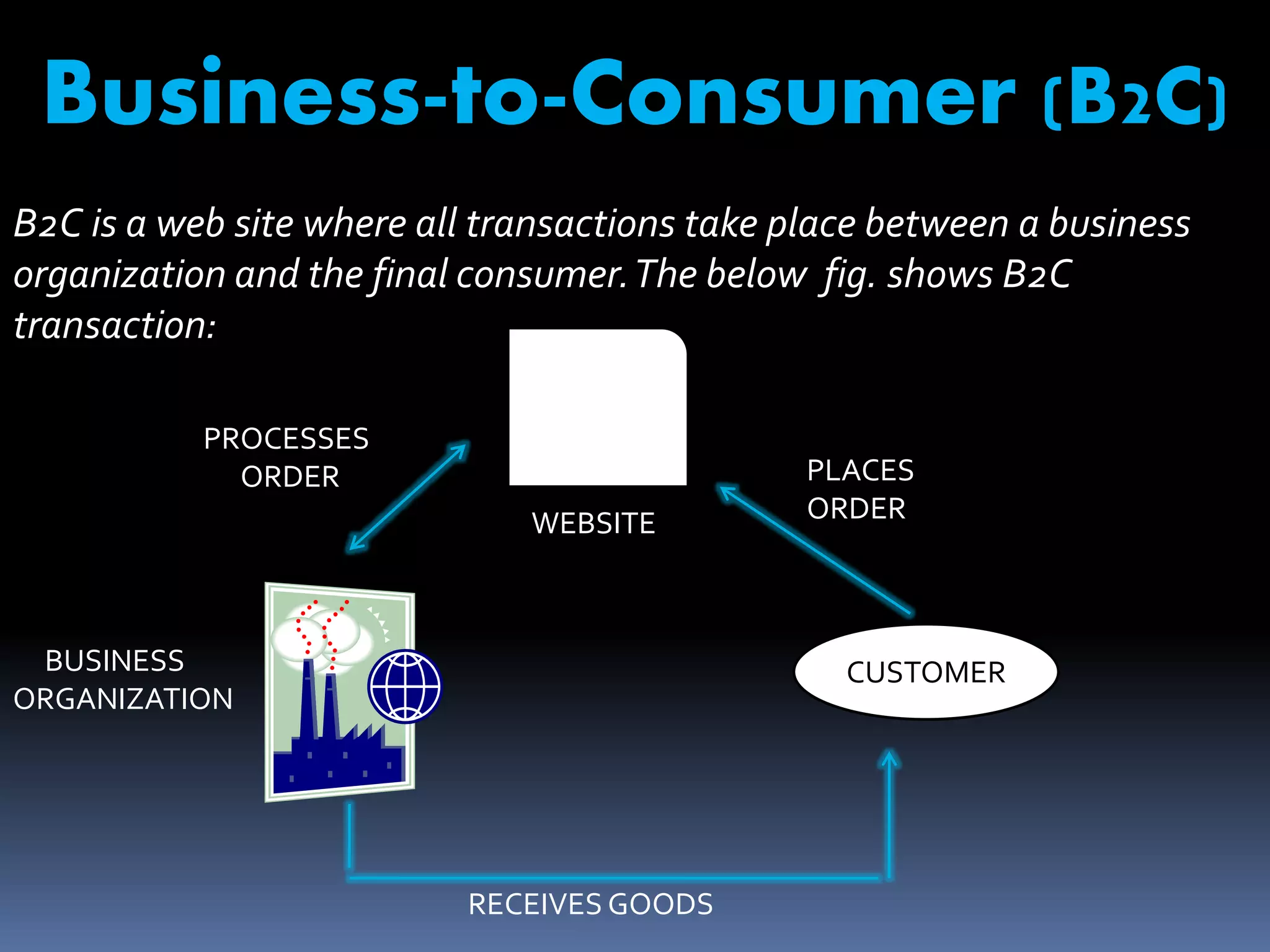
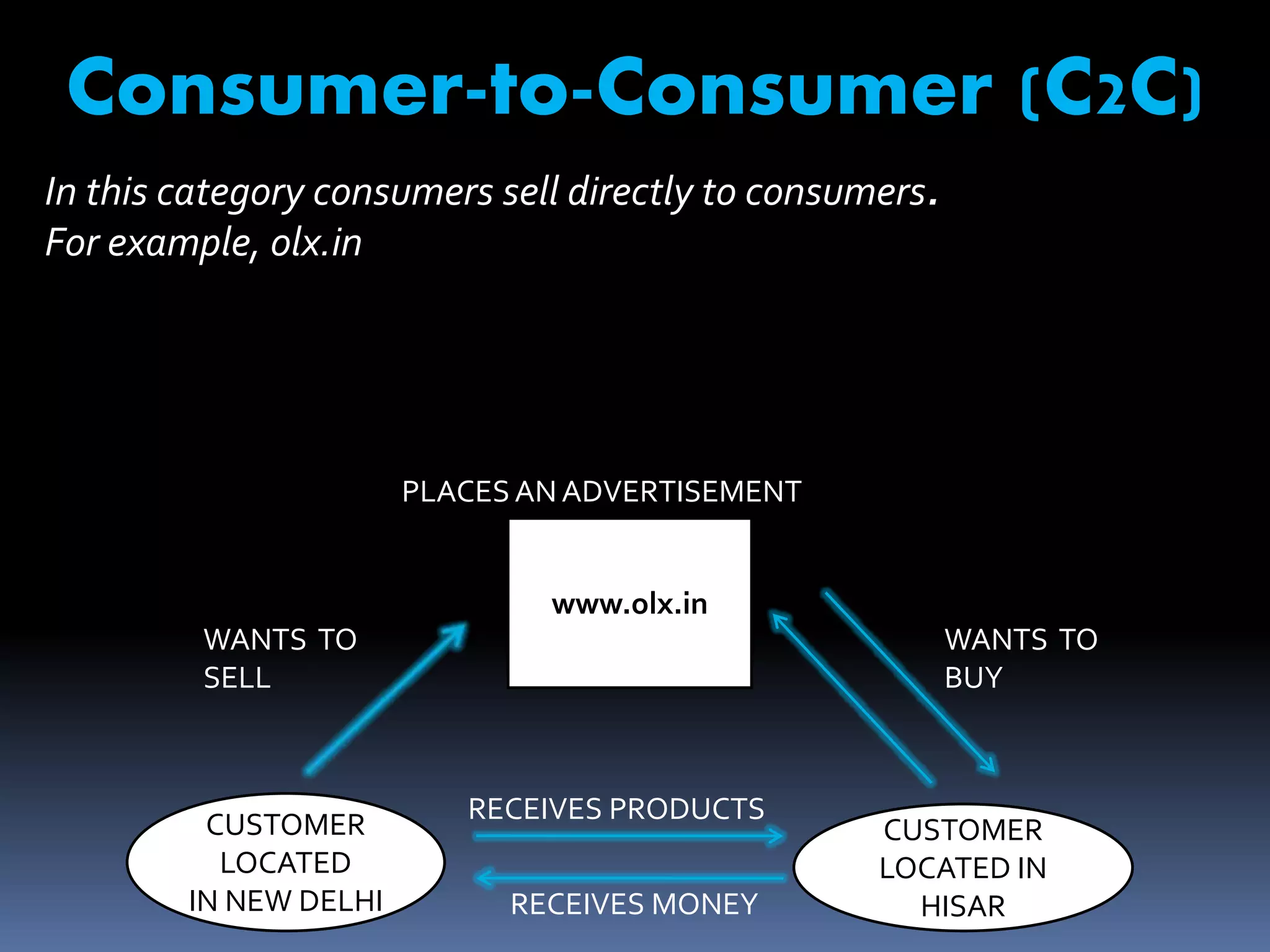
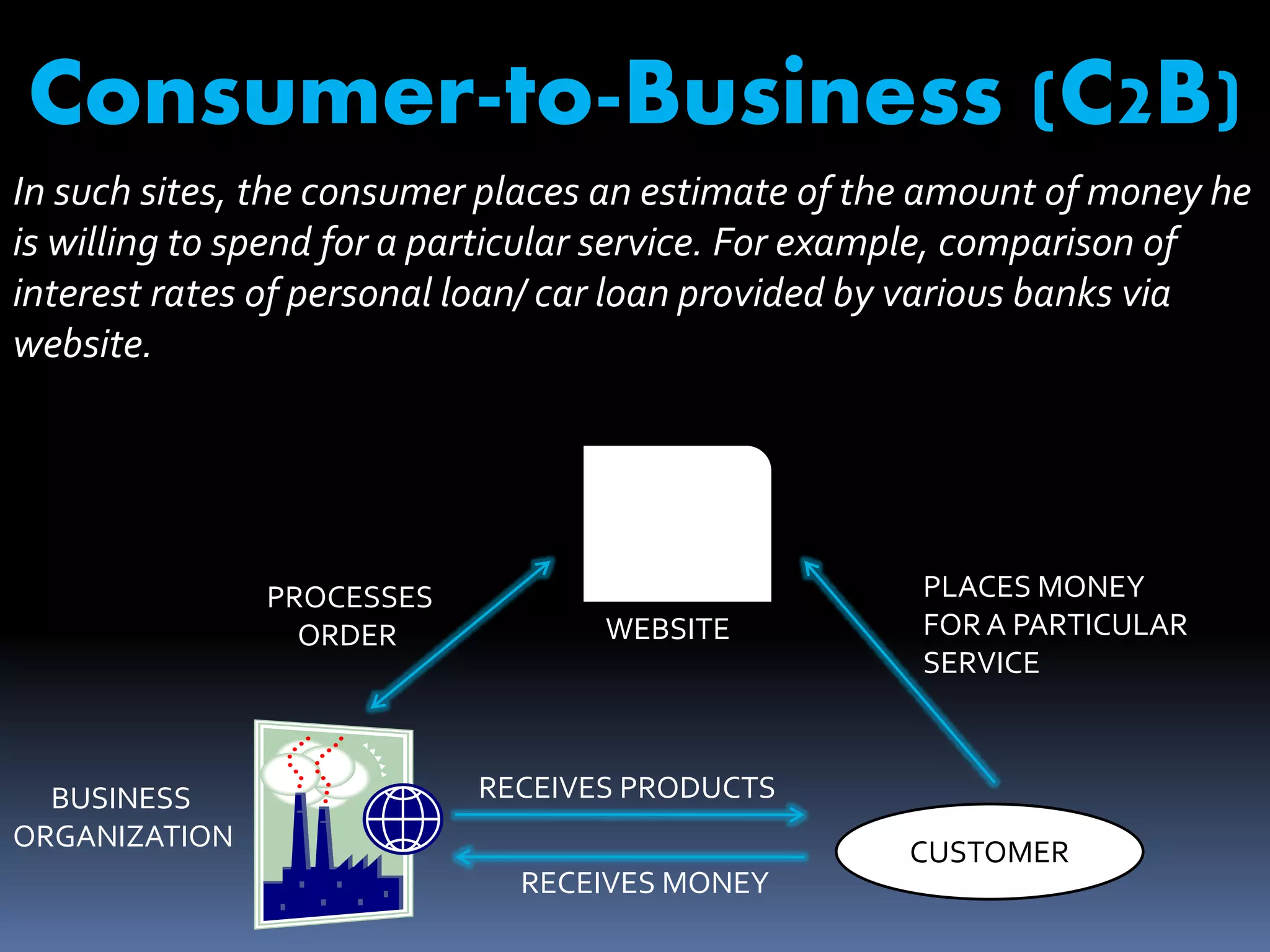
The document discusses e-commerce, including its meaning, features, types, benefits, limitations, and the future of e-commerce in India. E-commerce refers to the buying and selling of goods and services over the internet. There are various types, including business-to-business, business-to-consumer, consumer-to-consumer, and mobile commerce. E-commerce provides benefits such as expanded markets, lower costs, and increased consumer choice and access. However, it also faces limitations regarding security, access, and lack of physical interaction. The future of e-commerce in India is promising with its market size expected to grow substantially by 2015-2020.