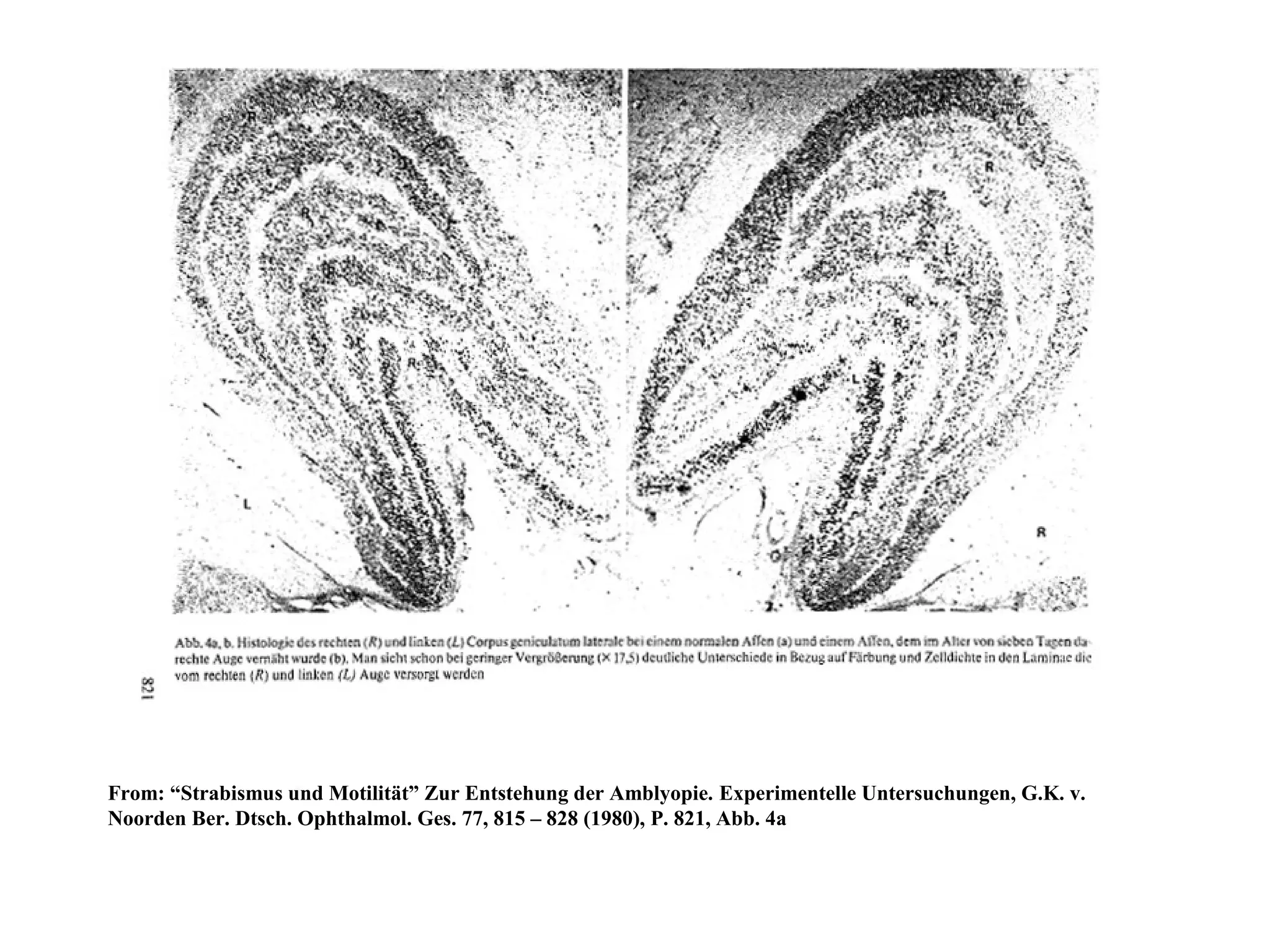
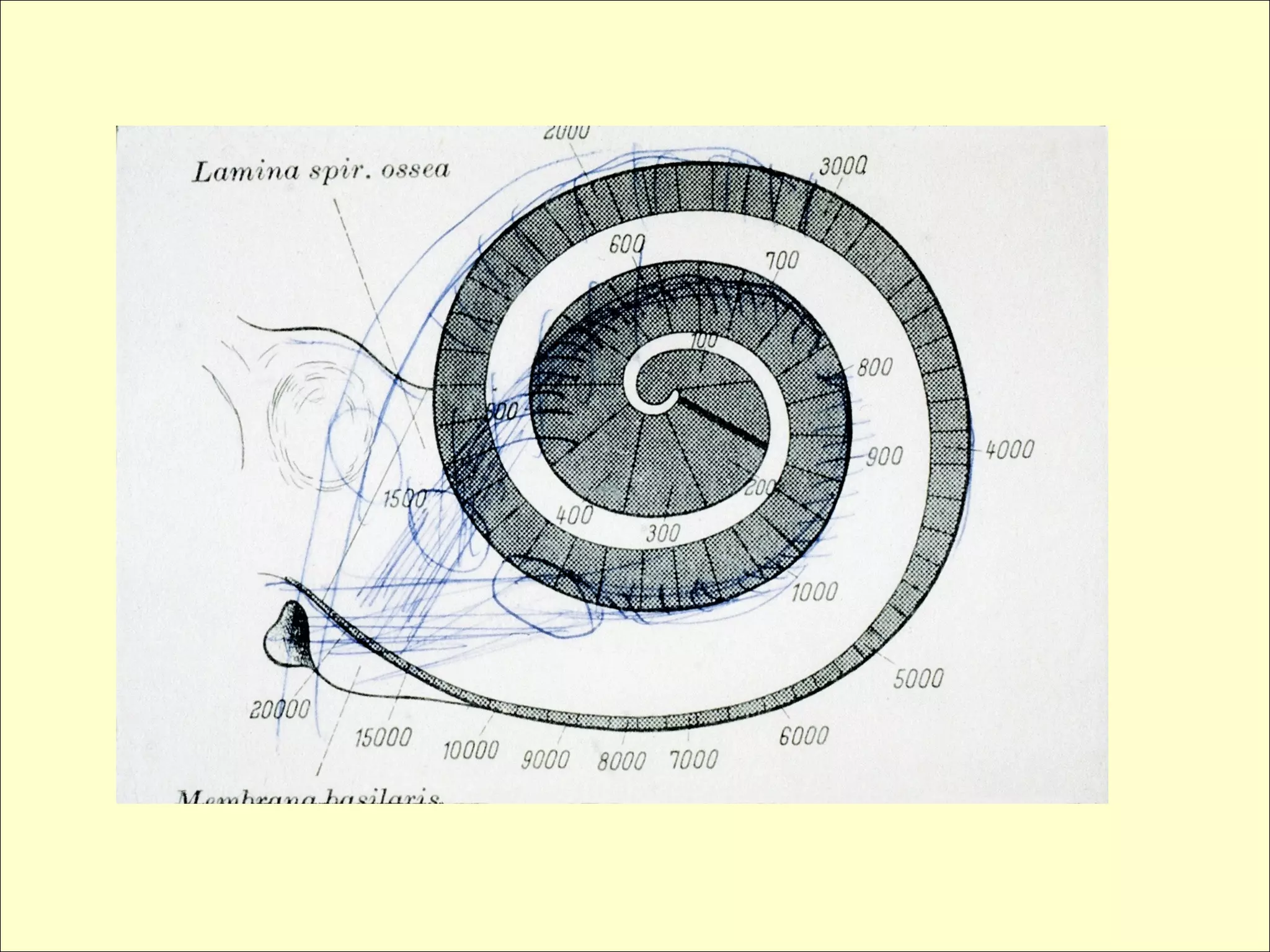
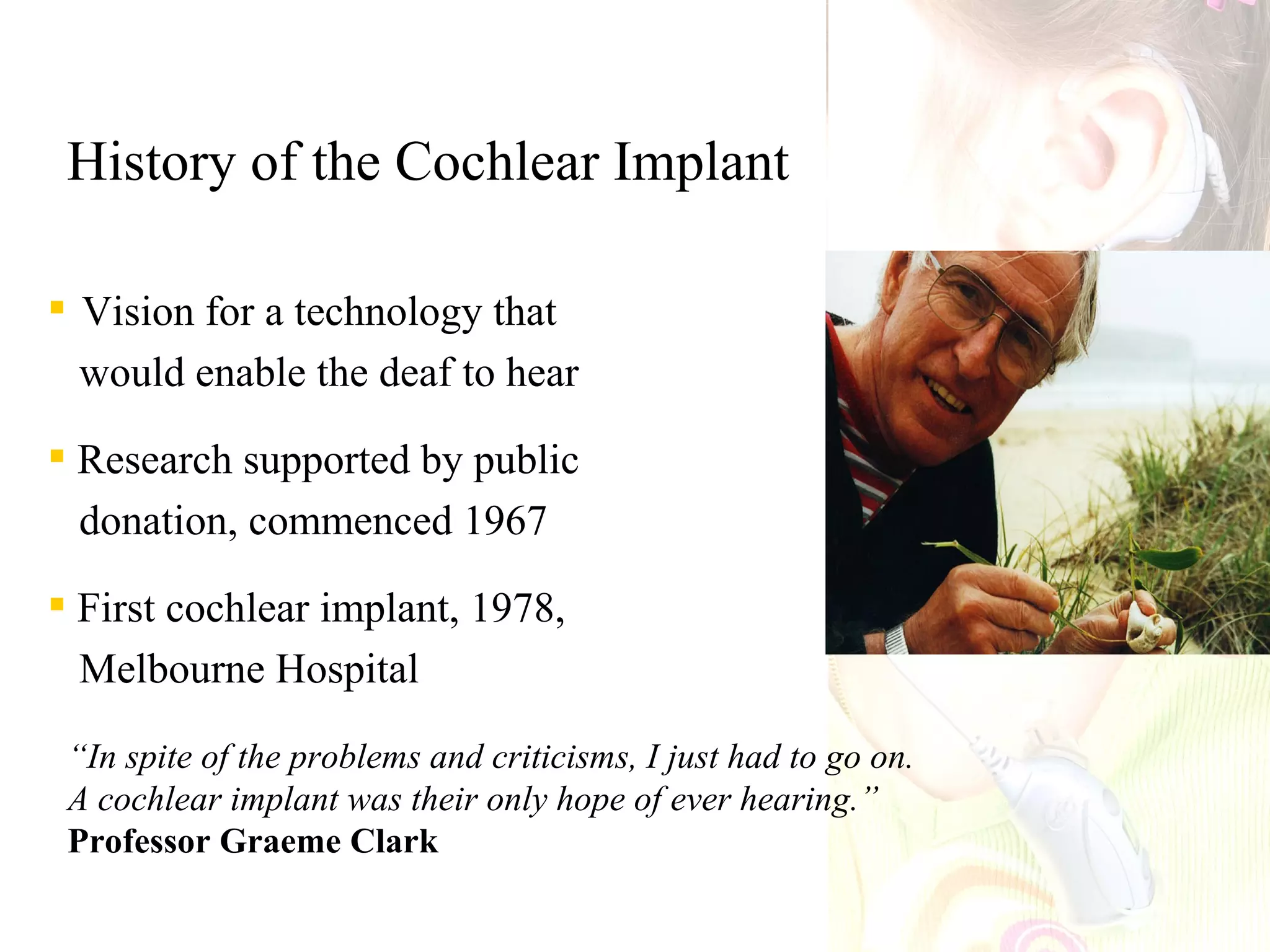
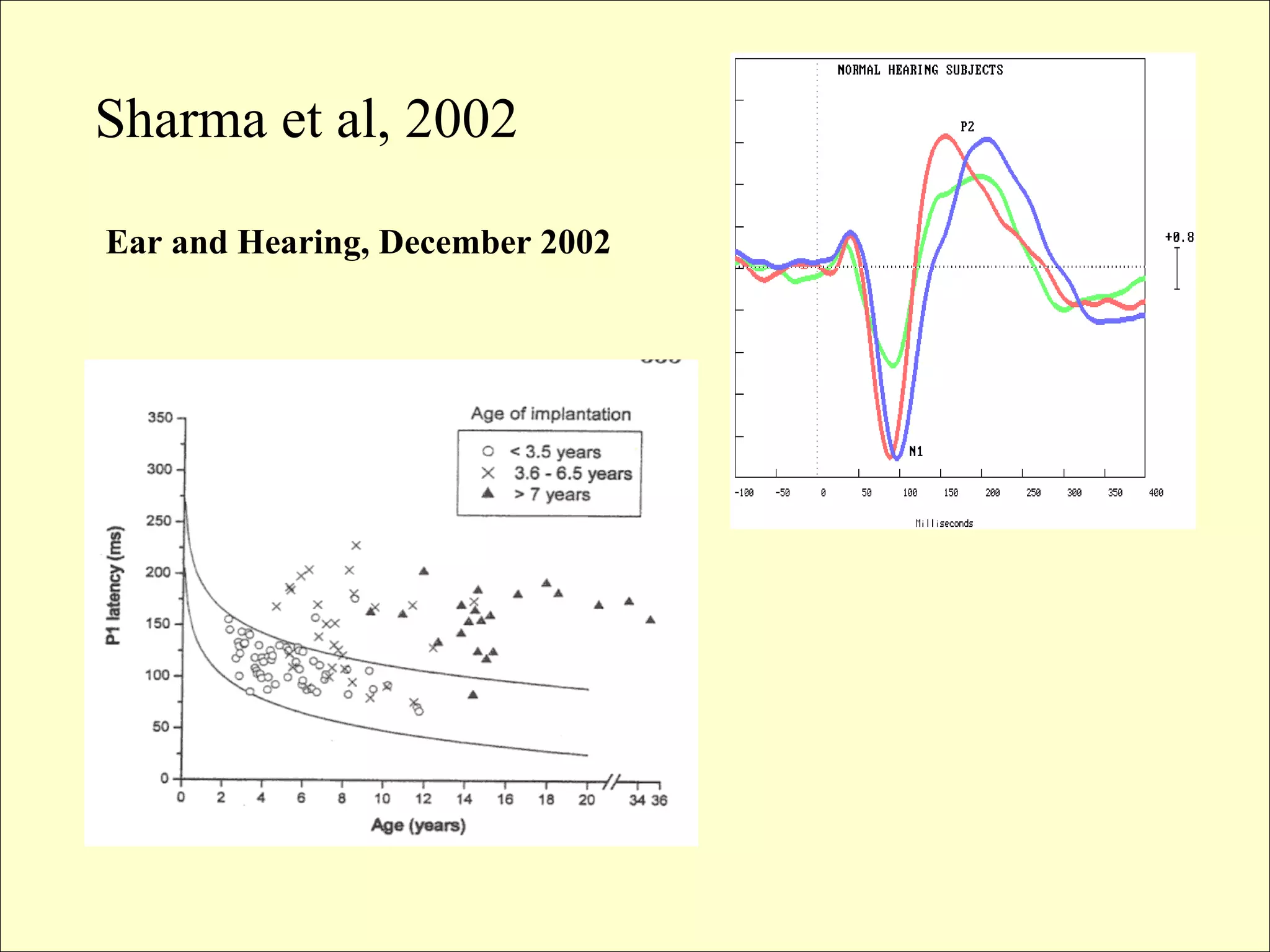
This document provides a summary of research on cochlear implants and early language development in deaf children. It discusses several key studies that found better speech and language outcomes for children who received cochlear implants at a younger age, particularly before the age of 3, and who used oral communication without sign language support. The document also references research showing higher levels of social well-being for deaf children who received cochlear implants at a younger age and were educated in spoken language environments rather than sign language schools.