Embed presentation
Downloaded 13 times






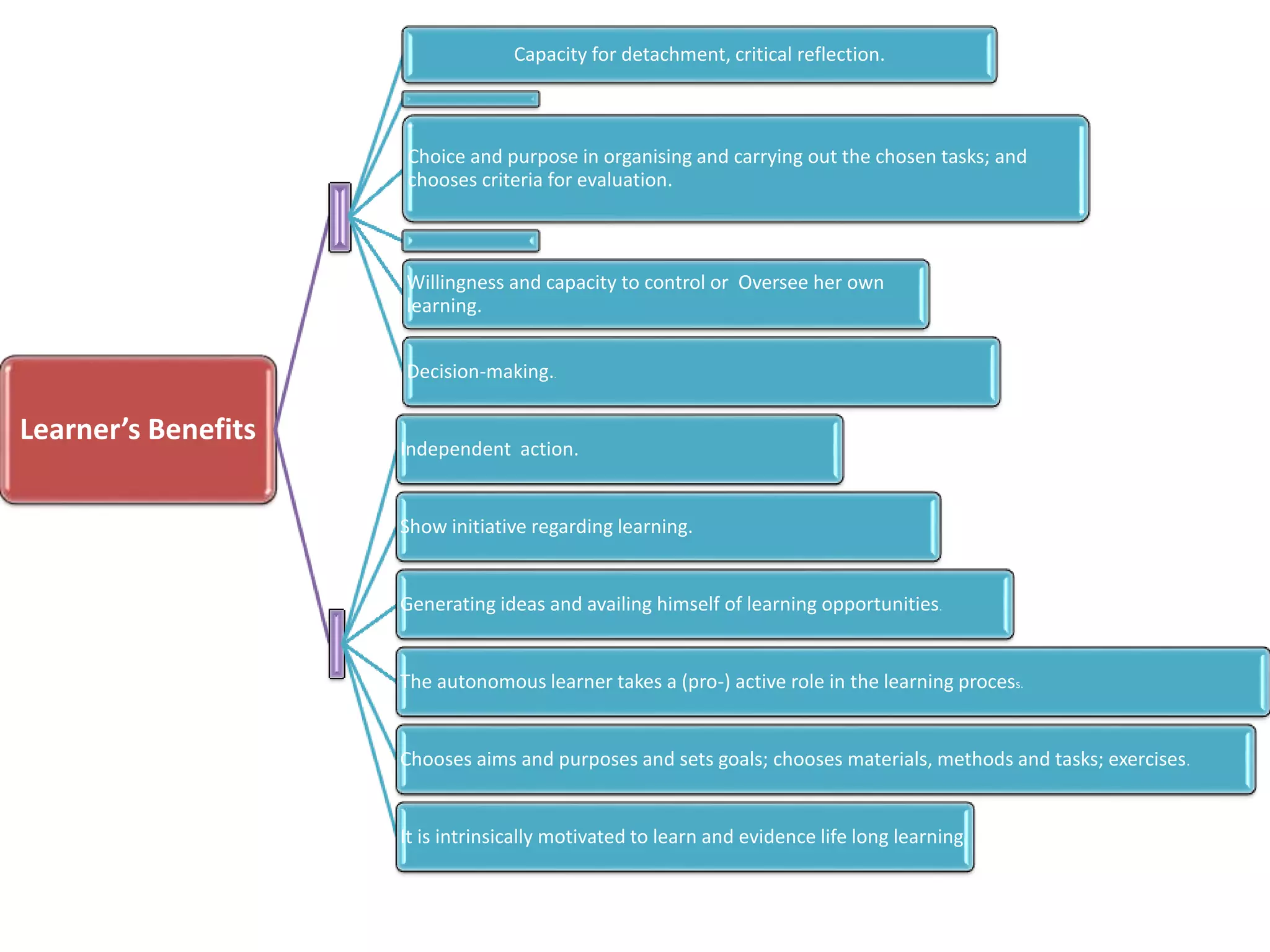


An autonomous learner is able to perceive knowledge as a social construct and feel comfortable choosing their own path, even if it differs from traditional ways of thinking. An autonomous learner can arrange and organize their own learning environment without help or guidance. The benefits of an autonomous learner include having the capacity for critical reflection, choosing their own criteria for tasks and evaluation, controlling their own learning, showing initiative, and being intrinsically motivated to learn lifelong.








